Executive Summary
This report encompasses the strategies of giant auto manufacturer in the world ‘Toyota Motor Corporation’ and it concentrates on the historical background of Toyota, strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, threats, PESTEL factors, BCG Matrix, Ansoff Matrix and competitive model analysis, overview of Toyota strategy and turning strategic viewpoints. The paper also focuses on the visions of Toyota, its significant strategies for environmental sustainability, and strategies to maintain relation with customers, and strategies to motivate and manage the employees. In addition, the paper would analyse Toyota’s strategies to assure high quality products and to work with global community, as well as discussing the regional, product, business level, financial, supply chain, and market entry strategies.
Introduction
Stewart and Raman (2007) added that the way of evaluating the Toyota complete cars and vehicles including its technical problem where the simple quality checking by the workers could identify any defect or rejected products that could easily traced out along with the TQC controller rather than quality checked by machine and suggest to the senior technicians for rework. Today’s tremendous success of Toyota Motor Corporation has derived from the company’s technological soundness and commitment, at the seventeenth birth anniversary of Toyota in 2007 the company introduced commercial hybrid vehicle Prius that contributed sales revenue of US$ 9.34 million within a year. Compared with GM and Ford 2007, the aggregate profit of Toyota after tax was US$ 13.7 billion when GM faced a loss of US$ 1.97 billion and Ford accounted a negative accounting of US$ 12.61 billion, in the same period, the market capitalization of Toyota was US$ 186.71 billion when GM accounted US$ 16.60 billion and Ford US$ 15.70 billion. Toyota’s success story derives from the prolonged hard work and strong commitment from the part of the top- level managers, human resources working in various departments starting from research and development, production, and customer care, as well as the leaders of the this global giant.
Historical Background of Toyota
Table 1: – Overview of the company
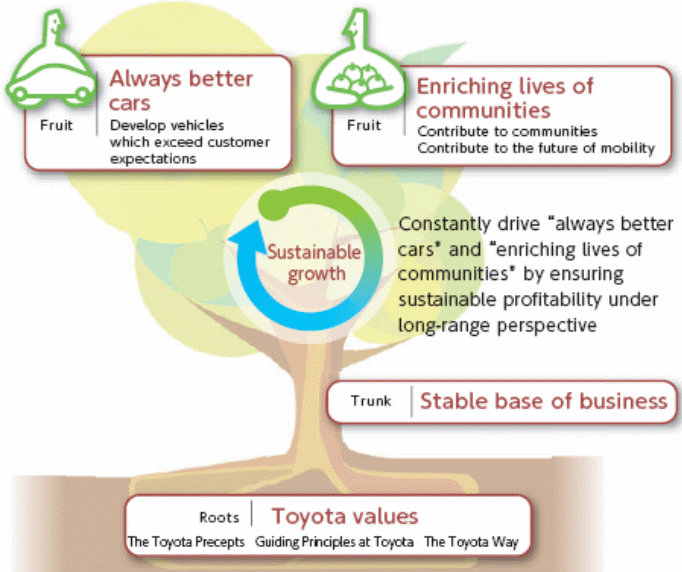
Visions of Toyota Motor
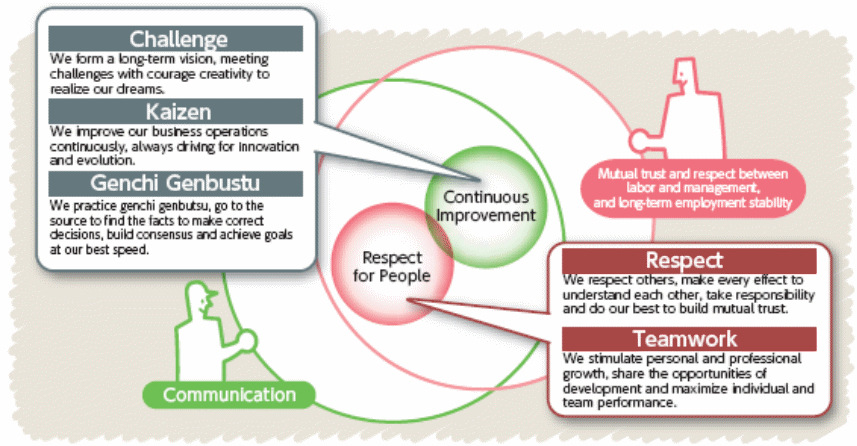
According to TMC (2011), the key vision of this global giant is to attain the long- term goal of steady growth in synchronization with the atmosphere, the international financial system, and the neighbouring societies, and to serve its stakeholders as a whole; it believes that this will lead the company towards future mobility, elevating the lives all across the earth. It also has a strategy to generate exceptionally atmosphere-friendly cars for sustainable growth by complying with the laws, traditions, and cultures of all countries and focusing on consumer first, respecting people, as well as focusing on continuous improvement and innovation to ensure that clients obtain the best-quality service that would help increasing its repeat-sales, and build and boost the team. The follow figure outlines the key factors, which compose the core visions of the company in order to indicate what are the main strategies in which it focuses on –
SWOT analysis of Toyota Motor Corporation
Strength
Strong brand image and Financial Position: Toyota Corporation has well-built brand awareness and it is one of the major competitor in the automobile industry, which has financial competence to fight with other car manufactures in local and foreign market by implementing its core business strategies; according to the annual report 2011 of Toyota, its current key financial variables are –
Table 2: – Financial information of Toyota Motor Corporation
Net income of the company has increased from the last years though total assets has decreased as well, nut it should note that Toyota failed to make profit in the fiscal year 2009
Labour force: Toyota Motor has more than 325,900 efficient and dynamic staff to produce quality products and successfully operate the business in unfavourable financial position and sustain as a market leader in economic crisis; however, all the employees are highly qualified, talented and skilled in their own field to give best service or innovative products for the customers;
Experience: As Toyota Motor established in 1937, it has a extensive experience to carry out selling all over the world (has presence in more than 170 countries) with strong brand image; in addition, the employees and management teams work with integrity
Market Share: Toyota is the leading automotive-manufacturer in Japan and Rowley stated that this company has effectively captured 50% of total market share in Japan (Rowley, 2007); however, yahoo finance reported that Toyota was the world’s third largest car company in the fiscal year 2000; the following table demonstrates the market share of Toyota in Japan –
Table 3: Market share of Toyota in Japan
JESDA (2011) reported that Toyota is the second largest company in terms of sales volume in the US automobile industry and it has already captured 17% market share, and gradually strengthen its position by capturing the market share of the General Motors, for example, the shares of Toyota and Honda climbed by 18.3% to 26.2% from 1990 to 2004. However, JESDA (2011) provided following estimation –
Product Line: According to the annual report 2011 of Toyota, this company concentrated on the product diversification to minimise business risks, for instance, Toyota Financial Services aims to ensure stable profit margin; in addition, it has many other products in the motor vehicle segment; however, next figure shows Overview of Toyota’s Financial Services Operations –

Performance of Subsidiaries: In addition, it has many regional subsidiaries, such as, Hino Motors , Ltd. (produces large trucks with a gross vehicle), Daihatsu Motor, Toyota Auto Body, Toyota Tsusho and wholly owned subsidiary “Toyota Financial Services Corporation” (provides a range of financial services) and many other subsidiaries those performance help to increase profit in consolidated financial statements.
