Samsung Electronics was chosen as a company for the evaluation of its strategy and performance with the assistance of the analysis of the financial reports. In this case, the potential risks, inputs of the company’s production, introduction of new products, assessment of the changes in prices and profitability, marketing analysis, and the evaluation of the various strategies, which are not related to the price formation, are assessed with the assistance of financial performance of the organization. In the end, the conclusions are drawn, and the relevant recommendations are proposed to enhance the operations.
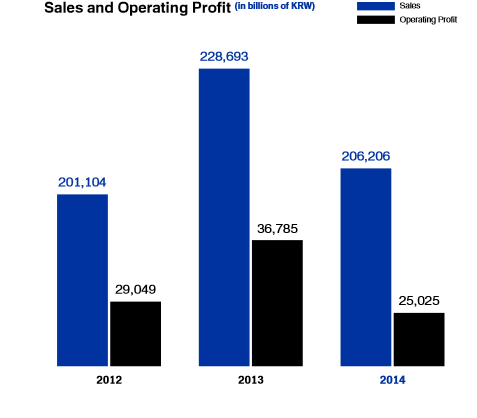
Samsung Electronics is a multinational company, which specializes in the production of technology while focusing on innovation and continuous technological improvement. It could be said that it is a segment of Samsung Corporation, which specializes on “high-tech electronics and manufacturing and digital media” (Samsung: Welcome, 2016, para. 1). In 1979, Samsung started its operations with the production of the microwaves, and now it is one of the leaders in the technological market (Samsung: Our History, 2016). Figure 1 portrays the financial situation of Samsung in 2014 while comparing with the company’s profit in 2013 and 2012. It could be said that the operating profit and sales were lower in 2014 than 2013. Nonetheless, the presence of this aspect will be assessed in the following chapters of the paper while evaluating the strategy of the enterprise and market environment.
Sources of Risk and Uncertainty
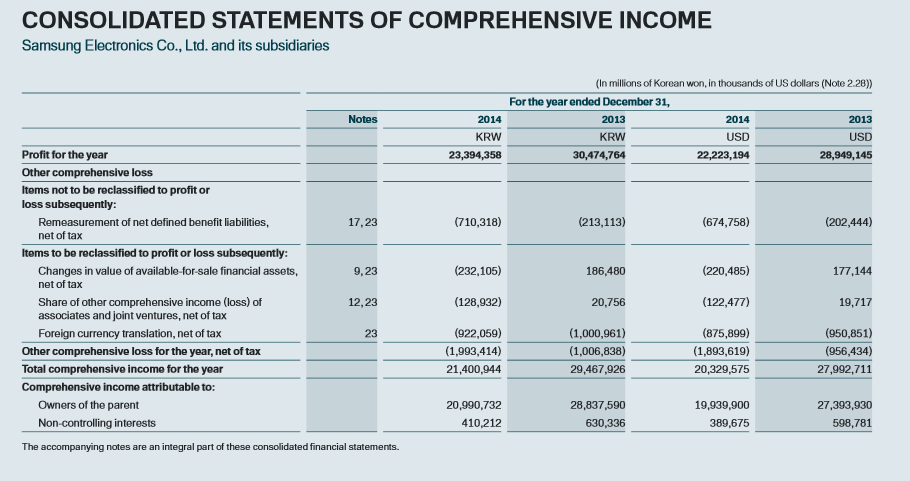
As for the risks and uncertainty, it is evident that the financial reports of Samsung have a tendency to indicate company’s position on the market and reflect the influence of the changes in the economic environment. Nonetheless, it remains apparent that the constantly changing business environment has to be considered and taken into account while estimating profits due to the presence of bias in assumptions (Grable, Lytton, & O’Neill, 2004). In this instance, Figure 2 presents the segment of the consolidated statements of comprehensive income. In this case, the aspects such as profit or loss related to joint ventures, modifications of the value of the assets, and foreign currency exchange rates could be considered as the potential risks and uncertainties, which the company takes into account while calculating the profit and evaluating Samsung’s current performance on the electronic market (Samsung Electronics Annual Report, 2014). In turn, it remains evident that these aspects strongly affected the company’s income, as the organization had to devote significant attention to these features in 2014. Consequently, the decrease of the profit can be explained by the presence of these matters in operating markets of Samsung.
