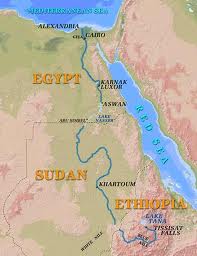
River Nile
The river Nile is the longest river in the whole world with an aggregate length of about 4,160 miles (6,670km). The river originates in Africa with its source being in Burundi in the southern part of the equator towards the far northeastern parts of Africa. Finally, the river Nile flows though Uganda, Ethiopia, Sudan, and then Egypt where 22% of its course meanders in it. From Egypt, the River Nile then terminates its course into the Mediterranean Sea. The true starting point of the river Nile is believed to be Ripon Falls although some claim that Lake Victoria is also the source. River Nile is served but many streams along the way but the major two intensive rivers that drain into the River Nile are the White Nile originates from Lake Victoria and the Blue Nile that originates from Lake Tana in Ethiopia. The river course is highly inhabited by the ancient Egyptians because of its multitasking nature. The River Nile is densely inhabited because it supplies plenty of food, water, rich fertile soils for agriculture, and finally serves as a transportation medium.
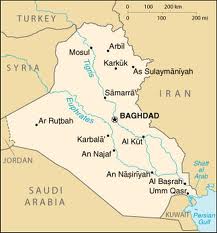
Flooding in River Nile and Euphrates and Tigris
The flooding of the River Nile is a result of ice or snow melts (glaciations) and heavy summer rains that used to fall in the highlands of Ethiopia. Due to the fact that the river overrode the Ethiopian lowland, the inclined gradient of the River Nile sent the water torrent which overflowed the river banks resulting in over flooding of the river. This led to a positive impact on agriculture because the thick enriched muddy soil was left on the river banks as the flooding went down. The black silt soil left was good at sustaining crops a factor that led to the dense population of the area. Growing of crops in the rich black silt soil left after flooding was the main reason why ancient Egypt’s migrated to the banks of River Nile thus making an evergreen River Nile region. The flooding impact of the River Nile increased food production thus making Egypt become opportunistic of the scenario.
On the other hand, the Euphrates in conjunction with the Tigris, form Rivers of Mesopotamia whereby the Euphrates originated from the eastern region of Turkey to meet Tigris that originated from the Shatt-al- Arab and drain into the Persian Gulf. The two rivers merged at Al-Qurna in the southern region of Iraq. The flooding of Tigris is a result of additional water from the two zabs (greater and lesser), Diyala, and Adhem Rivers an event that occurs during March and April termed as the flood months. Tigris is prone to flooding due to its gentle baseline level, unlike the Euphrates. The Euphrates on the other hand is known to be a low gradient lethargic river that is served by rivers of Murat and Karasu (eastern and western Euphrates respectively) from the mountains of Turkey. The two rivers are known to be the worst ever flooded regarding the biblical history of Noah’s ark. However, flooding was controlled by the construction of canals thus initiating the Sumerian civilization. Flooding in this area had a positive impact in the beginning because much of the inhabitants’ properties were washed away. The upcoming Sumerian civilization introduced irrigation systems that improved the agricultural sector of the arid land in Mesopotamia. As much as the flooding in Mesopotamia was destructive at the beginning, civilization changed the entire process and became productive just like in Egypt for the case of the River Nile. There was increased production of food due to alluvial soil deposits in Mesopotamia, green pastures were all over the field thus livestock keeping became successful.
Maps
Cultural Images

