Problem Statement – The significance of Immigrant Workers on the US economy
USA can be said as a nation built up of immigrants. Since, USA is an advanced economy, there is a strong desire to settle down in USA by other nations’ residents mainly to enjoy the advanced standard of living available there.
Immigration is a controversial issue when examined from an economic standpoint. Critics argue that USA’s resources are limited in nature and by having a liberal immigrant policy with an increase in population connotes that there are more or more people vying for the same restricted resources.
USA immigration policy is the highly debatable issue that whether the immigrant workers strengthens the U.S. economy or destabilize as it is a contentious issue both in the past and in the present.
According to National Association of Manufacturers (NAM), immigrants have made great contribution to the American economy and technological advancement and it is essential to have such access as USA is under the compulsion to compete and lead. According to Prof.
Hanson, there has been dramatic increase in immigration population in U.S. as it has rosen to 12% in 2006 from that of just 5% in 1970. As of 2006, immigrant workers in U.S. constituted 15.3% and supporters argue that without immigrant workers, the U.S. would have 15% less workforce.
It is argued that the average wages in U.S. would have been higher by 3% if there has not been influx of immigrant workers (Borjas 1335).
Mirroring the splitting up of the country on how to tackle immigration issues, Congress in the United States has thus so far not succeeded to enact any laws to reform their immigration laws.
One of the main reasons for this is the absence of much empirical data that can be employed to illuminate this issue so that suitable laws can be enacted or can the existing laws can be reformed.
Employing the data and the information available from the “U.S. Bureau of Census 2000”, the U.S. Department of Labor and from peer-reviewed sources, this research essay will make an earnest attempt to validate the hypothesis whether the higher concentrations of immigrants in USA’s metropolitan areas will have higher median household income or not.
Research Hypothesis
Critics argue that immigrants are responsible for fall in wage in USA and destabilize the U.S. economy, whereas the supporters argue that immigrants make economic contributions buoyant in metropolitan areas.
This research paper will address the question of the influence of immigrants on median household income for metropolitan areas in the United States.
This research paper’s main hypothesize is that metropolitan areas with higher concentrations of immigrants will have higher median household income.
Methodology
For this research paper, the data are employed from the United States 2000 Census, which was published on April 1, 2000.
The 2000 Census results are widespread in nature and demonstrate logical reports on population transformation, age, race, housing, family structure, apportionment, and household mean income.
The census demonstrates economic personality for the United States as well as chosen housing traits for the given year. The census recognizes 3,219 counties, which are aggregated them into 389 metropolitan areas for this research.
This research paper will employ U.S. Census data of 2000 to validate the association of the concentration of immigrants (percent foreign-born) and the median household income of the selective metropolitan areas in the United States.
This research paper will also in a succeeding analysis, evaluate the settlement of Asian and Latino immigrants which are examined separately to discover if there is any difference in immigrant origin exists among metropolitan economies.
Literature Review
At present, the immigrant workers account for one-seventh of the aggregate workforce in USA and illegal immigrants vouched for about 33% of the aggregate of immigrants in U.S.
Hanson is of the view that about 60% of the illegal immigrants have not completed their high school education and hence, they are posing a vigorous competition for low-skilled jobs with the native unskilled employees.
Hanson has observed the U.S Census data from 1960 and 2000 and exposed that there has been strong link between immigration with that of employment and wage rates.
According to Dr.Hanson, large influx of immigrants from 1980 to 2000 in the U.S. resulted in an excessive labour supply shock which enhanced the figure of workers in the U.S. by 10% which also resulted in the increase of high-school dropouts in the U.S. population by over 20%.
This has resulted in 18% fall in black employment rates and resulted in 8% fall in employment rate of low-skilled black men.
Supporters argue that as the large chunk of immigrant workers are high-school dropouts, immigration has really increased the salaries of native born Americans with a college degree considerably (Krugman 159).
One another major impact is the fact that the U.S. economy would find it difficult without immigrant workers since it requires workers who can carry out the unskilled jobs and other works that need not demand a college education.
In USA, there are some industries that could only succeed if business is able to minimize the cost of production. For instance, take orange juice product industry that could stay competitive only if they able to offer lower prices.
That is why, the orange farm industry in USA is more relying on immigrant labour which is cheaper. That is why, orange orchards in USA prefer Mexican workers mainly remain competitive.
Supporters proved that though immigrant occupied 12% of the U.S. population in 2000, about 26% of the Nobel Prize winners in 1990 -2000 from U.S. were foreign-born immigrants and likewise, 25% of the founders of public companies in U.S. were immigrants.
Supporters advocate that skilled immigrants contributed to more technical innovation in the U.S. than native-born citizens.
