Introduction
Sainsbury’s is a large retail outlet that was started by John Sainsbury in 1869, in the City of London, United Kingdom. During its earlier years, Sainsbury did not face any major market competition, and this helped it prosper in the market. As Griffin (2010, p. 67) notes, this firm grew to become the largest retailer in the United Kingdom in 1922.
It was the pioneer of self-service retailing, and it was able to maintain a pool of loyal customers (Roberts 2012, p. 89). The firm started facing serious market competition in the 1980s. However, it was still able to remain the market leader until 1995 when Tesco displaced it as the top retailer in the country. The level of competition became stiffer as Asda also managed to surpass it in terms of revenue generation.
The firm however, has been able to regain its strength, and the recent reports have indicated that it is currently the second largest retailer in the United Kingdom. The financial statements of this firm as at December 11, 2012, show that its revenue currently stands at £ 22.294 billion with a net income of £ 598 million. During the same period, its number of employees was estimated to be 152,000 people.
Industry in which this firm operates is very competitive. According to Clarke (2000, p. 113), the retail industry has become very competitive with the introduction of many players. Many firms are currently fighting for the market share in order to remain competitive.
With such stiff competition, it forces firms to come up with unique ways of remaining competitive. Major competitors like Tesco and Asda are real threats that the management of Sainsbury cannot ignore. The management must also understand other external factors in this industry that may affect its operations in one way or the other.
Marketing Mix
In marketing, it has become important to understand all the elements which may affect the normal operations of a firm in one way or the other in order to develop strategies that match market needs.
Marketing mix elements have been used as a way of understanding some of the market forces that may affect operations of a firm either directly or indirectly. In this study, the researcher will analyze the 7Ps of marketing mix elements.
The first element in the marketing mix is the product. In this industry, the retailers have a variety of products, ranging from electronics, to foodstuffs, housewares, apparels, and stationery. Most of the products that are offered by various players are similar because they come from same suppliers.
The retailers such as Sainsbury are forced to differentiate their products using unique packaging strategy as a way of gaining competitive advantage over other market rivals (Baker 2007, p. 38). Pricing has been the main differentiating element of the marketing mix. Sainsbury has been keen to avoid using pricing as a marketing strategy, and instead, it has employed cost leadership strategy.
Being the second largest retailer in the country, this strategy has proven to be very appropriate. Sainsbury has been employing the right workforce at various levels of the firm’s operations. The firm has employed highly qualified individuals at the top management unit.
The leadership team has made it possible for the firm to be flexible in its operations. The firm has also employed dynamic and highly skilled people who have the capacity to change with the changing market forces.
The place element for this firm has been defined by retail and wholesale outlets. Although this firm has embraced online marketing strategies, its operations are still primarily based on brick-and-moter strategy. Promotional element of the marketing mix has been considered as one of the major ways of gaining competitive advantage in this market (Aaker 2001, p. 87).
Sainsbury has been very active in both the social and mass media campaigns. In the social media, this firm has been using Facebook, Tweeter, and YouTube to reach out to the customers. The physical evidence has lately been considered as another important marketing mix element (Shanker 2002, p. 123).
The infrastructure and the physical design of the outlets have been considered to be a factor that can help attract customers to a given facility. Sainsbury has modernized all its stores to reflect the changing trends in the modern building strategies. At most of its stores, there are numerous outlets to reduce human traffic within the facility and make it easy for people to exit the facility in cases of emergency.
The process, as the seventh element of the marketing mix, has also played a role in helping this firm achieve its current success (Schneider 2011, p. 45). Sainsbury has always ensured that there is uniformity in its service delivery. Customer satisfaction has been the main aim of this firm when offering its products to the customers.
SWOT Analysis
In order to understand some of the internal factors that have helped this firm attain its current market position, it is necessary to analyze it using SWOT analysis.
PESTEL Analysis
It is important to analyze the external environment in order to determine some of the environmental factors that have had direct influence in the operations of the firm (Ruskin 2005, p. 96). As stated above, the political environment in the United Kingdom has been stable, offering Sainsbury a conducing market for its operations. The economic environment has experienced both positive and negative growths.
Although the economy has stabilized over the last three years, the 2008-2009 economic recession affected the operations of many firms in the market, including Sainsbury. According to Hoffman (2002, p. 18), the economic environment always direct impact on sales of firms.
When the economy slows, the rate at which people purchase various products slows. Consumers would consider avoiding consuming some product, especially those that they consider that are meant foe leisure (Bhattacharjee 2006, p. 29). The social environment in this country has brought positive impact to this firm.
There is a spending culture in this society, especially for products meant for leisure. The firm has also mastered the socio-cultural differences in this society that may shape buying patterns, and has designed its products to meet all their needs.
