Introduction
No one expected the full impact of the Information Age. No one anticipated the scope and degree of transformation that resulted from the widespread adoption of Information Technology. These changes came about because of the rapid technological developments in computer engineering and software design that radically altered the Internet and the World-Wide-Web. The banking industry experienced radical changes in the way clients can access and transfer funds.
The movement of funds from one account to the next can be accomplished without a human intermediary. A significant amount of money can be transferred even without the participation of a human being. This new capability enhances the business processes of banks and related organizations.
But at the same time it increases the level of risk. It is therefore imperative to develop a more dependable and secure management information system that can handle electronic banking. This study will attempt to provide an enhancement plan for the National Bank of Abu Dhabi using Deming’s PDCA framework.
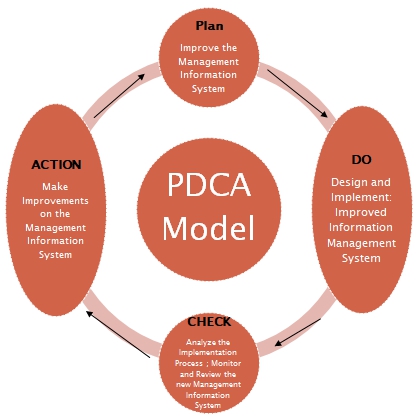
The PDCA model simplified the major processes necessary to secure and enhance the management information system of the National Bank of Abu Dhabi. It can be argued that there are different phases necessary to complete the application of Deming’s model (Tang, 2008).
The first phase is the planning stage. It is important to plan ahead because it does not only provide the impetus for the project but also informs all the personnel involved that there is going to be a major change that is about to occur in the business process of the organization. At the same time it enables the corporate leaders to muster all the resources needed for the plan and to determine if the company has the needed resources to accomplish the major goals stated in the plan.
The planning stage also identifies key human resources who are needed to initiate the change process as well as to develop the framework for the project. Key personnel are needed for the software and procurement requirements of the Information Technology aspect of the plan. The planning stage process also enables the leaders to have an overview of the current situation. It is during this stage that the corporate leaders and the project manager will be able to see the major weakness of the bank in terms of IT security issues.
The second part of the PDCA model is labeled as “DO” and it signifies the implementation of the plan. Once the plan has been completed and all the stakeholders had been identified, it is time to execute the plan. This is the stage of the PDCA model wherein the importance of leadership skills can be overlooked.
But it is imperative that the leader follows through the goals stated in the plan. The leader must make sure that the plan does not end and begin in the boardroom. The plan must be implemented and this is made possible by the creation of a practical timeline that the leader can communicate to his subordinates.
The next step in the PDCA model is called “Check” and it signifies evaluation of the process. Those who study and carefully follow Deming’s management principles noted that the PDCA model can be enhanced by changing “Check” with “Study” and therefore transforms the dynamics of the model.
It is an important observation because checking the system is not enough especially if the management information system in place was established a long time ago. Therefore, it is no longer enough to check the system but to properly evaluate the whole program and take a closer look at the components that are obsolete and requires replacement or upgrades. However, in the present study, the plan that will be implemented is new and therefore the original PDCA model will suffice.
Finally, the last stage of the PDCA model is labeled as “Action” and it signifies the action that will be taken right after the completion of the evaluation phase. In other words the plan and the strategies created are never perfected on the first try.
Therefore, continuous improvement is needed and continues changes are implemented in order to repair the weak links in the process. It can be argued that the process occurs in a cyclical manner. It moves from one phase to the next and goes back to the planning stage in order to rectify the errors made in the beginning of the process.
The Deming’s model is a proven management strategy. Thus, it is not prudent to tinker with something that is not broken as the wise saying goes. However, the PDCA model can benefit from enhancements, especially in light of the view that the said model was created from a manufacturing perspective.
Enhancements are needed because the PDCA model will be applied in the field of Information Technology, in the context of NBAD’s needs. Therefore, the ISO standard when it comes to the security of management information systems, specifically ISO/IEC 17799, must be utilized to develop a more effective plan for NBAD.
