Introduction to the problem
- Technologies are affecting multiple areas in people’s lives;
- Parenting has changed as children access technologies more and more;
- Social media and gaming are the most challenging;
- Personality and behavior changes result from excessive technology use;
- Parental guides to prevent problematic content are needed.
The current project is a social media campaign report targeted at addressing the increased use of social media and gaming among the growing generation. The need for parental guidance and awareness is the central issue in the current campaign as many of them underestimate the problem.

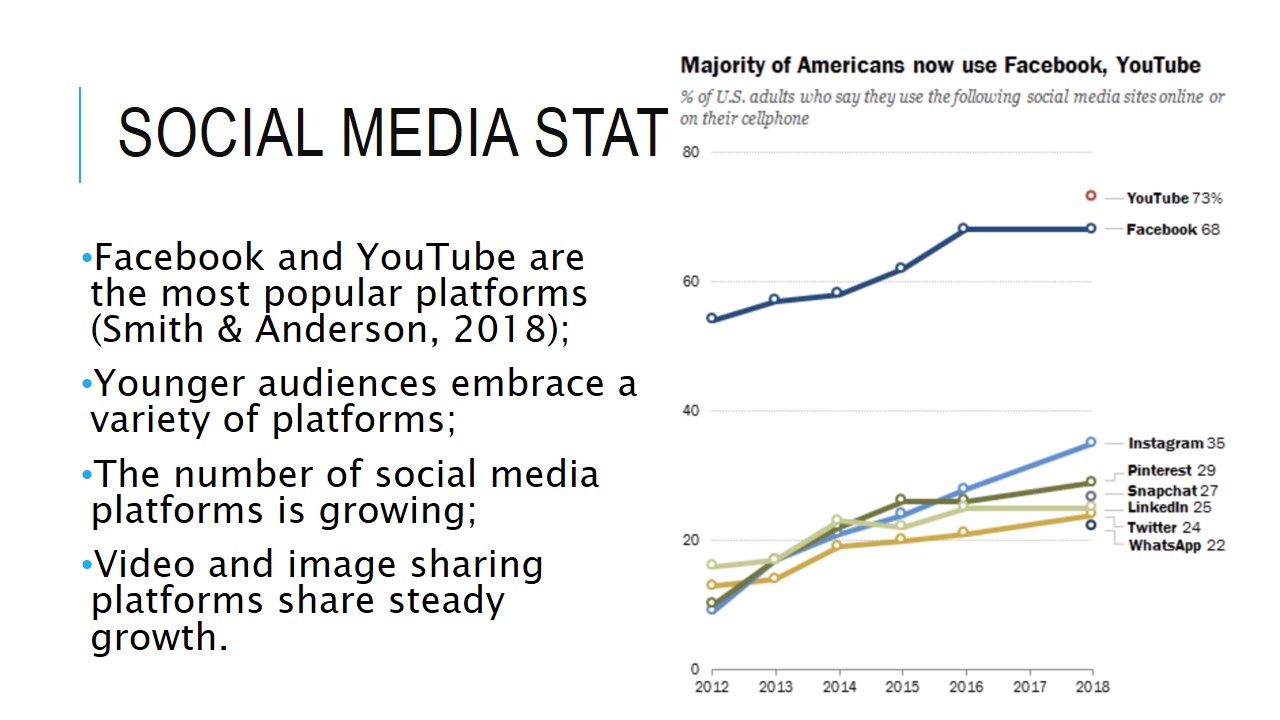
Social media statistics
- Facebook and YouTube are the most popular platforms (Smith & Anderson, 2018);
- Younger audiences embrace a variety of platforms;
- The number of social media platforms is growing;
- Video and image sharing platforms share steady growth.
The slide presents some general statistics on social media use among the general population. The majority of users prefer YouTube and Facebook as their main sources of entertainment and information sharing. Instagram is third in the ranking, followed by Pinterest and Snapchat.