As for the governmental regulations, it is apparent that authorities have an opportunity to affect the sales and distribution of the brand nationally and internationally (Needham & Dransfield, 2000). In the instance of Samsung, the alterations in the exchange rate policies could be considered as the potential influencers of the company’s financial operations. It is apparent that the company functions on several markets and has to exchange the currency in accordance with the exchange rate.
Inputs of Samsung’s Production
The primary goal of this section is to highlight the inputs, which are utilized in the production and the identification of the potential threats to their security. In this instance, it remains evident that there is a high interdependence between the price of the product and the inputs, as the initial costs affect the final price (Krupova, Krupa, Wolfova, & Michalickova, 2014). Samsung uses the assistance of the suppliers, raw materials, labor, and other matters. For example, it remains evident that Samsung exploits the suppliers to be able to combine the parts, which are required for the assembly of the initial product. Additionally, the fluctuations of the costs of the raw materials such as Columbite will affect the prices dramatically due to the essentiality of this component in the production of Samsung’s products (Rosenberg, 2015). Nonetheless, the prices for plastic, wood, metal and other raw materials will also influence the prices as they are necessities in the electronic manufacturing.
In this instance, the potential threats can be identified as the dependency on the costs of raw materials and labor. Another matter is the inability to find the replacement of Columbite due to the potential scarcity of the resource. Lastly, the necessity of the cooperation with the suppliers to maintain cost-efficiency might be the definer of the company’s financial success and productivity, as the participants of the supply chain outline the transportation and delivery expenses.
New Products and New Markets
In turn, it remains evident that the Samsung tried to introduce new products to the market and cultivate the demand by creating particular niches. In this instance, it is apparent that Samsung pays a substantial attention to this approach while defining the company’s business strategy (Samsung Electronics Annual Report, 2014). Consequently, Samsung highly invests in research and development to support the sufficient introduction of new products and services in the market. For example, Samsung generates a new SUHD TVs, which supports a higher quality of the image and corresponds to the green policies during the production process (Dredge, 2015). It could be said that the introduction of this product assists in generating of a new customer’s niche, which cares about the quality of the products and compliance with the ecologically friendly principles.
In this case, the development of novel technology contributed to the presence of the higher demand and initiated the increase in company’s profits. In turn, the development of new products draws a strong attention of the brand and causes the rise in the company’s revenues. In this instance, the revenues reached the top due to the introduction of the promotional events and sales of SUHD TV’s in the fourth quarter (Samsung Electronics, 2016). It is apparent that this matter resembles with Samsung’s non-price and price strategies, as it tends to modify the products of the competitors by introducing new solutions to the production approaches. In the end, the development and innovation of new products assist the company in maintaining the leading positions in the market and having positive financial performance.
Price Fluctuations and Profitability
Furthermore, the prices of Samsung’s product tend to change over time due to their dependency on demand and presence of other aspects. Firstly, it is apparent that Samsung’s products cannot be considered as commodities. Consequently, the demand will have a tendency to change depending on the fluctuations of the price. For instance, Samsung Electronics plans to reduce the prices for Galaxy S6 and S6 edge to generate higher demand for these products among the users of smartphones (Associated Press, 2015). As for the substitutes, they tend to be presented by Apple, Lenovo, Microsoft, and other companies, which are related to the production of electronics. It is apparent that the changes in the price are necessary to attract attention to the brand and generate higher revenues.
Lastly, the characteristics of the industry define the company’s costs and profitability. In this case, the manufacturers and producers tend to utilize similar materials for the production due to the resemblances between products. It could be said that the supplier can vehemently affect the profits of the electronic companies by increasing the prices due to the scarcity of the resources or the presence of the inelastic demand. This matter can influence not only the profitability of Samsung but be a primary cause of the price war between the brands.
