Background
The United Arab Emirates (UAE) is an intensively developed country where all the industries play an important role in contributing to the Emirates’ economic growth. From this point, the transport industry can be discussed as the key driver to stimulate the UAE’s economic development during the recent five years. Transport services influence all aspects of people’s social and economic life. As a result, the improvement of public transportation in the UAE is one of the priorities related to the progress of industries and the social sector’s development. The transport industry began to develop actively in the 1970s when the first bus services were opened in Abu Dhabi in order to respond to the increased public’s needs related to transportation services (Elsheshtawy 128). During the period of 1970-2013, the transport industry was developing; and today, the UAE transport industry includes such sectors the air transport, rail transport, metro system, bus services, taxi, and water transport services (Worku 109). Much attention is paid to constructing new roads and transport channels.
As a result, today, the UAE’s transport industry develops actively to address the increasing public demands. The main authorities’ focus is not only on developing the system of public buses and taxis but also on the support of metro and marine transit. The development of air and rail transport is strategic for supporting the UAE’s economic and social channels (Terterov 124-128). That is why new rail and road networks are constructed as a result of significant investment.
Billions of dollars are invested in developing the transport industry annually because of its extreme significance for the UAE’s economy (Government of Dubai). The developed transportation system is the key to improving the connection between the Emirates’ industries, companies, and resources. The transport industry is important for the UAE’s economy because all the economic activities depend on effective transportation solutions. The development of the transport industry in the UAE contributes to driving the country’s economic growth and increasing investment in the sector.
The purpose of this industry report is to provide an overview and analysis of the transport industry in the UAE with a focus on its development at different levels. Thus, the report provides information on the progress of the transport industry at the local level while focusing on Dubai, at the national level, at the regional level, and at the global level. The report also aims to provide the analysis of the transport industry in relation to the past five years to concentrate on obvious changes, to describe the aspects of the transport industry’s progress regarding its strengths, and to state how the industry supports the economy of the UAE in detail.
Methods
The analysis of the transport industry in the UAE with the focus on Dubai is based on the methods typical for qualitative and quantitative researches. To conduct the investigation on the stated topic, it is necessary to pay attention to analyzing the qualitative information on the role of the transport industry for the economy of the UAE and to the quantitative information presented in the form of the numerical data, including the economical rates and statistical data (“World-Statistics.org”). That is why the used investigation method can be discussed as the document analysis (Elsheshtawy 23). The research procedure includes such stages as the planning of the research, the collection of the data related to the transport industry in the UAE, the analysis and interpretation of the data, the discussion of the results, and the formulation of conclusions.
While referring to the research instruments and data sources used to conduct the investigation within the industry, it is necessary to note that the main focus was on collecting, examining, comparing and contrasting the data, developing the diagrams for summarizing the information, and making conclusions on the role of the industry at the local, national, regional, and global levels. To respond to the research questions and purposes, much attention was paid to analyzing the official numerical data on the transport industry’s development in the UAE. Thus, the data sources include the government agencies’ reports, industry reports, and market analysis reports retrieved from the government and agencies’ websites.
These resources are the most important to conclude about the tendencies in the industry’s progress in the Emirates. The researchers’ articles published in academic journals on the aspects of the UAE transportation are important to be examined to analyze the data in relation to the role of the industry for Dubai and other Emirates’ economic development (Lee 312; Worku 108). The researchers’ works on the aspects of the UAE, and Dubai’s transportation system were also consulted to find the necessary information on the topic.
The process of data collection is usually associated with such challenges as the inability to receive factual or statistical data on the concrete topic, which can be discussed as updated and credible. Referring to the industry reports, it is necessary to focus on the time periods during which the investigations were completed (Government of Dubai; “Sectorial Overview: Transportation and Logistics”). To overcome the challenges connected with collecting the updated information on the industry’s development, it is useful to focus on collecting annual reports in the field; to pay attention to the experts’ predictions; to compare and contrast the annual data; and to focus on the actual numbers supported with the industry surveys which are sponsored by the government and independent researchers to receive the full information.