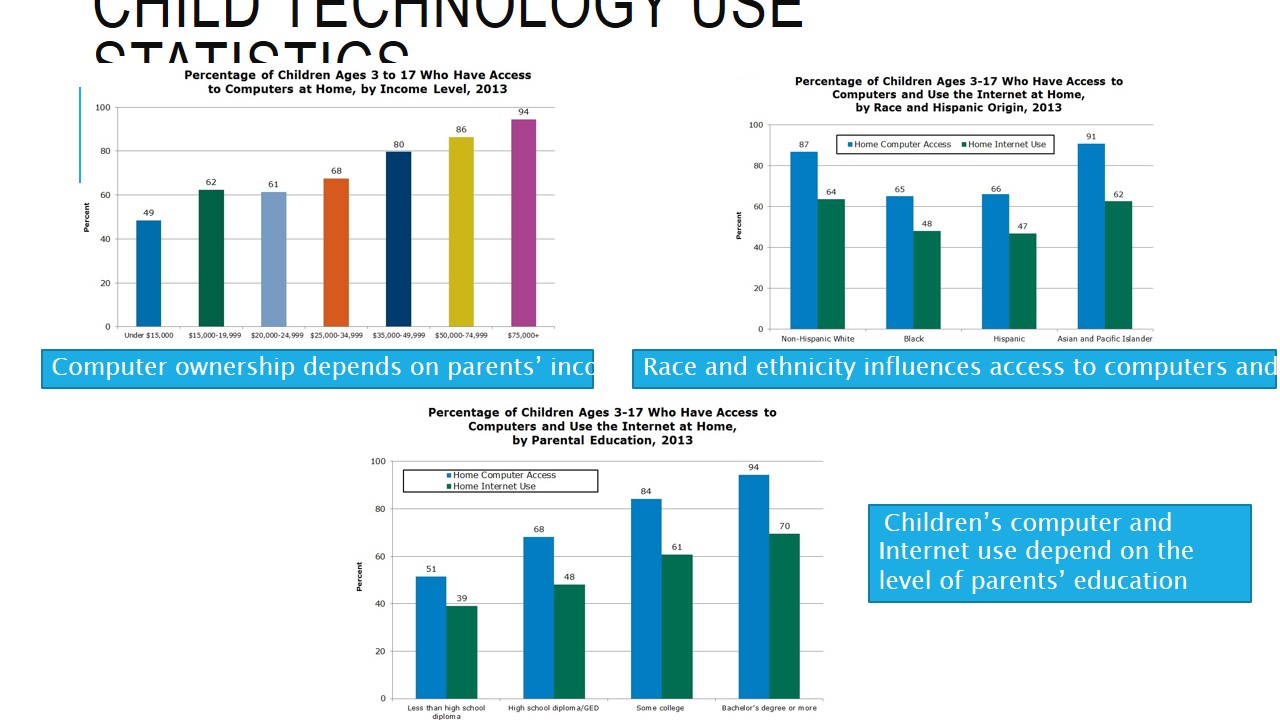
Child technology use statistics
The use of technologies among children aged 3-17 depends on several factors. The increased use of computers and social media presence is predetermined by the income level of their parents, race and ethnicity, as well as parents’ educational levels. Thus, the highest rates of home computer access and home Internet use is attributed to Asians and Pacific Islanders as well as children whose parents have a Bachelor’s degree or more.
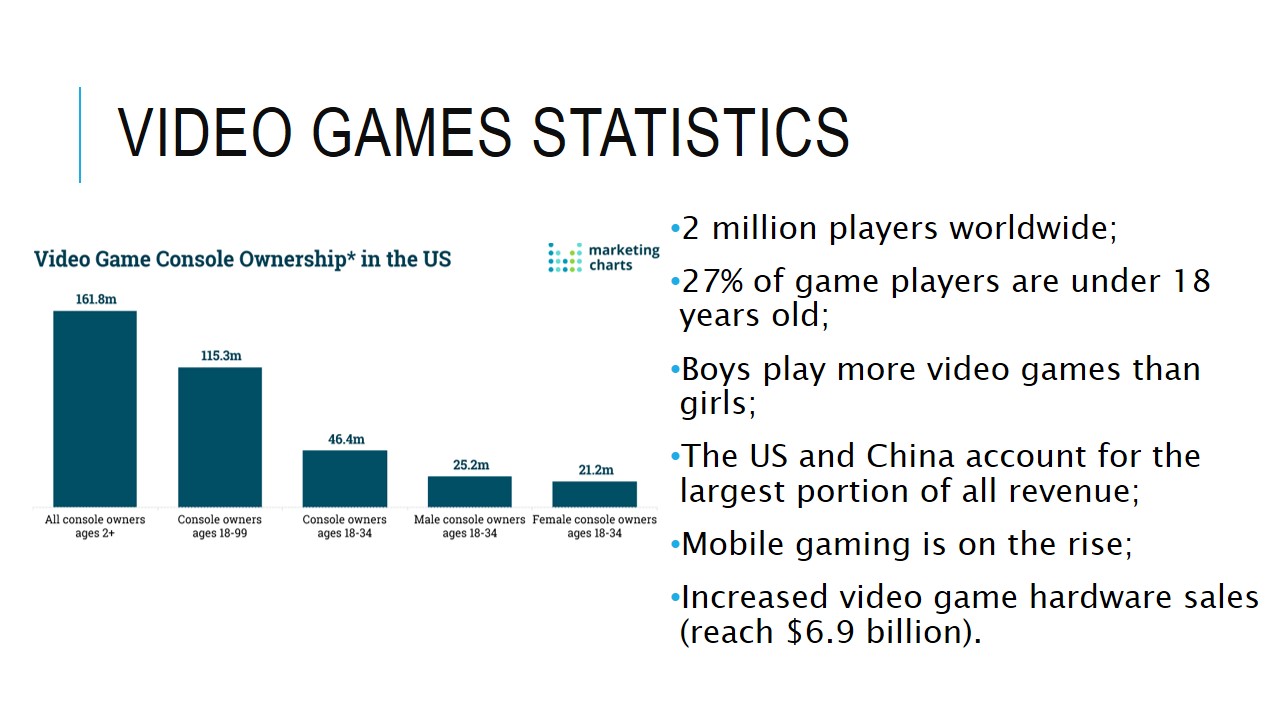
Video Games Statistics
- 2 million players worldwide;
- 27% of game players are under 18 years old;
- Boys play more video games than girls;
- The US and China account for the largest portion of all revenue;
- Mobile gaming is on the rise;
- Increased video game hardware sales (reach $6.9 billion).
In regards to video games, 27% of global players are under 18 years old, which points to significant parental guidance challenges. With mobile gaming increases, there is a need to regulate the way in which children access games and how much time they spend on them. Importantly, the video game market reached $99.6 billion in revenue in 2016.
Objectives
- Raising awareness among UK and US parents about the adverse influence of social media use on parenting, children’s development, and parent-child relationships. Taking action to introduce effective strategies to eliminate the negative influence.
- Empowering parents to be proactive in the management of children’s dependence on social media and games as well as become positive role models in making healthy lifestyle choices.
The first objective of the current social media campaign project is taking action to introduce effective strategies to eliminate the negative influence of social media and gaming through raising awareness of parents. The second objective is giving parents resources and knowledge for them to increase their proactiveness in reducing children’s dependence on technologies.

Target audiences
- Parents with children younger than 18;
- Young parents from the millennial generation (22-36 years old);
- Parents aged 36 and older;
- Parents that do not have enough knowledge of technology and social media use.
- Policy makers in the sphere of education and social media use;
- Teachers, school managers;
- Students.
The project will capture a large target audience, including young and mature parents, those who are not familiar with the most recent technologies, policy makers, teachers, and students.

Strategy
- Offer an overview of major issues associated with children and parents’ social media use;
- Conduct an analysis of the most pressing issues and address their solutions;
- Disseminate the project across social media platforms for educational purposes;
- Use such platforms as Twitter, Instagram, YouTube, and Facebook to disseminate findings.
- Key strategy: acknowledging the challenges of addiction to social media and letting the target audience know how they can address them on their own.
The focal point of the project is to acknowledge the challenges pertinent to social media and gaming addiction among children and provide a framework for proactive actions in the elimination of the issue.

