Introduction
Background
Cyber-attacks are becoming a major problem for government institutions, private companies, and individuals who are engaged in various online activities. According to Buchanan, emerging technologies have given rise to sophisticated cyber-threats as some techno-savvy individuals embrace hacking as their career (53). Some of them are even sponsored by their governments on intelligence-gathering missions, while others are motivated by pure greed.
The United States power grid cyber-attack was a clear demonstration of the vulnerability of important government infrastructures. Cybercriminals were able to have access to and manipulate important data, which was a clear demonstration that the threat posed by cybercriminals can no longer be ignored. As Dehghantanha et al. put it, these criminals are not only getting sophisticated but also bold and aggressive in their moves (32).
In this paper, the researcher will focus on the increasing threat of cyber-attacks that target critical government institutions, with a special focus on the recent power grid attack in the United States and how the threat can be managed.
Scope and Purpose
The scope of this study will be on analyzing the extent of the cyber-threat, institutions that are most vulnerable, the motivation of the hackers, the economic impact of the threat, and the steps that the relevant authorities can take to address the problem. The study will also look at the local and international laws that have been put in place to address the problem. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the emerging trends in cyber-attack in a way that would enable the local community to prepare for such problems.
The United Arab Emirates is one of the fastest developing economies in the region, and cybercrime is becoming a common problem. Looking at the trends in some of the countries around the world would help local stakeholders to understand and appreciate the magnitude of the problem. Such case studies may also help local firms to know how they can respond appropriately to such threats.
Report Structure
The report has several sections, each addressing different issues. The first section of the report is the introduction. It provides background information for the study, the scope, and the purpose of this research. The second section focuses on the incident analysis of the cyber threat. It provides the lifecycle of such attacks, purpose, target, and motivation of such attacks, planning process, and implementation of the plan. It also looks at the distribution of the attacks, triggers, timeline, and show of power. The next section provides a response plan for a possible attack. Other sections include cyber threat assessment and attributes, IOCs, TTPs, Cyberthreat protecting and defending mechanisms, cyber threat implications on the UAE, conclusion, summarization, and closing remarks.
Cyber Threat Incident Analysis
Incidences of cyber-attacks are becoming common not only in the developed nations such as the United States and the United Kingdom but also in developing nations of the Middle East and North Africa (MENA) region. Proper planning may help government institutions and private firms to avoid the devastating consequences of such an attack. In this section, the focus is to analyze the threat of possible incidences of an attack.
Lifecycle of the Attacks
According to Clark and Hakim, cyber-attacks have lifecycles that one needs to understand to have a plan on how to deal with it (48). As shown in figure 1 below, it starts with the initial reconnaissance, where the cybercriminal identifies a potential target and the benefit that would be accrued from a successful attack. The next step is to target an initial compromise, where they would try to have access to the database by simply hacking into the system or using a sophisticated virus to have access to the database (Kalb 39).
The criminals will then establish a foothold in the system of the target before escalating privileges where they can steal or manipulate data as they wish. They will conduct internal reconnaissance to identify what is important, move literally to have access to information they need, and maintain their presence for as long as it is necessary for them. When their mission is complete or if they are detected, the final phase is to move out of the system.
