Company profile
Toyota has developed a comprehensive product portfolio that is comprised of diverse automobile categories. For example, its hybrid cars comprised brand names such as Prius, SAI, Crown, CT200h, and HS250h. the conventional engine vehicles [compact and subcompact cars] entail the Yaris, Passo, Porte, Etios, Corolla Axio/Fielder, Spade, Vitz, Vios, and Ractis brands. Moreover, the firm produces auto-parts, commercial vehicles, passenger vehicles, and mini-vehicles under the Toyota brand. On the other hand, mid-size cars are produced under different brand names, viz. Avensis, Mark X, Camry, and REIZ. Toyota has also diversified into the luxury sports-utility and sports car segments. Its luxury car models are marketed under the Crown and Lexus brand names.
The company has adopted a hybrid organisational structure by blending the product and functional structures in order to enhance the firm’s ability to respond to market changes. Toyota adjusts its organisational structure continuously in order to enhance its capacity to attain its global vision. For example, in 2013, the firm adjusted its structure in an effort to improve its manufacturing capacity. The automotive manufacturing process will be undertaken through four main business units, which include the Unit Centre, Lexus International, Toyota No.1, and Toyota No.2. The Lexus International Division will be charged with foreseeing the Lexus brand while the Unit Centre division will deal with unit-related operations. The Toyota No. 1 division will oversee operations in Europe, Japan, and North America regions. Conversely, the Toyota No.2 division will oversee operations in the Middle East, Africa, China, the Caribbean, Latin America, and the East Asia regions.
The firm has attained optimal competitive advantage over the past decades, hence its ability to sustain market leadership. One of the core sources of the firm’s competitive advantage entails the investment in a unique manufacturing system, which has limited the likelihood of imitation by competitors. The uniqueness of the firm’s production system emanates from the fact that it is a blend of the company’s philosophy, problem-solving ability, people, and processes (Liker 2006).
Challenges facing Toyota Company
The global automotive industry has experienced major turbulence since the onset of the 21st century, which has motivated companies to implement major organisational restructuring. The challenges emanate from different sources such as the political, economic, technological, social, and legal environments. A study conducted by the International Organisation of Motor Vehicles Manufacturers [OICA] shows that the industry experienced a 50% growth from 1999 to 2012 (Das 2014). Thus, the industry’s average growth rate during the 21st century is estimated to be 3%, which is considerably low. Despite the view that some companies are implementing aggressive expansion strategies, especially in the low-cost production countries such as the BRIC economies [Brazil, Russia, India, and China], the industry has undergone significant changes such as downsizing especially in the traditional markets due to economic recession. For example, the developed economies such as the US, Germany, and Japan have experienced a significant reduction in the volume of automobile production since 1999 (Das 2014).
Das (2014) further affirms that much of the fluctuation within the industry was experienced in 2008 and 2009 when the industry underwent a significant reduction in the volume of output. On the contrary, the combined automobile production by India, Brazil, and China grew from 4 million to 26.8 million. Subsequently, their total market share increased from 7.11% to 31.80%. Das (2014, p.128) further emphasises that the ‘global recession hit the automobile industry badly due to the high pro-cyclical demand for vehicles and consumer credit crunch’. The recession increased the rate of unemployment amongst households, which culminated in the reduction of the consumers’ purchasing power. For example, the economic recession has affected the Australian economy. Currently, Australia is experiencing the highest rate of unemployment (Fickling 2014). The economic recession affected Toyota’s performance. The firm experienced a substantial slump in its sales volume, and hence its profitability. The chart below illustrates the trend in the firm’s level of profitability.