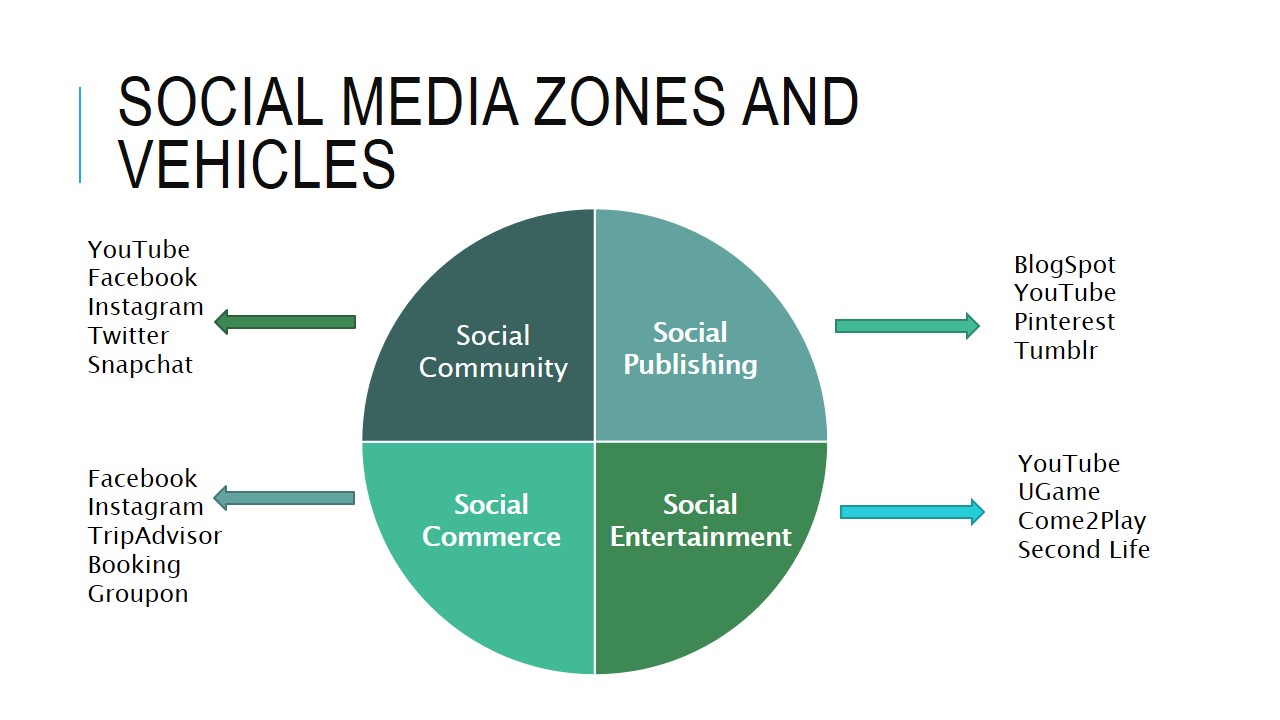
Social media zones and vehicles
- Social Community:
- YouTube;
- Facebook;
- Instagram;
- Twitter;
- Snapchat;
- Social Publishing:
- BlogSpot;
- YouTube;
- Pinterest;
- Tumblr;
- Social Commerce:
- Facebook;
- Instagram;
- TripAdvisor;
- Booking;
- Groupon;
- Social Entertainment:
- YouTube;
- UGame;
- Come2Play;
- Second Life.
To ensure the project’s success, social media zones and strategies were identified. In order to disseminate the results of the research and provide recommendations to parents, social publishing and social community zones will be used. The most likely platforms that will be used in the project include YouTube, Facebook, Instagram, BlogSpot, and Twitter.
Children and social media
- Children under 9 spend more than 2 hours on mobile screens;
- Less opportunities for parents to monitor what children do (Howard, 2017);
- Every household has an electronic screen that children can use (Nikken & Schols, 2015);
- States fail to safeguard children’s social media use;
- Cyberbullying and oversharing and dominant issues.
Time spent by children on social media is concerning, with children aged 9 and younger spending at least two hours per day looking in their mobile devices. As technologies advance, parents find it more and more challenging to monitor everything their children do while policymakers fail to enforce effective management legislation to address the challenge.