Results and Discussion
Transport Industry at the Global Level
Global Differences in Using Transportation Modes: Overview of the Recent Tendencies
At the global level, the progress of the transport industry in the world is closely associated with the development of public transport systems. The first transport systems were the networks of roads to connect towns and cities and water channels to connect the distant lands. The focus on developing rails in Europe during the 19th century reformed the public’s traditional vision of transport systems. The next step in developing the world transportation system was the progress of aviation in the 20th century (Terterov 14-16). While focusing on the development of the global transport industry during the recent five years and on the data of 2011, it is necessary to note that the air transport (51%) and road transport (41%) remain to be the most actively used travel transport channels in the world (Figure 1; “UNWTO”; “World-Statistics.org”). In the European countries, the use of buses increases every year, and today it is more than 70% (“World-Statistics.org”).
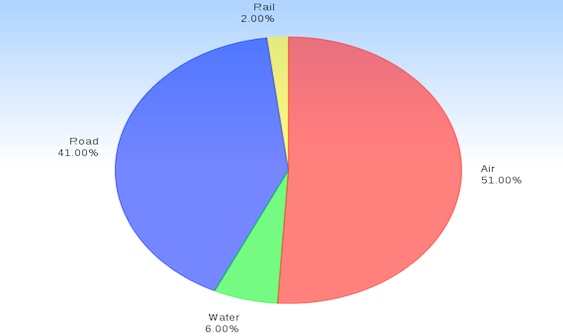
The Number of Air Transport Passengers Globally
Referring to Porter’s model and to the concept of world competition, it is necessary to note that the air transport is discussed in the world as one of the most popular public transportation modes for traveling and for connecting the country’s cities and territories abroad. Furthermore, air transport is one of the most profitable industries in the countries’ economies worldwide. While comparing the number of passengers carried by air transport globally, it is necessary to note that the United States provided the air transport services for more than 746 million people in 2012, and more than 59 million people used the air transport in the UAE (Figure 2; “World-Statistics.org”).
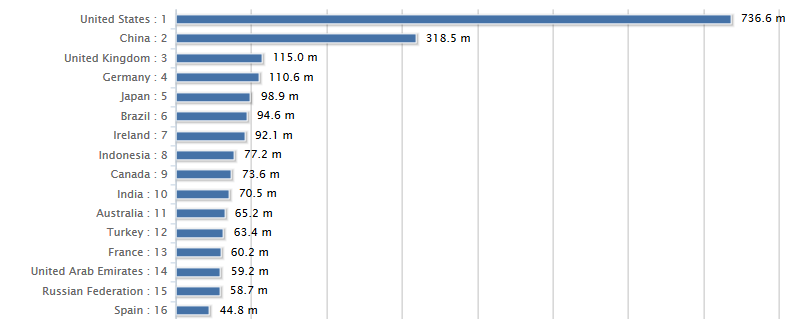
The difference in numbers depends on the size of the territories and city location, among the other factors. Air transport attracts the number of passengers because of the speed and safety, and the percentage of passengers carried by air transport is expected to increase (“Sectorial Overview: Transportation and Logistics”; “World-Statistics.org”). During the period of 2010-2013, the popularity of air transport among the passengers increased by 14% (“World-Statistics.org”). While discussing the situation in the Middle East, it is important to note that buses, air transport, and rail are the traditional modes of transportation in the region, but today more attention is paid to the development of the public water transport and taxi, as it is in the UAE (“RTA”).
Transport Industry at the Regional Level: GCC
GCC Transport during the Past 5 Years
The Gulf Cooperation Council is the union of the Arab states of the Persian Gulf region, which is based on the economic and political interests. The UAE is a member of the GCC, which was founded in Abu Dhabi in 1981. The transport industry is actively developed in the region for two decades (“Gulf Cooperation Council Railway Project”; Terterov 56-58). The GCC members pay much attention to combining their efforts in order to construct effective channels between the GCC states. Air transport and cars are the most popular among the GCC states’ population. However, the transport industry in the GCC is developed intensively to address the needs of the public.
