Company Description
The Roads and Transport Authority (RTA 1) started its operations in 2005.
The company’s main goal is to plan and oversee transportation networks in Dubai (Perry 197).
The mission of RTA (1) is to “Develop integrated and sustainable transportation systems and provide distinguished services to all stakeholders” (RTA 1).
Formed in 2005, RTA is a government organization that manages Dubai’s transport networks. Its activities are designed to meet the emirate’s pressing infrastructure needs. Particularly, it strives to bring order in Dubai’s infrastructure system by creating an integrated transport network that covers all aspects of public transport management.
RTA (1) offers several services including providing integrated transport networks, road transport licensing, formulating legislations, and managing the Dubai Metro (Oxford Business Group 123).
As shown below, the company mainly uses online applications to provide its services (RTA 1).
To keep up with the changing needs of Dubai’s road users, RTA offers several services to different customer groups, including drivers, taxi clients, and commercial transport companies. The company’s services include licensing, offering booking services, managing Dubai metro services among others. RTA mainly relies on its virtual service platform to offer such services.

Description of Operations
Driver Services (replacing damaged, or lost, driving licenses, providing international driving licenses, providing parking services, providing taxi rental services, providing booking services, and similar activities).
Licensing (replacing lost, or damaged, permits for site driving licenses) (RTA 1).
Public transport management (road, rail, and marine operations) (Elsheshtawy 148).
Drivers outline the main customer group for RTA. Some of the services offered to them include replacing damaged, or lost, driving licenses, providing international driving licenses, providing parking services, providing taxi rental services, providing booking services, and similar activities. Besides public transport, the RTA also manages Dubai’s rail and marine transport services. Mainly, these services have a smaller scope compared to road transport services.

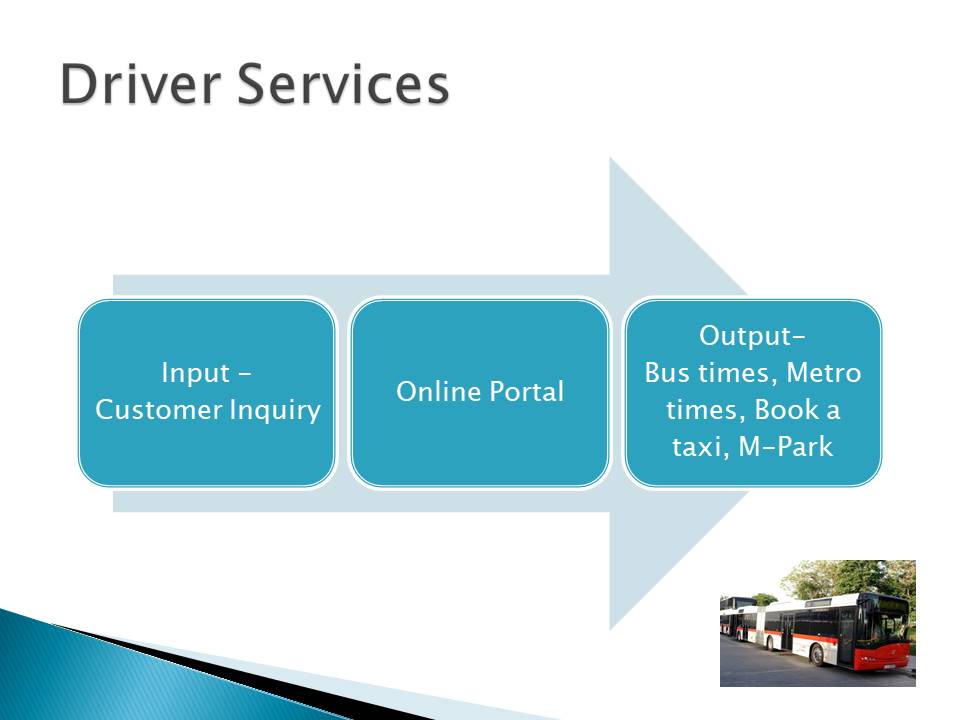
Driver Services
Since road transport operations are the main services offered by the RTA, the number of operations offered in this service group is high. Consequently, RTA uses virtual platforms to serve its customers. Customer inquiries are the main inputs for the online platform. A SMART system processes such inquiries and produces the desired outputs, such as bus times, metro times, M-park services to its customers.