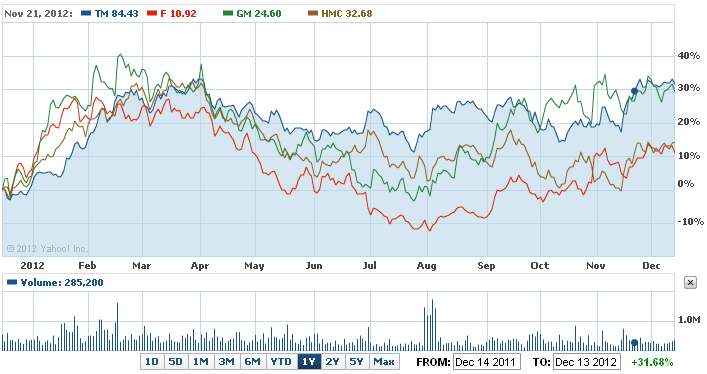
Performance of Toyota in Stock Market: – the historical share price of this company was not enough adequate comparing with these figures of the competitors, but the stock price chart of Toyota has demonstrated that the stock price is increasing slowly and it is in steady position and after adverse economic conditions, it regained its position once again–
Weaknesses
Production: There are few weak points of Toyota, such as, it has many subsidiaries those produce cars for the market with their own design and materials; therefore, testing and evaluating the design and operating effectiveness need to consider for minimizing any risk related with production and operational system.
Other Issues: The main requirement of huge investment, fixed expenses, extreme cost for training and development of employees and capitalization are significant factor to put extreme pressure on any auto manufacturer like Toyota;
Opportunities
New Brand: Annual report 2011 of this company presented that Toyota has opportunity to produce more environmental friendly model to increase market share in the US and Chinese automobile industry because Toyota has gained emotional support of community for the production of Prius model while adoption of sophisticated technologies has reduced the consumption of oil is responsible for improving sales.
CSR: Toyota has scope to contribute for the social and environmental development as their corporate responsibility program, for instance, it can arrange a number of awareness development program and introduce more hybrid fuels, electronic cars, and Eco- vas for the young generation;
Other: It has opportunity to expand business in the global market particularly in highly populated regions by adopting international strategy and decreasing logistical troubles, reduction of business operation for earthquake 2011 in Japan, and diminish the corporation’s operations budget (Funaru, 2010)
Threats
Competitors: Berthhiaume, Joshi, Longdo and Seshadri (2007, p.36) stated that Toyota has to compete with many direct and indirect auto manufacturers at both national and international market, for example, the main competitors of Toyota Motors are Honda, Ford motors, Chrysler, Nissan, Mitsubishi, Land Rover, Toyota, and BMW; in addition, indirect competitors include Phoenix Motorcars, Zap Cars, Mercedes Benz;
Currency and Interest Rate Fluctuations: According to the annual report 2011, the consolidated financial statements of this company represent in Japanese yen; therefore, changes in foreign currency exchange rates can influence its pricing of products sold and equipment purchased in foreign currencies; in addition, strengthening Japanese yen against the US dollar can have an unfavourable impact on its operating results.
The downturn in the financial markets change customers’ purchasing power, a number of financial institutions and investors face difficulties, affect on Toyota’s ability to raise the essential capital under proper conditions on a timely basis, boost in prices for raw materials (steel, precious metals, non-ferrous alloys, aluminum, and plastic parts) that Toyota and its suppliers use (Toyota 2011, p.36).
PESTEL analysis
Political factors
Several political factors exist in the markets that often adversely or favourably affect the automobile industry, including the operations of Toyota Motor Corporation and other industry giants. For example, there are certain governmental policies in different countries like India and Middle East, such as unfriendly taxation rate or excessively complicated regulations for the operations of foreign automobile companies, enactment of unfair autocratic laws, or incentives provided to local companies in order to protect them. All these factors may pose problems for the international automobile market players; however, in case of doing business in European member states, the EU ensures that such actions are prevented and that the member states are compliant with the EU-laws. On the other hand, governmental decisions may be favourable where they implement free trade policies, join the World Trade Organisation to ensure low tax burden imposed on foreign market players, etc. However, unstable political conditions, such as strikes in overseas markets could be great threat for the company, even though the political conditions of Japan is quite stable and the government of the country tries to afford the highest business friendly environment to all its industries with a view to raise the GNP. Most importantly, the government of the country always encourage and assist the growth of the local and international Japanese companies.
Economic factors
The global automobile industry is recovering gradually after the global financial turmoil, which means that new opportunities are arising again for the industry giants like Toyota, Ford Motors, General Motors, Honda, BMW, etc. It is notable that the global automobile industry could be influenced by alterations in demand, increasing inflation rates, uneven interest rates, fluctuating exchange rates, rising taxation rates, and more significantly, by global financial downturn, which has already contributed to lower expansion rate of the industry. According to the New York Times report, the impact of global financial crisis over Toyota was quite harsh, as it had observed its first loss in its 70 years history; most importantly, it took a significant time for the company to recover from the crisis (Fackler, 2008). However, Fackler (2008) also suggested that many other giant players of the global automobile industry are present, who had equal or even more significant adverse affects on them by the crisis in comparison to Toyota.