Thus, buyers become the main driving force to develop the industry in the region while referring to Porter’s model. That is why the GCC launched the Gulf Rail Project to respond to the buyers’ needs and to develop the countries’ economic potential. The total expected length of the railways to connect the GCC countries is about 2116 km. The project is planned to be completed in 2017 in order to increase the number of GCC rail passengers by more than 35% during the first decade of exploitation (“Gulf Cooperation Council Railway Project”).
The Forecasted Use of Different Means of Transportation in relation to the GCC in 2016-2028
Referring to the GCC data on the transport industry in 2000-2013 and forecasting the completion of the Gulf Rail Project, the experts predict the extreme increase in the number of passengers using the rail and metro transport in the industry (“Gulf Cooperation Council Railway Project”). According to Figure 3, the start of the operation of the Gulf railway network will lead to the situation that 6% of passengers will choose comfortable rail transport. The use of cars will decrease by 3%, and the use of air transport will decrease in 9%, when the total use of transport in the region will increase in 1.5% (Figure 3; “Gulf Cooperation Council Railway Project”). The numbers support the idea that the focus on constructing rail networks can provide the industry with the opportunity to gain more profits while satisfying the public’s needs.
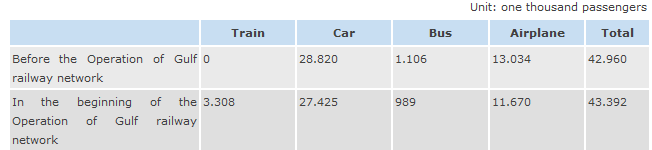
Different transport modes are used in the GCC region, but the development of the rail network is the main step to addressing the transport needs of the Arab countries’ population because the economy of the region develops, and it is necessary to focus on new effective methods to respond to the problem of transportation.
Transport Industry at the National Level: The United Arab Emirates
The UAE Transport Industry Profits
To understand the changes in the UAE transport industry profits during the recent five years, it is necessary to refer to the profits received by the Emirates General Transport and Services Corporation as the main provider of the transport services in the country. Emirates Transport was founded in 1981, and today it is regulated by the UAE government (“Sectorial Overview: Transportation and Logistics”; Terterov 112-117).
Referring to Figure 4, in 2001, Emirates Transport’s profits were about Dh180 million, and these profits can be discussed as the main revenues in the industry during the set period. In 2012, the profits of Emirates Transport along with the other industry actors’ profits was about Dh315 million, and this fact allows discussing the significant level of the market capitalization in relation to the transport industry in the UAE (“Sectorial Overview: Transportation and Logistics”; Terterov 112). Thus, the profitability of the industry increased in more than 40% while affecting the UAE’s economy significantly.
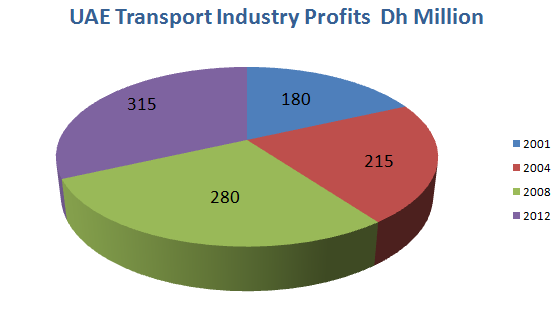
UAE Transportation Services
The development of the UAE transport industry depends on the spread of services in the country. While comparing the transportation services with the data typical for the 1970s-1990s, it is important to note that the country’s transportation services changed significantly. In the 1970s-1990s, the main focus was on using camels and cars. The next stage was the development of the air and rail transport (Terterov 156-167). Buses and metro were proposed as the public transport for all the UAE citizens in the 1990s-2000s (“The World Bank: Gulf Countries”). While focusing on the public transport, Dubai Metro is one of the most actively used transportation modes in the UAE. It is network’s length is 75 km, and it is used by more than 350 million passengers annually, while referring to the 1998-2013 data (“RTA”; “The World Bank: Gulf Countries”).
Passengers choose metro because of its suitability and speed. That is why, Abu Dhabi Metro is actively developed project which construction is the priority goal for the authorities of Abu Dhabi, and the project costs more than Dh7 billion. While focusing on Figure 5 which demonstrates the length of the expected Abu Dhabi Metro Project lines, it is important to state that today the underground heavy rail metro line in 18 km can be discussed as completed and operated to connect the districts of the Emirate (Lee 314; “The World Bank: Gulf Countries”).