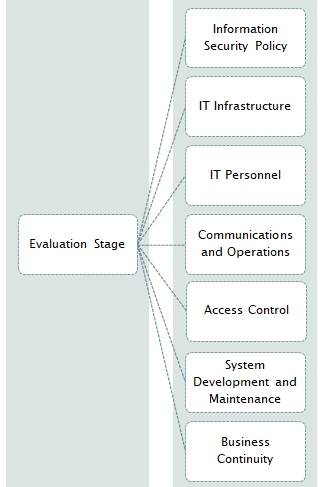
According to the current ISO standards in the security of management information systems there are 12 areas that a project manager must carefully consider and these are listed as follows: 1) Scope; 2) Terms and Conditions; 3) Security Policy; 4) Organizational Security; 5) Asset Classification and Control; 6) Personnel Security; 7) Physical and Environment Security; 8) Communications and Operations Management; 9) Access Control; 10) system Development and Maintenance; 11) Business Continuity Management; and 12) Compliance (Tang, 2008). The following report uses the PCDA model as a basis only for the creation of the appropriate security enhancements for NBAD’s electronic banking processes.
National Bank of Abu Dhabi
The National Bank of Abu Dhabi is considered as one of the best, if not the best bank in the United Arab Emirates. In 2005 it was acknowledged as the number one bank by the UAE’s bank industry. Standard & Poor, the agency that monitors the performance of world-class companies rated the NBAD as A-Stable.
The rating was considered as the highest in the Middle East. A credit research organization also gave favorable marks to the bank and gave NBAD with an A rating. The success of the bank can be attributed to many factors including the fact that during the early years of the creation of the UAE, the state founded NBAD in 1968 and made it the Central Bank of the state until the government was able to establish the currency board in 1975 (Oxford Business Group, 2007, p.97).
It has to be made clear also that the government indirectly controls the bank with a 73% ownership stake (Oxford Business Group, 2007, p.97). As a result, nationals outside the UAE can only have a limited stake and control of the bank. Only 25% of the bank can be owned by foreigners.
The success of the bank is closely linked to its association with the government. In most cases NBAD’s link with the government can be interpreted as a sign of stability and the assurance that it is regulated having the customer’s best interest in mind. Thus, the high approval rating of NBAD can be explained through this perspective.
But this particular strength can also be a weakness when it comes to the implementation of much needed improvement strategies. The goal to improve the security aspect of the bank’s management information system can be a challenge if the negative impact of bureaucracy will not be dealt with in the most productive manner.
Focus of Improvement
The bank has three major departments and these are 1) domestic; investment; and international (National Bank of Abu Dhabi, 2012, p.1). But the application of the PDCA model will be focused on the local component of the business organization.
The bank has 110 branches in the UAE and it has 450 ATMs that allow their clients to have access to funds on a 24-hour basis. At the same time the bank provides an SMS-based payment service. But the primary area of concern is the electronic banking system that has an Information Technology backbone.
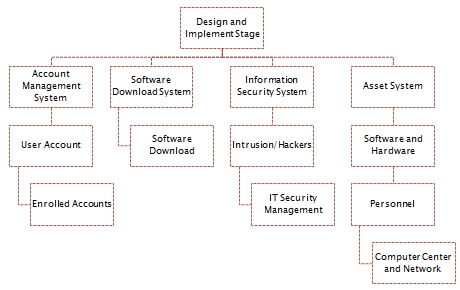
The specific area that requires major consideration is the capability to transfer funds using mobile phones. The fund transfer can be performed between two accounts under one client. Another way to transfer funds is to move money from a client’s account to an enrolled account. The enrolled account can be an account of a family member, a relative or a business associate. Money can also be transferred from a client’s account to a business organization as a form of payment for a particular service availed by the client.
The transfer of funds from a client’s account to another account under the same name is of no concern to the proponent of this study. The most important aspect of the digital banking process within NBAD’s local operation is the capability of the customer to transfer funds to another person’s account even if it is a relative or a family member. The enhancement of the security protocol is made more challenging by the fact that fund transfer can be accomplished using mobile devices like laptops and mobile phones.
The Application of Deming’s Model
Electronic banking is the future of the banking industry. The creation of electronic banking platforms can easily translate to increase in productivity, increase efficiency and overall better customer service (Pastor-Satorras, & Vespignani, 2004). The new wave of electronic banking is fueled by the creation of sophisticated portable devices.
