Introduction
Situation Description
It is noted that connection between people is becoming more and more important in contemporary society. This is given the fact that this connection has benefits to both parties that are involved in the engagement. One of such benefits is the ability to pass on messages, or what Cutcliffe (8) refers to as the communication benefit of human connection.
But it is not all people who are keen to connect with each other. Some are apprehensive about the whole thing for various reasons. Johnson (18) notes that when people want to contact one another, they look for an appropriate sample or means of communication that suits their purpose. Others prefer to communicate using means such as the email, phone calls and such others. Other people may find such means intrusive, for example the noise of a ringing mobile phone (Johnson 19).
Whichever the case, communication is indispensable in human society. For example, a lecturer may find it necessary to communicate with their students regarding their performance, their whereabouts and such other issues.
This report is a description of a project to design and install a text messaging device on the office door of the professor to enable them to communicate with students and other people that might visit their office while they are not there.
Problem Definition
The goal of this project is to create a device that can enable communication between two people, for example the professor and their student. Managers, doctors, professors and such other people are busy, and their schedules may keep them out of their offices for a long time (Ellis 34). However, given the critical role that these people play in their field, it becomes very important to establish connection between them and their clients even when they are away from the office.
When away from the office, the doctor may be at an operating room, the professor at a lecture hall, the manager at a meeting or such other places. In a nutshell, it is not possible to reach these people through conventional means such as the mobile phone, given that this will be intrusive to them. As such, it becomes necessary to come up with ideas to communicate with them unobtrusively (Coughlan 14).
The client for this project is the professor. One way to contact them is using their mobile or email address. However, there are situations where the student who needs to contact the lecturer does not have their email address or their phone number. The lecturer can be contacted in this case by using the new idea of a messaging device that will allow the student to contact them anytime from their office.
All that the student needs to do is select a message on the device that will be fixed on the office door and send this to the mobile phone of the lecturer. The lecturer can then contact the student via the same messaging device and inform them when they can contact him (Burns 12).
Project Objectives
The goal of this project is to come up with a device that will help one to contact the lecturer without noising them, and especially so when one does not have the mobile phone number or address of the professor and the professor is not available. The objectives of this project emanate from the problem that the project aims to solve, and the objectives are the solutions to the said problem.
The following are the specific objectives of this project:
- To design a device that will allow the sender to send a predetermined message to the professor, hence establishing contact
- The device will be programmed to send a message to a specific cell phone, that of the professor. This means that the device will have a SIM card capability
- The device so designed will be able to receive the answer from the professor’s mobile phone and display it on the LCD screen on the door
Project Background
According to Dane (28) and Cormack (22), several studies have been conducted in the area of mobile communication. These are studies that focus on issues similar to the one addressed by this project. According to Gomm (20), several strides have been made to this end. A case in point is the Peek Pronto Mobile Messaging Device (Burns 8).
Peek Pronto Mobile Messaging Device is one of possible solutions to the issue addressed in this paper. This device is simple and affordable, and it is a solution that can be accessed by anyone who needs email services on the go (Parahoo 20).
Peek Pronto has been described by some analysts in the communication industry as a clever gadget which is able to send and receive unlimited number of email and text messages (Ploeg 19). The benefits of this gadget are made more significant by the fact that the device can send and receive text and email messages from anywhere (Ploeg 19). As far as text messages and email are concerned, the device does not have limitations to this end.
One of the major weaknesses for this device is the fact the length of the text message that can be sent and received by this gadget is limited. Also, it will be tedious to the lecturer to type individual messages to each and every student in their class. As such, a device mounted on their door is more convenient.
But the limitations of this device are checked by the strengths that it possesses. For example, by using the Peek Pronto, one is able to contact whoever they want without making noise or intruding on them.
Curricular Resources
There are several topics, concepts and lab experiences taken by the members of this group from the different courses that they have taken over the years. These are the topics and resources that will be useful in this project, and will be incorporated at various stages of the project.
The following are some of the curricular resources that the members of this group will utilise and incorporate in this project:
Table 1: Curricular Resources.
Specification Development
Each project has specifications that are set forth by the stakeholders, which may include the implementers or the consumers (Gomm 20). Whichever the source of the specification may be, the implementers of the project find them very useful as they guide their activities as they go about the process of implementation.
The specifications for this project were provided by the client, Dr. Ramzi Obaid. The team members take down the specifications that he wants for the device. The students use the internet to collect information and to get some important details regarding the specifications that the professor provided.
The members of the team also get information from interviews and informal conversations that are held with professionals from the engineering industry. The aim of these conversations and interviews is also to get information regarding the parts that are needed to meet the specifications identified for the device that the professor wants to be developed.
Some discussions are held with consultants to get the specifications of the device right and to gain some technical knowhow on implementing the project.
Design Specifications and Constraints
Engineering Specifications and Constraints
Following are some of the engineering specifications that might have a direct impact on the efficacy of the device:
- The device will use an LCD display, where messages will be displayed on a monitor
- The device will use a keypad for typing the messages
- The device is programmed to send an SMS to one mobile number only, and to receive messages from this number too
- Given the above specifications, the device must have SIM card capability
- The device will have the capability to continuously display any SMS sent from the mobile phone, and this will act as an announcement to those looking at the LCD display
- The SIM card needs to be topped up to use the service
- The device will be using electricity to operate
Realistic Constraints
The following are some of the realistic constraints for the device:
Economical
Some costs will be incurred in servicing the device. This is for example topping up the SIM card and the cost of developing the device. But it will be very helpful.
