History, Development, and Company Growth
Background Information
Pieter Geelen and Frans Pauwels established TomTom in 1991. The firm is headquartered at the Netherlands. The firm initially operated under the name Palmtop and its core operations entailed developing software applications for handheld computers, which gained popularity during the 1990s. However, the firm diversified its operations by investing in the production of different software applications such as maps, dictionaries, and games.
Moreover, the firm invested in production of navigation software such as RouteFinder and Enroute. The emergence of Microsoft Operating Systems presented a threat in the firm’s survival. In a bid to deal with this challenge, Palmtop invested in the development of applications that were compatible with Microsoft’s personal computers.
Palmtop changed its name to TomTom in 2001 and ventured into satellite navigation market by launching a new mobile car satnav system named ‘TomTom Navigator’. In 2002, the firm generated € 8 million in sales revenue by selling its first Global Positioning System car navigator, viz. PDAs and its TomTom Navigator. In 2003, TomTom launched the Navigator 2, which is an upgrade of the first version. TomTom’s commitment to innovation has played a significant role in promoting the firm’s growth. Furthermore, the firm is focused to improving its competitive advantage by investing in its human capital. Currently, the firm has a highly qualified marketing and technical staff. Subsequently, the firm has gained substantial market share.
TomTom completed its Initial Public Offer [IPO] in 2005 and it was listed in the Amsterdam Stock Exchange. Through the IPO, TomTom raised € 469 million, hence increasing its financial strength. For example, the IPO increased the firm’s net worth to € 2 billion.
In addition to new product development, TomTom’s growth has also emanated from the adoption of the concept of merger and acquisition in its strategic management practices. During the period ranging between 2006 and 2008, TomTom acquired three firms, which include Tele Atlas, Datafactory AG, and Applied Generics. Strategic acquisitions have significantly improved the firm’s competitiveness. For example, the firm was able to deal with the intense competition posed by Garmin, which is its biggest rival. TomTom’s operations are based on three main areas and the firm intends to provide customers with better maps by developing a strong map database, which is continuously upgraded. With regard to routing, the firm owns the most elaborate database with regard to historical speed profiles across the world. Furthermore, the firm gives its clients traffic information as it happens.
Company’s Internal Strengths and Weaknesses
TomTom is committed to developing a strong competitive advantage. In a bid to achieve this objective, the firm has developed substantial strength with regard to continuous innovation. The firm’s strength with regard to continuous innovation is evidenced by the effectiveness with which it undertakes new product development and continuous product improvement. TomTom’s success with regard to new product development is enhanced by its strong research and development team. Since its inception, TomTom has introduced a number of new products and applications. Investment in innovation has positioned TomTom as a leading satellite-navigation technology company.
The firm recognises the contribution of resources and capabilities in enhancing its competitive advantage. Subsequently, the firm has nurtured sufficient capabilities and resources, which have promoted its competitiveness with regard to digital mapping, dynamic information, and routing technologies. One of the firm’s main resources relates to its in-house routing algorithms, which have played a significant role in its efforts to introduce new technologies such as the IQ Routes. Another major resource in TomTom’s operations relates to its digital mapping technology and the acquisition of Tele Atlas.
These resources have played a fundamental role in improving the firm’s capabilities with regard to mapping. For example, these resources have enabled TomTom to deliver a unique experience to customers by introducing new features in its products. The firm’s mapping capability enables it to update its navigation systems in accordance with the prevailing changes. In addition to the above, TomTom also derives its competitiveness from its partnership with Avis and Renault automobile companies. The partnership enables the firm to install its navigation systems in the two companies’ automobiles. The strategic partnerships with these companies have improved the firm’s competitiveness with regard to price. For example, the price of an inbuilt navigation system has significantly been lowered. Subsequently, TomTom has been in a position to increase its market penetration.
TomTom also derives its strength from its financial capability. Since its inception, TomTom has managed to grow its financial strength significantly. For example, between 2005 and 2007, the firm’s sales revenue and net income grew with a significant margin. However, in 2008, the firm’s sales revenue decreased with a 3.7% margin. On the other hand, net income decreased by 136%.
Since its inception, TomTom has managed to market its products to diverse customer groups, which include individual and institutional groups. Individual customers can now purchase portable navigation devices. In an effort to deliver a unique customer experience, TomTom ensures that specific customers’ desires and needs are met through product diversification. This move has significantly enhanced the effectiveness with which the firm meets the customers’ diverse needs. Furthermore, TomTom ensures that its navigation products are fairly priced. For example, the firm has set the price of some of its navigation products between $ 100 and $500 in the United States. However, the products differ with regard to their navigation capabilities.
