Introduction
Services play an extremely essential role in political, economic and social aspects. It is not possible to imagine people’s life without personal, government, business, financial and other services. On a state economics level, service sector is one of the most reliable parts of country GDP. Mutually beneficial service practice strengthens not only interpersonal, but international relationships, as well. Every day, customers want to satisfy their needs from a service provider.
Naturally, the role of bank services in the context of state economics and business can not be underestimated. Bank operations influence macro-economic indices and welfare of society. Worldly recognized first-rate banks of the world, located in Switzerland, the UK, the USA, Japan, France, etc. attract their clients with many-years experience, good reputation, reliability and safety of bank services and operation. Such banks use effective strategies to achieve the customer satisfaction. The aim of the present essay is to reveal the multifaceted nature of bank services through understanding bank strategies and examining the experience of specific banks.
Literature Review
The role of services in people’s life is great. All services are performed for a customer, called to provide his life with comfort, satisfying his needs. Services support and facilitate customer personal life. The essence of a service is to help and do work for someone. Mutually beneficial service providing has become the basis for business, trade, interpersonal and international relationships. There are many people employed in services. According to some researchers, in 2005, there were about 80 % of people in the USA involved in the service sector. The indices of another countries are also notably high: the UK – 77%, Canada – 76%, Germany – 68, 5%, etc. (Fitzsimmons, & Fitzsimmons, 2008). As one may see, services are appreciated and demanded by people.
In the history of human civilization, economic evolution has proved favourable environment created by services. A service offers commodity, and performs delivery function (on customer demand). It has an intangible nature, and customized attribute. Any service should be directed to benefits of both a client (buyer) and a provider (seller). Information technology and innovations are the main sources of service sector growth (Fitzsimmons, & Fitzsimmons, 2008).
Banking and bank services have been in the scope of interest of many researchers. For example, Mullineux and Murinde (2003) dedicated their book to the problem of international banking. Mishra (2010) examined a bank in the context of microeconomics and macroeconomics, and the essence of the financial system, where a bank plays an exceptionally essential role.
Analyzing the works of these and other relevant researchers, one may see that a bank is a complex and unique financial institution that performs numerous functions, and provides a wide range of services to its clients. Being a financial intermediary, a bank can be central (issues governmental money and regulates the money supply), commercial (accepts deposits and channels them into landing activities with the help of capital markets), and savings one (receives customer savings accounts, and pays interest to depositors). In addition, most of people have become clients of retail bank, as it provides its services to general public. A modern bank has so many functions that it is difficult to enumerate them all. In general, a bank “accepts deposits from the public, makes fund available to those who need them, and helps in remittance of money from one place to another” (Mishra, 2010, p. 181.). In other words, a bank deals with money and credit in a different way. This is the main essence of commercial banking.
Bank strategies were in the scope of the researchers, as well. For example, Botten and McManus (1999) described the British Internet-oriented strategy that gave bank clients to make financial operations in a cyberspace. Bank card system gave rise to application of other strategies.
Smart bank card applications technology contributes to electronic financial solutions. The network of Automated Teller Machines (ATM) allowed banks to dispense its services to customers through a Personal Identification number (PIN) and a magnetic card. ATM gave customers an opportunity to be engaged in “receiving and dispensing cash, funds transfer between accounts, balance enquiries, etc.” (Wonglimpiyarat, 2005, p. 6). At the same time, Visa, MasterCard and bank’s ATM networks serve to promote its brand, and spread its services among the world population.
Future of the bank services attracted researchers’ attention. In the 90s, it was evident, that globalization, commercialization and Internet expansion reflected on bank performance. Blery and Michalakapoulos (2006) believe that customer-oriented strategies will be applied in the future. Banks will tend to make services more effective, accessible, time-saving, quality and satisfying. New innovative technologies and additional Internet opportunities will contribute to this process.
Body of the Paper: Services in Banks
Numerous functions of a bank predetermined the presence of range of services to its consumers. According to Mishra, it is possible to differentiate the following principal services. First, it accepts deposits: many people prefer saving their money in banks. This function helps people to earn interests and avoid theft. The presence of different types of accounts allow banks to attract clients’ savings: fixed (money is deposited for a fixed period of time; the rate of interest is high), current (serves businessmen and traders to make payments every day, making them pay incidental charges for a service), saving (encourages and mobilizes small savings with a low rate of interest; the number and amount of withdrawals is limited), recurring (encourages regular savings with interest of maturity of depositions; a rate of interest is relatively high), home safe (promotes saving habits under a special scheme), etc. deposit accounts (Mishra, 2010).
