Abstract
Company assessment is essential to identify and address gaps in organizational structure or business processes. The goal is to deliver a high customer value and improve performance. Four assessment models, namely, 7-S framework, balanced scorecard, SWOT, and PESTLE, may be used to evaluate a firm’s internal and external environment. In this paper, these tools are applied to a printing, audiovisual, and graphic design center owned by a local airline. Based on assessment results for each factor, specific recommendations are provided. In addition, changes to the current organizational structure are proposed, including adding marketing, HR, and finance departments to conduct market studies and set prices, train staff on key skills, and perform bookkeeping functions, respectively.
Summary
The profit motive is the main driver of business strategy in organizations. To achieve this objective, most firms pursue strategic options that are appropriate for exploiting opportunities available in their industry. Examples of competitive strategies include low-cost products, expansion to new markets or sectors, and strategic alliances. Various assessment tools are available for analyzing business strategy and environmental factors impacting growth. These frameworks examine a firm’s competitive strengths, weaknesses, market position, and capacity of a company to deliver high customer value.
In this paper, four assessment tools previously discussed in this course are used to evaluate the performance of my organization. For each framework, specific recommendations for change and rationales are provided. These tools include the expanded McKinsey 7-S framework, Balanced Scorecard, SWOT analysis, and PESTLE.
About the Company
I work for an airline company that owns a print shop providing in-house printing services for tickets and boarding passes. I joined this audiovisual or graphic design center four months ago as its CEO. This specialized function is experiencing challenges, including poor inventory control, which threatens its growth and performance. I was hired to create and implement a turnaround strategy for its survival and cut costs.
The business objective of the center is to cut the airline’s media costs by 25%. This in-house service was launched to reduce spending on outsourced printing solutions and improve the airline’s net cash flow. In-house operations are pursued as a strategy for increasing margins and efficiency and achieving more operational control (Žitkienė and Dudė, 2018). Knowledge sharing is also promoted when insourcing rather than outsourcing is used for critical functions.
The center was established over 40 years ago without a proper financial or management structure. At its launch, it had five employees and a few printing machines. After two years, additional staff was hired to support business growth. However, the center has been losing money for a long time. Applying the assessment tools to this organization will reveal internal strengths and weaknesses, environmental factors, and structural problems contributing to underperformance, which will inform recommendations for improvement.
Assessment and Recommendations
McKinsey 7-S Framework
The McKinsey 7-S model provides a useful framework for designing an efficient organizational flow. It was developed in 1982 to guide organizations toward achieving their strategic objectives. The model comprises seven interdependent factors that are critical to effective strategic alignment, namely, “shared values, staff, structure, strategy, systems, skills, and style” (Cox, Pinfield and Rutter, 2019, p. 315). It is useful for building a dynamic organization by creating a mix of hard and soft competencies. Hard elements comprise tangible procedures and systematic aspects such as structure, strategy, and system (Park, Yoo and Lee, 2021). In contrast, soft factors are intangible skills and values influenced by culture. A complete classification of the seven factors is shown in Table 1.
Table 1: Elements of the McKinsey 7-S Model
Of the seven elements, structure, strategy, and system are directly shaped by managerial decisions. In contrast, soft elements, such as style and staff, are intangible and under the cultural influence. National or staff subcultures and company culture impact the soft aspects of an organization. The print shop has a staff of 120 that is drawn from various cultural, religious, and educational backgrounds. Multiple nationalities are also represented in its current staff population. The center has integrated these subcultures into its corporate culture, organizational structure, and functions. A careful analysis of the seven elements will yield recommendations for effectively implementing the seven elements at the print shop.
Strategy
The center was established to provide printing, filming, and graphic design services parent to the airline and its thirteen subsidiaries. The aim is to cut current spending on media by 25%. This in-house operations strategy was developed as a response to rising overhead costs and the need to increase the company’s margins. It was also meant to improve overall efficiency through enhanced knowledge sharing and collaboration internally. The strategy was adopted to improve the airline’s cash flow and financial position.
Structure
The print shop lacks a full organizational structure to guide role assignment and coordination. Currently, the center is headed by a CEO but has not had a proper financial or management structure since it was established. Line managers or supervisors oversee various functions, including printing, filming, and graphic design. The center is vertically integrated with the airline and its 13 subsidiaries. From an administrative viewpoint, this structure has some effects on the center’s operations. On the positive side, it supports better communication and collaboration among staff, including those working in the airline and its subsidiaries (Edmondson, Jang and Casciaro, 2019). The structure also promotes knowledge sharing and operational control of the disparate teams.