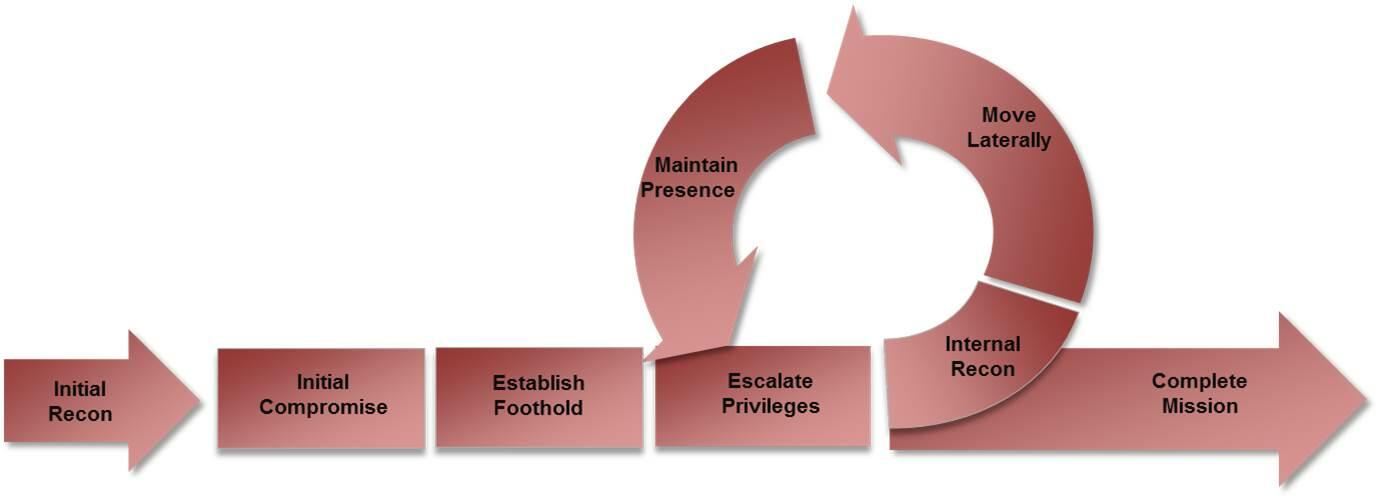
Purpose
The purpose of every cyber-attack varies significantly. Rugge argues that one of the common reasons why people target and attack specific databases is because of financial gains (59). Many cyber criminals focus on financial institutions where they can transfer huge sums of money into their bank accounts. They believe that such attacks offer them an easy way to become rich. Some of the attackers engage in this practice because of their perceived patriotism or loyalty to their government.
Radziwill explains that the attack on the US 2016 General Election was planned and executed by cybercriminals loyal to the Russian government (74). Sometimes the attack can just be out of malice, such as the recent power grid incident in the United States (Rugge 88). Others are just curious to know the information in databases of various organizations.
Target
A cybercriminal must have a clear target and what should be achieved by the end of the attack. In this case, the target was the power grid in the United States. The grid is critical in the normal running of the economy, and any form of manipulation that would interrupt its normal operations may have devastating consequences on the country’s economy. Operations of the grid have been digitized to make it easy for the officials and customers to engage. Other than a possible manipulation of the operations of this firm, hackers may have access to customer’s confidential messages that they can use maliciously to achieve selfish goals.
Motivation
The real motivation behind the recent attack of the United States power grid by Russian hackers identifying themselves as Dragonfly or Energetic Bear is not yet clear. However, reports show that these criminals had access to sensitive information such as login details of various individuals, passwords, and information about energy generation (Shackelford 93). The study indicates that the likely motive of these criminals is sabotage(Shackelford 93).
They may be planning to disrupt the normal operations of power generation. It was not clear if they were on a general phishing expedition or a specific purpose under the directives of the Russian government. The authorities were convinced that the intention was to plan a major attack on the power generation and supply system in the United States. The incident highlighted the vulnerability of the grid to international cybercriminals.
Actors Planning
Dragonfly, the criminal gang that planned and executed the attack, is an entity that brings together some of the Russian highly intelligent cyber-experts. These individuals have helped their government in cyber-espionage in the past, but it is not clear whether this time they were representing the interest of their government. Given that the goal of the attack was not determined, authorities assumed that they acted alone when planning and executing the attack on the power grid. However, it may be possible that they got government support to enable them to achieve their goals.
Initiation and Implemented Methodologies
The attack was initiated and implemented using conventional hacking methodologies. The criminals were able to use a sophisticated virus to override the standard procedure required of anyone having access to the database. They planted a virus into the database that enabled them to conduct surveillance on the database for some time before gaining full access to the system. The intrusion was detected before it could escalate further. Roscini argues that sometimes hackers can delete or distort data in the system, making it possible for authorized individuals to have access to information they need, as shown in figure 2 below (90).

