Introduction
Energy use is one of the biggest challenges faced by countries of the United Arab Emirates. This is primarily due to the escalating rate of population growth, high consumption rates, and increasing economic activity. These factors are unsustainable if the challenge of the use of energy is not addressed. In order to mitigate this problem, a forum was held courtesy of the Energy Working Group of the UAE to find potential solutions to sustainability problems facing the UAE. Projects that should be implemented in the UAE to improve sustainability by enhancing the efficiency of energy use include smart cities, water desalination, and green building.
Why Environmental Concerns and Sustainability Are Important
Environmental concerns and sustainability are important in the UAE because of the adverse impact of a rapidly growing economy and population. As the population grows, energy and water consumption increase, as well as the rate of environmental degradation (Brinkmann & Garren 2018). If measures are not taken to mitigate escalating levels of environmental degradation, the rate of population growth and economic activity might not be sustainable. According to the United Nations Environmental Program (UNEP), the UAE has one of the largest carbon footprints in the world due to the high rate of energy consumption (Sayigh 2014). Sustainability initiatives have been necessitated by the rapid economic development and population change taking place in the region. The most important drivers of sustainability in the UAE include waste management, energy efficiency, environmental conservation, sourcing and use of water, as well as the food supply chain (Karlsson, Decker, & Moussalli 2015). Sustainability is important in the UAE because of the rising fuel prices, effects of water desalination, global warming, high population growth, increased economic activity, and rapid industrialization.
The UAE is famous for its large reserves of hydrocarbon resources. Therefore, in the past few decades, energy efficiency has not been a challenge. However, with the risk of exhaustion of the reserves due to economic and population growth, sustainability has become a pressing issue. The UAE has recognized its contribution to global warming, and has implemented several green strategies to mitigate the challenge (Brinkmann & Garren 2018). The oil reserves have not stopped them from diversifying into alternative and renewable energy sources. The main goal is to balance the region’s economic development and the conservation of the environment for future generations (Sayigh 2014). Several milestones have been achieved based on strategies implemented by the federal and local authorities. UAE’s commitment to sustainable development is reflected in its domestic policy and international cooperation initiatives that focus on a respect for nature among other things.
The Challenge of Sustainability
According to government statistics, energy use in the UAE has grown immensely at an annual rate of 4 percent in the past decade. Projections indicate that the consumption will increase at an annual rate of 5 percent through 2020 (Brinkmann & Garren 2018). Sustainability is a challenge because of increased energy consumption. For instance, energy usage has increased by a rate of more than 50 percent in the last decade (Karlsson, Decker, & Moussalli 2015). The scope of the challenge requires a more holistic approach to sustainability than the one being currently implemented. The UAE needs a more integrated approach that combines several technologies and energy-saving strategies (Energy 2018). In that regard, the approach should comprise a stringent regulatory framework, a communication strategy to educate energy users on ways to reduce consumption, and a research and development division to find efficient ways to enhance sustainability through proper energy use (Sayigh 2014).
One of the key measures to reduce energy consumption is the implementation of an efficiency strategy. This strategy should be implemented swiftly and tailored in a manner that lowers the cost of execution. The advantages of lowering energy consumption include safeguarding energy reserves, lowering subsidy expenses, reducing the energy bills of consumers, and improving the durability of infrastructure. Many regions in the UAE have commenced the process of creating and implementing policies that promote energy efficiency measures. Numerous policies encourage key aspects of sustainability such as innovative building designs, the manufacture of energy-efficient appliances, the production of hybrid vehicles, and increased reliance on renewable energy sources (Sayigh 2014). These measures are being implemented by certain governments, though they are at the inception phase, and therefore, have little impact on sustainability.
Three main projects that governments of the UAE need to implement in order to improve the country’s sustainability with regard to improving the efficiency of energy production and use include smart cities, water desalination, and building efficiency. In order for these technologies to mitigate the UAE’s sustainability challenges, policy makers should implement an energy efficiency strategy, promote research and development initiatives, and create a regulatory framework that addresses energy usage challenges (Sayigh 2014). In addition, they should launch a communication initiative that teaches the various consumers on how to lower their energy consumption.
Key Projects
Smart Cities
A smart city is a municipality that uses smart technology and data analysis to boost its operational efficiency and enhance the quality of life for residents. Automation, internet of things (IOT) and machine learning are key aspects that improve efficiency. The smart city technology is important because the UAE is highly urbanized, with 85 percent of its population residing in urban areas (Karlsson, Decker, & Moussalli 2015). This population will continue to increase in coming years and as a result, the challenge of sustainability will become worse. According to the United Nations, the urban population of the UAE will be approximately 91 percent by 2050 (Brinkmann & Garren 2018). In that regard, an integrated infrastructure planning is needed in the design of municipalities. The development of smart cities will allow the UAE to use digital technologies to improve effectiveness by lowering energy consumption (Karlsson, Decker, & Moussalli 2015). It has been projected that the number of smart cities in the world will double by 2020 (Figure 1). Smart cities enhance sustainability promoting high performance at the intersection of key economic sectors that include energy, waste management, transport, water, and telecommunications.