Second, a client may take advantage of loans, becoming debtor of a lending bank. However, loans are granted by a bank, depending on the creditworthiness of the borrowers (depends on clients yearly income). Among various types of loans, there are the following ones: money at call (a short period loan, provided for banks and other financial institutions), cash credit (given to a borrower against his current assets, and allows to withdraw money from time to time), overdraft (a borrower is allowed to withdraw more money than his deposits), discounting of bills of exchange (a popular and self-liquidating loan that gives an opportunity to pay the bill with the help of bank commission), and term loans (medium- and long-term loan that allow the amount to be either paid or credited to the borrower’s account; it must be repaid) (Mishra, 2010).
Credit creation is the following bank service: “a bank has the ability to create credit many times more than its deposits, and this ability to multiple credit creation depends on its cash-reserve ratio” (Mishra, 2010, p. 183). Credit creation is favoured by many people, because it allows to obtain good or service before payment. Promoting cheque system is the other bank service that became popular in the age of business transactions: “through a cheque, the depositor directs the banker to make payment to the payee” (Mishra, 2010, p. 183).
Also, a bank provides a customer with the following agency services: remittance of funds, payment and collection of credit instruments (bills of exchange, cheques, etc.), execution of standing orders (for example, a bank may pay rent on behalf of its clients), sale and purchasing of securities (bonds, stocks, shares, etc.), collection of dividends on shares, income tax consultancy, acting as executor and trustee (preserves its customers’ wills after their death), acting as a correspondent and representative (a bank may get traveller’s tickets, passports, and receive letters on clients’ behalf).
Besides, a bank provides its customers with general utility services: locker facility (valuables and important documents are kept for safe custody in a bank), traveller’s cheques (a customer may travell without the fear of loss and theft of money), letter of credit (used in foreign trade to certify customer’s creditworthiness), collection of statistics (a bank keep important information about country money, industry, commerce, trade, banking; publishes bulletins and journals with research articles), underwriting securities, gift cheques (of various denominations), acting as referee (for seeking information about its customers’ business reputation, financial position, and respectability), and foreign exchange business (by discounting foreign bills of exchange, a bank finances foreign trade) (Mishra, 2010).Nevertheless, people’s daily life suggest the idea that payment services are the most demanded services of a bank that meet customer needs every day.
One of the world financially strength banks in the world that satisfy its clients with practically all possible services, accessible for both general and elite public, is National Bank of Abu Dhabi (NBAD), founded in 1968 (Oxford Business Group, 2007). It has served as a central bank that actively participates in formation of the currency abroad. In 2005, its net profit equaled “$702, 42 m, return on quality of 43, 9% and total assets of $22, 76 bn” (Oxford Business Group, 2007, p. 97). Nationals who live outside the UAE have certain preferences in bank services. In general, the bank offers quick, reliable and secure services, giving an opportunity to take advantage from personal, corporate, and free Internet banking. Provision with personal bar-code, bank archive data, credit cards, currency exchange, time deposits, account opening, online trading are only one of possible services, available there (National Bank of Abu Dhabi, 2011). The researchers believe that
“NBAD is the chief provider of corporate services to business, the government, key public sector institutions, and major corporate groups. Corporate services include cash flow management, foreign exchange, and capital market products and assess management” (Oxford Business Group, 2007, p. 97).
Providing the mentioned services, NBAD keeps up the evolving international market, as well, because the considerable number of its clients is foreigners. This bank is able to meet the needs of growing market owing to its successful and effective development strategies. Also, NBAD has developed the advantageous system of international partnership. For example, Italia and Japan take part in corporate cross-border transactions. The bank has 23 overseas units and banking divisions located in Paris, Cairo, Oman, etc. that constituted the branch network that allow to provide with bank services customers from different corners of the world (Oxford Business Group, 2007).
In general, banking is an important service industry for all countries. In a bank, all customer-provider relationships and interactions are concentrated around services. For this reason, services are the most essential integrative elements of banking. Bank services are appreciated by general public, because they help people to achieve what they want: to buy a good or service, to transact money, to get borrower’s credit, etc. Providing a client with a service, a bank is interested in success, as well: a service produces benefit for a bank (difference between amount of deposits and credit percentage) and additional money supply that plays important role for state economy. When a client comes to a bank to get a certain service (for example, he wants to be accommodated with a loan), it should meet consumer expectations.
According to some researchers, it is reliability, responsiveness, assurance, empathy and tangibles (Fitzsimmons, & Fitzsimmons, 2008). Hence, a bank should have credibility; bear responsibility for services provided. Besides, a client should be assured that a bank is able to provide the needed service on favourable terms. A provider should understand the reason of the demanded service, and demonstrate empathy to the client (in case of a loan, it can be family’s financial necessity owing to back pay, unexpected constrained loss of money, a desire to buy a house or a car). Loan is tangible if a consumer get desirable amount of money before he can repay the debt.