According to Reuters (2012), the basic chart of the company suggests that although there was a slump in the stock prices in 2009, after several fluctuations, this has recovered gradually and since December 2012, it is moving forward with a very optimistic trend. However, due to the tsunami in Japan in 2011, certain damages were caused to the plants of the company and the profits of the business reduced to some extent.
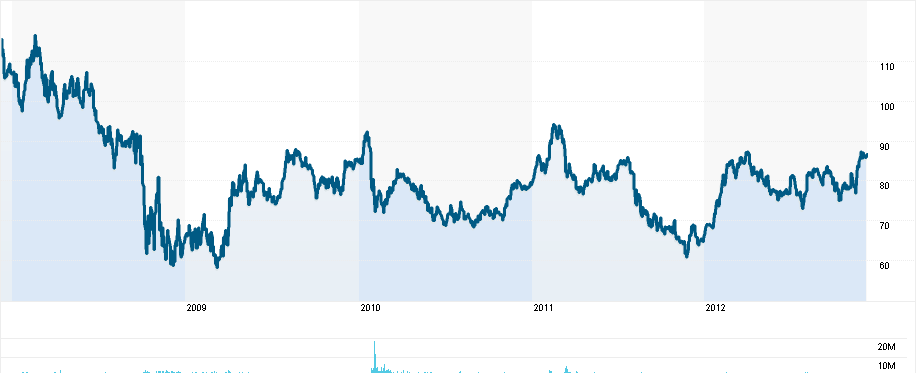
Socio-cultural factors
The market players of the global automobile industry have included their respective corporate social responsibility plans in order to make sure that they are carrying out ethical businesses and contributing to communities.
Toyota Motor Company is committed to ensure the highest level of satisfaction to all its stakeholders, including its employees and the local communities. It believes that it is socially responsible to reduce its adverse affects in the environment by introducing more and more eco-friendly production procedures. It also induces its shareholders, partners, suppliers, and other associates to care and to stay beside the neighbouring communities. It possesses a formal code of conduct and ethics policy that gives a direction to every single subsidiary about the type of culture that the group promotes in order to comply with the environmental laws.
Technological factor
The global automobile industry is profoundly dependent on the uses of technology and so the market players need to keep up with technological advancements in operations and in making new and innovative car models. In addition, because of decline of sources of natural energy resources, currently the global automobile industry is moving towards renewable energy sources, such as, hybrid technology, electricity, and nuclear technology. However, because of changing customer preferences and increasing public awareness, technologically Toyota Motor is in challenge with low demand for petrol cars and high demand for hybrid technology cars in certain market, forcing the company to move towards adopting hybrid cars like Toyota Prius. According to Annual Report (2011), Toyota wants to exceed consumer expectations in markets such as Europe, China, North America, Asia and Oceania, Japan, Middle East, Africa, and Latin America by integrating leading edge technologies in order to generate new value in car models, high-tech-infrastructure and superiority; the following figure shows how the company wishes to integrate technology in different countries:
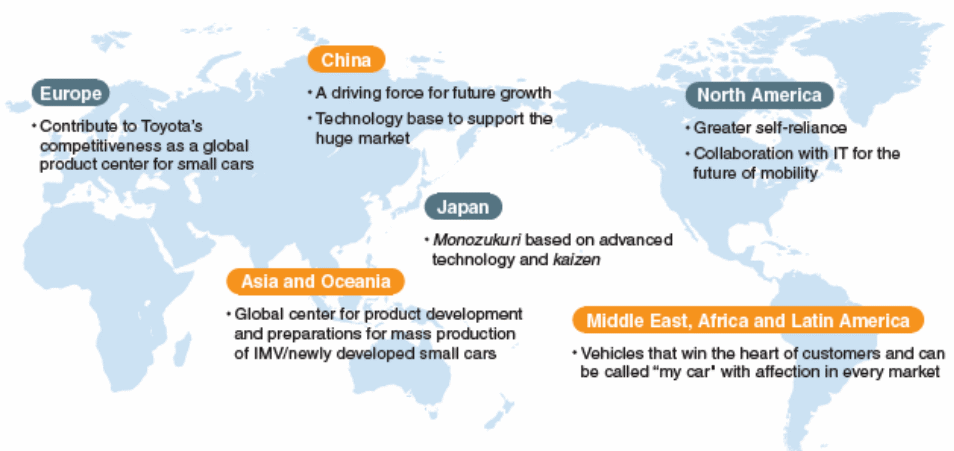
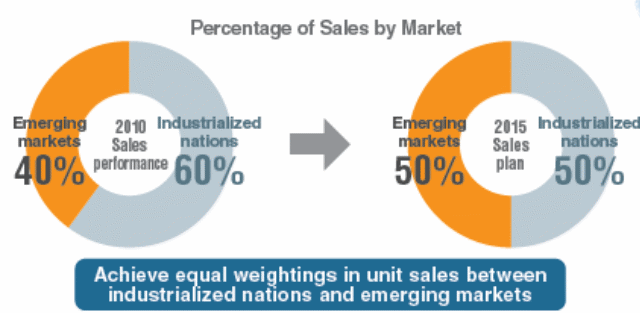
By integrating such diverse technologies, the company plans to achieve an equality in the sales figures in the developed and the developing countries; however, the following figure shows that presently, Toyota is getting 60% sales in developed and 40% sales in developing countries –
Environmental factor
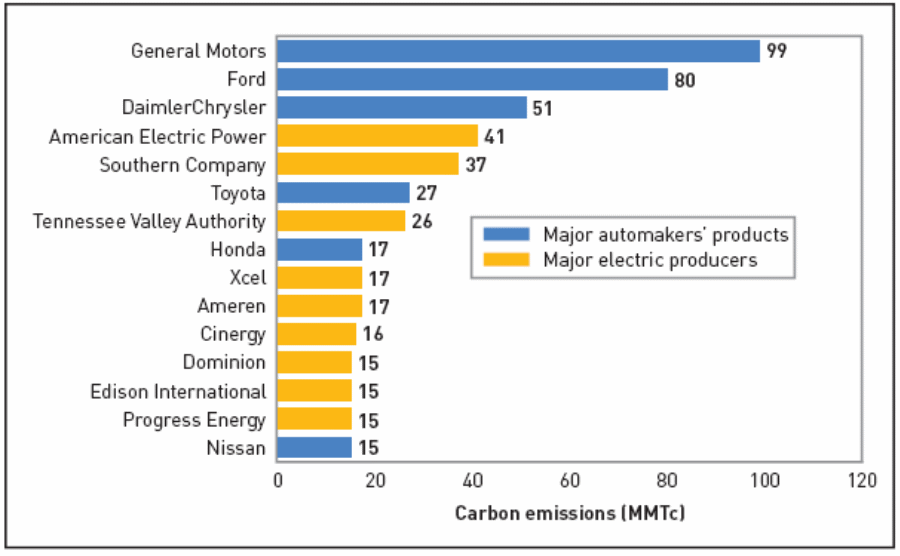
Mikler (2003) has pointed out that the global automobile industry needs to strictly comply with all the environmental laws and make sure that the emission of CFCs are lower; moreover, companies like Toyota need to use fuel efficient engines. On the other hand, DeCicco and Fung (2006) noted that different companies emit different levels of
CFCs, the following figure shows the comparisons of the CFC emissions of a number of firms in order to assess and compare how much Toyota Motors pollute the environment in contrast to the automotive industry –
Legal Factors
According to Mikler (2003), the global automobile industry is subjected to numerous rules and regulations; so, being one of the major players of the industry and operating in all the continents across the world, Toyota needs to obey all rules of the industry. Toyota thoroughly complies with the laws of the countries in which it operates; these include, for example, employment legislation (such as working-time and minimal wage-rate), health-safety-legislation, customer safety legislation, and so on; therefore, the company is expending further by spending more on health-insurance and focusing more on ensuring employees rights across the business by assuring fair pay and other benefits.