The other customer group is comprised of automobile manufacturing companies. The firm has entered in partnerships with various automobile companies such as Avis and Renault. These partnerships have enabled the firm to incorporate its navigation systems in the partnering companies’ automobiles. The firm produces different air-travel navigation devices, which has significantly enhanced its partnership with individual and institutional customers in the aviation industry. Moreover, the firm has attracted business enterprises such as shopping malls as part of its customers. These firms are increasingly adopting mobile workforces. In a bid to meet their needs, TomTom has partnered with Advanced Integrated Solutions in the development of a new advanced feature, which enables the business enterprises to manage their fleet. For example, the technology provides customers with an opportunity to optimise their fleet route.
TomTom has integrated mergers and acquisitions as one of its growth strategies. Previous studies have cited numerous cases of mergers and acquisitions failures. One of the major causes of failure is lack of effective integration. However, TomTom has achieved a high rate of success in all its mergers and acquisitions efforts. One of the factors that have improved the firm’s success relates to the effective management of cultural differences between TomTom and the firms being acquired. Subsequently, TomTom is in a position to determine the degree of cultural fit. Furthermore, the firm effectively manages the cultural differences through acculturation and assimilation strategies. The acquisitions have played a fundamental role in improving the TomTom’s ability to develop new products.
The firm is cognisant of the role of employees in enhancing its competitiveness. Subsequently, the firm has developed a strong workforce by investing in employee-talent development program. The firm’s employee development program is based on its talent needs and the employee’s career development goals. For example, in 2008, the firm implemented the Young Talent Development Program, which focused on increasing the employees’ personal and technical skills. Effective management of human resources has played a significant role in enhancing the level of satisfaction among employees.
The case identifies high cost of operation as one of the major challenges hindering the TomTom’s competitiveness. In an effort to deal with this challenge, TomTom has implemented a cost-cutting program. One of the ways through which the firm intends to achieve an acceptable cost of operation is by reducing the size of its workforce. Furthermore, the firm intends to minimise the cost of its operation by reducing expenditures on marketing activities. Moreover, the firm intends to achieve operational efficiency by restructuring its operations, for example by trimming down the number of contractors and reducing its discretionary spending.
The Nature of the External Environment in Company
Firms’ operations are affected by forces emanating from the external business environment. Subsequently, it is imperative for organisational managers to develop a comprehensive understanding of the prevailing industry forces. This goal can be achieved by adopting the Porters’ five forces. This model will aid in gaining insight on the likelihood of TomTom’s achieving long-term success. The main forces shaping the navigation systems industry are evaluated herein.
Threat of Substitute: High
The firm faces high threat of substitute arising from the high rate at which firms in the information technology industry such as Microsoft and Google are investing in research and development. This aspect has led to the emergence of diverse software applications. The threat of substitute is increased by the emergence of iPads and smartphones such as Palm Pre and the iPhone. These cellular phones have own inbuilt navigation systems.
Cellular companies such as Nokia have invested in developing their own GPS technology, which is integrated into its smartphones. Nokia intends to enhance its competitiveness via adapting different strategies. In a bid to achieve this goal, Nokia has partnered with Navteq, which is a key Tele Atlas competitor. Furthermore, the threat of substitute is further increased by the view that automobile manufacturing companies are investing in the development of their own navigation systems.
Buyer Bargaining Power: High
This aspect refers to the ability of buyers to influence the price of a product downwards. The case shows that TomTom has targeted diverse customer groups. For example, the firm has entered into a partnership with different institutional customers such as air travel and automobile companies. Renault and Avis are some of TomTom’s major institutional customers. These companies determine the navigation systems to be in-built within their automobile products. Subsequently, they have a high bargaining power with regard to the TomTom’s ability to penetrate the global market.
Supplier Bargaining Power: Low
The company has developed substantial market strength since its inception. One of areas that it has sourced its competitiveness relates to supply chain management. The navigation industry is characterised by a large number of suppliers. In an effort to exploit this market characteristic, TomTom has adopted the concept of outsourcing. TomTom has outsourced most of its suppliers, which gives the firm a high edge with regard to the size of its supply chain. For example, the firm has the capacity to expand or reduce suppliers in its supply chain, which has greatly enhanced its ability to sustain capital expenditure risk. Therefore, one can argue that the numerous suppliers of products and services that the firm requires to achieve operational efficiency give the firm an edge with regard to bargaining power.