Bank Strategies Used to Attract and Satisfy Clients’ Needs
There are many bank strategies called to attract new customers and satisfy their needs. One of them was applied in 1996 by the royal Bank of Scotland. It became the first bank in the UK that offered its clients bank services on the Internet. Since that time, direct banking by PC became possible. It was estimated that about 60 % of the UK population used to pay their bills and check the accounts using a home computer (Botten & McManus, 1999, p. 205). The Internet-oriented strategies of the UK banks allowed internet users to print statement, pill bills, transfer account data into home-banking software package, and take advantage from on-line services and PC banking services (including mobile commerce) (Botten & McManus, 1999).
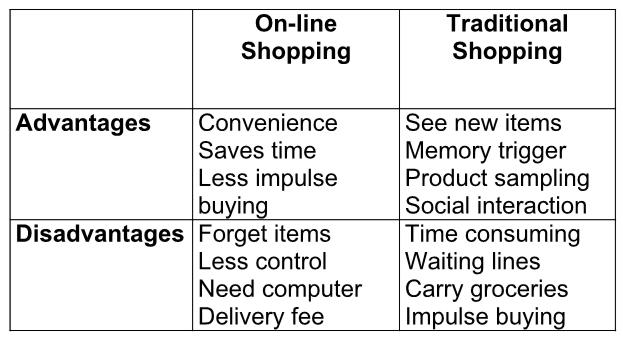
Bank card innovations of the 1970s gave rise to new competitive strategies in the UK and USA banking sectors. However, the bank card on-line system was quickly extended across the world, because it made bank services (especially, payment ones) accessible and efficient; it notably contributed to electronic commerce that allow to make electronic transactions on the Internet, and buy a product. As one can see on the figure 1 (see appendices), on-line shopping has notable advantages (for example, timesaving capability), in comparison with traditional shopping, that meet modern consumer needs. However, there are some disadvantages, as well (for example, it requires delivery fee) (Fitzsimmons, & Fitzsimmons, 2008).
Nowadays, credit plastic cards, issued by banks, are used every day: they allow to purchase goods and services on credit. Besides, electronic cash currency system proved to be extremely convenient (Wonglimpiyarat, 2005). Credit card and electronic service strategies facilitate the social life: owing to these strategies, people easily make certain banking operations, get cash money from a card, and buy certain goods and services through mobile e-commerce.
Globalization, decreasing customer loyalty, economic volatility, resource outsourcing and other factors made banks to elaborate survival strategies for financial services. The essence of these strategies lies in the following processes: workforce performance improvement, cost reduction, revenue enhancement, return increase, cost-effective activities, integration of up-to-date technologies, etc.
Capitalization of banks plays an extremely important role in bank strategies. Retail banking strategies that practiced in Europe were adopted on the CEE ground. As the internet decreased the customers’ loyalty, banks needed special customer-oriented strategies called to increase bank clients’ loyalty. The loyalty programs that provided special benefits to customers were introduced. Traditionally, cooperative banks possessed “a strong loyalty tool, membership of the bank”.(Groeneveld & Wagemakers, 2004, p. 6).
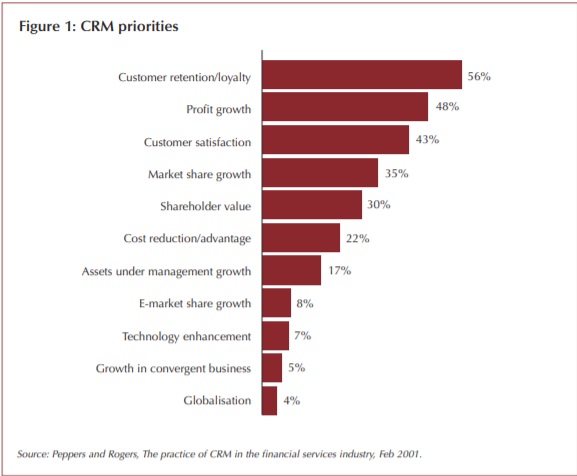
Besides, Customer Relationship Membership (CRM) systems provide banks with good knowledge of their clients that allow banks to meet their needs. For this reason, many banks used to chose a niche-strategy, and focus on a specific customer need (real estate segment, for example). Retail banking is an extremely competitive industry, for this reason, CRM have certain priorities. Figure 2 (see appendices) shows that three top priorities are customer loyalty, profit growth and client satisfaction (PricewaterhouseCoopers, 2003).
Retail networks are used to sell all kinds of possible products: multidistribution provides with alternative options. For example, multi-channeling strategy, described as “selling products and servicing of clients with different channels, such as branches, ATMs, telephone and internet”, attracts clients with free choice, diversity of channels for different clients, and cost savings. (Groeneveld & Wagemakers, 2004, p. 7). The European largest internet bank, Rabobank, is a virtual distribution channel that offers transaction services on internet-mode technology that allows all users of mobile phones to make bank transaction operations.