These are actually small computers. Furthermore, the portable and powerful computers housed within these devices are not the only factors that fuel its popularity. As the years pass by these devices become cheaper and therefore accessible to a greater number of people.
It must be pointed out also that electronic companies and manufacturers of laptops and mobile phones compete with each other to produce cutting-edge technologies. But the more powerful technologies are integrated into the electronic banking system, the more difficult it is to secure the banking facility. It is therefore important to be aware of these changes and to develop strategies that can deal with these challenges.
Using Deming’s management framework, the first step in the process is to develop a plan to solve a particular problem. But before going into the specifics of the problem, it is imperative to acquire the pertinent information that can assist corporate leaders and the project manager to create a plan that can effectively strengthen the capability of NBAD. The first step in the planning phase is to gather information regarding the significance of the electronic banking in relation to the World-Wide-Web.
IT specialists may be familiar with the technical aspects of Information Technology but the bank’s president and CEO may have a basic idea of how it works. It is critical that all key personnel, most especially high-level officials have a clear idea that the vulnerability of management information system is due to the fact that it is part of a network of computers.
In order for a client to access NBAD’s electronic banking facility, he or she must use the Internet and the World-Wide-Web. It has to be made clear that the web relies on underlying networks, especially the Internet, as the vehicle to exchange the information among different users (Dale & Lewis, 2010). The bank and the client share this network.
Cybercriminals can use the same network to probe for vulnerabilities and exploit weaknesses in the system. The migration of real-world crimes into cyberspace does not reduce the impact of crimes committed online. Cybercrime such as the use of Information Technology creates the same level of damage when it comes to identity theft, embezzlement of funds, and extortion.
The solution is to develop a management information system. It is not just the capability to store and access data. Security experts remarked that “In the past, companies have struggled to make decisions because of the lack of data.
But in the current environment, more and more organizations are struggling to overcome ‘information paralysis’ – there is so much data available that it is difficult to determine what is relevant” (Nemati and Barko 2004, p. 2). NBAD requires an intelligent data management system, one that enables executives to use it even if they are not experts when it comes to Information Technology.
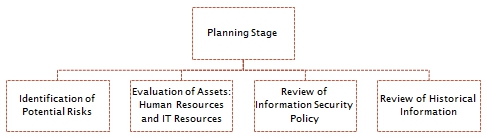
In the planning phase, there are at least five problem areas that requires a greater degree of examination and these are listed as follows: 1. Destruction of data; 2) Theft of sensitive information; 3) Deletion; 4) Corruption; and 5) Bugs and Virus Infection. Thus, it has been made clear that aside from the need to prevent intruders and cybercriminals from exploiting the weaknesses in the system it is also imperative to plan for business continuity.
The planning phase must also consider the fact that this project requires a never ending process of planning, testing and fine-tuning. The creation of an efficient management information system is unlike other projects that can be designed, implemented, analyzed, and maintained without the need to make changes for many years to come. This particular MIS requires constant adjustments because changes in the system occur regularly.
But before designing a new security protocol for NBAD, the project manager must learn to understand the needs of the personnel needed to operate the system as well as the end-users, the clients who will eventually use the system. After all the aspects of the new MIS system had been covered, the next challenge is the installation and implementation of the new system (McCumber, 2005, p. 173).
The challenge now is to make end-users comfortable with the new format and new features. This can be an exhilarating experience for some while at the same time it can be frustrating for those who struggle to keep up with constant modifications in the system.
In the implementation stage of the project, the managers and officers working at NBAD as well as their clients may object to the proposed changes. There are many reasons why they may complain about the difficulty of adopting a new system. Personnel and clients may point out to the problem of rapidly evolving technology.
Clients may argue that they cannot keep up with changes and the need to absorb new information. It is therefore important to design a system that does not require complicated processes that a client may not be able to follow.
Although it is important to consider the needs of the clients in terms of the creation of a simplified system, it is also critical to consider that management information systems has become complicated and pervasive because of innovations in the field of Information Technology. It is important to realize that it has become more difficult to secure an organization’s management information system.
In the evaluation phase of the project, the officers and managers at NBAD may find it difficult to follow the new security protocols without clear guidelines. Thus, it is imperative that the project manager evaluates the old information security policy and upgrade it to suit the needs of the present time. The information security policies must be complimented with governing policies; technical policies; job aids; and guidelines.