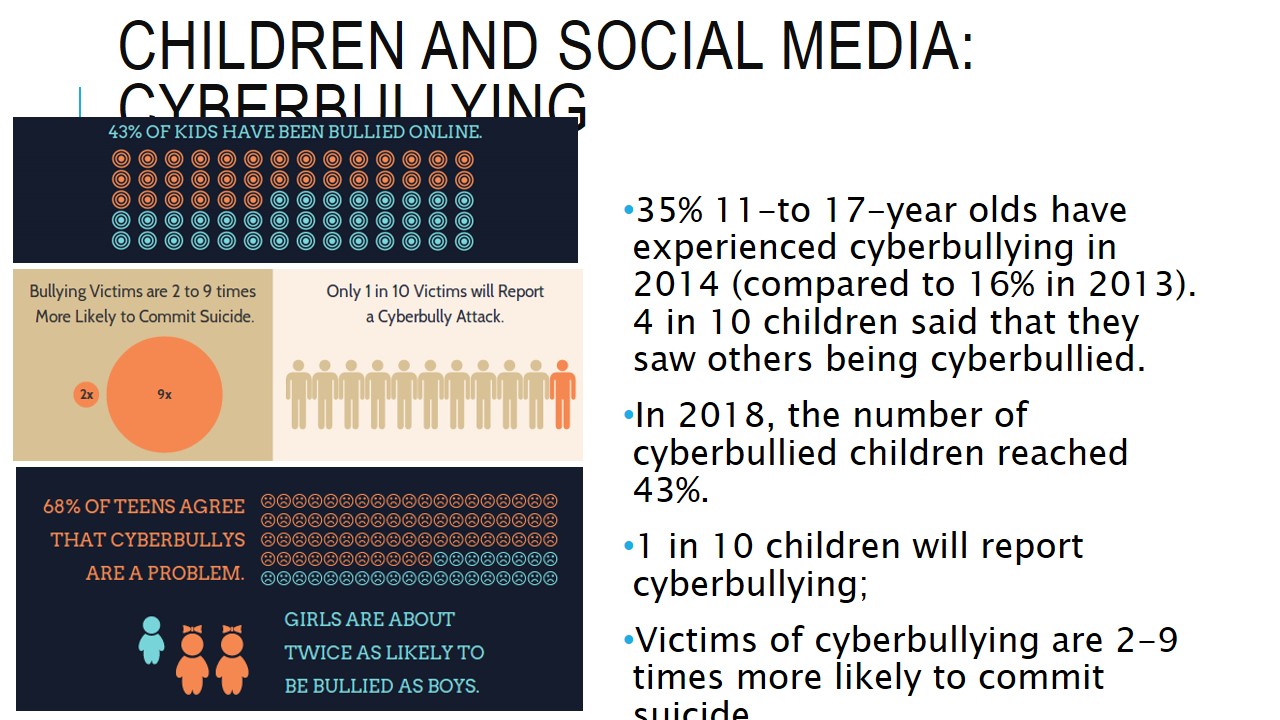
Children and social media: Cyberbullying
- 35% 11-to 17-year olds have experienced cyberbullying in 2014 (compared to 16% in 2013). 4 in 10 children said that they saw others being cyberbullied.
- In 2018, the number of cyberbullied children reached 43%.
- 1 in 10 children will report cyberbullying;
- Victims of cyberbullying are 2-9 times more likely to commit suicide.
Cyberbullying is a significant problem associated with the excessive use of social media by children. 43% of children have experienced bullying online, and only 1% of them will report such an experience. Girls are about 50% more likely to be bullied compared to boys, which also points to the gender characteristics of the problem.
Children and social media: Snapchat & Tinder
- Concerns arise regarding children’s exposure to adult audience;
- Risks of grooming and abuse;
- 37% of children use Snapchat up to 10 hours every day;
- Explicit images of children on Snapchat increase risks of exposure.
There are areas of children’s social media use of which parents are not aware, and most of them are associated with using dating platforms and applications. 46% children aged 15 and younger use Tinder (online dating app) every day, which is a concerning fact that requires careful monitoring. Importantly, the use of such platforms results in increased crime rates associated with harassment, kidnapping, and rape of underaged children.

Children and social media: influencers
- Influencers market products/services to their target audiences;
- Young children are also becoming influencers (Pollack, 2019);
- Children review games, toys, and stream themselves playing video games;
- Brands start reaching children to advertise games and toys to other kids (Pollack, 2019).
The trend of social media influencers continues to grow (Pollack, 2019). Importantly, younger children, aged below 10 are now becoming influencers with the help of their parents.
Viewing the content made by such children triggers desires of video games, toys, and technologies advertised on social media. This points to the increased need to increase the management of children’s Internet use.