Distribution
Cyber-attack is a widespread problem that affects firms and government entities all over the world. The chart shown in figure 3 below identifies how widespread the problem is and countries that have been the main targets of cybercriminals. The United States of America is the greatest target of these criminals, accounting for 23% of the global cyber-attacks. China is another major target, accounting for 9% of the attacks (Kaplan 24).
Germany, Britain, Brazil, Spain, and Italy accounted for 6%, 5%, 4%, and 3%, respectively (Kaplan 24). Other major targets include France, Russia, India, Canada, Russia, South Korea, Japan, Mexico, Australia, and Israel. It is evident that these criminals often target economically empowered nations around the world. As the local economy in the United Arab Emirates continues to grow, the cases of cyber-attacks are likely to increase in the coming days.
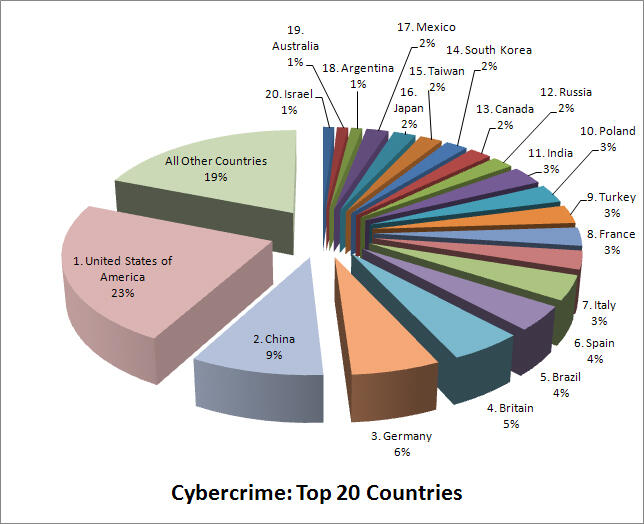
Triggers
The triggers of attacks, such as the one directed towards the power grid in the United States, vary. One of the main triggers is the availability of opportunity. The firm could have employed an individual who is loyal to the criminal gang. As such, they used their informant to have access to data without the approval of the relevant authorities. Major weaknesses of the security system of the database, which is easily detectable to these criminals, maybe another trigger.
When on their routine survey of targetable companies, these criminals must have noticed the weakness, which promoted them to try to gain access. Another possible trigger would be a directive from their government, if the attack were sanction by Russian authorities, to have access to the database and obtain specific information. Kosseff notes that the authorities were unable to identify specific triggers of the attack (35).
Timeline
The timeline of the plan and course of action that the Russians took when attacking the power grid is not clear. However, indications show that soon after the last general elections, these criminals shifted their focus to the grid (Kosseff 77). It means that the plan must have been initiated in late 2016, and its implementation started in 2017. However, it was not until 2018 that the government realized that the power grid was under constant monitoring by Russian cybercriminals. Measures were taken in 2018 to ensure that such events do not occur at the institution in the future. However, it is still not clear if the measures have thwarted further attacks.
Sustainability/ Show of Power
Cyberwarfare is emerging as a new battlefront for the world’s superpowers, and it is clear that the attacks witnessed in the United States and planned and executed by government operatives (Ohlin 48). The claim that Russia meddled in the last general election and thereby participated in determining the president of the United States is a show of power. It is an achievement to the Russian government as it feels it deserves to be the superpower.
On the other end, the United States has the responsibility to protect itself from such attacks as the only way of demonstrating that it has the technical capacity, financial muscle, and political will to engage in the new battle for supremacy in cyberspace (Schünemann and Baumann 38). In such an environment where cyber-attacks are considered a show of power, it may not be easy for the existing laws to help fight crime. As long as these criminals enjoy state protection, they know that they cannot be subjected to any form of punishment by foreign governments.
Response
The approach that an organization takes in case of a cyber-attack is very important. According to Roscini, an organization needs to ensure that it makes an immediate response to such an attack in a way that would discourage future attempts to breach the system (60). When the United States power grid was attacked by Russian cybercriminals, the government responded promptly to protect its integrity.