Threat of New Entrant: Medium
The entry of cellular manufacturing companies such as Nokia, Samsung, and Apple has increased the threat of entry. These companies are increasingly focusing on increasing their market share. One of the ways through which these firms intend to achieve their goal is by integrating navigation and mapping technologies in their mobile phone products. Subsequently, there is a high probability of the industry experiencing a moderate increment in threat of entry due to the emergence of personal navigation devices. Despite this aspect, the PND market has experienced a significant reduction in its growth rate over the past three years. The reduction can be explained by the recent global financial crisis.
Rivalry: High
The industry is facing intense competition emanating from traditional and emerging companies. Some of the TomTom’s main competitors include Garmin and Magellan. The two companies have been in operation for a number of years and they have developed a substantial market share. For example, the Garmin’s market share is estimated to be 45%, which is almost twice that of the TomTom’s. On the other hand, Magellan is estimated to be at 15%. Garmin is recognised for its on-the-go navigation systems. The two companies specialise in the production of Navteq-based maps. Magellan is recognised for its Maestro series and RoadMate car navigation systems.
In addition to traditional competition, TomTom faces intense competition from new forms of competition, which is emerging with the ever-changing technology revolution that bring with it novel ideas. These forms of competition have led to a significant increment in the intensity of competition, and hence the degree of rivalry. The degree of rivalry is further enhanced by the view that competitors cannot achieve high competitive advantage based on price, which reduces the likelihood of achieving price differentiation.
SWOT Analysis
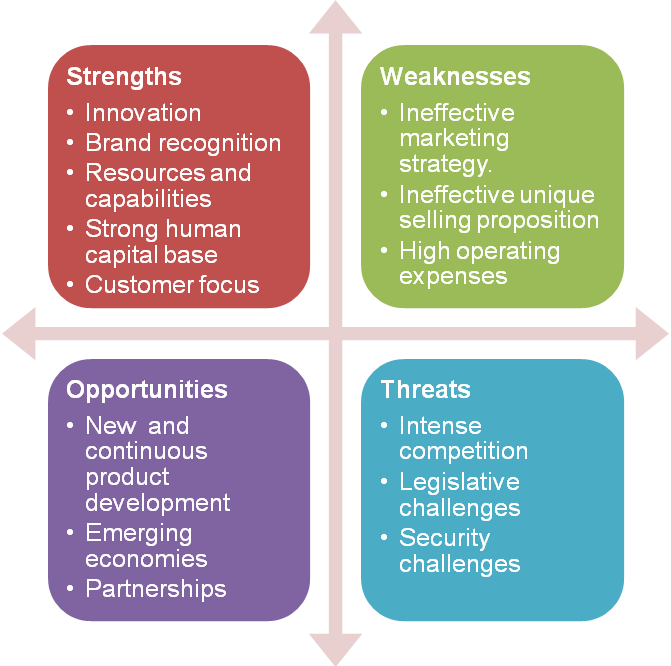
Strengths
Innovation
TomTom intends to achieve long-term success in the navigation industry. Subsequently, the firm has adopted innovation as one of the key avenues in its quest to achieve its goal. Since its inception, TomTom has developed a number of navigation systems and devices, which have been adopted by individual and institutional consumers. Furthermore, the firm undertakes continuous product improvement in an effort to align its products with the prevailing market forces. This goal is achieved by incorporating new and unique features. However, the firm ensures that the new features integrated are based on the customers’ feedback.
Brand Recognition and Customer Focus
Over the years that the firm has been in operation, it has been concerned with delivering unique experience to its customers, which has been achieved by developing effective navigation systems. Furthermore, the firm is committed to developing products that align with the customers’ needs and desires. In an effort to penetrate the global market, TomTom has invested in a comprehensive marketing campaign, hence increasing the level of market awareness. Subsequently, the firm has managed to develop strong brand recognition within the navigation industry.
TomTom is focused on providing customers with unique products. Consequently, the firm has invested in a comprehensive marketing strategy, which is aimed at developing a strong level of customer loyalty. For example, the firm ensures that the products developed are in line with the customers’ needs and desires. This strategy has played a fundamental role in enhancing the level of satisfaction amongst customers.
Resources and Capabilities
TomTom has managed to develop strong financial and human resource strength and capabilities. Its financial strength has arisen from the adoption of product diversification strategy. Subsequently, TomTom has managed to increase the level of its profitability over time. Furthermore, the firm has developed a strong human capital base by investing in talent development amongst employees. Its investment in employee development has improved the effectiveness with which the firm develops new products.