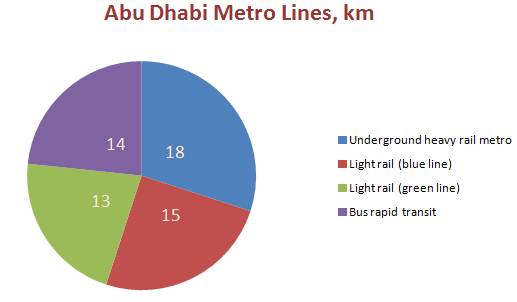
The next popular transportation mode used in the UAE is the rail transport. The UAE government is focused on developing the project the main goal of which is to connect the metro and rail networks to construct the most technologically developed rail system in the GCC region. The developing Etihad Rail project is also one of the priorities of the UAE transport industry because the planned 1,200 km rail system is expected to satisfy the transportation service needs of millions of passengers and business annually (“Gulf Cooperation Council Railway Project”).
Transport Industry at the Local Level: Dubai
The Number of Passengers Carried in Dubai Annually
The transport and roads industry in Dubai is presented by the developed bus system, taxi system, rail network, metro system, air and water transport. The transport industry in Dubai is the actively developed sector because the number of passengers carried by different transportation modes increases in more than 20 million people annually. Thus, analyzing the data presented in Figure 6, it is important to note that about one million people are carried by buses, taxies, metro, and abras in Dubai every day (“Government of Dubai”; “RTA”).
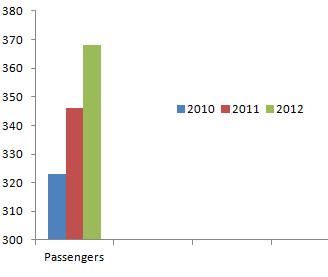
Dubai Bus System
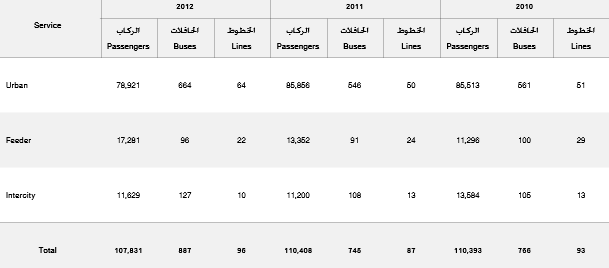
The Roads and Transport Authority in Dubai regulates the development of the bus system in the Emirate. The whole system is consists of more than 190 routes (“RTA”). The number of routes is influenced by the public demand for services. The necessity to transport thousands of passengers weekly makes the authorities to launch new routes regularly. The used buses are equipped with the modern technologies, and the regulation to the services provision is the main task of the RTA. While analyzing the data presented in Figure 7, it is important to focus on the correlation between the number of passengers carried and the number of buses proposed during the period of 2010-2012 (Figure 7; “Public Transport Buses: Emirate of Dubai”).
In 2010, 756 buses were proposed for Dubai urban population and as intercity vehicles. In 2012, the number of used buses is 887 which means that more than 130 buses were added to the Dubai routes. The number of buses for urban routes increased in 103 buses, and the number of intercity routes increased in 22 buses (Figure 7; “Public Transport Buses: Emirate of Dubai”).
The stated changes support the fact that the percentage of the population who demands effective bus services in urban territories is higher than the percentage of passengers who choose bus for intercity travelling.
Dubai Taxi System
The taxi services attract passengers because of such factors as comfort and speed in spite of the fact that the level of taxi accidents is higher in comparison with the other transport services. Taxi companies are categorized in operated by the government and privately owned (“RTA”). While referring to the aspect of competition, taxi companies provide more than 7300 cars to address the passengers’ needs in Dubai in comparison with 600 buses (Oxford Business Group). The availability of taxies influences their popularity among the passengers in Dubai. However, there is the problem related to the traffic in Dubai because more than 48,000 people usually use taxies and buses during the three hours period in morning (“UNWTO”). As a result, Dubai authorities are inclined to address the problem with the help of developing the alternative transportation modes.