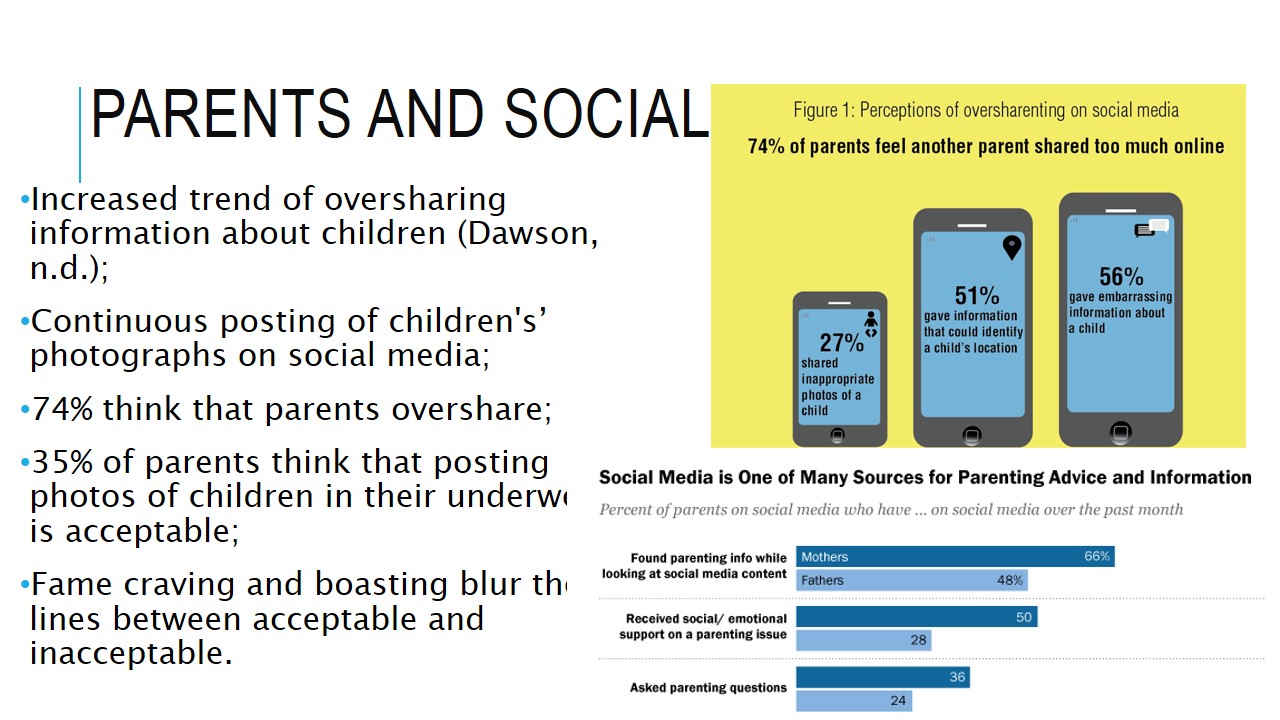
Parents and social media
- Increased trend of oversharing information about children (Dawson, n.d.);
- Continuous posting of children’s’ photographs on social media;
- 74% think that parents overshare;
- 35% of parents think that posting photos of children in their underwear is acceptable;
- Fame craving and boasting blur the lines between acceptable and inacceptable.
This slide contains some important information about how parents use social media at the detriment of their children.
Children are sometimes used as subjects of fame craving and boasting as well as oversharing. Children become adept to posing for their parents, 56% of post embarrassing information about their children and 51% of whom share identity and location data.
Parents and social media: Sharenting
Oversharing on social media by parents is referred to as “sharenting” (University of Michigan Health System, 2015). While social media is used to share advice or ask for it, parents fail to protect their children’s privacy and share too much.
When children are older, they may see what parents shared online and become embarrassed. Young children do not have much control over what their parents share online.
Sharenting is a trend that has been receiving increased attention from the public as parents share more and more photos of their children online.
The risks of this trend are linked to children potentially being embarrassed of their online presence when they get older.
Action plan
- Develop a short, informative parental guide to disseminate across media;
- Use the most popular platforms (YouTube, Facebook, and Instagram) to communicate main findings and solutions;
- Develop a short survey to question parents on whether the parental guide was effective;
- Analyze survey findings and address gaps identified by parents;
- Provide an improved and enhanced guide based on analysis findings.
The overview of relevant information on social media and gaming use resulted in the formulation of an action plan.
With the use of social media platforms, a guide on how to address children’s technology addiction will be developed.
After the dissemination of the guide, a sample of parents will be surveyed on the plan’s effectiveness to introduce improvements based on their experiences.

Children and gaming: Parental guide
- Risks:
- Inappropriate content: sexual or violent images;
- Multi-player gaming: abuse and harassment from other players;
- Inappropriate language and unwanted contacts;
- Accidental running up of bills for in-game purchases.
- Recommendations:
- Checking games’ ratings for age appropriateness;
- Advising not to share personal information on gaming profiles;
- Using family safety settings;
- Installing up-to-date anti-virus software;
- Educating children on how to block other users for harassment.
- Need for psychoeducational parental guides to prevent problematic video gaming in children (Krossbakken et al., 2018);
- Guides should be accessible to a significant number of parents;
- Children should be allowed to play games that are appropriate for their age;
- The wide range of available games offers a large choice for parents;
- Possible to introduce children to old games that their parents used to play (Gibson, 2017);
- Finding balance between screen time and other activities is essential;
- Agreeing on a time limit for gameplay will prevent potential conflicts.