The governing policy for the said management information protocol involves the identification of users, levels of access, responsibilities, accountability etc. The governing policy also provides an overview of the system as it pertains to the overall structure of the company.
The technical policy provides a more technical understanding of the system. It is important to have a technical policy because it informs the workers and the clients what to do in case of a problem encountered in the process of electronic banking.
The technical policy also provides a framework of the chain-of-command and helps people know what to do in case of an emergency or a problem. The technical policy also provides detailed instructions on what has to be done in case of a breach in the system.
The job aids and guidelines help key personnel understand the step by step procedure on how to solve a problem related to the management information system. It is the byproduct of a realization that a problem can be solved one step at a time. In the analysis of the new system it will be discovered that there is a need to document the processes involved in the new security protocol that will be implemented by NBAD.
There is also the added realization that a management information system must be developed with a keen sense of sensitivity to the feedback of personnel and clients. The strategies must require constant fine-tuning. The work of the project manager requires constant evaluation of the processes involved. Those who are involved in this project must never think for a moment that they can develop a failure-proof system.
Gene Spafford a professor from Purdue University’s IT department remarked that, “The only system that is truly secure is one that is switched off and unplugged, locked in titanium-lined safe, buried in a concrete bunker, and is surrounded by nerve gas and very highly paid armed guards. Even then, I wouldn’t stake my life on it (Mason & Newcomb, 2001, p. 73). The exaggerated remark was meant to put in context the extreme difficulty in creating a perfect system.
The project manager draws inspiration not from the possibility of creating a perfect system but the realization that an improved system can help maintain the integrity and reputation of NBAD and prevent the illegal use of the electronic banking facility of the bank.
In the Information Security Management Handbook the authors provide a glimpse of what will happen in the event of intrusion and they wrote, “Such a malicious process can result in the creation of an illegal account with administrator privileges upon the victim’s machine” (Deograt-Lumy & Naldo, 2005, p. 5). The mere thought that intruders can cause such problems should be enough to inspire corporate leaders to support the creation of much improved management information system for NBAD.
Summary
The PCDA model developed for the manufacturing industry can also be utilized to deal with the issues related to management information system. The PCDA framework can be used to develop strategies and other protocols that can help secure the electronic banking facility of NBAD. The PCDA model is a helpful framework because it provides a process for the successful development and implementation of the plan.
Leaders are aware of the importance of a plan but they sometimes struggle to initiate the planning phase because they have no idea where to begin. The PCDA framework helps project managers limit the scope of the plan. At the same time, the said framework guides the project manager to focus on key areas of the organization where he or she can use the review mechanism in order to develop the key components of the plan. Thus, the project manager does not waste time but immediately focuses on key areas of the business organization.
The PCDA model also provides a clear framework when it comes to the implementation phase. It is not enough to simply implement a new program. There are certain problem areas that have to be dealt with before a new system can be implemented. A very helpful insight is the one that pertains to obtaining the feedback of key personnel as well as the clients.
It is not enough to develop a strategy that looks good on paper. The said plan must be realistic from the point of view of the users. A well-designed program is useless if it will be rejected by the clients because it is overly complicated.
Finally, the proponent of this study realized the challenges faced by IT security experts. Their main concern is not only to secure the banking facilities but at the same time they need to consider the needs of the clients. Some of the clients are already middle-aged men and women and they may have no inclination to study all the facts pertaining to a new system. Thus, the new security protocols must be designed intuitively so that customers are able to follow the instructions easily.
References
Deograt-Lumy, G. & R. Naldo. (2005) Insight into intrusion prevention systems. In H. Tipton & M. Krause (Eds.) Information security management handbook. Florida: CRC Press LLC.
Mason, A. & M. Newcomb. (2001) Cisco secure internet security solutions. IN: Cisco Press. National Bank of Abu Dhabi. NBAD online banking. Web.
Nemati, H., & Barko, C. (2004). Organizational data mining. PA: Idea Group Publishing.
Oxford Business Group. (2007). The report: Abu Dhabi. New York: Oxford Business Group.
Pastor-Satorras, R. & A. Vespignani. (2004). Evolution and structure of the internet. New York: Cambridge University Press.
Tang, J. (2008). The implementation of Deming’s system model to improve security management: a case study. International Journal of Management, 25(1), 54-68.