Dubai Rail Network and Metro System
The Dubai Rail Network and Metro System project is discussed as the response of the Emirate’s authorities to the need of developing the effective public transport systems in Dubai because passengers note the lack of the resources to satisfy their daily needs regarding the issue. In spite of the fact that the Dubai Metro system is one of the most automatically developed in the GCC and round the world, it is only partially constructed (Worku 110-111). Dubai Metro consists of two completed lines which are Red and Green lines, and Blue, Gold, and Purple lines are planned to be fully added to the metro system during the next three years (“Sectorial Overview: Transportation and Logistics”).
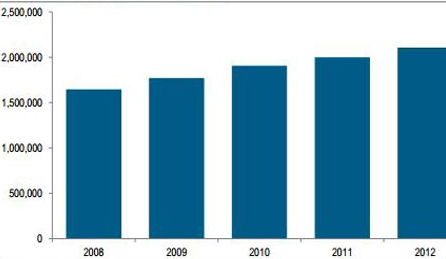
The metro develops intensively because the number of passengers who use it daily increased in 32% while comparing the data of 2011 and 2012 years (Elsheshtawy 84). The rail and metro system in Dubai is continually developed because of the necessity to address the needs of the actively increased population. The number of immigrants in the region increased in 3 times during the period of 2011-2013 in comparison with the previous years (Worku 110-111). Furthermore, the number of the Emirate’s population also grew to 2 million people, as it is stated in Figure 8 (Figure 8; “World-Statistics.org”).
Moreover, the economic and social environments in Dubai also changed with the focus on developing more businesses and households. That is why, the authorities plan to increase the number of Metro stations from 40 stations today to more than 100 stations in the future (Government of Dubai).
Dubai Air and Water Transport
Air transport in Dubai develops in relation to the progress of the Emirate’s business life. To address the necessity to support a lot of business contacts in the UAE, GCC region, and globally, the authorities of Dubai pay much attention to developing the effective and comfortable air transport. The center of aviation in Dubai is Dubai International Airport which provides services for millions of passengers annually. Dubai International Airport was opened in 2008, and the airport plays the important role in supporting the economic and business activities in Dubai today (“The World Bank: Gulf Countries”). The next stage in enhancing the air transport in Dubai is the construction of the modern and technologically developed Al Maktoum International Airport (“Sectorial Overview: Transportation and Logistics”). These two airports are expected to respond to the passengers’ needs in the Emirate.
The water transport is the alternative transportation mode used in Dubai. In spite of the fact that the water transport became to be in focus only during the period of the 2000s, Dubai ports play the traditionally important role in supporting the Emirate’s trade. Water transport is also used in Dubai as the public transport while focusing on the use of abras or water buses. This system works since 2007, and today the number of passengers using abras increased in 16% (“RTA”).
Analysis of the Transport Industry in the UAE and Globally according to Porter’s Model of Competition during the Past Five Years
While focusing on Porter’s model of competition, it is possible to analyze the development of the transport industry in Dubai during the past five years. The main competitors within the industry are the transportation services controlled by the government and privately owned companies specialized in providing transportation services for the population of the UAE. The UAE authorities control the air transport, rail transport, metro system, buses, and water transport (large ships), when the taxies, certain bus routes, and abras are often privately owned (“RTA”; “Sectorial Overview: Transportation and Logistics”; Worku 114).
While comparing the passengers’ preferences in using the transportation modes typical for the period of 2009-2012, it is possible to note that the popularity of privately owned transportation modes such as taxi increased significantly in 2012 in comparison with the data on 2009 (Figure 9; “RTA”; Worku 114). Five years ago the percentage of passengers using taxies in Dubai was about 8-9% (“RTA”). Today, taxi is among the most popular transportation modes in the Emirates. This situation is a direct result of growth in the number of the population in the UAE during the discussed period.