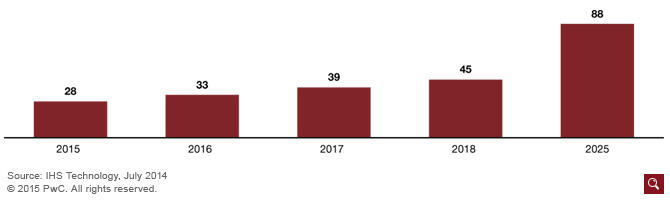
Smart cities are created with improved electrical grids, which contain monitors that track energy usage over certain periods to determine the rates of consumption. In Abu Dhabi, electricity usage has an annual growth rate of 10 percent, which exceeds the rate of population increase (Karlsson, Decker, & Moussalli 2015). In order to mitigate the challenge, the government introduced an advanced metering system that reduces power consumption through the application of a number of measures. Dubai has implemented distributed generation, which reduces the challenge of energy generation by producing energy on-site in order to lower transmission loses (Karlsson, Decker, & Moussalli 2015). The UAE should encourage the use of electric cars in the cities. In that regard, it should build the necessary infrastructure to support the technology. For instance, additional power charging stations ought to be put up within the cities. Currently, the UAE is constructing several charging locations as a way of encouraging its citizens to embrace the revolutionary technology.
Green Building
The UAE should embrace “green” or “sustainable” construction in order to improve energy efficiency. Green building is resource-efficient because it utilizes improved technologies throughout a building’s life cycle, thus enhancing the usage of resources (energy and water), reducing environmental degradation, and protecting the health of occupants (Karlsson, Decker, & Moussalli 2015). Efficiency is increased in all processes, including planning, design, construction, maintenance, and the operation of buildings. Green building incorporates key measures to reduce energy consumption. For example, builders use high-performance windows, solar water heating technologies, on-site generation of renewable energy, and technologies that reduce air leakage (Karlsson, Decker, & Moussalli 2015).
Power generation is one of the most expensive aspects of construction. In that regard, builders implement on-site generation of energy through solar, wind, and biomass power in order to enhance efficiency. The UAE has several building efficiency programs. For example, Estidama is a building program that regulates the design, construction, and operation of buildings by measuring the sustainability performance of projects (Karlsson, Decker, & Moussalli 2015). The government of Dubai has implemented green building regulations and specifications to guide the construction industry. It is important for authorities to develop clear regulations and frameworks to direct the processes of design and construction in order to ensure that they are energy-efficient.
Governments should encourage builders to use innovative building technologies such as wall insulation, glass glazing, coatings, and concrete mixes. These technologies are widely used in different regions of the world, and they have been shown to enhance sustainability by lowering energy consumption (Sayigh 2014). The government should also implement policies that encourage builders to increase energy efficiency through automation, monitoring and reporting of energy usage, and integrated applications (Karlsson, Decker, & Moussalli 2015).
Water Desalination
Water usage is one of the areas that have contributed to the high growth rate of energy consumption in the UAE because of the amount of power needed in desalination. Currently, about 30 percent of the Emirates’ power is utilized in the purification of seawater (Karlsson, Decker, & Moussalli 2015). A large percentage of UAE’s water is generated from thermal energy plants that have high power demands. It is difficult to optimize power and water resources in order to lower energy usage. In order to mitigate this challenge, the UAE has implemented several measures. First, policymakers have developed water treatment technologies that consume less energy. Examples of innovative technologies currently in use include the desalination of water through reverse osmosis and the use of permeable landscaping materials (Sayigh 2014). It is important for the UAE to use innovative recycling technologies in order to lower their reliance on desalinated water, which is a major consumer of power (Karlsson, Decker, & Moussalli 2015). The introduction of nuclear energy will lead to the utilization of efficient desalination technologies that will enhance sustainability.
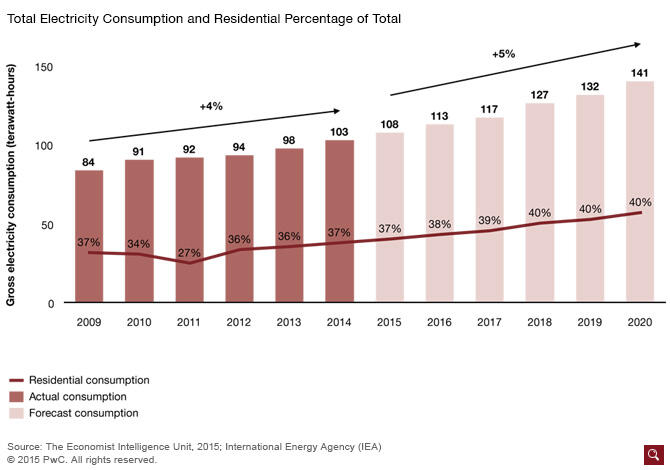
The United Arab Emirates should commission mega water projects that use advanced technologies to desalinate water. The demand for water will increase over the next decade as the population continues to grow and as more people migrate to urban areas. Moreover, the demand will be fuelled by increased economic activities in areas such as manufacturing and agriculture. This growth will increase the demand for, and the consumption of power sources such as electricity. Research has shown that the rate of electricity consumption will grow by 5 percent through 2020 (Figure 2).
