Introduction
The presence of an acid or base in the reaction medium catalyzes the reaction between acetone and iodine.
CH3COCH3 (l) + I2 (aq) →CH3COCH2I (aq) + HI (aq)
The immediate change in the concentration of a reactant the moment a reaction begins is the initial rate of that reaction. It is possible to establish a pattern regarding alterations in the concentrations of the reactants.
Aim of the Experiment
This experiment aimed at establishing the concentration of iodine with time by quantifying the absorbance of the reacting solution at a wavelength of 410 nanometers and finally determining the initial velocity of the reaction. It also aimed at finding the overall rate law for the reaction between iodine and acetone by comparing the rate laws of different reaction mixtures.
Method of the Reaction
The wavelength of the spectrophotometer was checked and set at 450 nanometers. The knob was adjusted until the percentage transmittance (%T) read zero with nothing in the sample holder. The spectrophotometer was then calibrated using a cuvette containing deionized water. Seven different solutions were made, each with varying amounts of 4.0 M acetone, 1.0 M HCl, and deionized water. The appropriate amount of iodine solution was finally added into the cuvette. The reactants were mixed and immediately placed in the spectrophotometer to obtain the absorbance readings at intervals of about 6 seconds. These readings were recorded in a table.
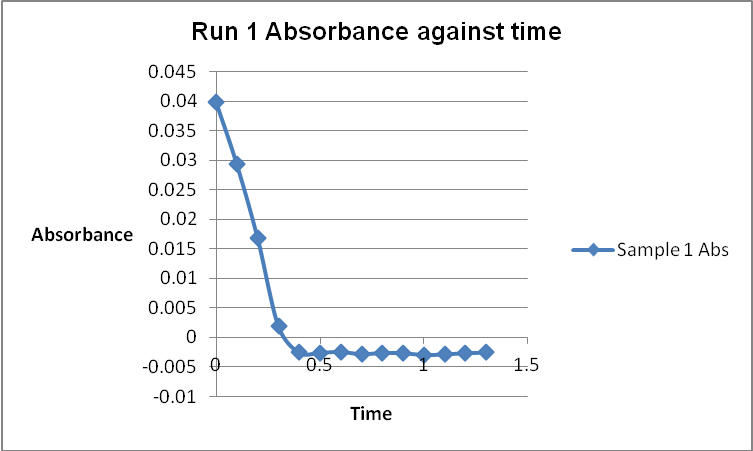
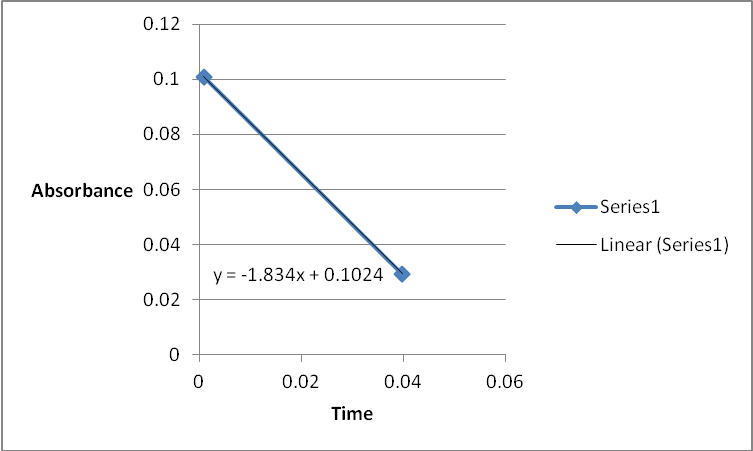
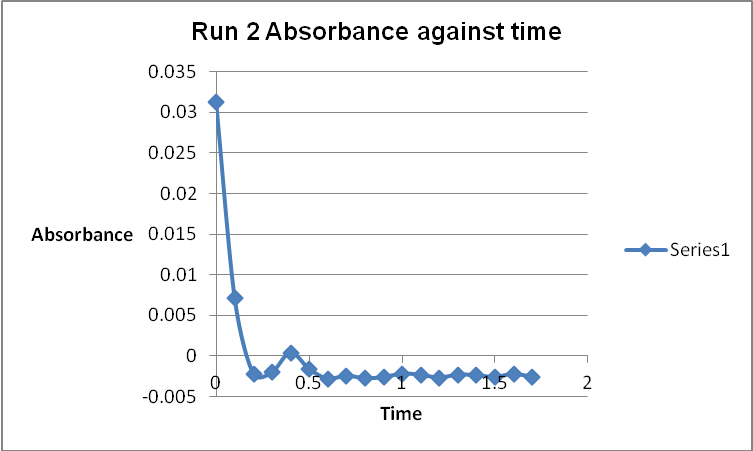
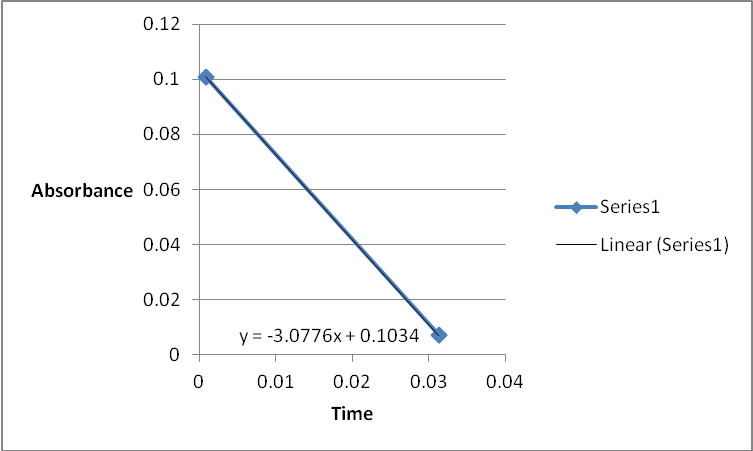
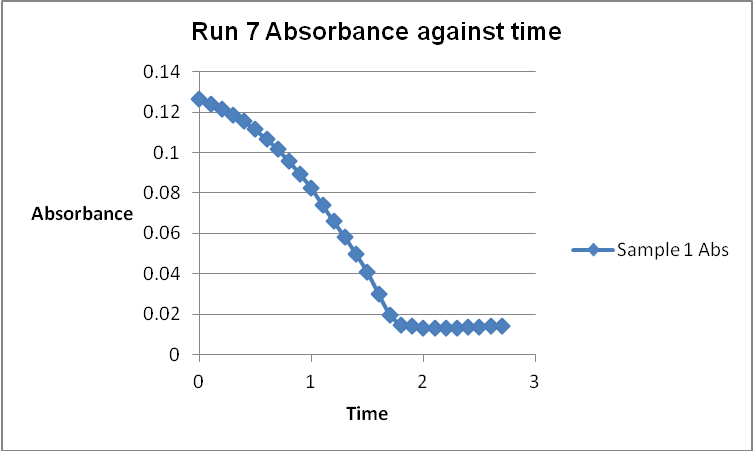
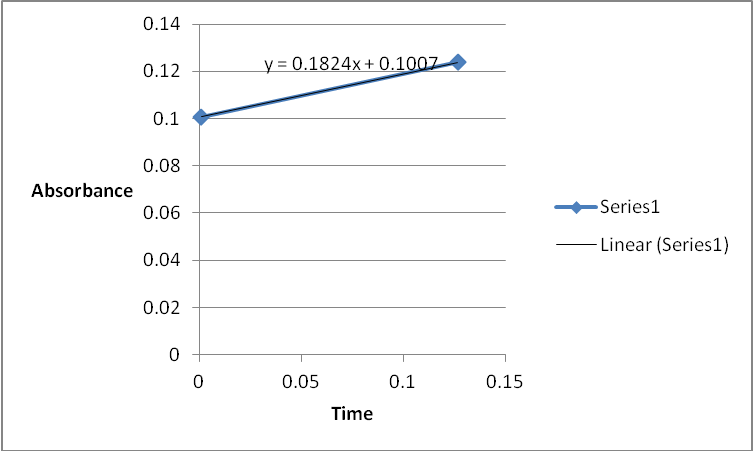
A graph of absorbance against the concentration of iodine was plotted for each run. The initial rate was determined by drawing a straight line through the first two points and calculating the slope of the line. The method of initial rates was used to find the order of each reagent in the rate law of the reaction.