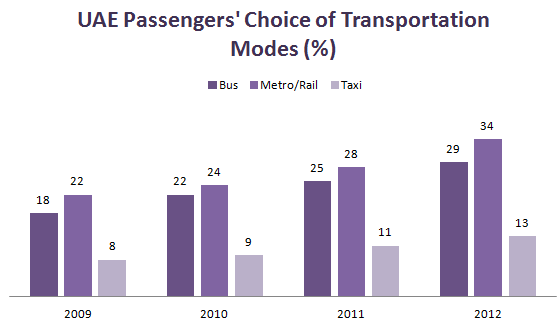
Referring to the criterion of the threat of new entrants in the industry, it is necessary to state that the increased popularity of abras as the public water transport attracts the attention of experts while discussing the changes in the industry during the past five years (Government of Dubai).
According to the idea of the buyers’ power, the transport industry significantly depends on the annual changes in the number of passengers using different transportation modes in the UAE. To respond to the needs of millions of passengers and various businesses, the UAE authorities are focused on developing the Etihad Rail project to build about 1,200 km of the railways in the country (“Gulf Cooperation Council Railway Project”).
While focusing on the competition strategy followed by the UAE in relation to the industry and on Porter’s model to analyze the changes in the industry during the past five years, it is necessary to note that the UAE government is focused on combing the competitors’ efforts to construct one effective transportation network for all the Emirates, contributing to the competitive advantage of the industry in the region instead of stimulating the further inner competition.
From this point, the main changes observed in the transport industry in the UAE during the past five years are correlated with the changes at the global and regional levels. Thus, the extreme focus on the use of taxies and abras as the public transport and on the rail transport to travel globally is typical not only for Dubai, but also for the UAE (“Public Transport Buses: Emirate of Dubai”; “The World Bank: Gulf Countries”). Regionally, the authorities’ focus was on rail and metro systems in 2013 (“Gulf Cooperation Council Railway Project”). Globally, the shift to the use of air transport is observed during the past five years as the prolonged tendency in the transport industry (“World-Statistics.org”).
Role of the Transport Industry for the UAE’s Economy
The transport industry is discussed as extremely important for the UAE’s economy because the progress of this industry is closely connected with the development of business, trade, and market in the UAE. While referring to the correlation of the sectors share in relation to Dubai GDP, it is important to note that Transportation share in 2013 was 14%, as it is stated according to the data presented in Figure 10 (“Dubai GDP”; Figure 10).
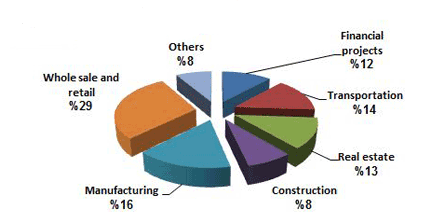
The situation in Dubai reflects the situation which is typical for the other large Emirates’ economy. Abu Dhabi and Dubai are focused on developing the transport industry because the effectively developed transportation services guarantee the response to the Emirates’ business and public’s personal needs (Elsheshtawy 57). The number of the population in the UAE increases rapidly, as a result there is a need to satisfy the needs of more people and to provide the opportunities for the effective economic and social development of the Emirates (Government of Dubai; “World-Statistics.org”).
In spite of the fact that the transport industry develops according to the UAE’s general projects to address the progress of infrastructure in the region, the role of the transport industry in the economy of the country is more significant in comparison with the situation in the other countries of the GCC region because the UAE are oriented to support the status of the most powerful and economically developed country in the region (“Gulf Cooperation Council Railway Project”; “World-Statistics.org”).
There are no loose connections between the business world, country’s economy, and infrastructure in the form of transportation because the transport industry is discussed as one of the fundaments for the UAE’s active economic and social growth (Lee 314-315). The UAE are at the stage of their intensive growth influenced by the progress of the oil industry and tourism (“UNWTO”). These industries directly depend on the development of the transportation networks in the Emirates (“Sectorial Overview: Transportation and Logistics”; “World-Statistics.org”). That is why, the development of many projects within the transport industry in the UAE can guarantee the support for the whole economy of the country.
Conclusions
Having analyzed the development of the transport industry at the global, regional, national, and local levels, it is possible to determine five important aspects which can characterize the details and features of the industry’s progress in the world and in the UAE most effectively. These five main points are
- the focus of the world transport industry on the air transport opportunities;
- the increase in the public’s interest to the taxies at the regional, national, and local levels;
- the focus of the regional and national authorities on using the advantages of the rail and metro transport in the GCC region;
- the interdependence between the population growth and the transport industry’s progress at the national and local level; and
- the distribution of control over the transport industry between the government agencies and local companies in Dubai.