The Competitive Environment of Samsung
Samsung Electronics operates on the vehemently competitive market, as many companies tend to have diversified product lines in this segment. For instance, Samsung’s market share dropped to 26% in India due to the appearance of Micromax (Growing Micromax, 2013). In turn, a similar situation occurs in different countries. Nonetheless, despite the rising competitions in dissimilar locations, Samsung has one of the leading positions in the industry due to the rapid reaction of the changes.
As for the competitors, the primary ones are Apple, Google, and Microsoft in the mobile sphere. It is apparent that Apple is the strong player in the electronic market due to the innovative solutions and exclusive product design (Jun & Sung, 2013). Nonetheless, despite high exit and entry barriers due to the high costs of initial investment and production, new companies tend to appear quickly, as the production’s resources are not scarce and rare. It is apparent that Samsung has to be able to adapt rapidly to the fluctuations of the economic environment due to the high competitiveness and presence of new players. Additionally, the company has to pay attention to the other areas of operations, as the inability to maintain the flexibility on the high level leads to the appearance of the uncertainty, risks, and profit loss.
Samsung’s Market Structure
Firstly, the nature of the market has to be defined. It could be said that current cellular phone market can be described as oligopoly due to the presence of the defined leaders in the industry (Dwivedi, 2002). Nonetheless, the small competitors exist, but they occupy insignificant market share and cannot be considered as a threat of high significance to Samsung. It is evident that the prices of the competitors tend to influence the demands of Samsung’s products. Figure 3 presents the comparison of income of 2013 and 2014.
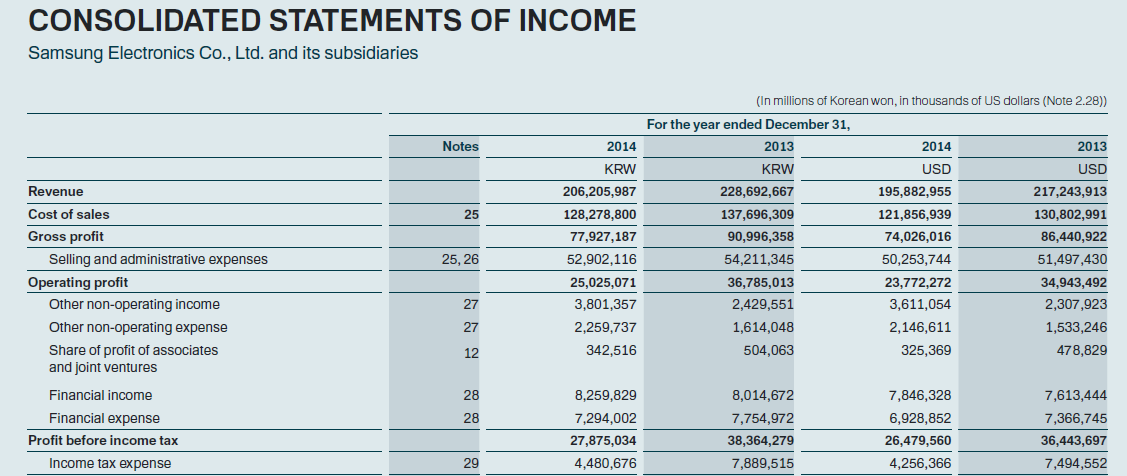
In this instance, it is apparent that the income of the company is lower in 2014 due to the absence of the high demand for new Samsung’s products. The primary reason for this issue is the actions of the competitors. Consequently, it could be said that the company is highly dependent on other key players in the market due to their ability to influence prices and sales. It is evident that the operations in the oligopoly are harder due to the dependence on the market leaders. In the end, understanding of Samsung’s position helped the company become a leader in the industry and define the trends for the rest of the market.
Samsung’s Non-Price Competitive Strategies
It remains evident that Samsung also utilizes various strategies, which are related to the maintenance of the image without paying particular attention to pricing. It could be said that Samsung tends to be one of the leaders in the market due to its ability to provide a vast plethora of products in short-term (Samsung Business Strategy, 2012). It assists the company in having a significant market share and increasing the attention to the brand.
Additionally, the company cultivates a perception of being a green organization, which cares about the condition of the environment. In this case, it utilizes green advertisement techniques while creating an association with the environmentally-friendly producer (Abbasi, Abbasi, Faraji, & Hajirasouliha, 2014). Additionally, the research related to the green advertising revealed that the green advertising modifies the view about the brand in a positive direction (Abbasi et al., 2014).