Weaknesses
Cost Management
TomTom incurs a huge cost of operation, which hinders its competitiveness. In a bid to deal with this challenge, TomTom has implemented a cost-cutting strategy, which focuses on a number of areas such as marketing and human resource management. However, reducing the size of the workforce might affect the employees’ morale adversely. On the other hand, reducing the marketing budget might affect the firm’s ability to develop strong brand recognition through the creation of sufficient level of market awareness.
Opportunities
New and Continuous Product Development
The firm faces intense competition emanating from traditional and emerging competitors. Subsequently, the navigation industry is experiencing an increment in the number of new products being introduced in the market. In an effort to increase its competitiveness, TomTom should consider investing in new product development. This goal can only be achieved if the firm engages in continuous scanning of the environment in order to identify the prevailing market opportunities. Moreover, the firm should undertake continuous market research in order to understand the customers’ needs and wants. Consequently, the firm will be in a position to undertake effective product improvement
Venturing Emerging Markets
The navigation industry has undergone a high rate of consolidation over the past few years. For example, the European and US PND market has attained its maturity. This move has led to a significant decline in the TomTom’s sales revenue with regard to its PND products. This trend might affect the firm’s ability to develop new products due to the reduction in its financial strength. In a bid to deal with this challenge, TomTom should consider entering emerging markets. For example, the firm can design navigation services and digital maps for emerging countries. However, it is essential for TomTom to conduct a comprehensive analysis of the target market in order to determine the potential for growth
Partnerships and Acquisitions
TomTom can improve its competitiveness by identifying potential firms to enter into partnership. Some of the firms that the firm should consider entering into a partnership with include automobile, airline, and ship manufacturing companies. This move will increase the likelihood of achieving a high level of market penetration. Furthermore, TomTom can also improve its production capability by identifying potential firms in the navigation industry that it can acquire. Such acquisition will increase the firm’s ability to develop effective navigation systems and devices.
Threats
Intense Competition
The firm faces intense competition from online navigation applications and mobile phone markets, which are increasingly integrating navigation capabilities in their products. The availability of free maps from diverse search engines presents a threat in the firm’s effort to maximise its profitability. Customers are increasingly using these maps in getting direction of their intended destinations. The occurrence of the global recession has increased preference towards free maps. Moreover, the high rate at which manufacturing companies are developing navigation systems might affect the firm’s competitiveness in the navigation industry.
Legislative Challenges
The case highlights the adoption of adverse legislation and restrictions as one of the major threats that have the potential of affecting operation of firms in the navigation industry. One of the legislations entails banning the incorporation of navigation devices in automobiles. Countries such as Australia argue that PNDs cause major distractions. Subsequently, the country intends to ban PNDs in automobiles. Similarly, Canada announced that it would restrict navigation systems from being in-built in other parts of the automobiles other than the dashboard and or the windshield. In a bid to deal with this threat, it is imperative for TomTom to consider integrating effective safety measures. Additionally, environmentalists argue that the operations of firms in the navigation industry pose a threat to the environment. Subsequently, it is essential for TomTom to integrate the concept of corporate social responsibility.
Security Challenges
The high rate of terrorism being experienced today poses a threat to TomTom in its effort to achieve global operations. For example, some countries such as Egypt have banned GPS systems due to terrorism concerns.
Analysis of Corporate-Level Strategy
These strategies outline the detailed actions that an organisation should undertake in order to gain competitive advantage. Corporate level strategies outline the mix of businesses that an organisation undertakes in order to achieve the desired level of competitiveness. The three main approaches to corporate-level strategies include diversification and formation of mergers and acquisitions. Furthermore, corporate level strategies also include internationalisation and globalisation. From the case, TomTom has adopted different corporate level strategies, which are evaluated herein.
Mergers and Acquisitions
TomTom has undertaken a number of acquisitions since its inception. The firm acquired Tele Atlas in 2008, which significantly improved its competitiveness. The acquisition enabled TomTom to enhance its production expertise, hence improving the level of customer experience. For example, the acquisition improved the effectiveness with which the firm designs navigation products.