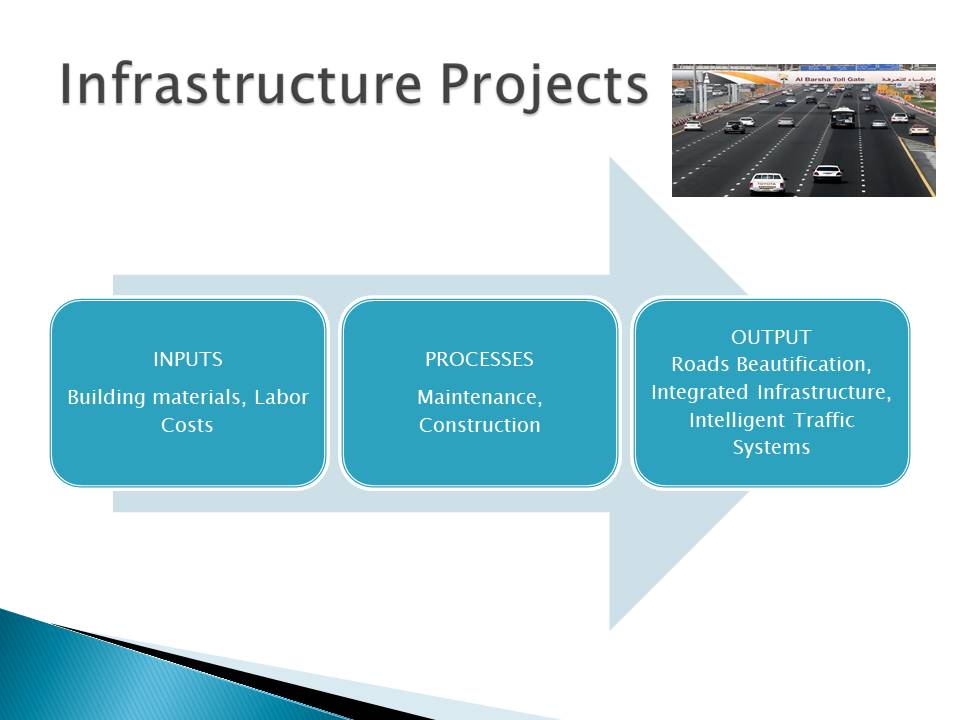
Infrastructure Projects
The infrastructure services offered by RTA mainly focus on constructing and maintaining rail and road transport networks. The main inputs associated with offering such services include building materials and labor costs. These inputs are used in construction and maintenance services to produce integrated traffic systems, integrated infrastructure, and beautified roads, as the main outputs.
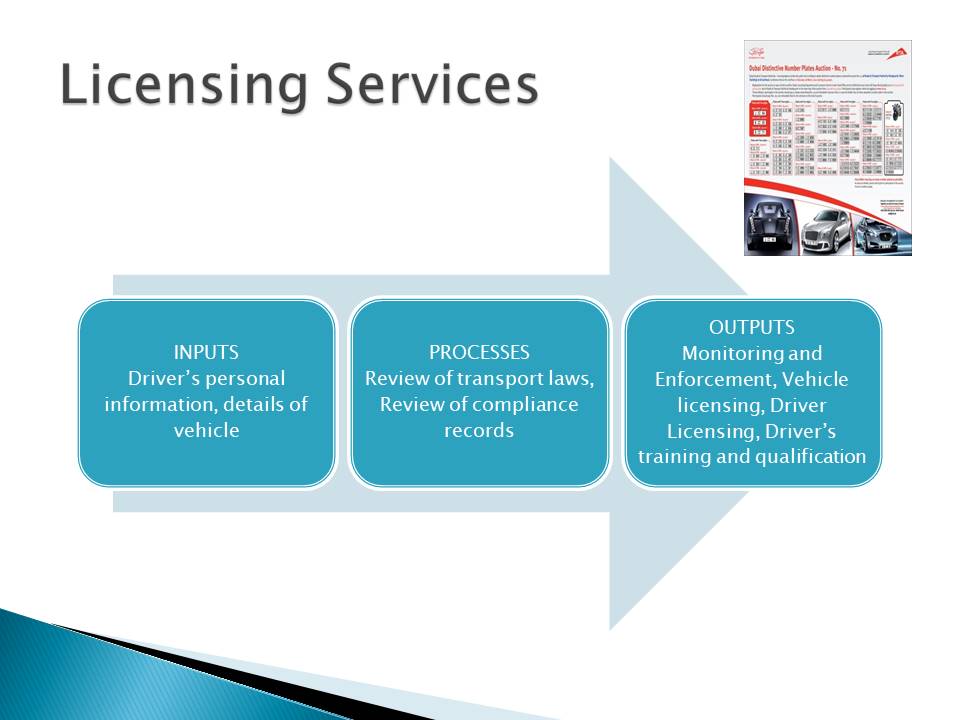
Licensing Services
RTA mainly offers licensing services to road transport users. Drivers provide their personal information about their nature of business (private or otherwise), as the main inputs in the process. RTA uses these pieces of information to investigate if they comply with existing laws. Similarly, the company makes sure