The current management and financial structures have many weaknesses that need to be addressed. Services are not well defined and an organizational mission and vision are lacking. The center also lacks an accounting department for proper bookkeeping of invoices and incoming payments. Only a record of purchase orders and handing over reports are maintained. Current performance bottlenecks include improper pricing strategies, market placement, cost of labor, and inaccurate stock accounting. In addition, the center does not maintain proper accounting books. The numbers shown in the financial records do not tally with actual stock. For example, the books show that we have stock worth $5 million but actual items are valued at $300,000.
Recommendations
- Redefine all services (video, design, and printing) by creating a center profile about who we are, with a mission and vision, and where we are going.
- Regarding the organizational structure, a substantive accountant should be hired to handle bookkeeping and process invoices and payments.
- The center should have a proper financial structure independent of that of the airline for its operations. This strategy will give it more control over forms of financing for its operations and expenditure.
System
The center operates on an as-needed basis based on orders from the airline and its subsidiaries. A careful analysis of the needs of the most frequent fliers is done to determine the printing or graphic design solutions in demand. The airline will then place an order from the center, including the quantities needed. The materials will then be printed and sent to the airline or dispatched directly to the clients.
Shared Values
The purpose of the print shop is to provide low-cost printing, filming, and graphic design solutions to the airline and its subsidiaries. The values shared by staff include service excellence, integrity, innovation, and teamwork. As a vital component of the airline’s mission, the print shop is committed to delivering quality printing and graphic design solutions to clients. Integrity is also promoted through honesty and transparency in all our operations.
Recommendations
- The center should use real-time analytics to provide solutions based on customer experience data. Our clients no longer need print on-board magazines and food menus. Instead, they prefer to use digital materials, which has affected demand. However, beginning in 2022, the old trend is re-emerging, as more clients require printed magazines and food menus again.
- A proper organizational structure is needed at the center to provide staff with more clarity on their roles and support collaboration (De Smet, Gagnon and Mygatt, 2021). Currently, there are no job descriptions for employees, a scenario that affects teamwork.
Style
The previous CEO used an autocratic management style, which was not very effective. In this leadership approach, the manager makes all the decisions without input from the subordinates. It is characterized by low leader-member exchange, which negatively impacts the performance of team members (Wang, Liu and Liu, 2019). The managerial choices made previously at the center did not consider suggestions from employees. Audiovisual and graphics services staff have been in the same position for twelve years. Further, employees have not been trained in new tools or programs for audiovisual graphics.
Recommendations
- The autocratic management style should be replaced with a more democratic approach that values diverse perspectives in the team.
- Employee training programs are needed to empower staff to actively participate in decision-making.
Skills
The center was established 40 years ago with five employees. Despite having a staff population of 120, the print shop has a shortage of skills. Critical employees have not been trained on the latest tools and programs for audiovisual and graphic design or tips and tricks that would make them effective in their role. They have stayed in the same position for over twelve years. Therefore, the team lags on market knowledge and cannot drive the growth objective of the center.
In addition, a clear HR policy on desirable employee skills and roles is lacking. Job descriptions for employees have not been developed to align personnel with the expertise required at the center. For example, the print shop lacks an accountant to handle bookkeeping for invoices and payments received. Despite consistently underperforming, the operational costs of the center have remained high. The center spent $3.7 million on salaries in 2021 alone. Therefore, a training program to improve soft and technical skills is needed.
Recommendations
- Train the team on new skills in filming and editing software.
- Train the team on proper communication skills.
- Attract new talent with attractive packages and workplace conditions.
- Prepare a talent pool in strategic skills such as 3D printing technology.
- Allocate adequate financial support for in-house training and career development programs.
Staff
Employees are a critical asset of a firm that drives growth. According to Morris (2020), personnel diversity and inclusion are a source of competitive strengths because diverse talent provides different perspectives and solutions to an issue. Diversity in age, sex, nationality, and cultural background is needed to rapidly respond to external challenges. The center has embraced diversity and inclusion in its HR practices. Currently, there are 120 employees, both male and female, of different ages and backgrounds.
Recommendations
- Having a diverse team increases the potential for conflict. Effective conflict resolution mechanisms should be implemented to address disagreements.
- Cultural competence training is needed to enhance employee awareness of individual biases that may negatively impact teamwork and collaboration.