The UAE should embrace innovative desalination technologies for water treatment in order to reduce energy consumption. They include thermal-based, membrane-based, and alternative technologies. Nanocomposite membrane technologies have been successfully used in the desalination of water in various countries across the world (Sayigh 2014). Membrane distillation and adsorption desalination are also innovative technologies that can be used to lower energy usage. Large water volumes are used in irrigation systems that consume a lot of energy. Efficient practices such as the use of landscaping materials that enhance water reclamation and advanced irrigation systems should be encouraged.
Ethical Considerations in the Planning Of Environmental Laws and Policies
Laws are the main instruments that governments use to implement policies that regard environmental sustainability. Environmental laws and policies relate to issues such as global warming, pollution of water, air, and soil, and renewable energy resources (Energy: the energy sector 2018). In the implementation of policies and laws, ethical considerations should be incorporated with regard to pollution control and remediation, violations of laws, administration of regulations, and the creation of a balance between environmental conservation and economic development (Al Tayer 2018).
There are several ethical considerations involved in the planning of current and future environmental legislation. First, the laws and policies should aim to create a balance between development and sustainability (Gillespie 2014). This balance is achieved through the enactment of legislation that provides incentives and imposes fines. In that regard, the UAE needs to ensure that the planning process incorporates mechanisms to maximize sustainability efforts and change behaviors that encourage pollution. Second, the planning should take into consideration the moral obligations that human beings have with regard to the improvement of the environment. Such laws and policies should aim to connect human values and environmental protection (Gillespie 2014). Humans have a responsibility to take care of the environment for future generations (Energy: the energy sector 2018).
Therefore, they should take measures to improve and protect it from degradation. Third, pollution control and conservation of natural resources should be taken into consideration. Environmental laws and policies should aim to conserve natural resources by inhibiting destructive activities and mandating those that enhance sustainability (Al Tayer 2018). For example, it is unethical to hunt endangered species, test environmentally destructive weapons, and dump electronic waste in landfills. In that regard, these activities should be illegalized. Fourth, it is unethical to engage in activities that pollute or degrade the environment. Therefore, it is important to consider the effects of certain behaviors on the environment in order to enact laws and policies that discourage their practice (Gillespie 2014). For example, laws could be created that give mandatory prison sentences to individuals who violate property use laws in protected environments.
It is unethical to degrade the environment for financial benefits. However, it is almost impossible for corporations and companies to conduct their operations without having adverse effects on the environment. It is necessary to understand that economic development and environmental degradation are inseparable (Gillespie 2014). The main issue is to determine how to reduce the impact of development on the environment. In the process of planning laws and policies, care should be taken to avoid suppressing development activities in favor of environmental sustainability as well as suppressing environmental sustainability in favor of economic development (Al Tayer 2018). A balance should be maintained between the two through the enactment of laws and policies that give incentives to encourage sustainability initiatives and penalties to discourage environmental degradation.
Conclusion
In the past decades, the UAE did not have sustainability challenges because of an abundance of oil reserves that did not necessitate the implementation of energy efficiency initiatives, laws, and policies. However, due to rapid population growth and economic development, sustainability has become a major concern. In order to mitigate the challenge, the UAE should implement several projects that include smart cities, green building, and water usage. Smart cities will involve the utilization of new technologies in urban planning while building efficiency will involve the use of innovative construction materials that enhance energy efficiency. In addition, it will involve the use of creative designs that reduce energy consumption. Water conservation will involve the implementation of desalination projects that utilize advanced technologies, which reduce energy consumption. Several emirates have started projects in the aforementioned areas. However, the scope of the sustainability challenge necessitates the creation of an elaborate approach as well as the commissioning of mega projects. These projects should be supported by a regulatory framework that comprises environmental laws and regulations, an awareness-creation initiative, and research and development program to find new ways of boosting efficiency.
References
Al Tayer, SM 2018, ‘UAE powers towards a sustainable future’, Gulf News, Web.
Brinkmann, R & Garren, SJ 2018, The Palgrave handbook of sustainability: case studies and practical solutions, Palgrave McMillan, New York, NY.
Energy: the energy sector 2018, Web.
Gillespie, A 2014, International environmental law, policy, & ethics, 2nd edn, Oxford, Oxford University Press.
Karlsson, P, Decker, C, and Moussalli, J 2015, Energy efficiency in the UAE: aiming for sustainability, Web.
Sayigh, A 2013, Sustainability, energy and architecture: case studies in realizing green buildings, Elsevier, New York, NY.