The technological environment has been challenging for this firm. The management of Sainsbury has been struggling to manage the changing technological environment. However, the report by Jorgensen (2002, p. 90) shows that this firm recently hired techno-savvy employees who have been able to understand the dynamic technological environment.
The legal environment has not been disruptive of the firm’s operations. The law in this country is very clear on how a business unit should relate with its customers, other business units, the government, or any other stakeholder within this society.
Sainsbury has not faced any major litigation in the recent past over its operations (Rama 2011, p. 38). The management has been keen on ensuring that its operations are sensitive of environmental concerns. It has been actively participating in environmental conservation programs, through its corporate social responsibility strategies.
Competitive Analysis Using Porter’s Five Forces
According to Boutellier (2008, p. 90), competition is one of the most destructive forces in the environment if a firm fails to manage it properly. Kodak was once the largest firm in the film industry and its sales were very attractive, but the stiff competition it faced from Fujifilm almost brought it to its knees (Homua 2009, p. 82).
However, positive competition is very good as it offers firms the opportunity to improve their service delivery. Analyzing competitive forces for Sainsbury using Porters Five Forces would help determine the competitiveness of this firm in the market.
Porters Five Forces
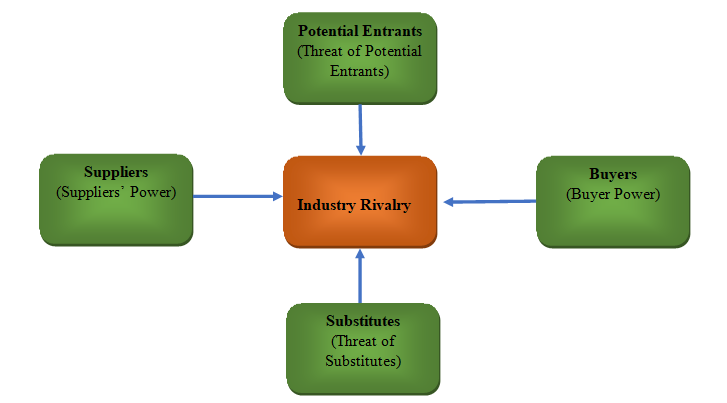
The diagram above shows Porters five competitive forces. To manage industry rivalry, Sainsbury has improved its promotional and service delivery strategies in order to protect its market share. It has also made an effort to ensure that its products are unique and focused on meeting the changing market needs.
In order to manage suppliers’ power, the management has developed strategic alliance with most of its major suppliers to ensure that they deliver their products to this firm at fair prices that allows it make attractive profit margins.
To manage the increasing buyer power, the Sainsbury has consistently been offering high quality products through quality product delivery strategies that has convinced its market that the prices they charge are worth the value they offer. To manage the threat of substitutes, the management of this firm has introduced variety of products in its stores, making it possible for it to compete directly with substitute products.
The large size of the firm and its profit margin has enabled it fight new market entrants. The firm has several outlets in major cities across this country. This makes it easy to monitor activities of the new entrants, making it easy to define appropriate competitive approach to take when dealing with them.
Conclusions
Sainsbury is the second largest retail outlet in the United Kingdom. The firm is facing stiff competition from other market rivals such as Tesco and Asda supermarkets. The external environment has posed many challenges but this firm has been able to overcome them.
The firm has been able to use its internal strength to maximize on some of the market opportunities. This has helped it retain its position as the second biggest supermarket in this country.
List of References
Aaker, D 2001, Developing Business Strategies, Wiley, New York.
Baker, M 2007, Marketing strategy and management, Palgrave Macmillan, Basingstoke.
Bhattacharjee, C 2006, Services marketing: Concepts, planning and implementation, Excel Books, New Delhi.
Boutellier, R 2008, Managing Global Innovation: Uncovering the Secrets of Future Competitiveness, Springer, Berlin.
Clarke, G 2000, Marketing a service for profit: A practical guide to key service marketing concepts, Kogan Page, London.
Griffin, D 2010, Business with a purpose: Starting, building, managing and protecting your new business, Outskirts Press, Denver.
Henioe, A 2008, Understanding strategic management, Oxford University Press, Oxford.
Hoffman, K 2002, Essentials of services marketing, Harcourt College Publishers, Fort Worth.
Homua, G 2009, Services marketing: Concepts, strategies & cases, Cengage Learning, New York.
Jorgensen, A 2002, The food service professionals guide to: 365 secrets revealed, Atlantic Publishing Group, Lauderhill.
Rama, M 2011, Services marketing, Pearson, New Delhi.
Roberts, B 2012, Walmart: Key Insights and Practical Lessons from the World’s Largest Retailer, Kogan Page, London.
Ruskin, I 2005, Marketing your service business, Thorogood, London.
Schneider, G 2011, Electronic commerce, Cengage Learning, Boston.
Shanker, R 2002, Services marketing: The Indian perspective: text and readings, Excel Books, New Delhi.