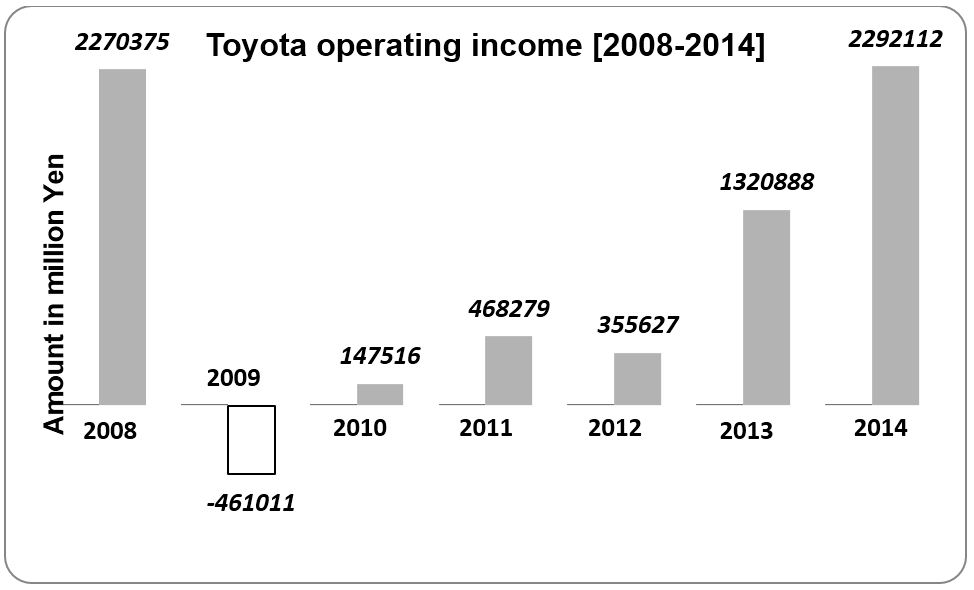
The decision to exit the Australian market might affect the firm’s dominance in the country, which is ranked third with reference to car-ownership (Fickling 2014).
Key problem areas
The economic recession has affected Toyota’s operations in a number of ways as evaluated herein.
Organisational restructuring
The Toyota Company has been forced to restructure some of its operations in an effort to minimise the costs of operation, hence its economic performance. The firm projects to optimise its profitability within 6 years (Mukai & Horie 2013). One of the strategies that the firm intends to implement entails downsizing. For example, the firm announced its intention to exit some of its international markets such as the Australian market by 2017. The firm intends to implement this strategy by closing its production plants. The move will cause 2,500 of its employees to lose their job (Boston Consulting Group 2014). The decision to adopt the downsizing strategy has been spurred by different economic challenges in Australia such as high cost of manufacturing and the ‘unfavourable Australian dollar’. Moreover, the decision to exit the Australian market has also been instigated by the increment in the intensity of competition due to the free trade agreements adopted by the Australian government.
Despite the view that the downsizing strategy will enable the firm to minimise the cost of its operation, the move might affect the firm’s long-term performance, hence its ability to achieve an optimal performance (Altekar 2005). The downsizing strategy might lead to a reduction in the level of motivation amongst its workforce. For example, Toyota’s workforce in its different production facilities and distribution centres might perceive the downsizing strategy as a threat to their job security, which might trigger voluntary employee turnover (Ingrassia 2009).
Change in the company’s share price
The company’s effort to revive its performance was affected by the devastating tsunami and earthquake that hit Japan in 2011. The phenomenon affected the company’s share price, hence its attractiveness. The firm lost its market share and attractiveness amongst investors to General Motors and Volkswagen. The economic recession and the tsunami led to a 20% decline in the value of the firm’s share price within a period of one month.
SWOT Analysis
Strengths
- Extensive distribution and production network: the firm has established a comprehensive production and distribution network. The firm has established over 50 manufacturing plants located in 20 countries around the world. The manufacturing plant enables Toyota Motor Corporation to improve its production capacity and diversify its operations, hence minimising risk.
- Market share and brand recognition: the firm has attained global market recognition, hence promoting its market share. The firm accounts for 11.8% of the total global market share as illustrated by appendix 1.