In the slide, risks of children’s excessive gaming are presented. They range between in-game purchases to images of sexual or violent character.
Addressing the problem of inappropriate language is also imperative since children learn it quickly.
The recommendations are based on developing a set of positive behaviors that parents can implement in order to reduce the adverse impact of gaming.
According to the study by Krossbakken et al. (2018), a parental guide for addressing problematic video game behaviors among children must address several important issues.
These issues range from sleep problems to screen time, and their management implies catering to the needs of each child separately.
The key plan behind the guide is linked to being accessible to a large target audience, and social media should be a tool to fulfill this aim.
The list of recommendations above is focused on offering parents some helpful strategies to overcome children’s continuous social media use. With the help of traditional games that are not as explicit and violent compared to current ones. In addition, parents are advised to establish an environment with a balance between screen time and other activities.


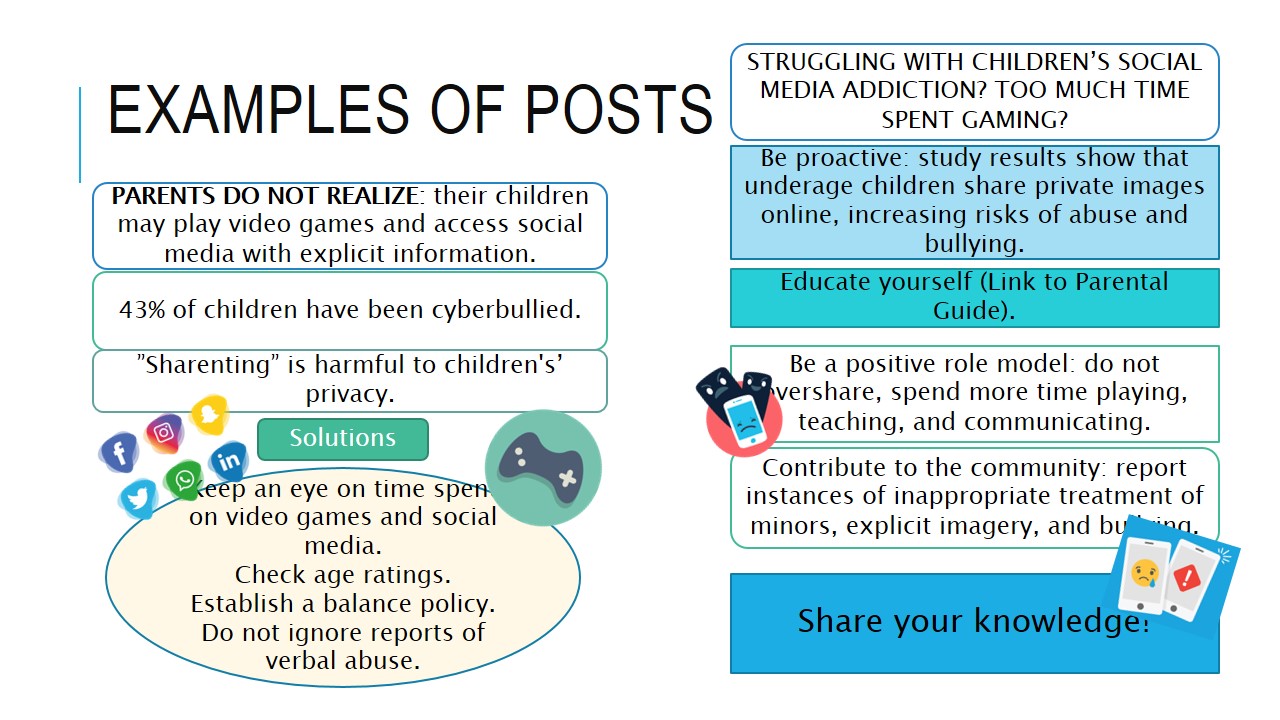
Examples of posts online
- PARENTS DO NOT REALIZE: their children may play video games and access social media with explicit information.
- 43% of children have been cyberbullied.
- ”Sharenting” is harmful to children’s’ privacy.
Struggling With Children’s Social Media Addiction? Too Much Time Spent Gaming?
- Be proactive: study results show that underage children share private images online, increasing risks of abuse and bullying.
- Educate yourself (Link to Parental Guide).
- Be a positive role model: do not overshare, spend more time playing, teaching, and communicating.
- Contribute to the community: report instances of inappropriate treatment of minors, explicit imagery, and bullying.