Environmental
The device does not have any negative effect on the environment
Ethical
The device will help in contacting the lecturer without noising. But there will be no privacy in using the device. This is given that the messages will be displayed on the monitor mounted on the door to be read by everyone, even those not intended to read them.
Health
The device will have a GSM magnetic field, whose effect on health is similar to that of the mobile phone.
Social
The device has no social effects
Political
No political effect
Ergonomic
The parts that will be used will be standard, with sufficient comfort in using
Aesthetic
The device will have an attractive shape and cover, and it will be easy to use.
Validation Procedure
Validation of the device will be achieved through various means. The saved messages can be shown, and each can be sent to ensure that the device is working properly. To validate the program, a message will be written and sent to the mobile to check reception. The SIM card will be checked manually, and the receiving device will be validated by checking whether the messages that are sent are received and displayed.
In order to validate whether the SIM card can be recharged, a scratch card will be loaded manually. To see whether the device can work using electricity, it will be connected to the charger. A lot of validation will also take place during the designing process. Electronic circuits will be tested in the laboratory using available test equipments such as voltmeter and oscilloscope. The final product will be tested by making trial runs on it.
Conceptual Design
Introduction
The major aim of the device is to contact someone that we cannot reach on the phone or personally. This will be achieved by designing a device that can send and receive a text message from the professor’s phone. The professor will be able to reply and the message will be displayed on an LCD monitor.
Alternative Solutions to the General Problem
The problem in this case is how to contact someone when physical contact is not possible. The following are some alternative solutions:
- Use of fax
- Use of email
- Use of telephone
- Leaving a message on their voice recorder
Relevant Alternative Solutions
One alternative solution is to design a device that will enable one to write a message and send it to email, a message that can be accessed by anyone with the device (Burns 10). The problem here is that the person may be away from their computer or have no access to internet. Another is designing a device with a speaker, a microphone and button. The device will be operated by pressing the button and raising a person with a similar device, more or less like the police radio. The problem in this case is the high cost of running the device. The good thing with the device in this project is that the professor will be reached through their mobile phones, which they always have on their person. The cost of running or operating this device is also relatively low.
Comparing the Alternatives and Deciding About the Solution
There are two alternative solutions to this problem. The first alternative is the device that sends a message to an email. In this situation, such a device is not practical. This is given that the recipient may not be able to access the internet and read their emails. Time will be wasted and a lot of inefficiencies will arise.
The second alternative is better than the first one as far as time saving is concerned. But the cost of running it is prohibitive, and this will make it unsuitable for the problem even though it can solve it.
Design Methodology
Review of Course Needed
The first step will be to review the course that will be needed for the design.
Collection of Information
The second step is to collect information from the internet regarding the GSM Kit. This includes the input, the output, power supply, antenna and the AC rectifier (Parahoo 21).
Collecting more Information
The next step is to collect further information on typing messages on the device. It was realised that this will take a very long time to design, and it was agreed that saved and predetermined messages can be used, from which the sender can select one.
EE201 and EE202 was reviewed but found not to be enough. So, further investigations were carried out on how to program and code the GSM kit. The kit was ordered and further analysed. The parts needed for the project were then purchased. These included LCD, the antenna, memory and AC rectifier. The GSM kit was then programmed so that it can run as desired. The various parts of the kit were connected, and a design cover for the whole contraption made.
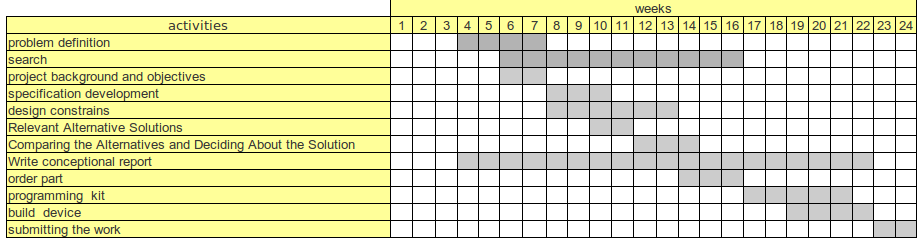
Project Tasks and Timetable
To complete the design, it was necessary to review some courses that had been taken in the past. Some experiments that had been conducted in the laboratory were also reviewed. There are some skills that are needed on the part of the team members. For example, the members must have knowledge on GSM kit and how to connect it. The members must also be aware of how to program the GSM kit, together with connecting the LCD screen.
The following is the work plan for the whole project:
Works Cited
Burns, John. Electronic Design in 21st Century. Long Beach: Prentice Hall, 2010.
Cormack, Humphrey. “Students and Laboratories”. The Electronic Quarterly, 2010.
Coughlan, Peter. Communication Projects and Developments in the Society. London: Willincot, 2009.
Cutcliffe, Isaac. Electronic Design Procedures. New York: Free Press, 2007.
Dane, Eric. Experiments in Communication Science. London: Prentice Hall, 2011.
Ellis, John. Students’ Guide to Experimental Electronics. New York: Free Press, 2010.
Gomm, David. Ergonomics in Designs. New York: McGraw-Hill, 2010.
Johnson, Andrew. “Experimental Communication Technology”. Journal of Electronic Education, 2:2, 2010.
Parahoo, Richards. Students’ Guide to Electronic Designs. New York: Free Press, 2007.
Ploeg, Gregory. New Designs, New Ways of Life. London: London University Press, 2009.