Lastly, Samsung tends to monitor the innovations of the competitors and adapt them in the context of its products rapidly (Lee & Slater, 2007). It could be said that it is a useful attribute in terms of the operations in the technological sphere, as the ability to adjust to the constantly changing tendencies can define the market share. Nonetheless, Samsung implements this strategy successfully since it remains one of the leaders on the market and tends to introduce new products within the limited time frame.
In the end, the utilization of the non-price strategies is essential for Samsung, as it helps the company maintain its market share while emphasizing the essentiality of innovation and R&D. Nonetheless, it has to apply the pricing strategy based on the analysis of the elasticity demand, as it determines the company’s grounds for success in future. Lastly, it is evident that all of the strategies have to be used as a combination to achieve higher efficiency and productivity.
Recommendations
In the end, the summary of the findings related to the Samsung’s operations has to be drawn to determine the potential basis for the recommendations. Additionally, the company’s mistakes in financial actions and general functioning has to be assessed to portray the current condition of the business by referring to the financial reports. Firstly, it is apparent that the company is dependent on the actions of the competitors, as they affect Samsung’s profits. This approach is depicted in Tables 1, 2, and 3. Additionally, Samsung has a tendency to decrease the prices due to the high elasticity of demand. Nonetheless, Samsung is still one of the leaders in the market due to the oligopolistic nature of the competition.
Furthermore, the potential recommendations were identified to enhance a future organizational performance of Samsung. Firstly, the company has to maintain the sufficient analysis of the competitors to assure the presence of the demand for the products. Table 1 and 3 portray that the company made a mistake in 2014, and it was a primary reason for the decrease in demand and revenues. Additionally, paying attention to innovation, development, and the creation of new products will help the company increase its market share. Lastly, Samsung has to remember to devote time to the development of the non-price strategies, as green policies tend to be vehemently critical while establishing a positive image of the company in the industry.
References
Abbasi, H., Abbasi, H., Faraji, A., & Hajirasouliha, M. (2014). Investigating the effects of green marketing on development of brand fascination. Management Science Letters, 4(5), 921-924.
Associated Press. (2015, July 30). Galaxy S6 smartphones don’t ring true for Samsung Electronics’ profits. The Guardian. Web.
Dredge, S. (2015, January 9). CES 2015: 25 new products and technologies worth talking about. The Guardian. Web.
Dwivedi, D. (2006). Microeconomics: Theory and applications. Harlow, UK: Pearson Education.
Grable, J., Lytton, R., & O’Neill, B. (2004). Projection bias and financial risk tolerance. Journal of Behavioral Finance, 5(3), 142-147.
Growing Micromax rings alarm for Samsung in smartphone market. (2013). India Business Insight, 5(1), 214-215.
Jun, S., & Sung, P. (2013). Examining technological innovation of Apple using patent analysis. Industrial Management & Data Systems, 113(6), 890-907.
Krupova, Z., Krupa, E., Wolfova, M., & Michalickova, M. (2014). Impact of variation in product traits, inputs costs, and production prices on profitability in multi-purpose sheep. Spanish Journal of Agricultural Research, 12(4), 902.
Lee, J., & Slater, J. (2007). Dynamic capabilities, entrepreneurial rent-seeking and the investment development path: The case of Samsung. Journal of International Management, 13(3), 241-257.
Needham, D., & Dransfield, R. (2000). Advanced Business. Oxford, UK: Heinemann Educational Publishers.
Rosenberg, M. (2015). Strategy and sustainability: A hard-nosed and clear-eyed approach to environmental sustainability for business. Hampshire, UK: Palgrave McMillan.
Samsung Business Strategy. (2012). Web.
Samsung Electronics. (2016, January 28). Samsung Electronics announces fourth quarter & FY 2015 Results [Press release]. Web.
Samsung Electronics Annual Report. (2014). Web.
Samsung: Our History. (2016). Web.
Samsung: Welcome to Samsung. (2016). Web.