Risks/Weaknesses
When responding, it is important to understand the risks and weaknesses of the organization. The fact that these criminals managed to have access to the database of the grid was a major sign of weakness. It was an indication that the security measure put in place to protect its digital data was not capable of achieving these goals when faced with a complex problem. The risk of such a serious weakness was that unauthorized individuals could easily have access to the information considered confidential. These criminals could also sabotage the operations of this entity in case they are ordered to do so by their government.
Innovation/Payoff/Result
Innovation is the only way of dealing with the current cyber threat in the United States and other parts of the world. It is necessary for the management of the power grid and many other government institutions and private entities operating in the country to consider investing in new technologies when it comes to data protection. They need to be one step ahead of the criminals by maintaining innovative ideas in their operations (Schünemann and Baumann 68). The payoff or results of such investment would be a secured database that cannot be compromised by criminals. The government will be assured that this important institution is not sabotaged by a hostile state.
Cyber Threat Assessment and Attributes
Profiles of the Cyber Threat
It is important to conduct a cyber-threat assessment to understand their magnitude on an organization, the possible frequency of their occurrence, and the manner in which an organization can deal with them effectively. One of the first steps of the assessment is always to determine their profile. Table 1 below shows the generic threat matrix. It summarizes how a firm should profile cyber threats.
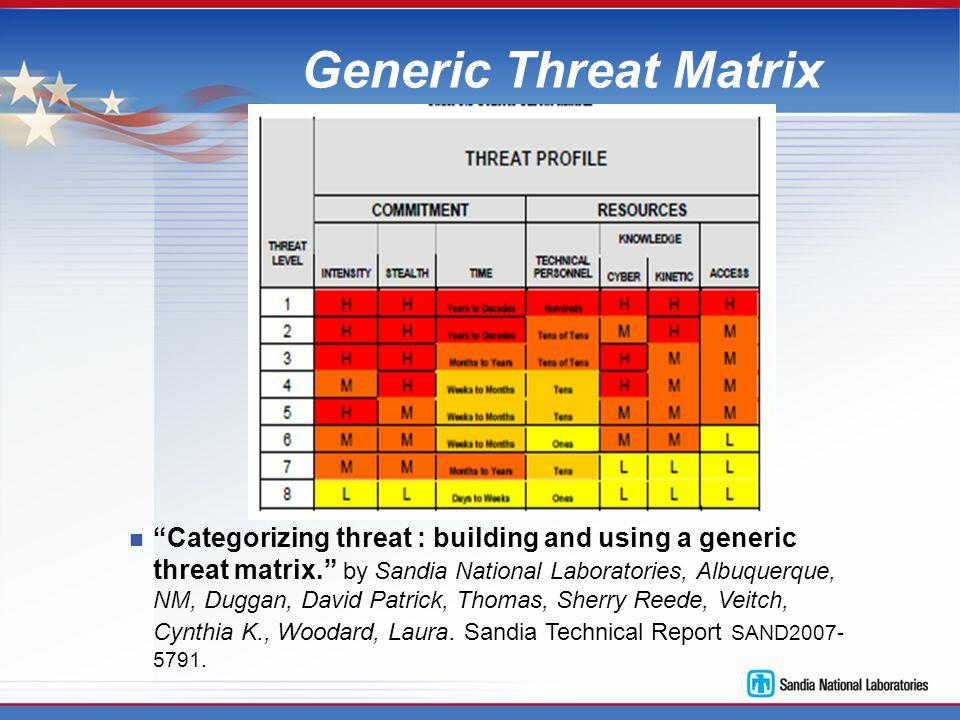
Incident Data
The power grid cyber-attack was a major indication to the American society that cyber-security is becoming one of the most important issues that can no longer be ignored. The government did not reveal the exact data about the incident stating dates and level of data compromise. However, it was established that the incident must have started in late 2016 or early 2017, and the criminals were able to have access to critical information that would sabotage the operations of the institution (Roscini 28).