- Strong focus on research and development: the firm is extensively committed on research and development in an effort to improve its product portfolio. The firm’s focus on research and development is further motivated by the need to improve its products continuously hence meeting the market demand.
Weaknesses
- Decline in sales – the firm has experienced substantial reduction in its sales volume across different regions because of the recession. The decline in sales profitability might pressurise the firm’s profits.
- Brand image – the firm’s brand image has been impacted negatively by product recalls over the recent past. For example, the firm recalled over 111,000 of its Lexus and Toyota models in 2011 due to failure it the hybrid system. In November 2014, the firm also recalled over 85,000 vehicles outside the US due to faulty airbags (Soble 2014).
Opportunities
- New product development – it is expected that growth in the automobile industry will be driven by new brands. Thus, Toyota can maximise its sales revenue and profitability by investing new development of new automobile models.
- Growth of the global automobile industry – the firm might benefit from the increment in the demand for automobiles, especially in the emerging economies. The economic recovery being experienced in both the developed and developing economies will lead to job creation, hence increasing the consumers’ purchasing power.
- Strategic partnership – Toyota Company can optimise its profitability by adopting effective strategic management practices. For example, the firm announced its strategic partnership with BMW in order to improve its ability to dominate the sports car market segment. Therefore, strategic partnership will enable the firm to attain competitiveness with reference to technology.
Threats
- Currency fluctuation – Toyota international marketing activities are subject to fluctuations of major currencies such as the Japanese Yen, the Euro, and the US dollar.
- Intense competition – the firm faces intensive competition from other industry players such as Renault-Nissan Group, Honda Motor Corporation, Peugeot SA, General Motors, Volkswagen AG, Ford Motor Co, Hyundai-Kia Group, Fiat-Chrysler Group, and SAIC Motor Corp Limited. The intensity of competition is further increased by the high rate of globalisation and consolidation within the industry. The intense competition may pressurise the industry’s pricing structure downwards.
- Occurrence of natural disasters – the company’s operations are subject to disruption by natural events such as floods and earthquakes. For example, the firm was adversely impacted by the 2011 tsunami and earthquake that hit Japan. The event temporarily halted the firm’s production activities.
Finding the solutions
The above analysis shows that Toyota Corporation is experiencing significant challenges due to the global economic recession. Despite the economic recovery efforts being adopted by different governments such as implementation of economic stimulus package, the firm is still experiencing operational challenges, hence affecting its performance. However, the firm can improve its performance by adopting effective strategic management practices. Some of the solutions that the firm can adopt are explained herein.
Strategic considerations and planning
Market expansion
Toyota Motors Corporation should integrate the concept of international market expansion. The firm should consider entering the emerging markets such as the BRIC economies and the Gulf countries [the UAE, Qatar, and Bahrain]. Despite the adverse effects of the global economic recession, the emerging economies are experiencing remarkable economic growth due to the adoption of effective economic policies such as open economic policies and economic liberalisation. A study conducted by Ricardo Strategic Consulting [RSC] shows that despite the slow automotive demand in the developed economies such as Japan, North America, and Europe, the rise in demand for automobile in the BRIC economies would foster the industry’s growth until the year 2020 (Lowry 2014). Other markets that the firm should consider include Thailand, Vietnam, Ukraine, South Africa, Peru, Morocco, Nigeria, Mexico, Iran, and the Philippines amongst other economies (Lowry 2014).
Low-cost and lean manufacturing
The firm is currently in the process of exiting the Australian market due to the adverse effects of the global economic recession. The recession has led to an increment in the cost of production, hence reducing the firm’s profit margin. Despite the fact that the firm does not have control over macro-environmental changes such as the high rate of unemployment in Australia, it is imperative for the firm to consider the most effective way of sustaining its dominance in Australia. Subsequently, the firm should consider restructuring its production system by adopting the concepts of low-cost and lean manufacturing.