Hunt and Gaulthier-Loiselle study demonstrates that a one percent increase in the percentage of college graduate immigrants in the American population Patents per capita data to enrich more knowledge in the technological advancement, a force for the productivity development and finally impacts the economic growth.
They argue that if the immigrants enhance the patents per capita, they may also enhance the output per capita thereby making the American citizens better off. David Card was of the view that there is less evidence that the immigrants have impaired the less educated Native Americans.
Card is the view that immigrants may be adopting the American lifestyles and culture more better and the kids of the second-generation of immigrants have higher wages and education opportunities than compared to the Native Americans (Hunt & Gaulthier-Loiselle 32).
As per 2010 Census, there were about 800,000 Hispanics residing in a metropolitan province in USA out of 5.6 million people thereby accounting for about 14% of the aggregate of U.S. population.
Further, as per American Community Survey (ACS) (2007), the median household income for Latinos immigrants who were residing in Washington metropolitan area in 2007 was estimated at $ 63,782 which is relatively greater than the nation’s median household income for the whole U.S. population which was estimated at $ 50,740.
According to O’Neil Parker (2005), Latinos population in Washington’s metropolitan is considered to be the richest Latinos in the U.S. (Pumar 135).
As per Scott and Soja (1998), Los Angeles is regarded as a replica for understanding present processes and trends of metropolitan structure and change. However, New York’s immigrants suburbs differed considerably by socioeconomic status, ethnic background and racial structure as compared to Los Angeles.
The Alpine suburb of New York consisted about 25% foreign –born population in 2000 mostly comprised of Europeans and Asians and had a median household income of Alpine was reported at 130,000 in 2000.
In the case of East Garden City , the median household income and the poverty rate was at 8% and 25% of the population was foreign-born mostly from Caribbean and non-Hispanic Black.
Thus, Alpine and East Garden City both had an analogues proportion of immigrants but each had a distinct socio-economic and ethnic structure (Hanlon, Short & Vicino 147).
Likewise , about 50% of the Rosemead’s population was foreign-born in 2000 and about 60% were Asians and the median family earnings of Rosemead was about $32,000 and about 25% of population in Rosemead was poor in 2000.
However, Glendale, a suburb of Los Angeles considered to be affluent suburbs in Los Angeles as per 2000 Census as the one-tenth was foreign –born in 2000 and 75% of these foreign-born were Asians and Afghans.
The poverty rate of Glendale in 2000 was estimated at 3% and the median family income was $92,000.
It is to be noted both Glendale and Rosemead had high percentage of Asian population but these suburbs contrasted in a major way as regards to socio-economic condition (Hanlon, Short & Vicino 148).
Likewise, more than 50% of Lennox of Los Angeles population was foreign born in 2000 comprised of Latin Americans and the median family income was $ 30000 and more than 50% of Hispanic population in Lennox was poor.
Pacific coast metropolitans like San Francisco and Los Angeles is having large number of Asian immigrant and the New York suburb is also having a higher percentage of Asian immigrants.
However, the other regions like Miami, Denver and Cleveland suburbs had very little Asian immigrants. Miami is the abode of majority of poor Hispanics predominantly from Haiti.
Likewise, Reston suburbs of Washington DC consisted more than 25% of immigrant population in 2000 and the annual median family income was $74,000 and the poverty rate was just below 3% in 2000 (Hanlon, Short & Vicino 148).
According to Miller & Tanners (1995), Nigerian immigrants are highly educated like the immigrants from Korea , India and Japan and they always prefer to reside in great property wealth suburban districts thereby offering their kid good schooling.
According to “Massey et al., (2007)”, about 25% of the immigrant population from Africa is concentrated in and around 10 largest metropolitan provinces in the U.S. but they are likely to prefer to reside in racially integrated surroundings.
Though, Nigerian immigrants in the U.S. are having good higher education, their median family income lags behind that of Caucasians and Asians as per 2003 Census data.
According to “Massey et al., (2007)”, the Nigerian immigrant median annual income is greater than the Afro-Caribbean and African-American groups. (Anekwe 18).
Though immigrant population consisting of 13% of the total population of the USA , contribution by the immigrants’ to the development of the USA’s economy has been witnessed in the construction, agricultural, health care housing, education services, real estate, food services and mining industries.
It is to be noted that these industries are considered to be the founding stone of the American economy.
Analysis of Immigrant Concentration in American Metropolitan Areas and Its Impact on Median Household Income
Immigrants are reshaping the American metropolis and as per the 2000 Census , about 29 millions immigrants residing in metropolitan provinces in America which is higher by 10 million since 1990.