Attack Vectors
The vector of the attack, as was revealed by the Federal Bureau of Investigation, was the critical database of the firm that defines the plant’s operations, its strategic goals, and steps that it is taking to meet the increasing demand in the country (Schallbruch and Skierka 57). The investigators revealed that once these Russians have access to the database, they focused on data explaining strategic plans and specifics about the daily operations of the entity. The fact that these hackers went for passwords and login details also demonstrates that they had the desire to manipulate the operations of the system by posing as the administrators authorized to initiate specific operations in the plant.
Target Characteristics
When conducting a cyber-threat assessment, Buchanan explains that one of the important issues that an institution has to consider is the target characteristics (43). The response team must consider the threat as a target that needs to be evaluated to determine how to respond. The significance of the threat, the possible outcomes, and the frequency of the threat are some of the factors that have to be considered. Table 1 below shows how the cyber-threat should be classified and rated.
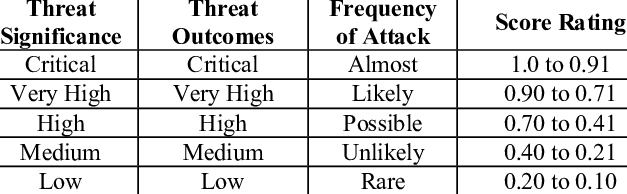
IOCs, TTPs Cyber Threat Protecting, and Defending Mechanisms
Using indicators of compromise (IOCs) to identify potentially malicious activities in the database and tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTP) to determine the modus operandi of cyber adversaries are some of the steps that a firm should take database. In this section, the focus is to determine appropriate defense mechanisms in cyberspace.
General Protection Framework and Applying the Framework on the Attack
The FBI and the Department of Homeland Security played a major role in ensuring that data breach of the power grid was managed effectively. They used an appropriate framework to monitor and respond to the threat in an appropriate manner. They used Open-source intelligence (OSINT) to deal with the threat. OSINT allowed them to collect data automatically about irregular activities in the database without the knowledge of the attacker. The framework enabled the authorities to monitor darknets for any changes in the status quo, which symbolizes irregular activities. The approach made it possible to monitor the activities of the hackers, the information they were interested in collecting, and their primary aim.
Best Protection Model
The use of both the IOCs and TTPs is the best protection model that the power grid and many institutions that face similar threats should embrace. One of the benefits of using this model is that it allows the victim to monitor the activities of the attacker without the criminal’s knowledge. One can determine the primary goal of such attacks by determining the information they focus on (Kalb 58). It is easy to mislead them while at the same time protecting vital information in the company. It can also help in determining the identity of the attacker, which makes it easy to find a lasting solution to the problem.
Cyber Threat Infographic
A cyber threat infographic makes it possible to use pictures and data together to explain the nature of the problem and the manner in which one can deal with it. As shown in figure 4 below, the number of those who have been victims of cybercrime is on the rise. The respondents in the statistics shown in the figure also indicate that such attacks are becoming increasingly expensive.

Description Infographic
The description infographic on the power grid cyber-attack provides a summary of the main pillars of the threat. The analysis framework of the cyber threat, a timeline of the attack, sustain/show of power, innovation/payoff/results, response, planning/initiation, and triggers. The infographic also identifies risks/weaknesses, distribution, methods, purpose/target, and protection/mitigation plans as discussed in this paper. Figure 5 below provides the information.

Cyber Threat Implications on the UAE
The United Arab Emirates’ economy is growing rapidly, and the cities of Dubai and Abu Dhabi have been attracting international investors over the past decade. The positive economic outlook of the country means that it is also becoming a major target of cybercriminals. As Rugge notes, cybercriminals do not just target financial institutions (86). They also attack government agencies, as was the case with the power grid attack in the United States, and private entities that are not operating in the financial industry. Their goal in every attack varies, and it is important for different stakeholders in the country to be ready for such an eventuality.
Cyber Security Strategy
The government of the United Arab Emirates should promote public-private partnerships in the fight against cybercrime in this society. According to Radziwill, the biggest concern in fighting this vice is that these criminals do not have to be physically present in the country to execute an attack (40). Such attacks are often planned and executed in a remote location that may not be easy to trace.