Balanced Scorecard
The balanced scorecard entails a set of metrics derived from organizational strategy. These measures are used to indicate growth drivers and communicate them externally and internally (Sachs, 2020). Therefore, the balanced scorecard is a useful tool for monitoring performance against strategic objectives. Under this model, the firm is evaluated via four perspectives: financial, customer, learning and growth, and internal business processes (Figure 2) (Sachs, 2020). Each of these factors has specific objectives, measures, targets, and activities tied to it.
Financial Perspective
This metric focuses on ways of improving the bottom line through effective strategy. It entails setting financial goals tied to strategic growth plans and profitability and defining measures such as cash flow, quarterly sales, and market share (Sachs, 2020). Additional financial metrics for assessing performance include return on investment, earnings per share, and profitability. For the center, key measures should include revenue growth in video, design, and printing segments, production costs, and sales.
The financial perspective will first require restructuring and improving the accounting function of the center. Accurate financial data will be critical for evaluating performance. Currently, the center has no accountant to perform proper bookkeeping of invoices, inventory, and payments. Only records of purchase orders and handing over are maintained. On this basis, the following recommendations are proposed for change:
- Hire Deloitte to audit the center’s accounting systems and provide proposals for improvement.
- The management should perform a 100% inventory count guided by the Deloitte team.
- Once points 1 and 2 have been completed, we will begin phase 2 of developing an inventory policy for the center.
- Explore inventory reduction opportunities and ways to improve services offered to business partners.
- Deloitte will support the general ledger (GL) team and the IT team in cleaning up the GL.
- Conduct a market study to provide a basis for SLA review and a new pricing strategy.
Internal Business Perspective
To attain superior performance, firms must prioritize their internal stakeholders. Monitoring and assessment of internal operations are required to promote strategic alignment. Internal business metrics that firms may use to assess this perspective include “number of defects, machine downtime, transaction efficiency, and daily production volume” (Dudic et al., 2020, p. 5). In addition, more specific measures, such as the length of time printing machines lie idle, may also be used. In this center, internal measures may include the duration between production and delivery.
The analysis of the center’s internal business processes reveals gaps in its operations, including improper pricing strategies, market placement, high labor costs, bad management styles, and inaccurate count systems for stock and other usable materials. In addition, its accounting system is inefficient, resulting in errors in ledger accounts. For example, the actual stock was less than the amount shown in the books. On this basis, the following changes to the internal business processes are recommended.
- A cleanup of general ledger accounts should be conducted to correct errors and gaps in data.
- Perform walkthroughs of major processes in graphic design, video, and printing segments.
- Optimize internal customer service level agreement (SLA) to enhance the quality and timeliness of our services.
- Adopt internal measures, such as the number of defective products and daily production volume, to monitor its operational efficiency.
Learning and Growth Perspective
Today’s business environment is highly competitive, demanding that organizations continually evolve to survive. To achieve financial goals, including growth in market share, the firm must embrace organizational learning and provide opportunities for staff to acquire and practice new skills (Tuan, 2020). In addition, employee career goals must be aligned with the organizational mission and vision. Learning and growth metrics are variables for evaluating management-employee engagement to grow the firm and support career development. Various measures can be used to assess this perspective, including the number of ideas originating from team members that have been implemented by the company, turnover rates, and staff training hours (Tuan, 2020). The print shop may also utilize hours of customer care training to evaluate this perspective.
Currently, the print shop lacks a training and development program for its staff. As a result, employees providing audiovisual and graphics services do not have the right technical skills and market knowledge to drive growth. They have not received training in the latest tools and programs or software for editing and filming. Moreover, the team has never been trained in effective communication skills to improve the center’s customer relationship management. Based on this assessment, the following changes are recommended for improving learning and growth at the center.
- Workforce relationship training is needed to enhance employee engagement and retention of key talent.
- A reward system should be established to incentivize innovation and the development of new ideas.
- The team should be trained in new filming and editing software and communication skills.
- Employee promotions should be connected to annual performance appraisals.
Customer Perspective
Customers are important to the growth and survival of any business. Therefore, firms must monitor their performance regarding the number of customers. Useful variables for evaluating this perspective are customer satisfaction, repeat purchases, new clients, and market share (Ratnaningrum, Aryani and Setiawan, 2020). Customer metrics that are more specific to the print shop include being rated as the number one provider of graphic design and filming solutions by clients. In addition, the center can monitor the number of new and loyal customers to determine its performance in this domain. The main changes recommended for the center include:
- Regular customer satisfaction surveys should be conducted to determine consumer experience and approval of the products. This approach will help respond to changing trends, such as clients’ preferences for printed on-board magazines and menus rather than digital solutions.