It has been observed that immigrants will have an analogues socioeconomic profile with that of persons of the same ethnicity / race in the U.S.
There has been uneven distribution of immigration in the U.S. and about 50% of the immigrant populations in America are residing in just 13 metropolitan provinces like Chicago, New York, San Francisco and Los Angeles and the majority metropolitan areas have still have less than 10% of the foreign born.
The following graph shows metropolitan regions where immigrants reside in large numbers, i.e. more than the 10% of the local population and also shows their numbers are very thin just below 5%.
In Mississippi and in Midwest, the immigrants reside in low numbers. We can notice that large number of immigrants live in the Southeast, East Coast and in the West Coast.
For instance, Nashville metropolitan had very less immigrants in 1990 numbering 18,000 where the immigrants’ number increased by three times during the recent decade and grew to 4.7% now from that of” 1.8% in 1990.”
Graph 1 – Metropolitan Regions where more than 10% or less than 5% of residents are immigrants, 2000
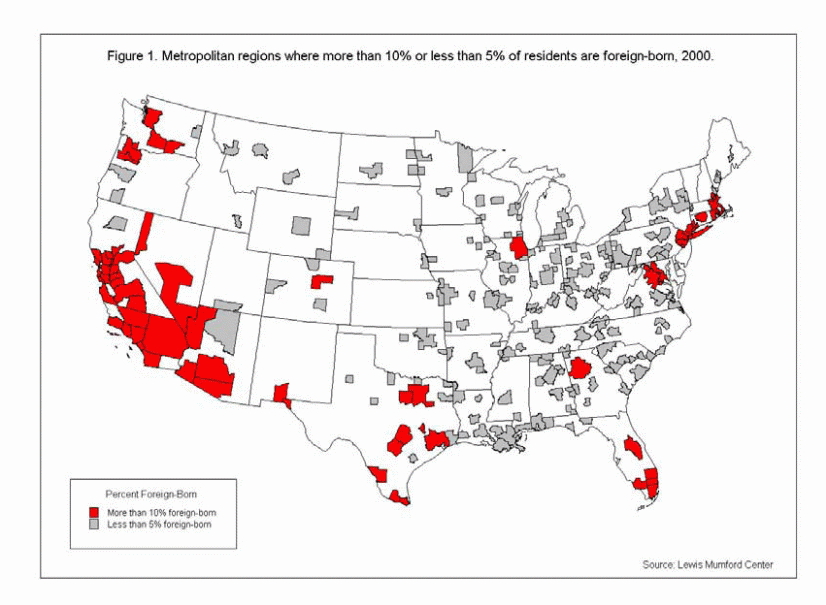
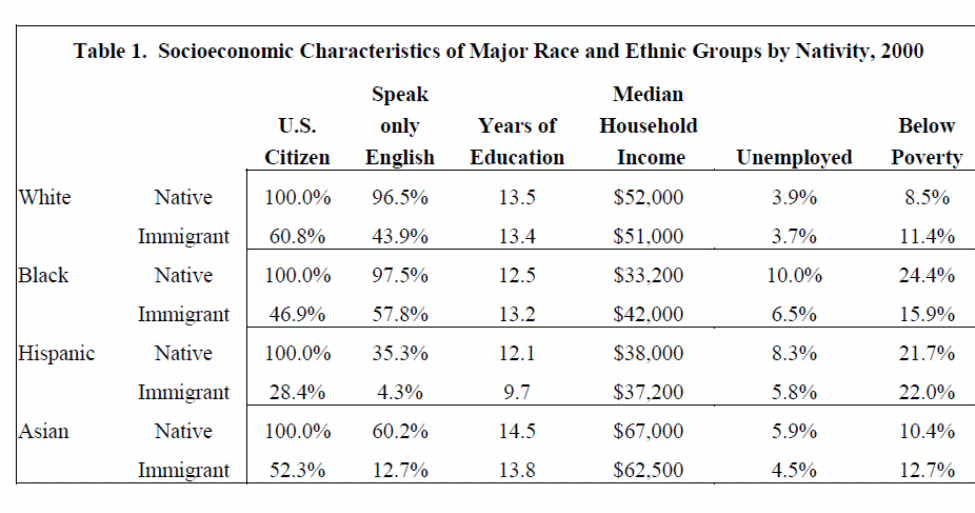
The following table illustrates the household median income of immigrants and also Native Americans which is based on the 2000 Census data.
Data Analysis
From the following table1, one can understand that white immigrants’ income was at $ 52,000 , black immigrants income was at $42,000, Hispanic income was at $ 37,200 and Asian immigrants was at $ 62,500 in the year 2000.
