Introduction
The multimedia developers are mainly concerned about the sample resolution and quantization when scanning a full-color photograph in digital processing. Digital processing digitalize images both spatially and in amplitude. The analog video signal is sampled and quantized by the digitizer. Continuous data is converted to digital form using sampling resolution and quantization. The spatial resolution of a digitized image is affected by the sampling rate, whereas the amount of grey levels in a digital snapshot is controlled by the quantization level. During processing an image, the size of a sampled image is presented as a digital value (Torii, 2018).
Quantization Levels
The quantization levels of the image should be high enough for people to detect small shade variations. When an image is quantized with insufficient brightness levels, incorrect outlines are the primary problem. The authors discuss color picture quantization algorithms that are adjustable and tapered. The goal of the research is to show high-quality color reproductions with small frame buffers. According to the research, various color images that normally need a frame buffer with 15 bits for every pixel could be quantized to 10 or fewer bits with little subjective deterioration. The images produced are usually superior to those created using uniform quantization (Torii, 2018).
The Task of Color Picture Quantization is divided into Four Stages:
- Obtaining color statistics from the original image
- Using color statistics to select a color map
- Mapping original colors in the color map to their closest neighbors
- Redrawing and quantizing the original image.
Sampling and Quantification
If the camera or sensor’s output is not already digital, the image is recorded by a sensor (e.g., a camera) and converted using an analog-to-digital converter. The image to be processed first is saved in a computer as a continuous voltage waveform then the computer converts the images into digital form. It converts the continuous image to digital form by digitalizing the coordinate and amplitude values.
The digital image gives the response value and spatial position of the image. The analog image represents a continuous signal, while the digital image represents a discrete value. Sampling contributes to a spatial resolution, and quantization gives a gray image resolution (Torii, 2018).
In sampling, a line is can from the bottom to the top vertically at certain intervals; on each horizontal line, remove the one-dimensional scanning of gray value. The discrete signal is then obtained by sampling the one-dimensional scanning line signal at a specific interval.
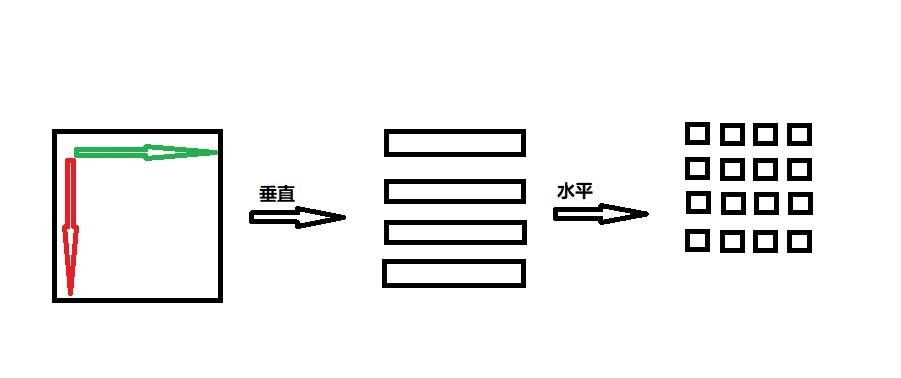
Sampling is done in two ways, uniform sampling and non-uniform sampling.
- The image is uniformly divided into MN blocks after uniform sampling. The sampling function is used to determine the sample result value for each image block, and the most generally used sampling function is to get the regional average value.
- Uneven sampling entails increasing the sampling frequency where details must be represented while decreasing in areas with minor picture changes. To produce accurate photographs, for example, when sampling on an image map, it is required to raise the sampling frequency at the turning point of the road or river while decreasing the sampling frequency on the straight road. More pixels produce an image of high resolution (Torii, 2018).
Conclusion
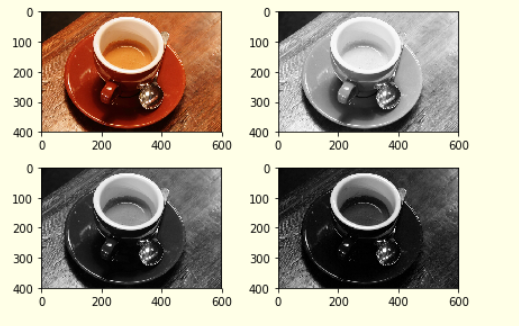
Black and white image processing, gray image processing, and color image processing are the three types of image processing. Brightness, contrast, and color channel are all essential image properties.
Final output of the images.
Reference
Torii, S. (2018). Preface: Flow visualization, image processing and related techniques. Journal of Flow Visualization and Image Processing, 25(1), Web.