One of the core aspects that Toyota Company should consider in the process of planning and implementing the low-cost and lean manufacturing process entails outsourcing (Nikkei Incorporation 2014). The company’s management team should identify countries characterised by low costs of manufacturing. After identifying these markets, the firm should establish manufacturing plants in these countries. By outsourcing its manufacturing processes, Toyota will minimise the cost of production. The firm will also minimise the cost of labour by hiring from the local market. Furthermore, the firm will be in a position to foster the level of creativity by sourcing in the local market.
Change management
In the course of entering the international market, the firm might experience significant resistance from the incumbent employees. For example, during the initial entry phase, the firm might be required to take a number of expatriates into the host country. However, the selected expatriates might resist due to diverse personal reasons such as the existence of cultural differences. The prevailing cross-cultural boundaries between its domestic market and the host country might affect the productivity and commitment of the expatriates, hence the firm’s performance. Countries are characterised by diverse national cultural differences, which might affect a firm’s success in the international market. For example, Toyota’s expansion into the Gulf Countries might be affected by the cultural differences such as the countries’ norms and beliefs, which are extensively anchored in the Islamic religion. The cultural differences might trigger conflict between the firm’s expatriates and the new employees hired from the local market. Subsequently, the firm’s ability to implement its ‘Toyota Way’, which comprises the firm’s guiding principle, might be affected adversely.
Managerial functions
Despite the existence of employee resistance and cross-cultural differences, the firm can expand into the international market successfully by adopting effective change management practices. This goal can be achieved by improving the effectiveness of its managerial functions and roles as illustrated herein.
- Organising – in order to penetrate the host country successfully, the company should improve its workforce by outsourcing labour from the local market. The newly hired employees should be trained in order to understand the organisation’s culture, hence incorporating ‘the Toyota way’ in executing their duties. This move will aid in sustaining the organisation’s culture (Tripathi & Reddy 2008).
- Planning – prior to expanding into the target market, the firm should conduct a comprehensive analysis of the prevailing market dynamics. For example, the firm should conduct an extensive cultural analysis in order to determine the cultural fit between the domestic and the host country. Planning a cultural fit analysis will enable the firm to determine and plan the changes that will be implemented in its organisational structure and culture. For example, cultural fit analysis will aid in understanding the degree of individuality/collectivism between the host and the domestic country.
- Directing – the firm should ensure that employees are motivated optimally, hence their commitment towards the set organisational objectives. In order to ensure that the employees are focused on the organisational goals, Toyota Company should implement a comprehensive reward system. The firm should integrate unique monetary and non-monetary rewards in its reward systems. For example, the firm should offer employees the opportunity to purchase the company’s shares, hence becoming a part of the shareholders. Furthermore, the firm should assure employees of their job security and opportunity to progress through their career path. This move will aid in optimising the level of productivity amongst employees, and hence their loyalty and contribution to the organisation.
Managerial roles
In addition to the above managerial functions, Toyota Company should also consider improving its managerial roles in order to order succeed in implementing the above solutions. Some of the managerial roles that the firm should consider are explained herein.
Interpersonal roles
- Liaison – the firm’s management team should consider the subordinates as a source of management intelligence. In a bid to achieve this goal, Toyota should collect opinion continuously from subordinates on different aspects. This aspect will aid in integrating a participatory management style.
- Leadership – Toyota should ensure that effective leadership style is adopted in order to establish a strong relationship between the executives and the subordinates. For example, the firm should ensure that the organisation’s goals align with the employees’ needs. This move will improve the level of focus amongst employees in implementing their duties.
Informational roles
- Monitor: Toyota should scan the environment continuously in order to gather sufficient insight from the external environment. Consequently, the firm will be in a position to adjust its management strategies effectively.
- Disseminator – the firm should ensure that employees are adequately informed about the firm’s decisions. This move will minimise the level of resistance, hence improving the success with which the decisions are implemented.