Results of the Reaction
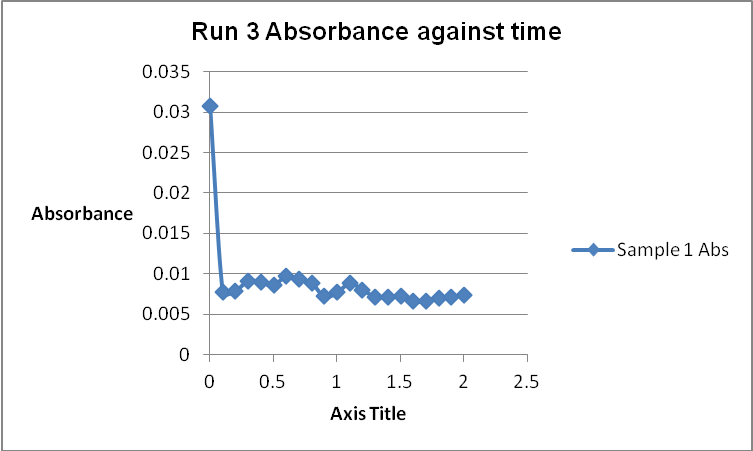
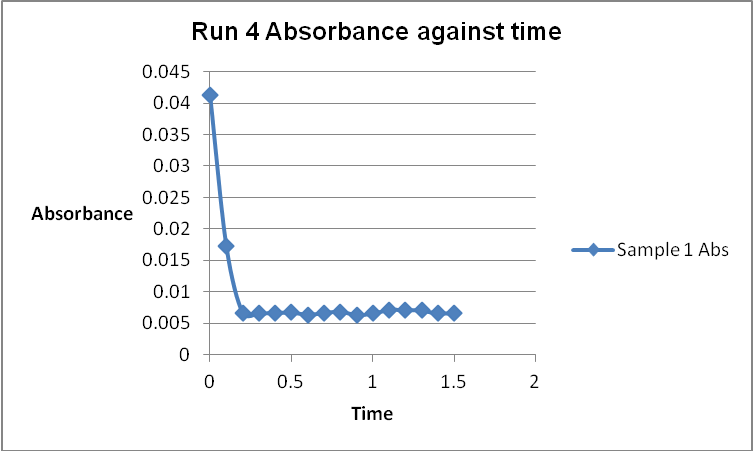
The colour of the reacting mixture changed to colourless from the initial yellow-brown colour as the reaction progressed. This was because iodine concentration decreased as the reaction progressed and was reflected by a decrease in absorbance during the progress of the reaction.
Table 1: Initial Reaction Rates and Reagent Concentrations of Various Runs
The rate law for the reaction = k [CH3COCH3]a [I2]b [H+]c.