they do not contravene any existing laws. These processes help to monitor, enforce, and evaluate existing laws. The drivers get their licenses if the RTA is satisfied with their compliance records.
Supply-Chain Decisions
RTA’s supply-chain decisions fall into three categories: operational planning, tactical planning, and strategic planning. The operational plans cover the day-to-day operations of the company. However, the tactical planning and strategic decisions cover the medium-term and long-term decisions of the company.
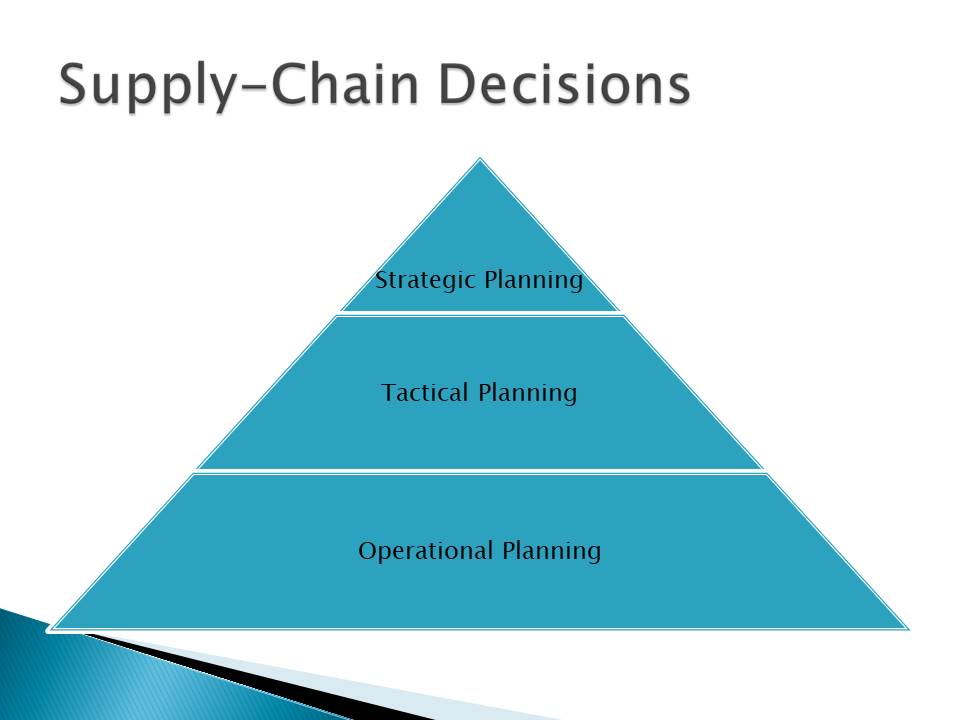
How Supply Chain Decisions Affect Company Strategic Objectives
Strategic Level:
- Customer segmentation (Oxford Business Group 108).
- Online market positioning (Schulte-Peevers & Shearer 390).
- Service differentiation.
- Adopting international best practices.
