- Synopsis
- Knowledge and skills assessment implemented for Qantas
- Two major approaches to learning are…
- Heutagogy is the third approach to learning
- Nowadays, the process of learning is characterized by several factors…
- There are several universally accepted techniques for adult learning
- Training Design Components
- References
Synopsis
- Knowledge and skills assessment used to implement and justify the training program proposed (Sleezer & Russ, 2014);
- Key learning objectives;
- Instructional plan;
- Materials used for training;
- Adult learning principles;
- Methods and techniques implemented for training;
- Training evaluations – Kirkpatrick’s Model of Evaluation (1979);
- Other relevant training components;
- Conclusion.

Knowledge and skills assessment implemented for Qantas
Qantas Airways Ltd.
- Statement of the Problem: Qantas Airways Ltd. as an airline needs to prioritise communication and teamwork of all staff within the organisation to ensure that the safety of all stakeholders are to their utmost standard. The main priority of this airline are their customers and service from all patrons. To ensure this is occurring, all aspects of communication and teamwork must be their utmost importance. The importance of unity within a company like Qantas can be shown through sales and performance.
- Situation Analysis:
- Goals:
- Approach:
- Preliminary Findings:







Two major approaches to learning are…
Pedagogy
- Teacher-centered;
- Learner depends entirely on the teacher;
- Learner begins the process with little to no experience (Hägg and Kurczewska, 2018).
Andragogy
- Student-centered;
- Learner usually demonstrates relevant experience;
- Promotes learner’s individuality;
- More suitable for adult learning (Mukhalalati and Taylor, 2019).
Generally speaking, there are two major principles that have shaped learning throughout a person’s life. First of all, there is pedagogy, which is used in the majority of cases. This principle is teacher-oriented, meaning that the learner depends entirely on the teacher. It concerns the subjects, materials, and other relevant aspects of the learning process. Pedagogy usually implies that the learner begins the process with little to no experience. Therefore, he or she is expected to rely on the teacher, whose role is to provide guidance in the new area. On the other hand, andragogy puts the learner in the center of the process. This approach requires some relevant life experience and promotes learner’s individuality, which is why it is the primary method of adult education.

Heutagogy is the third approach to learning
Heutagogy
- Self-determined learning;
- Promotes learner’s autonomy;
- Adult-oriented approach;
- Suitable for life-long learning;
- Teacher = coach.
Nevertheless, it is possible to say that pedagogy and andragogy form a false dichotomy. In other words, there is another principle that can be used in learning. This approach is called heutagogy, and, in a way, its principles derive from andragogy. Heutagogy is also called self-determined learning, as, in this scenario, the learner demonstrates complete autonomy in terms of choosing what, when, and how to study. Heutagogy is an adult-oriented approach, as it focuses on making learning efficient and enjoyable outside of educational establishments. Accordingly, heutagogy promotes life-long learning in a variety of settings. Naturally, in this case, the role of the teacher is different, as well, and seems similar to coaching. Overall, this is a developing concept, which is currently gaining popularity in adult learning.

Nowadays, the process of learning is characterized by several factors…
- Diversity is the reality of the 21st century;
- Every individual has their particular background;
- All people are different in terms of age, gender, and culture;
- Other variables become important in the corresponding contexts;
- Ethics should be the driving force when devising learning programs (Al Mahmoud et al., 2017).
At the same time, the 21st century has made it obvious that diversity has become a universal reality. This tendency encompasses all spheres of human activity, and learning is not an exception. Nowadays, it is important to take into account an array of variables demonstrated by people. In general, the range of differences includes those, which are related to one’s age, sex, and background. Nevertheless, the full comprises other variables, which can gain additional importance depending on the circumstances. In other words, it is vital to consider all aspects of the learner’s personality, when determining the program of learning. Additionally, teaching and coaching is an area, where ethics play a role of paramount importance, which is why all learning should remain ethical in all cases.

There are several universally accepted techniques for adult learning
- Learning should be relevant;
- Learning should take into account the individual’s background;
- Emotions make learning more efficient;
- Learner’s desire to explore should be encouraged;
- Assignments should remain as convenient as possible for the learner;
- Learner must receive adequate and relevant feedback (6 Effective Strategies, 2016).
Overall, adult teaching and learning techniques vary depending on the particularities of each situation, but there are several points which can be applied in the majority of cases. First of all, as adults value their time and experience, learning must be relevant to their goal. Secondly, as mentioned earlier, each person has a different background, which must be taken into account by teachers and coaches. Third, adult learning benefits from incorporating emotional aspects into it, as learners tend to remain motivated through emotions. Fourth, it is important to encourage the learners’ desire to explore, as it promotes a more in-depth understanding of the subject. Fifth, assignments and other aspects of learning should remain convenient, as adults tend to avoid unnecessary discomfort in their lives. Finally, it is crucial to ensure quality feedback to let the learners know where they excel and which aspects require additional attention.