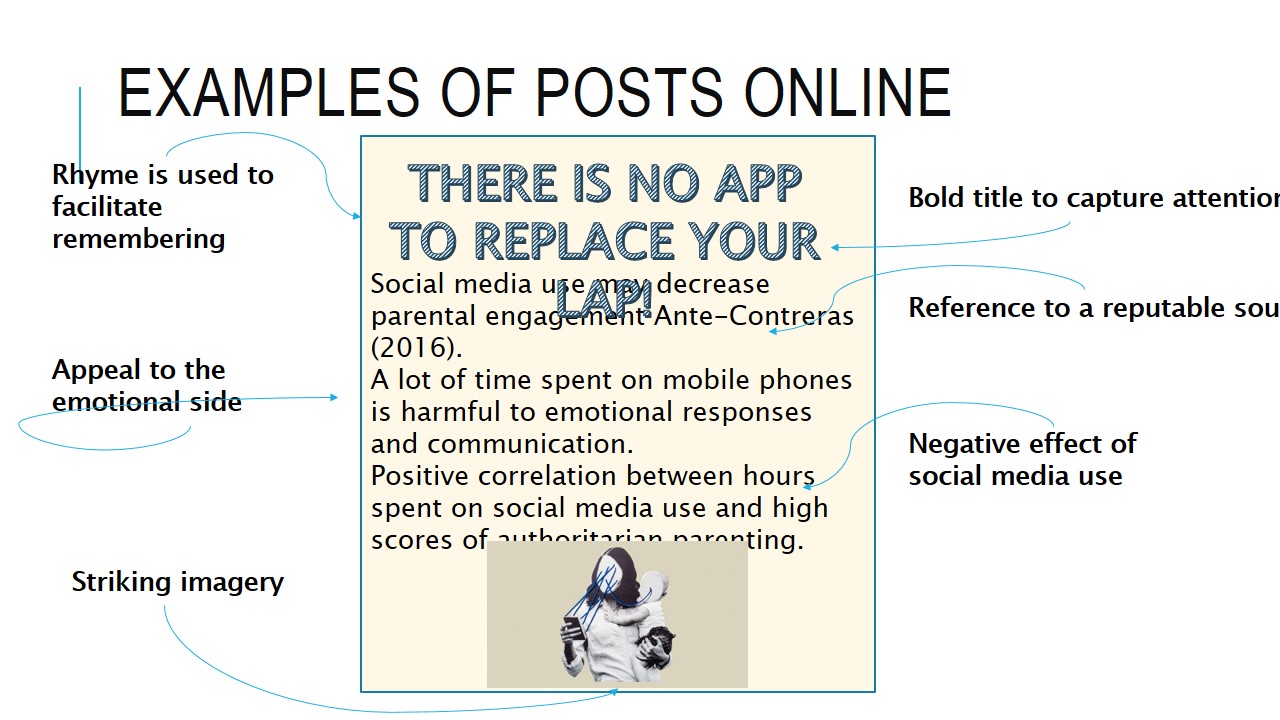
The examples of social media posts om the slide will take form leaflets containing the most important information on the program. The benefit of these designs is associated with the fact that it is easy to disseminate as well as print and hand out.
Evalution of effectiveness
The project has reached the expected levels in effectiveness in the categories of increased awareness of general problems, improved management of gaming and social media use, improved communication, parents’ shared knowledge, and knowledge of cyberbullying. It is expected that the ”sharenting” trend will require further improvement.

References
Ante-Contreras, D. (2016). Distracted parenting: How social media affects parent-child attachment. Web.
Dawson, M. (n.d.). Parenting in a Fakebook world: How social media is affecting your parenting. Web.
Howard, J. (2017). Kids under 9 spend more than 2 hours a day on screens, report shows. Web.
Krossbakken, E., Torsheim, T., Mentzoni, R. A., King, D. L., Bjorvatn, B., Lorvik, I. M., & Pallesen, S. (2018). The effectiveness of a parental guide for prevention of problematic video gaming in children: A public health randomized controlled intervention study. Journal of Behavioral Addictions, 7(1), 52-61.
Nikken, P., & Schols, M. (2015). How and why parents guide the media use of young children. Journal of Child and Family Studies, 24(11), 3-14.
Smith, A., & Anderson, M. (2018). Social media use in 2018. Web.
University of Michigan Health System. (2015). ‘Sharenting’ trends: Do parents share too much about kids on social media? Web.