Strategic Partnerships
The firm has also integrated strategic partnerships as one of its corporate level strategies. Some of the firms that the firm has entered into a strategic partnership with include Renault, Avis, Twentieth Century Fox Licensing and Merchandising, Locutio Voice Technologies, and Advanced Integrated Solutions. The firm’s partnership with Renault and Avis has increased its marketing capability. On the other hand, partnership with other firms such as Advanced Integrated Solutions, Twentieth Century Fox Licensing and Merchandising, Locutio Voice Technologies has improved the firm’s system design and marketing capability.
Business Level Strategy
An organisation can incorporate different business level strategies in its operations. The business level strategies are aimed at enhancing the firm’s competitive advantage. in addition, an organisation can integrate different business level strategies. Some of these strategies include cost leadership, differentiation, and focus strategy.
TomTom has adopted differentiation strategy in an effort to improve competitive advantage. In a bid to differentiate its navigation system devices effectively, TomTom incorporates unique features in its products. The firm is committed to nurturing a strong level of customer interaction in order to understand the customers’ needs. This aspect enhances the effectiveness with which the firm differentiates its products during its continuous and new product improvement. The firm’s differentiation strategy is evidenced by its extensive product line. For example, the firm has introduced a range of personal navigation devices such as TomTom Go Series, TomTom One, TomTom Rider, TomTom Navigator, TomTom iPhone, TomTom Mobile, and TomTom XL.
TomTom’s differentiation strategy is also evidenced by its commitment towards providing navigation products that are of high quality and easy to use. By integrating IQ Routes in its navigation devices, TomTom has been in a position to provide drivers with exact information on different characteristics of a route such as traffic lights and speed bumps. Moreover, the firm differentiates its products by ensuring that its products are optimally designed in order to deliver optimal performance.
In addition to the above differentiation features, TomTom has also adopted price as one of its product differentiation aspects. The firm has incorporated different price ranges in marketing its PNDs, which include mid-range and high-range. However, the average price of PND is € 99. Price differentiation has significantly enhanced the firm’s ability to attract diverse customer groups.
Structure and Control
Structure
TomTom is committed to achieving long-term success and ensuring that its core capabilities and resources are optimally utilised in order to achieve economies of scale. In a bid to ensure optimal utilisation of resources, the firm has centralised some of its operations such as research and development. This goal has played a remarkable role in ensuring that the resources are efficiently utilised hence improving the firm’s innovation capability.
TomTom also ensures a high level of operational efficiency by undertaking organisational restructuring. However, restructuring is mainly undertaken after major organisational change such as acquisition. For example, after acquiring Tele Atlas, TomTom restructured its operations in order to enhance the likelihood of achieving the desired level of synergy. Such restructuring enabled the firm to achieve success in its quest to develop broader navigation solutions. Moreover, restructuring the organisation’s operations has enabled it to be focused on customers. This goal was achieved by establishing different main business units.
The firm has also structured its operations by integrating the concept of outsourcing, which is mainly applied in its supply chain model. Subsequently, the firm has been in a position to achieve a high degree of operational efficiency by ensuring that the supply chain is optimally controlled.
The firm’s structure has also taken into account the employees’ needs, which is evidenced by its commitment to developing a high degree of organisational identification. For example, the firm has incorporated an employee-training program, which is aimed at ensuring that its workforce has the right knowledge, skills, and capabilities to assist in attaining its goals. The training program has played a significant role in improving the level of job satisfaction amongst employees. The firm’s employees appreciate that it is conscious of their career development needs.
Control
The case cites cost of operation as one of the major challenges that the firm is facing. In a bid to deal with this challenge, TomTom has integrated cost-cutting strategy. The firm’s management team is of the opinion that these strategies will enable it to minimise the cost of operation.
Recommendations
The case shows that TomTom has integrated effective strategic management practices. This aspect is evidenced by its success with regard to diverse issues such as marketing, operations, management of organisational resources and capabilities, and human resource management. Furthermore, it highlights the various challenges that the firm is facing. Some of these challenges include relate to competition, and legislative challenges coupled with operational and security challenges. Despite these challenges, TomTom is committed to achieving long-term success. In a bid to achieve this goal, the firm should consider the following.
- The firm should invest in new and continuous product development in order to deal with the competitive challenges posed by traditional and emerging forms of competition.
- TomTom should review its cost-cutting program. Some of the areas targeted such as reducing marketing expenditure and reducing the size of the workforce might affect the firm’s ability to achieve long-term competitiveness adversely. Thus, the firm’s management team should establish a balance between achieving long-term success and cutting the cost of operation.
- The firm should consider expanding into the international market by targeting emerging markets in order to increase its sales revenue and net income. Consequently, the firm will be able to enhance its financial strength.