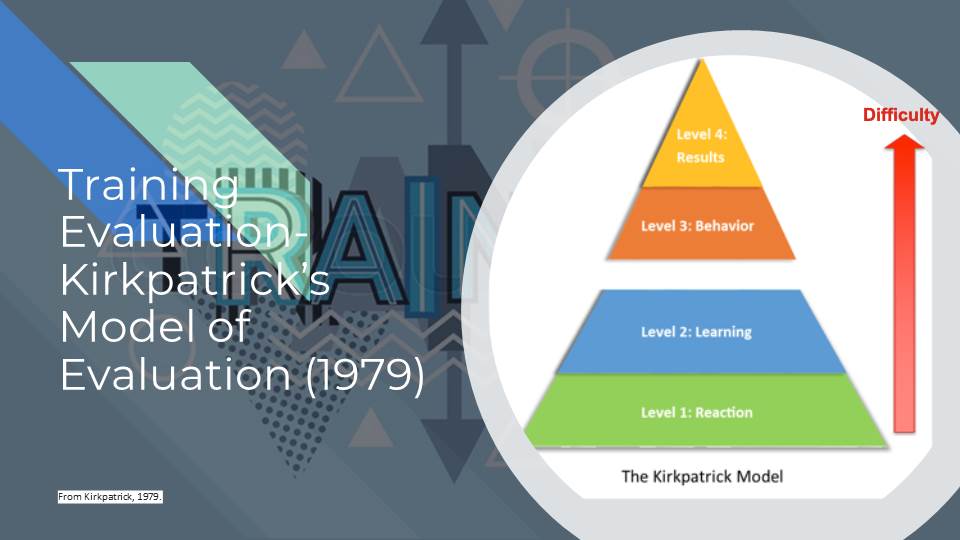
Level 1- Reaction
This is instant feedback from the trainees.
According to the survey, it’s generally to evaluate:
- How participants react to the training;
- The level of enjoyment;
- Relevant to their roles;
- How effective the overall training was.
Ideally, the outcome:
- positive feedback;
- training program is helpful and effective;
For example, based on the survey that we provide , we received 75% positive responses to our organisation.
If the outcome were not in accordance with what we expected, we can improve based on the suggestions of the participants.

Level 2 – Learning
Based on the survey we made is to:
- Measure how well participants in learning based on knowledge, skills and attitude.
- Measure of the learning in terms of content being absorbed by participants.
- Other methods such as quizzes and tests.
- The ideal outcome from the survey should be positive.
- E.g 90% of the participants feel that the course of the training is useful in order to develop teamwork.

Level 3- Behavior
The practical sides of training evaluation.
Based on the survey, to understand the participant’s behavior post-training:
- How much of the learning is applicable to the day to day work
- How well participants can apply what they learned
- Have a professional manner to serve customers
- How does training affect performance
Moreover, conducting reviews with the trainees (for instance, in-depth discussion between trainees and the trainers).

Level 4- Results
The overall results the trainees give to Qantas Airways Limited:
- Reached the goals through training;
- Making fewer errors and getting project/tasks more quickly and efficiently.
Could identified based on post-training 2 days checkpoint.
The ideal outcome we expected such as:
- Meet the overall key objectives of the training program;
- The sales and customers increased;
- Took better care of customers –work as a team;
- Cabin crew kept ground staff informed (customers requiring special assistance);
- Satisfied customers and more loyal to Qantas.

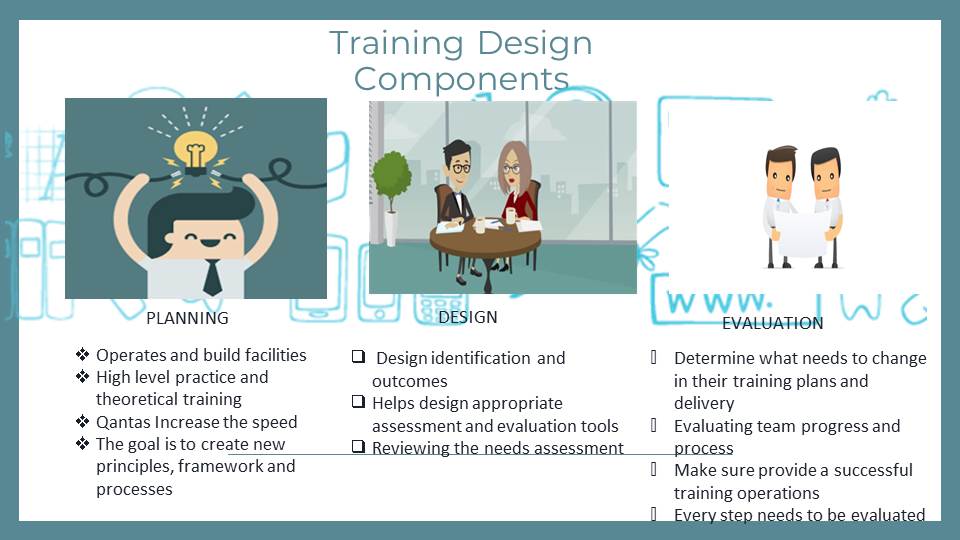
Training Design Components
Planning
- Operates and build facilities;
- High level practice and theoretical training;
- Qantas Increase the speed;
- The goal is to create new principles, framework and processes.
Design
- Design identification and outcomes;
- Helps design appropriate assessment and evaluation tools;
- Reviewing the needs assessment.
Evaluation
- Determine what needs to change in their training plans and delivery;
- Evaluating team progress and process;
- Make sure provide a successful training operations;
- Every step needs to be evaluated.
References
Hägg, G., and Kurczewska, A. (2018) ‘Who is the student entrepreneur? Understanding the emergent adult through the pedagogy and andragogy interplay’, Journal of Small Business Management, 57(1), pp. 130– 147.
Mukhalalati, B. A., and Taylor, A. (2019) ‘Adult learning theories in context: A quick guide for healthcare professional educators’, Journal of Medical Education and Curricular Development, 6.
Abraham, R. R., and Komattil, R. (2016) ‘Heutagogic approach to developing capable learners’, Medical Teacher, 39, pp. 295-299.
Al Mahmoud, T., Hashim, M. J., Elzubeir, M. A., and Branicki, F. (2017) ‘Ethics teaching in a medical education environment: preferences for diversity of learning and assessment methods’, Medical Education Online, 22(1).
6 Effective Strategies for Teaching Adults (2016) Web.