The best strategy is for the local stakeholders to pool their resources and fight this vice as a unit. It would be necessary to identify common cyber threats and formulate a common effective plan for addressing them. Embracing international best practices, such as those used in the United States where the problem has been rampant for the last decade, can be helpful. Embracing innovation can also help local stakeholders to deal with the threat.
National Cyber Crime Law
According to Shackelford, the United Arab Emirates is one of the countries in the MENA region, which have taken major steps in enacting strict cyber-security laws (64). The amendment of Article 26 introduced a new penalty of jail time of 10 to 25 years and a fine of between AED 2-4 million for those found guilty of various forms of cybercrime (Kaplan 86). The amendment also states that those who engage in hate speech could be sentenced to five years in jail and pays a fine of not more than AED 500,000.
Article 28 of the country’s constitution also specifies that those who manage websites or use the internet to engage in inciting acts would pay 1 million Dirham as a fine. They can also face a jail term specified by the judge. Article 43 provides for immediate expulsion of a non-citizen resident of the county who engages in cybercrime within the country (Ohlin 59). The country has also embraced regional policies and regulations on how to deal with the problem of cyber insecurity.
International Cyber Laws
The international community has come to appreciate the importance of coming together of nations to fight the problem of cybercrime. One of the initial international laws on cybercrime was the Convention on Cybercrime that was drafted by European Council together with the United States, Japan, and Canada in 2001 (Kosseff 112). It defined the meaning of cybercrime and the measures that should be taken to address it. Commonwealth’s Convention on Cybercrime, the London Action Plan, and Cyber Security Enhancement Act (CSEA) are some of the active international cyber laws (Schünemann and Baumann 78).
Conclusion, Summarization & Closing Remarks
Cyber-security is a major concern in modern society as digital data become increasingly important to the current generation. The attack on the United States’ power grid in 2017 was a clear indication of the extent to which some of these cybercriminals are willing to go to achieve their interests. The government of the United Arab Emirates should be ready to deal with this threat by embracing the following recommendations:
- The government should work closely with stakeholders in the private sector to formulate effective solutions to common cyber problems;
- The stakeholders should pool their resources to further research on how to deal with the problem innovatively;
- It is necessary to embrace international best practices when dealing with the problem of cyber-security.
Lessons Learned
This project provided important lessons to the researcher that will define the approach taken when dealing with similar problems in the future. One of the most important lessons is that cybercriminals may not be necessarily motivated by monetary desires. Some are just curious, while others serve the interest of their government. The researcher also learned that every institution, including government institutions, is vulnerable to cyber-attacks.
Works Cited
Buchanan, Ben. Cybersecurity Dilemma: Network Intrusions, Trust and Fear in the International System. Oxford University Press, 2017.
Clark, Robert, and Simon Hakim, editors. Cyber-physical Security: Protecting Critical Infrastructure at the State and Local Level. Springer International Publishing, 2017.
Dehghantanha, Ali, et al., editors. Cyber Threat Intelligence. Springer, 2018.
Kalb, Marvin L. Imperial Gamble: Putin, Ukraine, and the New Cold War. Brookings Institution Press,, 2015.
Kaplan, Fred. Dark Territory: The Secret History of Cyber War. Simon and Schuster, 2016.
Kosseff, Jeff. Cybersecurity Law. Wiley, 2017.
Ohlin, Jens. Cyber War: Law and Ethics for Virtual Conflicts. Oxford University Press, 2014.
Radziwill, Yaroslav. Cyber-attacks and the Exploitable Imperfections of International Law. Brill, 2015.
Roscini, Marco. Cyber Operations and the Use of Force in International Law. Oxford University Press, 2014.
Rugge, Fabio. Confronting an Axis of Cyber: China, Iran, North Korea, Russia in Cyberspace. Ledizioni LediPublishing, 2018.
Schallbruch, Martin, and Isabel Skierka. Cybersecurity in Germany. Springer, 2018.
Schünemann, Wolf J, and Max-Otto Baumann. Privacy, Data Protection and Cybersecurity in Europe. Springer, 2017.
Shackelford, Scott J. Managing Cyber Attacks in International Law, Business, and Relations. Cambridge University Press, 2014.