- Solicit positive reviews or ratings from current customers through its e-commerce platforms.
- Reward new customers and referrals with attractive discounts for products to grow its client base.
- Establish customer service level agreements (SLAs) to guarantee quality and timely services.
A corporate balanced scorecard for the print shop is given in Table 2 below.
Table 2: Balanced Scorecard
SWOT Analysis
SWOT is a useful tool for evaluating the internal and external factors relevant to a firm. It entails the analysis of key strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats (Akman, 2019). SWOT identifies variables that could support better performance and barriers to effective strategy implementation. Therefore, this tool is used to guide corporate decisions and ensure executives understand the opportunities and risks in a market. It essentially groups factors impacting an organization into two: external and internal elements.
Looking internally, a firm’s performance is determined by its strengths and weaknesses. Competitive strength depends on the presence or absence of inimitable and valuable assets and capabilities in a firm. Financial resources, personnel, skills, patents, and technology determine an organization’s capacity to achieve its strategic goals (Benzaghta et al., 2021). Strengths represent the internal potential of a firm, while weaknesses are limitations to be surmounted. The external environment includes opportunities and threats that provide growth prospects and impediments, respectively.
A SWOT analysis for the print shop is summarized in Table 3.
Table 3: SWOT Analysis
Strengths
The print shop has some unique strengths and capabilities that provide leverage for growth. Internal SLAs with the airline and its subsidiaries reduce contractual issues and improve productivity and efficiency (Rosencrance, Louissaint and Brush, 2021). This factor will also guarantee access to new market opportunities and a large client base, including travelers using the airline. In addition, the center has well-established audiovisual and design departments that would support business development and expansion to meet higher demand. With a staff population of 120, the print shop has a large talent pool to drive its growth. The center also has access to capital and liquidity from the airline to finance its operations. Strong creative capacities have allowed it to provide both print and digital magazines and food menus to clients.
Weaknesses
The center lacks proper pricing and market placement strategies, which results in poor brand attitudes and customer loyalty. Competitive prices and product placement will increase sales and repeat purchases. High labor costs represent another key weakness that the center needs to contain. For example, salaries for 2021 amounted to $3.7 million, reducing revenues and profits. In addition, the autocratic management style used previously affected staff morale and productivity. Career advancement opportunities and better remuneration constitute an essential extrinsic motivating factor in the workplace (Rahaman et al., 2020). A performance-based promotion policy was lacking; hence, employees stayed in the same position for over twelve years.
The center also has some structural weaknesses that need to be addressed. Its count system for stock and other supplies is inaccurate, affecting optimal inventory control. There is a huge discrepancy between the numbers shown in the books and the actual stock. For example, $5 million worth of stock is indicated in the records but actual goods are valued at $300,000. The work environment is poor due to ineffective communication, uncompetitive culture, and punitive HR policies. These conditions are likely to affect employee morale and productivity.
The COVID-19 pandemic necessitated changes in business models for firms to survive. However, the print shop did not adapt its business to the COVID-19 situation. Unclear organizational structure and job description for each position constitute other key weaknesses. The lack of role clarity will affect collaboration and accountability in the organization. Employees also lack skills in the latest filming and editing software, which reduces the quality and competitiveness of the center’s products. Furthermore, the team has not received training in effective communication to improve their customer service skills.
Opportunities
The onboard magazines and menus present growth prospects for the center. Our clients moved from print-on-board magazines to digital media during the pandemic. However, the old trend is now re-emerging and demand for printed materials is rising gradually, providing an opportunity for the center to expand its market share. Optimization of internal service agreements with employees and partners will lead to standardized products as quality expectations will be specified (Rosencrance, Louissaint and Brush, 2021). It will also promote communication and collaboration between the center and the airline. Employee-focused SLAs will enhance productivity and reduce turnover among key employees.
The center has sufficient staff to support future demand increases. Its workforce of 120 employees can meet potential growth in the print menus and magazines segment. However, training in key skills is needed to enhance efficiency and innovation at the center. The prospect of reducing costs by optimizing inventory management is high. By designing and implementing a training program (technical and communication skills), the center will improve its core competencies and capabilities in audiovisual, video production, and printing.