The focus of the world transport industry on the air transport opportunities is reflected in the increased numbers of passengers carried by air transport globally every year. Air transport is attractive for passengers which focusing on the issue at the global level because the air transport allows flying at different distances within comfortable environments. That is why, air transport is the main choice for business.
During a long period of time, buses were the most popular transportation mode in the countries of the GCC because of the price of services and their convenience. However, during the recent five years, there is the obvious change in the population’s preferences regarding their choice of public transport modes. As a result, the increase in the public’s interest to the taxies at the regional, national, and local levels is the comparably contemporary phenomenon which is based on the progress of the privately owned sector of the transport industry in the UAE and Dubai. Furthermore, the increase in the public’s interest is closely connected with the fact that today taxies are comfortable and speedy. In addition, the important factor to influence the passengers’ choice is the availability of the taxies in the UAE and Dubai.
The focus of the regional and national authorities on using the advantages of the rail and metro transport in the GCC region can be explained with references to the fact that rail and metro transport is usually discussed as the most comfortable and speedy to be operated at the urban territories and at wide lands of the GCC region. Only the rail transport with the focus on the innovative technologies in the field can provide the citizens of the GCC countries with the high-quality transportation services. To connect the distant territories of the GCC states and close districts of the Emirates, it is effective to use the opportunities associated with the rail transport.
There is the obvious interdependence between the population growth and the transport industry’s progress at the national and local level because the increased number of population means that more people need the appropriate transport services. Furthermore, the changes in the number of buses, taxies, and other transport vehicles provided for the population can result in the public dissatisfaction. The amount of the transport modes available for the population should be strictly correlated with the amount of persons served within the concrete region or district.
The distribution of control over the transport industry between the government agencies and local companies in Dubai led to the active development of the local transport industry because many companies providing the transportation services open annually, and this factor influences the economy of Dubai positively, while making the transport industry one of the most profitable industries in the region. Privately owned companies and the transport corporations controlled by the government work to respond to the large number of passengers and their needs in order to create the effective infrastructure background for the other industries’ progress.
The UAE’s transport industry develops to support the UAE’s economy because of the close connections between the transportation industry and other economic, industrial, and business sectors. The transport industry can be discussed as important for the UAE’s economy because the main economic activities in the region and locally depend on the effective transportation solutions provided by the transport agencies in the UAE. From this point, the development of the transport industry in the UAE can contribute significantly to driving the economic progress of the Emirates while providing the effective and high-quality services in the region. As a result, the transport industry can be considered as the effective fundament for the UAE’s intensive economic progress. The focus on developing many projects in the transport industry is one of the important steps to improve the economic rates in the UAE.
Works Cited
Dubai GDP. 2013. Web.
Elsheshtawy, Yasser. Dubai: Behind an Urban Spectacle. USA: Routledge, 2009. Print.
Government of Dubai. Dubai Strategic Plan 2015. 2007. Web.
Gulf Cooperation Council Railway Project. 2012. Web.
Lee, HongJu Jason. “Dubai’s Brand Assessment Success and Failure in Brand Management”. Place Branding and Public Diplomacy 5.4 (2009): 312-324. Print.
Oxford Business Group. The Report: Dubai 2008. USA: Oxford Business Group Publishing, 2008. Print.
Public Transport Buses: Emirate of Dubai. 2012. Web.
RTA. 2014. Web.
Sectorial Overview: Transportation and Logistics. 2013. Web.
Terterov, Marat. Doing Business with the United Arab Emirates. USA: GMB Publishing Ltd, 2006. Print.
The World Bank: Gulf Countries. 2014. Web.
UNWTO: How People Travel. 2011. Web.
Worku, Genanew Bekele. “Demand for Improved Public Transport Services in the UAE: A Contingent Valuation Study in Dubai”. International Journal of Business and Management 8.10 (2013): 108-125. Print.
World-Statistics.org. 2014. Web.