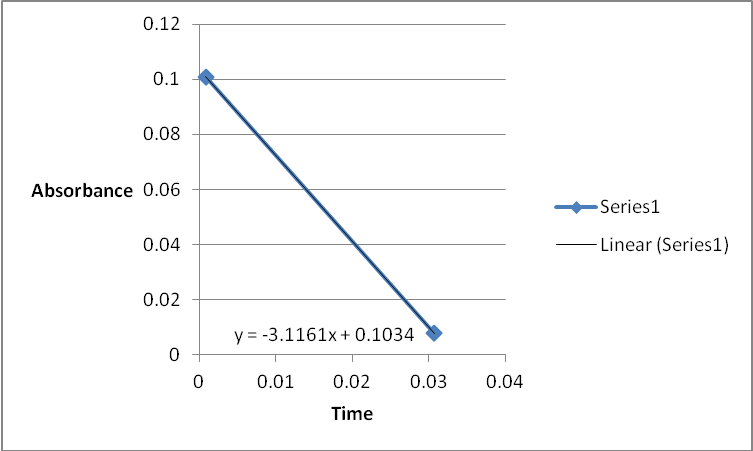
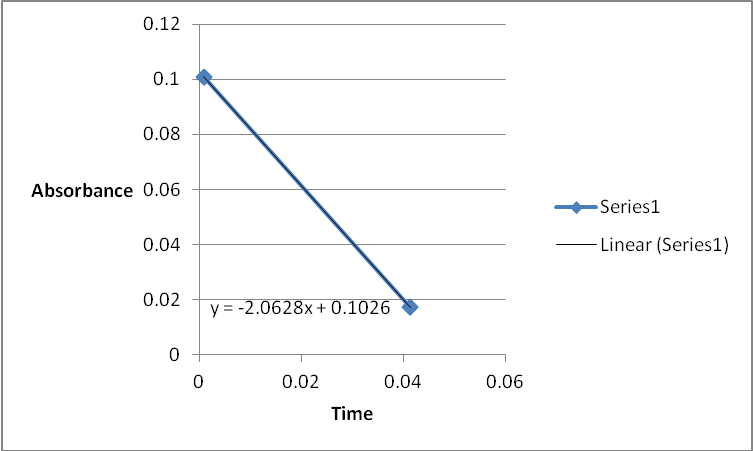
The order of the reaction was established for each reactant in the reaction using the method of isolation (Determining reaction order n.d.). This was accomplished by comparing two investigational runs that had a discrepancy in the concentration of only one of the reactants. In the first and second runs, the concentration of acetone was changed doubling up the initial reaction rate. Therefore, the reaction was assumed a first order relating to acetone meaning that the value of a was equal to 1. Comparing runs 4 and 5 revealed that changing the concentration of HCl did not affect the initial reaction rate (assuming that the difference in 2.0628 and 2.2591 was negligible). Therefore, the order for HCl was taken as 0 (b). Comparing runs 6 and 7 indicated that varying the concentration of iodine increased the initial reaction rate by 2. Therefore, the value of c was 1.
This gave the following rate law: Rate law =k [CH3COCH3]1 [I2]1 [H+]0.
The rate constant for the reaction was calculated using one of the experimental runs and substituting the rate orders as follows:
3.1161M/s= k (4.5)1(2)1(1.5)0
3.1161M/s= k 9.0
K= 0.3462M/s.
Discussion
The literature values for the reaction order of the reaction between iodine, acetone and hydrochloric acid were k [CH3COCH3]1 [I2]0 [H+]1 (Athawale 2001, p.89). However, the experimental results obtained the following rate law: Rate law =k [CH3COCH3]1 [I2]1 [H+]0. There were variations in literature values and experimental values. This was probably due to experimental errors because of timing. The time was recorded at intervals of 6 seconds as opposed to the suggested intervals of 10 seconds. There may also have been inaccuracies in the instrumentation hence leading to the disparities in the results.
Iodine-Acetone Reaction: Summary
The absorbance of the solution decreased as the reaction progressed. However, the obtained rate equation was different from literature values because of experimental errors.
