In microeconomics there are various economic concepts that come into play in any given market. All the concepts work together to attain the market equilibrium. The concepts include, but are not limited to supply and demand in the market, opportunity cost, scarcity interest rates, choice of commodity and money.
A real life example of an economic concept is the concept of supply and demand in the electronics industries with special emphasis on the supply of Toshiba laptops. To start with, supply is defined as the amount of a commodity that the seller is willing to bring to the market at a given time, place and at a given price. On the other hand demand is the amount of commodity that the buyer is willing to buy at a given price and at given time and place (Wetzstein 19).
Toshiba laptops are a low-cost product and therefore they are a favorite of many. The manufacturer had enough supply in the stores and they were in high demand, thus were fast-moving and soon the stores ran out of the laptops. The fact that the laptops ran out of the store did not prevent clients from purchasing them as many more were sold over the internet.
Most of the clients bought the products because they were in high demand although they were in limited supply. This forced Toshiba to add more products in the market and at the same time increase their price marginally to counter the high demand and thus achieve a market equilibrium where they would make a profit and at the same time maintain a price that was affordable to the majority of its clients.
Production is another micro-economic factor that would affect Toshiba. The company has to produce its laptops with a target market in mind. In line with this, the company would require various factors of production such as labor. Labor is the effort applied by its staff in the production process. Land is the natural resources required for the successful performance of the business. The target market would be people with certain income levels and budget constraint. Therefore, the laptops must be affordable.
Scarcity is another economic concept that would affect Toshiba considerably. In economics, scarcity is the inherent problem that faces people where they want a product, but the product is prohibitively limited. It’s a situation where you have to make a choice under scarcity. People especially students like us demand all sorts of electronics and at a cheaper price.
Can Toshiba supply all these laptops at a low cost to meet the ever growing needs of students? The answer is no because there is a limited supply of staff to distribute the gadgets to all the students, there is geographical disparity between the manufacturer and the client and there are many government regulations that inhibit the full scale production of low cost Toshiba laptops.
And even if Toshiba was able to supply the laptops, it means that the student would have to make a choice between his or her scarce resources to buy the laptop or to spend on something else like food or books. If the student resources were not scarce, then the issue of decision and choice would not arise and the student would just rush to the nearest electronics store and buy his favorite laptop.
The other economic concept I had to deal with is the opportunity cost. Wetzstein clearly states that “in microeconomic theory, the opportunity cost of a choice is the value of the best alternative forgone; in a situation in which a choice needs to be made between several mutually exclusive alternatives given limited resources” (213).
For example, I might want to go for a vacation to Miami and I have two hundred dollars and still I want to buy a Toshiba laptop with the same amount. Can I go for the vacation and at the same time I buy a laptop? No. I have to do one and not the other. The opportunity cost of going for a vacation is that I have to forego the purchase of a laptop.
Production Possibilities Frontier is another economic concept. Clients can only consume a given amount of goods and services and as such, Toshiba cannot produce an infinite number of laptops. This is because the resources will always be limited and scarce at any given time. The graph below illustrates.
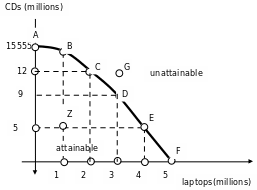
Table 1
It can be observed that, for more laptops to be produced, the company must produce CD’s in less quantity since the resources are fixed. The points that can be achieved by the company are the points lying in the curve or the points on the curve. That is the point where the Toshiba Company would produce best was there to be a trade off between production of the CD’s and the laptops. Unattainable points lie above the production possibility frontier curve.
Works Cited
Wetzstein, Michael. Microeconomic Theory: Concepts and Connections. New York: Routledge, 2013. Print.