Assessing performance
Upon implementation of the above solutions, it is imperative for the firm to assess its performance. There are different measures that the firm can undertake as illustrated herein.
- Market share – it is imperative for Toyota Company to monitor growth in the size of its market share. Thus, the firm will be in a position to determine its success in dominating the international market.
- Financial performance – the firm can assess its success in the international market by evaluating its financial performance. For example, Toyota should evaluate the change in its level of profitability from the international operations. This information will enable the firm’s management team to assess and project the profitability potential of the new market.
- Brand loyalty – the firm should also assess the level of brand loyalty within the new market. This information will enable the company to assess the effectiveness with which its production system is aligned with the market needs.
Ethical issues
In the course of implementing the above solutions, Toyota Company might experience a number of ethical issues. For example, in the course of implementing the lean manufacturing process, the company will be required to desist from activities that trigger environmental pollution. Environmental pollution is one of the ethical issues that firms in the global automobile industry are facing. The firms have previously been criticised of increasing the rate of climate change through their direct and indirect contribution to environmental pollution.
In a bid to develop a strong corporate reputation, it is important for the firm to consider implementing technologies that will minimise environmental pollution. For example, the firm should consider investing in comprehensive research and development in order to improve its innovativeness. One of the areas that the firm should focus on entails improving fuel efficiency. The firm should ensure that the automobile technology adopted is fuel-efficient and it does not emit greenhouse gases. For example, the firm should consider producing automobiles that can utilise alternative forms of energy such as bio-fuel to reduce environmental pollution.
Conclusion
The above analysis shows that Toyota Company has been affected by the recent economic recession. The firm has experienced a significant decline in its profitability, hence the attractiveness of its stocks amongst investors. The recession has also made the firm to consider exiting some markets such as Australia, which illustrates the magnitude of the economic recession. However, the firm can enhance its competitiveness by adopting the concept of market expansion. The firm should target emerging markets in its market expansion. Secondly, the firm should consider improving its production system by integrating the concept of lean manufacturing.
Recommendations
In a bid to enhance its market dominance in the global automobile industry, it is essential for the firm to consider the following issues.
- Localisation – the firm should ensure that its products are customised to the customers’ needs. This aspect will improve the attractiveness of the firm’s automobiles in the international market.
- Research and development – Toyota should invest in research and development continuously in order to produce fuel-efficient cars. This move will improve the attractiveness of the firm’s vehicles to consumers in the emerging economies.
- Cultural fit – the firm should undertake an extensive cultural analysis prior to venturing the international market. This aspect will aid in determining the degree of fit between the national cultures of the host and the domestic market.
- Toyota should identify countries characterised by a low-cost manufacturing structure in order to improve its capacity to attain cost advantage.
Reference List
Altekar, R 2005, Supply chain management: concepts and cases, Prentice-Hall, New Delhi.
Boston Consulting Group: Success factors for winning the rising auto markets 2014, Web.
Das, K 2014, Globalisation and standards: issues and challenges in Indian business, Springer, New Delhi.
Fickling, D 2014, Australian car manufacturing faces extinction with Toyota exit, Web.
Ingrassia, P 2009, Toyota is not immune from the recession, Web.
Liker, J 2006, The Toyota way field book; a practical guide for implementing Toyota 4Ps, McGraw-Hill, New York.
Lowry, W 2014, Why companies like Toyota lead in global automobile market share, Web.
Mukai, A & Horie, M 2013, Toyota forecasts profit will rise to highest in six years, Web.
Nikkei Incorporation: Japanese automakers must keep pushing forward 2013, Web.
Soble, J 2014, Toyota recall of cars with takata airbags, Web.
Statista: Toyota operating income from FY 2008 to FY 2014 in million yen 2014, Web.
Tripathi, P & Reddy, P 2008, Principles of management, Tata McGraw-Hill, New Delhi.