Some banks offer other essential strategies that improve customer experience, leverage up-sell and cross-sell opportunities, and promote customer satisfaction. Some of retail bank strategies sound in the following manner: “facilitate integrated and consistent interactions across all channels”, “offer an inviting “Customer Front Door”, “integrate self-service with agent assistance”, etc. (Genesys, 2008, p. 3). On the whole, the strategies mentioned in this part of the essay, are beneficial for both banks and customers; moreover, all of them are called to attract and satisfy customer’s needs in a different way.
New Plans for the Future
CRM systems have proved its effectiveness in aggressive bank competition, and will be used in the future. The strategic importance of CRM is obvious: it helps banks “to build long-lasting relationships with their customers and increase their profits through the right management system and the application of customer-focused strategies” (Blery & Michalakapoulos, 2006, p. 116). The Greek bank and other banks that use CRM system will be able to focus on most profitable customers with the help of efficient segmentation that corresponds to clients’ individual behaviour.
The commercial approach based not only the product but a client, as well, will help to satisfy and retain bank customers. Obviously, more banks will implement voice and phone banking services (loans, stock exchange transactions, etc.) and customer segmentation system (that responds to clients’ needs, interests, habits, etc.), and more clients will take advantage from synchronized networks, offered by banks (branch ATM, Interactive Voice Response, telephone center) (Blery & Michalakapoulos, 2006).
Even modern successful banks are concerned with plans for the future that will bring them more customers, more innovations, and better profit. The research of Oxford business group showed that development strategy of NBAD for the future is directed to expansion and positive innovative changes: installation of new ATM, opening of new branches, provision with first mobile phone banking service in the Middle East and North Africa region (Oxford Business Group, 2007).
Revolutionizing e-commerce is one of the reasons why banking system should be improved and transformed. Internet banking of the future will “reduce transaction costs, enhance customer service, increase the customer base and improve cross-selling opportunities” (Nath et al., 2001, p. 21). The phenomenon of Internet banking can not be underestimated, as it is future of modern society: the number of Internet and PC users grows every day. Online loans, brokerage services, bill payment will be popular clients’ banking activities in cheap cyberspace of electronic banks. Additional and expanded online bank services will be available to clients in private and business life. In addition, “banks are adding real-time loan applications, the ability to make Individual Retirement Account investments, and the opportunity to trade stocks through their web sites” (Nath et al., 2001, p. 26). Thus, the concept of “one-stop shopping” will be wide spread in the future.
Conclusion
Taking into consideration all the information mentioned above, one can make the following conclusion. Bank services serve for the benefit of people, engaged in financial relationship, commerce, business, and other activities. Owing to a great variety of bank services, a customer may deposit, save, transact, exchange, loan money, get a credit card, purchase goods and service via Internet, etc. There are many effective, development and competitive bank strategies used to attract and satisfy clients: customer-oriented strategies, electronic service strategies (Internet-oriented, e-commerce), retail banking strategies (multi-channeling), etc. However, successful future for banks consists in improved, expanded and quality e-banking services that serve for the customer’s benefit in the commerce, business and private life, customer segmentation, increasing and improving clients’ opportunities.
References
Blery, E., & Michalakapoulos, M. (2006). Customer relationship management: a case study of a Greek bank. Journal of Financial Services Marketing, 11 (2), (pp. 116-124). Web.
Botten, N., & McManus, C. (1999). Competitive Strategies for Service Organizations. Basingstoke, UK: Purdue University Press.
Fitzsimmons, F., & Fitzsimmons, M. (2008). Service Management: Operations, Strategy, and Information Technology (6th ed.). New York, NY: McGraw-Hill.
Genesys. (2008). Industry strategy guide: customer service strategies for the retail banking industry. Web.
Groeneveld, J., & Wagemakers, J. (2004). Retail bank strategies in Europe. Economic Research Department. Web.
Lele, U. (2000). The World Bank Forest Strategy: Sticking the Right Balance. Washington, DC: World Bank Publications.
Mishra, S. (2010). Engineering Economics and Costing. Philadelphia, PA: PHI Learning.
Mullineux, A., & Murinde, V. (2003). Handbook of International Banking. Cheltenham, UK: Edward Elgar Publishing.
Nath, R., Schrick, P., & Parzinger, M. (2001). Bankers’ perspective on Internet banking. E-Service Journal, 1 (1), (pp. 21-36). Web.
National Bank of Abu Dhabi. Official Website. Web.
Oxford Business Group. (2007). The Report: Abu Dhabi 2007. Dubai, UAE: Oxford Business Group.
PricewaterhouseCoopers. (2003). Tackling the key issues in banking and capital markets. Web.
Wonglimpiyarat, J. (2005). Strategies of Competition in the Bank Card Business: Innovation Management in a Complex Economic Environment. Brighton, BN: Sussex Academic Press.
Appendices