Appendix
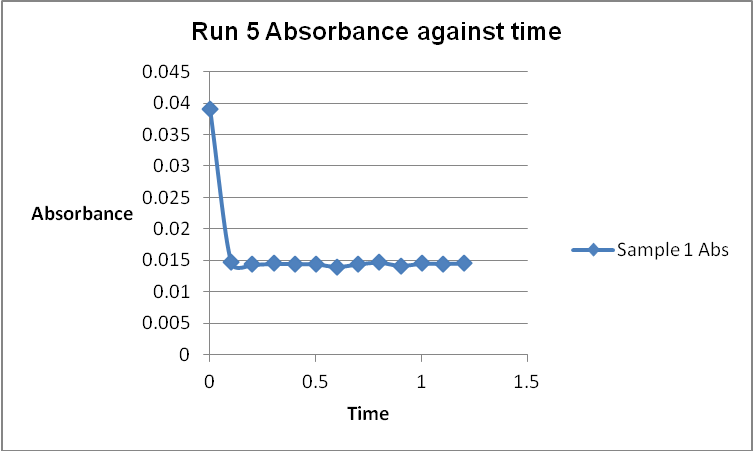
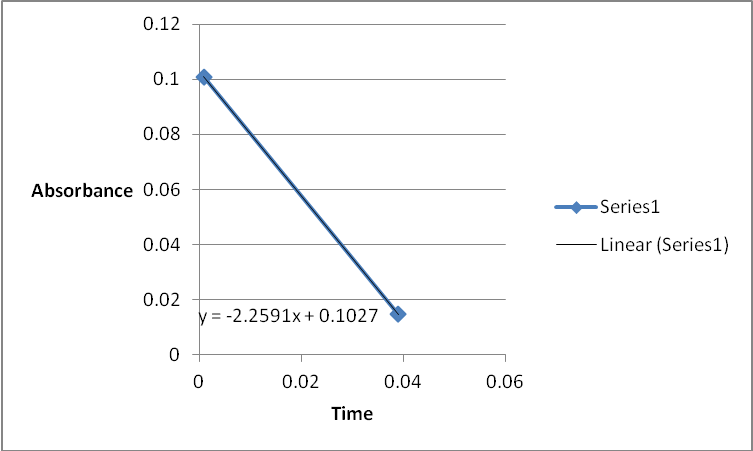
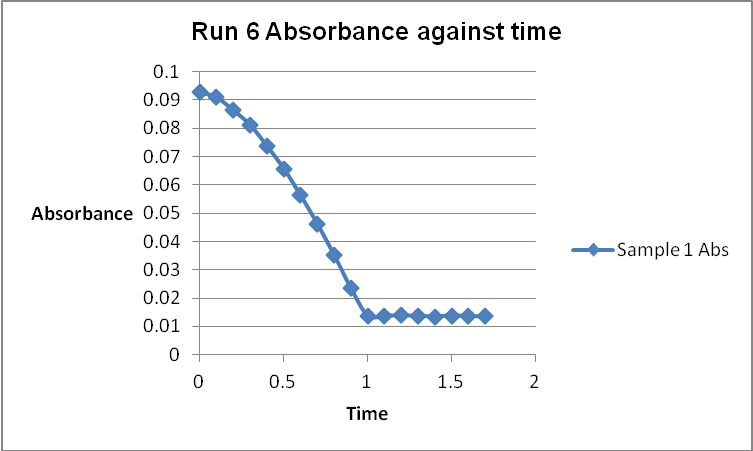
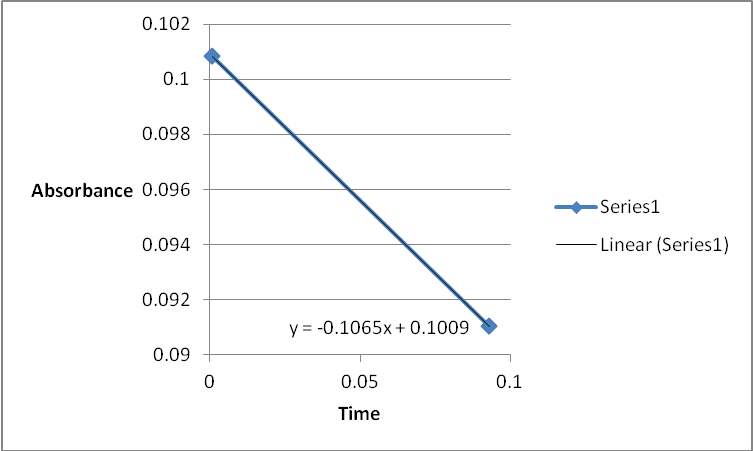
References
Athawale, V. D 2001, Experimental physical chemistry, New Age International, New Delhi.
Determining reaction order, n.d. Web.