Porter’s Five Forces Model
Threats from new entrants
Threats from new entrants are reasonably low in the industry because of a range of obstacles to enter the market, and difficulties to operate with efficiency, expertise, and profitability and also to carry on the business; moreover, new entrants more often lack adequate finances, proficiency, satisfactory knowledge about specialized car manufacturing methods, and skilled personnel. On the other hand, global financial crisis made it difficult for the new entrants to collect sufficient capital to inter in the market though there are few companies like to take the opportunity to enter new market in adverse economic condition; in addition, such new players could face troubles to expand business in new countries because of adverse governmental policies regarding new foreign firms. However, many other factors exist that influence the new entrants of this industry, which are listed in the figure below along with the indication of whether or to what extent those factors are strong or weak –
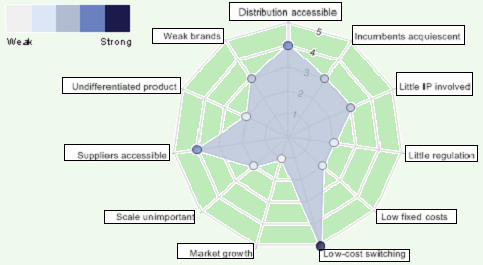
From the figure above, it is noticeable that the new players face the problem of low cost switching to a strong level, although the problem of market growth is low
Bargaining power of buyers
It has already notified that there are a number of automakers are operating the business in global market; therefore, the switching off costs of the buyers is relatively higher than any other industry sectors; furthermore, the client loyalty is also not considerably perceptible in the adverse economic condition though leading companies sustain with glorious success at present. This power depends on following factors –
On the other hand, the bargaining power of the buyers depend on several factors in the global automobile industry, such as, product differentiation, buyer independence, price sensitivity, and so on; however, this scenario is different for the large companies like Toyota because of brand awareness of the products; nevertheless, the next figure demonstrates drivers of customer power of this industry –
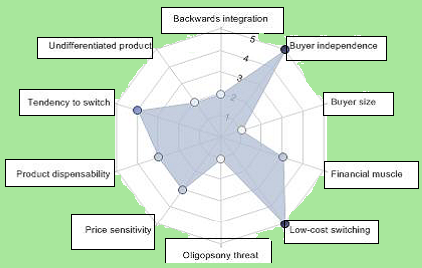
Bargaining power of suppliers
In Japan, bargaining power of local suppliers fluctuates in accordance to differences of quality and price; on the other hand, there are many companies available to offer raw materials to Toyota and other automakers, which help to reduce bargaining powers in this case. Nevertheless, the following figure discusses the key driving force of the suppliers in the industry –
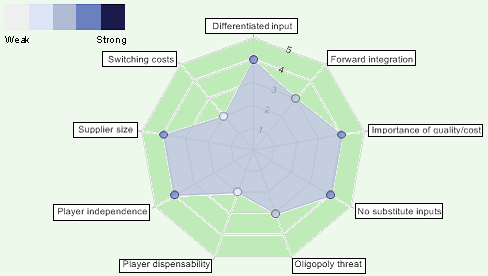
Threats of substitute products
The vehicles of Toyota require contending with several similar quality products from the rival firms; for instance, the hybrid cars of Toyota need to compete with the hybrid cars of Ford, Honda, Hyundai, and GM, where as its motor cars also compete with those rival brands. On the other hand, Capon and Berthiaume (2007) further stated that the customers have the opportunity to choice different transportation system besides automobile, for instance, train is low cost transport, which become more popular nowadays;
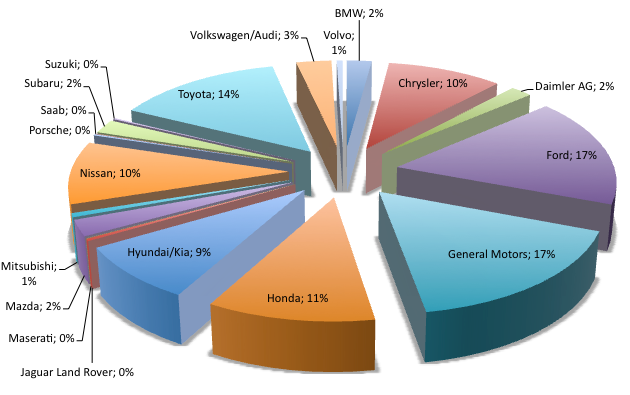
Rivalry among existing firms: Consistent with the annual report 2011, the world automaker industry is highly competitive because of many substitute products of different companies and all of these firms change their strategies to increase its market share; however, the following figure compares the position of Toyota Motors with other direct competitors –
Figure 4: Direct Competitor Comparison
On the other hand, all the potential companies have tried to introduce new products like environment friendly cars to sustain in the market by influencing more customers and increase market share, so, Toyota selling of hybrid cars in compared with other market players can be shown as-
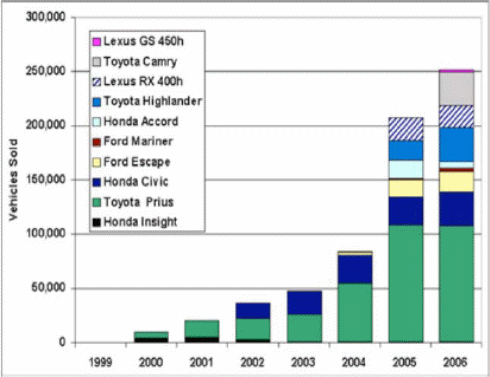
Overview of Toyota Strategy
Sugata (2012) pointed out that the strategic control of the headquarters has seriously threatening its Asian operation in different countries with unethical business policies and practice that has generated unrest and uncertainty among the management and workers of Toyota in this region. For instance, Toyota is not planning to shutdown it