At the strategic level, RTA makes sure its activities are differentiated from similar services in the market. Similarly, the company strives to be a market leader by adopting global best practices in public transport management. It achieves a high level of efficiency through online market positioning and effective customer segmentation. These highlights show the company’s strategic map.
Tactical planning:
- Meeting demand forecasts through technological adoption (RTA 1).
- Introducing timely and sizable marketing promotions.
- Using latest technology to provide customer services (Dawawala 3).
- Benchmarking building and construction services.
RTA uses several tactics to meet its strategic goals. Adopting the best and latest technology in service delivery is at the center of its quest to be a market leader in public transport management. Similarly, the company relies on this strategy to improve the quality of its customer services. In terms of its public transport management role, the company benchmarks its building and construction services. Mainly, this strategy contributes to the company’s adoption of global best practices in its building, construction, and maintenance activities. To effectively appeal to its different customer groups, RTA uses timely and sizeable marketing campaigns to engage its customers.
Operational Planning:
- Achieving Departmental goals (RTA 1).
- Decreasing response time.
- Maintaining Quality and Excellence (OBG 56).
- Employing competent and tech-savvy employees.
- Encouraging innovation (RTA 1).
The operational plans of RTA refer to the day-to-day activities of the company. Departmental managers are responsible for most of the company’s operational plans. For example, each department has unique goals that all employees strive to achieve everyday. Since customer service is a key role of RTA, decreasing response time is a common operational plan, especially in the provision of driver services. Furthermore, since technology helps RTA to undertake most of its activities, the company invests in hiring competent employees. Maintaining a high standard of quality in its departmental operations and encouraging innovation among employees also supports the company’s quality objectives.



Productivity
- Number of users (OBG 56).
- Customer Complaints.
- Customer retention rates.
- Hold time and abandonment rates.
- First Contact resolution.
- Escalation rates.
- Quality of Infrastructure (OBG 56).
RTA’s profitability is mainly dependent on its customers. Therefore, its productivity relies on customer satisfaction indicators. Consequently, the company’s number of users, customer complaints, customer retention rates, hold time rates, and escalation rates show the efficacy of the company’s services. If RTA experiences high escalation rates, customer complaints, and abandonment rates, its productivity would be low. However, if it has a high number of users and retains most of its customers, its productivity would be high. Its quality of infrastructure measures its productivity, in terms of construction and maintenance services.
How to Improve Productivity
- Introduce a customer satisfaction measure.
- Establish customer expectations and tailor company services to meet these expectations (OBG 56).
- Improving online customer experience by increasing website usability.
- Benchmark customer satisfaction (Kramer, Bothner, and Spiro 35).
Improving RTA’s productivity mainly depends on initiatives that aim to improve customer experience. Based on this fact, the company should introduce a customer satisfaction measure because it lacks one. Currently, it cannot measure its performance in this regard because it cannot measure its productivity either. The company should benchmark its performance in this regard. RTA should also design its customer services to respond better to customer needs because customer preferences keep changing. The company can do so by conducting periodic surveys about customer preferences and incorporate their findings to its service delivery regime. Lastly, although RTA has a website portal, its usability is low because it is difficult to navigate the site. Consequently, the company needs to make the website simpler to improve online customer experience.

Works Cited
Dawawala , Aamir. Green IT – A Global Problem and an Imperative Business Opportunity, New York, NY:GRIN Verlag, 2010. Print.
Elsheshtawy, Yasser. Dubai: Behind an Urban Spectacle, London, UK: Routledge, 2009. Print.
Kramer, Lois, Bothner, Aaron, and M. Spiro. How Airports Measure Customer Service Performance, New York, NY: Transportation Research Board, 2013. Print.
OBG. The Report: Ras Al Khaimah 2008, London, UK: Oxford Business Group, 2009. Print.
Oxford Business Group. The Report: Dubai 2007, Oxford, UK: Oxford Business Group, 2008. Print.
Perry, Mark. Business Driven PMO Success Stories: Across Industries and Around the World, New York, NY: Ross Publishing, 2013. Print.
RTA 2013, About RTA. 2014. Web.
Schulte-Peevers, Andrea, and I. Shearer. Oman, UAE & Arabian Peninsula, London, UK: Lonely Planet, 2010. Print.