Threats
High operational costs, mostly due to salaries, pose a threat to the financial health of the center. Rationalization of the workforce is needed to enhance its operations and increase revenue (Racko, 2019). This process will entail eliminating redundant positions and creating job descriptions for each role. The lack of a clear inventory management policy is another threat faced by this organization. Imbalanced inventory increases warehousing costs and leads to delays in product delivery and low customer satisfaction (Racko, 2019). The COVID-19 impact on the airline industry is also a threat to the center’s business model and performance.
Recommendations
- The center should adopt remote or hybrid work systems and digital products in response to the threat of COVID-19 to its business.
- Core competencies and capabilities should be improved by implementing well-designed training programs.
- Workforce rationalization is needed to reduce operational costs and enhance efficiency.
PESTLE Analysis
Political Factors
PESTLE analysis involves an assessment of six environmental factors relevant to an organization’s industry. The first element encompasses political considerations, such as government economic policies and interventions that impact business (CIPD, 2021). Examples include bureaucratic procedures, tariffs, and tax regimes implemented to support the economy. The Kingdom of Saudi Arabia enjoys relative political stability in the Middle East. With a stable government (Islamic monarchy), economic policies do not change radically. The centralized policymaking process is centralized involving a central council is highly effective (Mogielnicki, 2021). On the other hand, restrictions on media and political activity in Saudi limit foreign direct investment and business partnerships with foreign-owned firms.
Recommendation
The center should exploit social reforms by the government to attract overseas clients.
Economic Factors
Saudi Arabia’s economy has experienced steady growth and relatively low interest rate over the past decade. In 2020, its GDP was estimated at $680 billion and ranked position 19th globally (Shaw, 2021). The economy is heavily dependent on oil, gas, iron, steel, and steel exports to countries such as China. The economic policies developed favor foreign direct investment but fluctuating oil prices and unemployment remain key challenges.
Recommendation
Given the low interest rates, the center should use debt refinancing to expand its operations.
Social Factors
They include factors that influence the attitudes and preferences of consumers. For example, cultural aspects, demographic trends, customs, and rules that shape consumer behavior determine consumption habits (CIPD, 2021). The key social factors impacting the country include a youthful population (about 50% of the people), the use of Arabic as the national language, and a highly religious society with a strict dressing code, especially for women (Shaw, 2021). People enjoy soccer and camel racing events across the country.
Recommendations
- The center should only publish media products that are permissible under Islamic law.
- On-board magazines should be in Arabic to target local clients.
Technological Factors
The Saudi government has invested heavily in technology infrastructure across the country. The aim is to reduce its dependence on oil exports and transform Saudi Arabia into a technological hub in the Middle East. Resources are being channeled to innovation, R&D, and creating conditions favorable to foreign direct investment in technology projects. For example, the Badir Program for Technology Incubators was established to support new companies in this sector (Ritter, 2021). Other technology projects initiated in Saudi include UnitX and Monisha.
Recommendations
- New filming and editing software should be acquired from local and international developers.
- Employees should be trained in new technologies for filming and editing.
Legal Factors
Legislation and policies determine corporate governance, production standards, and practices regarding contracts and business alliances. Compliance with industry rules and conventions will avert lawsuits and punitive measures that affect operations and performance (CIPD, 2021). Saudi is a highly religious country that applies Sharia principles to punish offenders. Businesses and corporations in Saudi Arabia must operate under Islamic law. Only its leader has the power to pardon any accused person.
Recommendation
The center should follow Sharia law in its operations to avoid punitive lawsuits.
Environmental Factors
Saudi is confronted with serious environmental challenges, including prolonged drought and air pollution from industries. In addition, deforestation is a major problem that needs to be addressed. The country attracts millions of Muslim pilgrims yearly to its religious sites. This annual pilgrimage is important to the Saudi economy but poses an environmental challenge to holy cities being visited, resulting in effects such as water pollution.
Recommendation
The center should provide digital products (e-magazines and menus) to reduce its carbon footprint and position itself as an environmentally and socially responsible organization.
Recommended Changes
As the CEO, I will prioritize the following changes to cut operational costs, enhance efficiency, and strengthen key skills and competencies:
- Clean up general ledger accounts to ensure all payments are recorded and avoid double billing.
- Review and restructure management at the center’s audiovisual and design departments
- Review service-level agreements and set new prices based on market study.