In fact, Asian immigrant median income was more that of White natives. This is the conclusive evidence that immigrants have really contributed higher income for the metropolitans in USA.
Table 1: Socioeconomic Characteristics of Major Race and Ethnic Group by Nativity, 2000.
The following table comprises the data from the Census 1990 and 2000 data. The following table illustrates the total number of US-born and foreign born persons in each of the major ethnic /racial group who lived in the metropolitan areas in the U.S. both in 1990 and in 2000.
It is to be noted that the percentage of immigrant residents increased sharply to 13% in 2000 from that of 9.5% in the year 1990. It is to be noted that more than 40% of the immigrants were Hispanics whereas about 666% were immigrants from Asia.
Thus, there has been about 40% increase in the metropolitan population in 2000 was mainly attributable to the sudden increase in the immigrant population in the metropolitan areas of the USA.
Table 2 – Native and immigrant populations in metropolitan areas
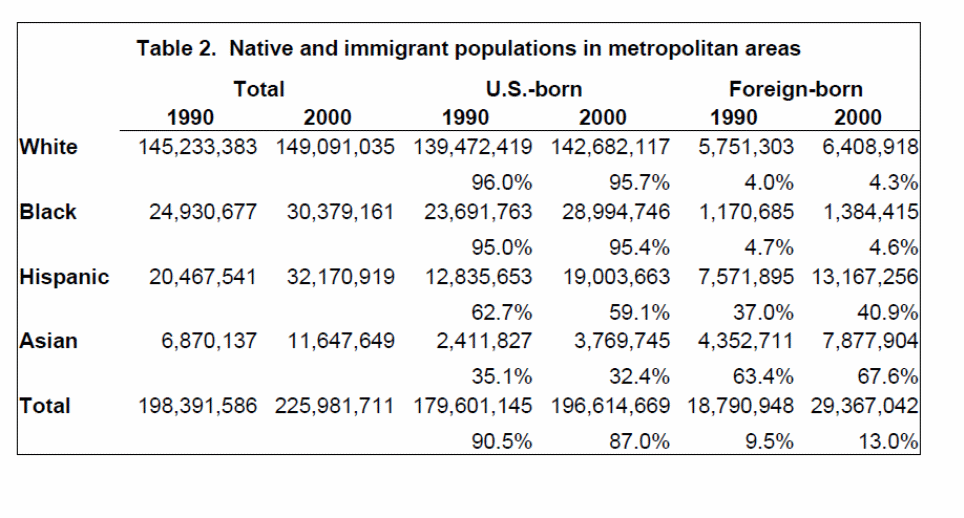
Table 3 – Metropolitan regions with the largest numbers of immigrants in 2000
The major effect of immigration is that it transforms the mixture of ethnic and racial cluster in a province.
For instance , in San Francisco Bay area, the large skilled Asian immigration settlement has increased the income levels of that metropolitan whereas areas like Los Angeles where Mexicans unskilled immigrants have settled, no much increase in the income level is seen these metropolitans.
It is to be noted Los Angeles due to its proximate to Mexican border has the highest immigrant population viz.” 3.4 million in 2000.” Likewise, Los Angeles has the highest number of Asian immigrants which was about 900,000.
Further, it had about 400,000 immigrants from Iran. Though, Los Angeles had a population of 15.4% immigrants in 1990 but the figure came down sharply in 2000 and it declined to “11.7% in 2000.”
This is due to the migration of the Hispanic immigrants to neighborhood provinces like San Diego, Orange County and Riverside-San Bernardino and thus, these California metros housed more than 19% of immigrants in USA.
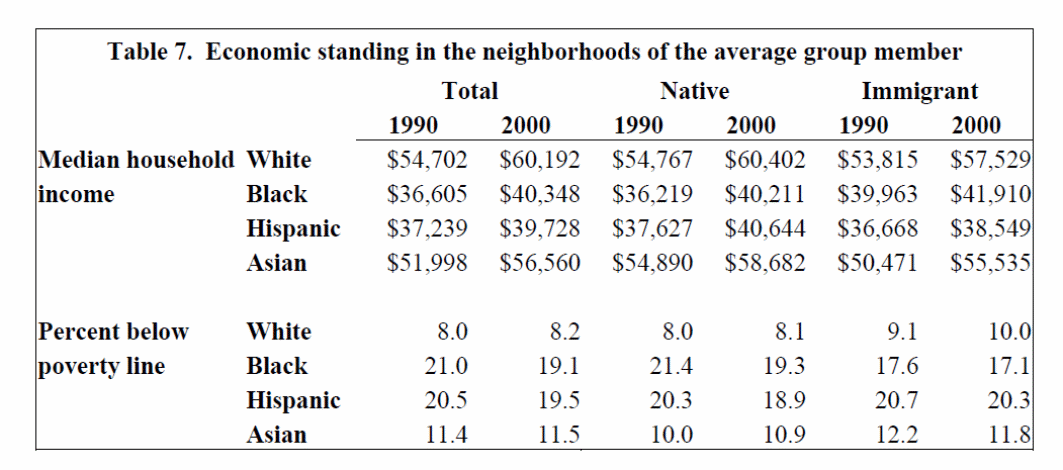
From the following table 4, we can understand that immigrants have contributed substantially for the overall increase of income of the metropolitans in USA.