Philippines operation, but the headquarters sent a literature of another rival company describing the way in which Ford is reducing its Plant in Philippines and at the end of this message the headquarter directed the president of Toyota Philippines that if he fail to reduce cost effectively, he must be sacked. The head of Toyota Philippines reacted that it is a matter of proud that the rival company is collapsing its operation, but it is not ethical for Toyota Corporation to pressure its Philippines counterpart for cost reduction but simultaneously increase donation for housing project for indigenous people in Santa Rosa city, Philippines. The brutal behaviours of the Toyota Corporation has made its management and employees in Philippine arrogant where most of the members of the management team has aimed to left the company considering that the they need to find out the alternative way out of survival while living on hands to mouth is better than going with Toyota.
Turning Strategic Viewpoints of Toyota
Toyota along with other Japanese automakers penetrated into the US market during 1964, with a steady market growth rate it occupied around 40 % the US automobile market that has seriously injured through the downturn caused by global financial crisis come into evidence in September 2007 that global economy failed to overcome, thus Toyota needs to introduce with effectual strategy. ILO (2010, p-21) pointed out that the global financial crisis hits the automobile industry with destructive effects where all the automakers globally lost their double-digit sales revenue and Toyota evidenced operating loss for the first time in the history during the last seventy years, moreover, tried to sustain in the market with remarkable lose by few major reengineering their strategy. The recessionary strategy of Toyota responded to encounter with the situation with best sharp tools of job cut and cost minimization in order to sustain them in the market until the global economy get back its standard movement and market potentiality that would lead the customer to choice Toyota products.
Moreover, the recessionary strategy of Toyota deliberately grounded to utilize the retraining officials instead of new employees who required enough training, and the company applying this strategy in every production facilities of USA, Japan and Europe, at the same time worker whose performance is not satisfactory, must be targeted for early retirement. Weakening strength of the unions of Toyota production facilities and global character of the crisis that prolonged for several years and failed to demonstrate with any positive impact through the governmental bailout or rescue package, strategic actions carried out by Toyota is the appropriate measure to sustain the company during the period through reduced working hours with reduced wages.
Toyota Motor’s Market Entry Strategies
In 1960s, Toyota adopted nation-specific-strategies to enter overseas markets; as Brazil was an emerging-country, Toyota took this chance to enter the market with its 4WD-Land-Cruiser; however, for entering Thai market, it made joint venture with one of the car manufacturers of Thailand; moreover, it had undertaken globalization strategy to expand in the US and other Latin American countries (Scribd, 2012).
Funaru (2011) pointed out that the most effectual strategy that Toyota always adopt in its international expansion is the Japanese ‘KAIZEN’ strategy that indicates continuous efforts for improvement of the degree of product quality productivity and competitiveness, it is a combining strategy that incorporate the cross-functional strategy, steady progress, non-stop action for quality, by direct participation of all staff.
On the other hand, the product strategy of Toyota has based on elevated quality to emergent new innovative technologies connecting with the outcomes of further research and creativity, hard work that contributed the company to be the pioneer of the automobile industry with leader advanced automotive technologies of the Toyota Corporation that gathered intelligent responses for future generations.