- Hire Deloitte to perform inventory count and clean up ledger accounts.
- Train employees on new filming and editing software.
- Conduct staff training in effective communication and customer service.
- Redefine all services, including video, design, and printing, and create a center profile with a mission and vision.
Organizational Charts
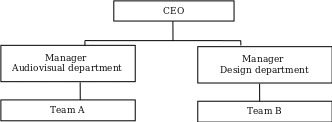
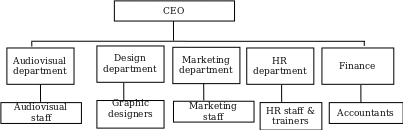
Reasons for the Changes to the Organizational Structure
The current organizational structure is too simplistic and does not give clear employee roles. The lack of job descriptions creates inefficiency and increases operational costs due to role duplication. The proposed organizational structure aims to address these challenges and create a functional and efficient team. Three more departments have been added, namely, marketing, HR, and finance, with each having specialized functions essential to the center. The reasons for the changes to the current organizational structure include:
- The marketing department will conduct market studies, set prices, manage inventory, and review service-level agreements with clients.
- The HR department will develop and implement staff training programs on communication skills and filming and editing software.
- The finance department will handle the bookkeeping of invoices and payments, keep records of purchase orders, and process employee salaries.
Reference List
Akman, M. K. (2019) ‘SWOT analysis and security management’, European Journal of Management and Marketing Studies, 4(2), pp. 78-89.
Benzaghta, M. A. et al. (2021) ‘SWOT analysis applications: an integrative literature review’, Journal of Global Business Insights, 6(1), pp. 55-73.
CIPD. (2021) Pestle analysis. Web.
Cox, A. M., Pinfield, S. and Rutter, S. (2019) ‘Extending McKinsey’s 7S model to understand strategic alignment in academic libraries’, Library Management, 40(5), pp. 313-326.
De Smet, A.,Gagnon, C., & Mygatt, E. (2021) Organizing for the future: Nine keys to becoming a future-ready company. Web.
Dudic, Z., Dudic, B., Gregus, M., Novackova, D. and Djakovic, I. (2020) ‘The innovativeness and usage of the balanced scorecard model in SMEs’, Sustainability, 12(3221), pp. 1-22
Edmondson, A. C., Jang, S., & Casciaro, T. (2019) Cross-silo leadership. Web.
Mogielnicki, R. (2021) The centralization of economic policymaking in the Kingdom. Web.
Morris, C. (2020) Diversity, equity and inclusion: how to power the engine of business growth with diversity and inclusion. Web.
Park, H., Yoo, Y. and Lee, H. (2021) ‘7S model for technology protection of organizations’, Sustainability, 13(13), pp. 1-25.
Racko, G. (2019) ‘Does economic rationalization decrease or increase accounting professionals’ occupational values?’, Journal of Business Ethics, 158, pp. 763-777.
Rahaman, A., et al. (2020) ‘What factors do motivate employees at the workplace? evidence from service organizations’, The Journal of Asian Finance, Economics and Business, 7(12), pp. 515-521.
Ratnaningrum, V., Aryani, A. and Setiawan, D. (2020) ‘Balanced scorecard: is it beneficial enough? a literature review’, Asian Journal of Accounting Perspective, 13(1), pp. 65-84.
Ritter, R. (2021) ICT start-ups in Saudi Arabia. Web.
Rosencrance, L., Louissaint, S. and Brush, K. (2021) Service-level agreement (SLA). Web.
Sachs, H. (2020) The importance of the balanced scorecard for creating business objectives and evaluating business strategies and the advantages and disadvantages of companies leveraging the French strategic management system or the balanced scorecard. London: Independent Publisher.
Shaw, A. (2021) PESTLE analysis of Saudi Arabia. Web.
Tuan, T. T. (2020) ‘The impact of balanced scorecard on performance: the case of Vietnamese commercial banks’, The Journal of Asian Finance, Economics and Business, 7(1), pp. 71-79.
Wang, Z., Liu, Y. amd Liu, S. (2019) ‘Authoritarian leadership and task performance: the effects of leader-member exchange and dependence on leader’, Frontiers of Business Research China, 13(19), pp. 1-14.
Žitkienė, R. and Dudė, U. (2018) ‘The impact of outsourcing implementation on service companies’, Entrepreneurship and Sustainability Issues, 6(1), pp. 342-355.