Median Household Income in 2000 between natives and immigrants is given below for clear understanding.
Thus, the immigrants, whether they are white or Hispanic or Black or Asian, their concentration in the metropolitan suburbs of USA has definitely contributed to have higher median household income.
Table 4: Economic Standing in the Neighborhood of the average Group Member
Conclusion
Despite of various political overtures, many empirical evidences have proved that immigrant with diversified skill levels have a net positive impact on the American economy (Hunt & Gaulthier-Loiselle 56).
There is concrete evidence that immigration has helped to enhance the aggregate productivity of the economy of the USA and hence it also enhances the USA’s GDP. (“Gross Domestic Product”).
No doubt, immigration brings more productive resources to the U.S. economy due to greater utilization of both capital and the land and thus, enhances the aggregate of both income and production in the USA.
We should realize that immigrants are really boon to the American economy and definitely not a ban. There is a general apprehension that immigrant workers would snatch the available jobs was footed upon postulations and not a reality.
Actually, immigrant workers helped to take over the jobs that were unappealing to native-born citizens.
At the same juncture, immigrants were influential in the establishment of new jobs and the best illustration is the Silicon Valley where highly skilled IT specialists from Europe and Asia are responsible for lifting the house-hold median income in these metropolitans.
Nonetheless, USA also needs the cheap labor force which was important in many industries for their survival.
There are some industries in USA that could not compete without the assistance of low-wage immigrant workers as the native Americans never prefer to do menial jobs which are presently carried out by immigrants.
Americans also desire that their food products stay affordable. They want low paid immigrant labour for their gardening landscaping, and other services. Americans may find it impossible to maintain a luxurious lifestyle without the assistance of immigrant workers.
According to Hanson, immigrants help to minimise the prices of the products and services due to lower wages paid to immigrant unskilled labour who are engaged in the home constructions, tourism, restaurant, cleaning, home care, hotels and child care.
If one lives in a metropolitan where immigrants reside in large numbers, the service offered by these immigrants will be available at competitive rate and hence, it helps the Native Americans to save more dollars.
According to Borjas (1997), due to immigrants, the industrialist in USA would enjoy an increase in their income by about $ 140 million and there would be a national benefit from immigrants to the tune of $ 9.1 billion.
According to National Research Council, immigrant population would help to enhance the GDP by $14 billion.
According to Smith and Edmonston (1997), the National Research Council has found that net monetary advantages to the USA’s Federal Government have surpassed the monetary costs to both metropolitans and states.
Hence, my proposition was established to be true since immigrant brought at any rate three positive effects to the America. First, creation of innovative products and solutions was possible due to immigrant population.
Second, for certain industries in USA like orange orchards, restaurants etc., immigrant workers offered a cheap labor force. At last but not the least, if immigrant number increases, median household income in metropolitan areas also increases and vice-versa.
Works Cited
Anekwe, Patricia N. Characteristics and Challenges of High Achieving Second-Generation Nigerians. New York: Universal Publishers, 2009.
Borjas, George. (2003). “The Labor Demand Curve is Downward Sloping: Reexamining the Impact of Immigration on the Labor Market.” Quarterly Journal of Economics, 118(4):1335-74.
Hanlon, Bernadette, John R.Short, & Thomas J. Vicino. Cities and Suburbs: New Metropolitan Realities in the US. New York: Routledge, 2009.
Hunt, Jennifer, & Marjolaine Gaulthier–Loiselle. (2010). “How Much Does Immigration Boost Innovation?” American Economic Journal: Macro Economics 2(2):31-56
Krugman, Paul. International Economics: Theory and Policy. New Delhi: Pearson Education India, 2008.
Pumar, Enrique. Hispanics Migration and Urban Development. New York: Emerald Publishing, 2012.
Smith, James P. and Barry Edmonston, eds. 1997. The New Americans: Economic, Demographic, and Fiscal Effects of Immigration. Washington, DC: National Academy Press.