Toyota Motor’s Significant Strategies for Environmental Sustainability
TMC (2011) has pointed out that the company has undertaken several strategies to ensure that the ecology is not hampered in any ways while it carries out its production process or other marketing activities. The firm’s key strategy is to invest more on ecologically friendly solutions throughout its operations in order to lessen the impact of its cars in the ecology. As a result, it is important to note that the business, from the last five or ten years, is striving a lot to bring out ecologically friendly or green cars with hybrid technology. Such cars are made so that there is lesser emission of dangerous gases to the air when the customers use those. Because of fuel- efficient engine and certain other special differentiations, the company became able to create a high demand for these cars in numerous European markets. In addition, increasing public awareness regarding ecological pollution and other related concerns coupled with the strategy of impressive advertising campaigns by the firm has made these hybrid cars very profitable. However, the following figure shows the entire framework of the ecological action plan strategy of the company in order to explain the idea in detail –
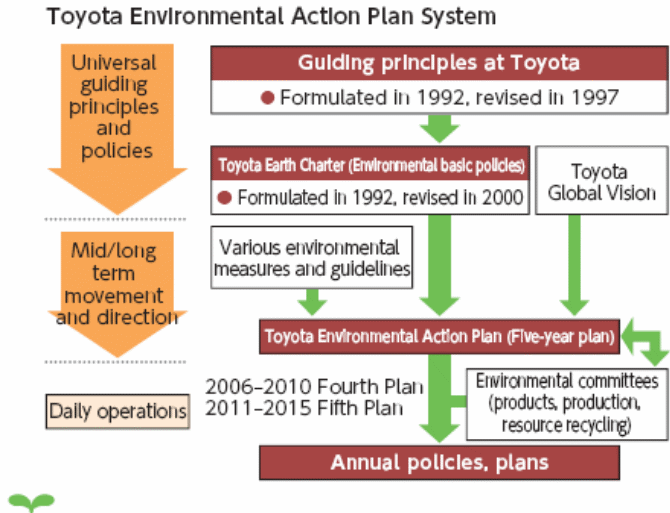
On the other hand, the firm has also implemented several strategies to ensure that its contribution towards the aggregate global warming is significantly lower than that of the other car producers, so that it can assure its customers that if they help increase the sales of the company, it would not mean that its rising car productions would increase pollutions. In order to turn this idea into reality, the firm has impressively increased its fuel efficiency of car engines, lowering its polluting car production. For example, the following figure shows that the firms was able from 1997 to 2010 to significantly raise fuel efficiency in the Japanese market –
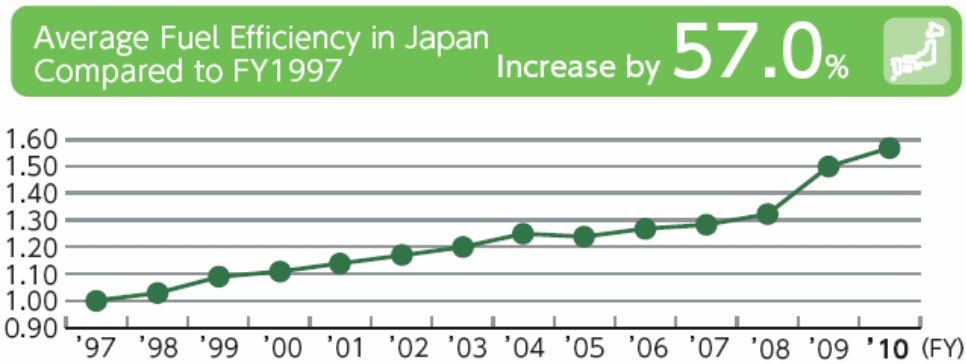
In addition, the firm has also remained successful in considerably increasing its recycling facilities in order to make sure that the old or redundant cars of the firm are not thrown away to the earths crust for polluting the ecology, but instead, those are recycled into new vehicles. The following figure explains that the firm has received excellent rate of vehicle recycling as well as ASR recycling from 2006 to 2010 period as a whole –
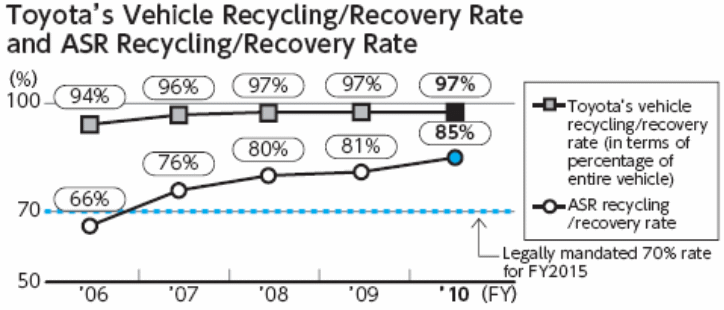
On the other hand, the firm has also successfully executed its strategy to lower carbon dioxide emissions; most importantly, it is essential to state that the firm was able to lower accumulated carbon dioxide emissions by 19 million tons from 1997 to 2010; the following figure clearly illustrates this point –
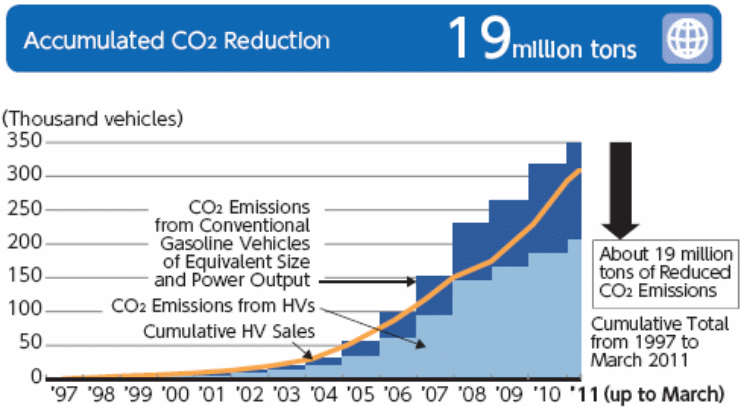
The following figure shows the key strategies of the firm for environmental sustainability
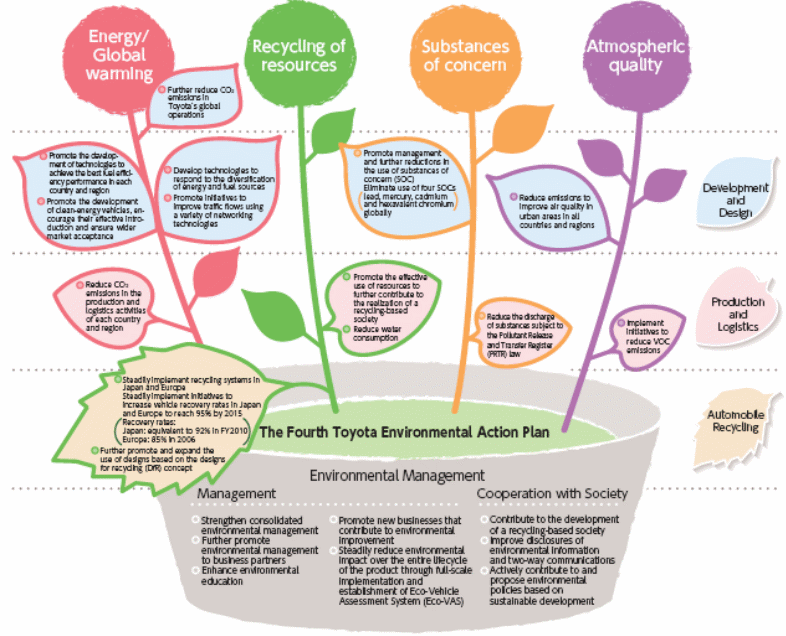
Toyota Motor’s Strategies to Maintain Relation with Customers
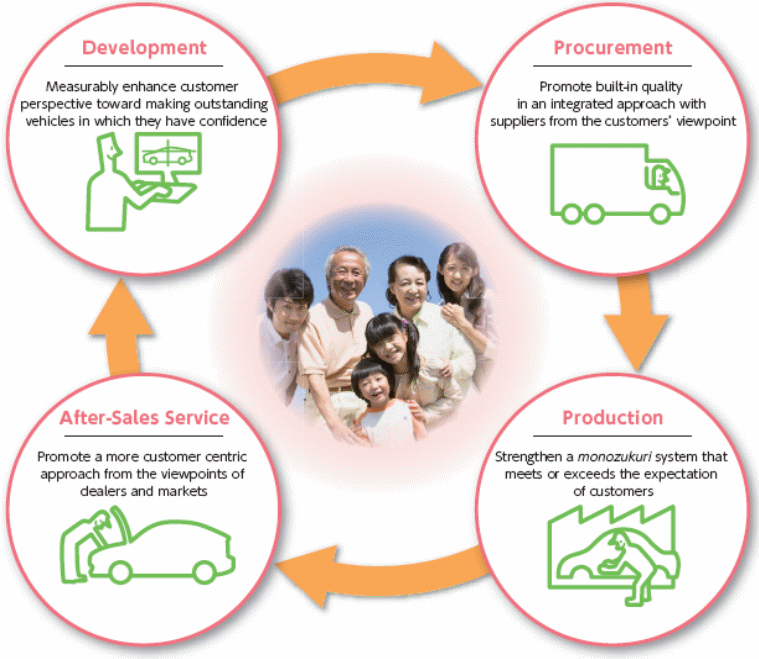
In order to manage relations with customers, the firm has the strategy to obtain clients’ personal assessments and viewpoints so that it can modify the areas of the business where the client has complaints. In addition, the firm also has the strategy to clutch changes in their demands, continually inspecting for conventionality with its values, and performing speedily to solve inconsistencies; clients’ viewpoints are then promptly communicated to all correlated business units and branches in research and development, production, and sales where those are treated as helpful suggestions for product planning and raising product-quality. To implement its CRM strategies, the firm has formulated a Customer-Relations-Division, which is the hub where the firm can directly get in touch with customers for satisfying their needs; this section stresses on the viewpoints of individual clients by consulting with them and treating their grievances swiftly to improve their satisfaction; it handles around 200000 customer grievances on average annually. Starting from development and procurement, to production and after- sales service, the firm applies it highest efforts to satisfy the clients from all spheres; the following figure shows how the firm achieves this in detail –
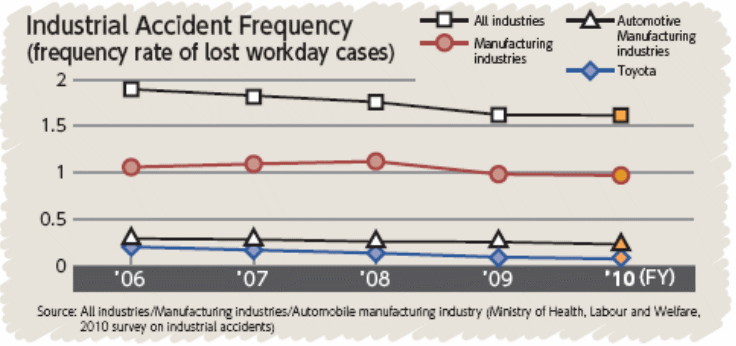
On the other hand, as part of Toyota’s strategy to lower customer complaints regarding accidents, the firm has taken proper initiates to lower the accidents frequencies significantly. The following figure shows that from 2006 to 2010, the accident frequencies are lowered in a way so that it has now in the lowest position in terms of accidents in comparison with the rest of the industry –
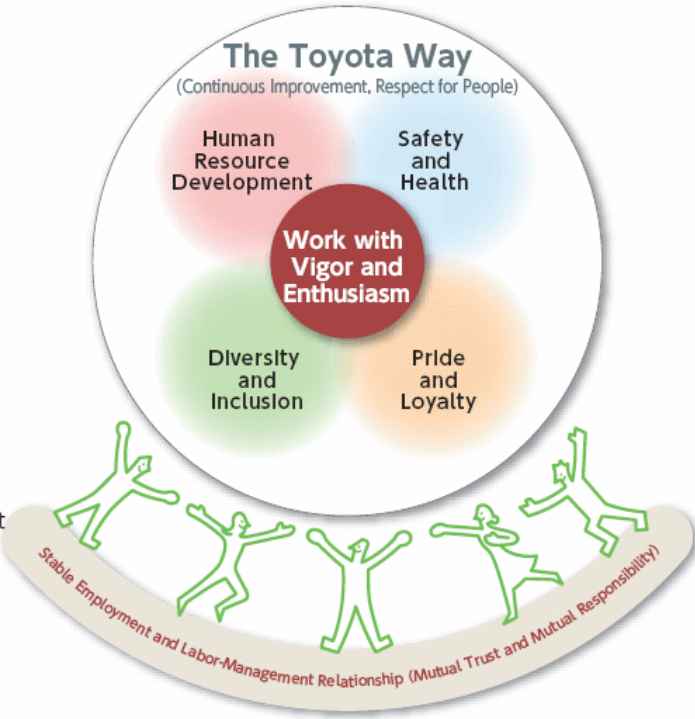
Toyota Motor’s Strategies for Motivation and Management of the Employees
In order to motivate and manage the employees, the firm has strategies of human resource development, health and safety assurance, diversity and inclusion within the workforce, as well as the pride and loyalty development on the part of the workers because of very low staff turnover rate (Ward, 2002). The figure below shows the strategic framework of the firm to handle the employees further elaborately –
Strategies to Assure High Quality Products
Toyota executes the smartest strategies from development and procurement to production and after- sales service to ensure the product quality by several methods like modifying the faults on the products instantly after detection (EDER, or early detection, early resolution), carrying out standardised production process, and enhancement of drawing necessities, and so on. The following figure shows the detailed strategic circulation to assure high quality products –
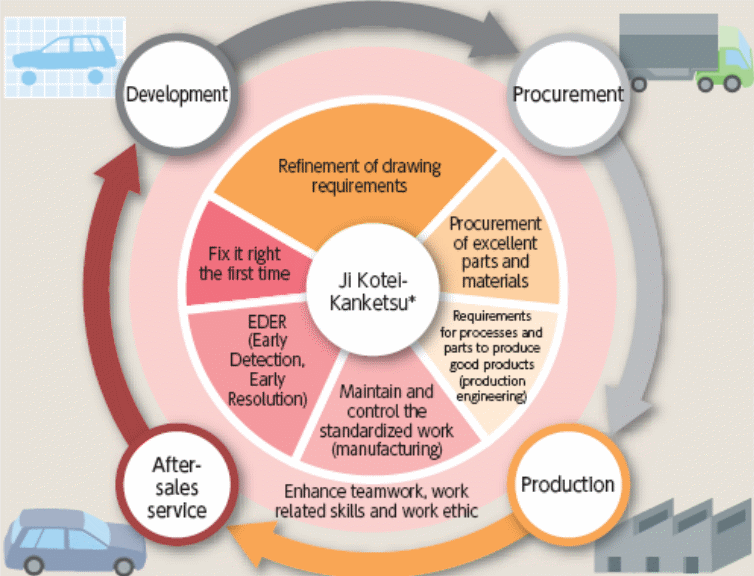
Most importantly, a number of strategic tools are present that the firm uses to assure high quality products, which, for example, include the idea of continuous improvement, adaptation of a lean manufacturing system, implementation of Kaizen and the TQM approach; however, this is outlined briefly in the figure below –
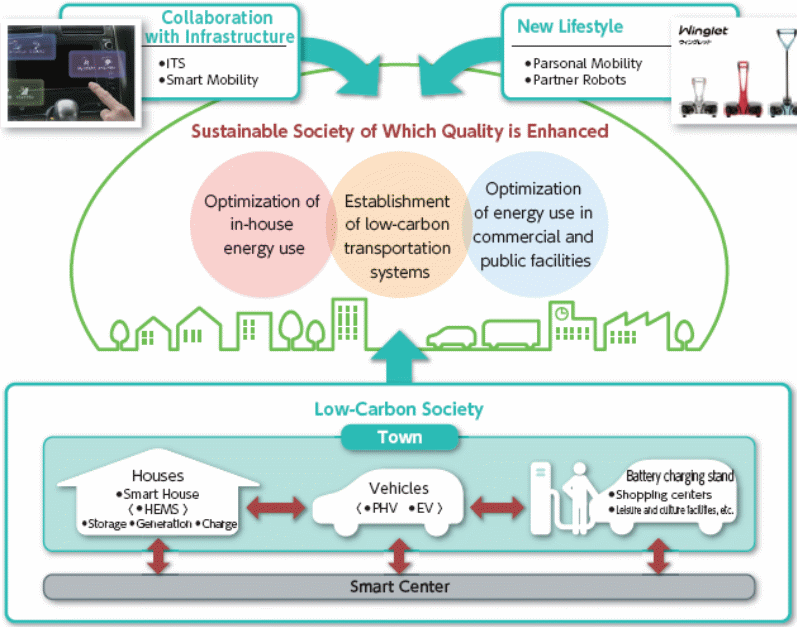
The Strategy to Work with Global Community
The corporation aligns with the global communities through the following strategies
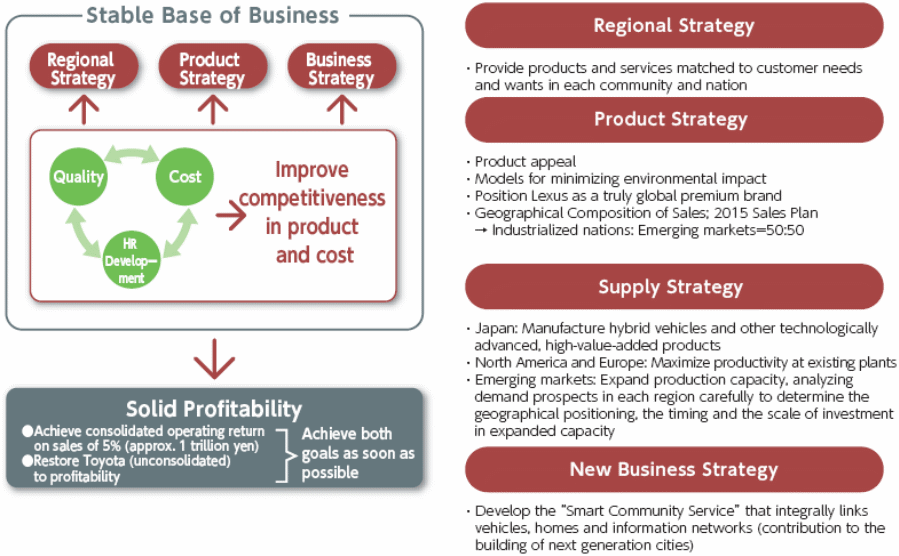
Regional, Product, Business Level, Financial, and Supply Chain Strategies:
For the long- term growth and sustained profitability, the corporation has certain regional, product based, business level, financial, and supply chain strategies; the following chart broadly analyses these strategies.
Labour Management Strategy
Dobi and Bugár (2008) argued that next to the few decades of World War II, the US technology and management engaged to propagate its supremacy over Japan, as Japan has faced defeat in the war, but the advanced management system of Japan proved its supremacy by introducing Total Quality Management (TQC) instead of US Quality control system. At the same time, the US statistical quality control techniques that generally works from the to the ground- the employees required to follow the manual given by the headquarters, on the contrary the Japanese TQC urged to talk with the ground level sales staff first with strong emphasis on the inputs provided by the workers for aggregate system. In fact Japanese management system that the Toyota put into practice through has integrated with TQM that provided enhanced scope for the Toyota workers to keep their valued opinion at the process of factory management including their labour management.
Toyota considered that the Conflict-free labour management could assist to overcome the difficult times of financial crisis along with all the active overcapacity of production could be postponed by painful cutting at the number of employees that may lead to the temporary conflict resolution process in the automotive industry during the crisis. In context of labour management strategy, Toyota has replaced the traditional workplace model and turned the relationship of worker and management into a social contract integrating with the local labour law and company act that enhanced wider opportunity for the investors to evaluate the offerings before investing on that company which has clear findings at this connection
Segmenting strategy
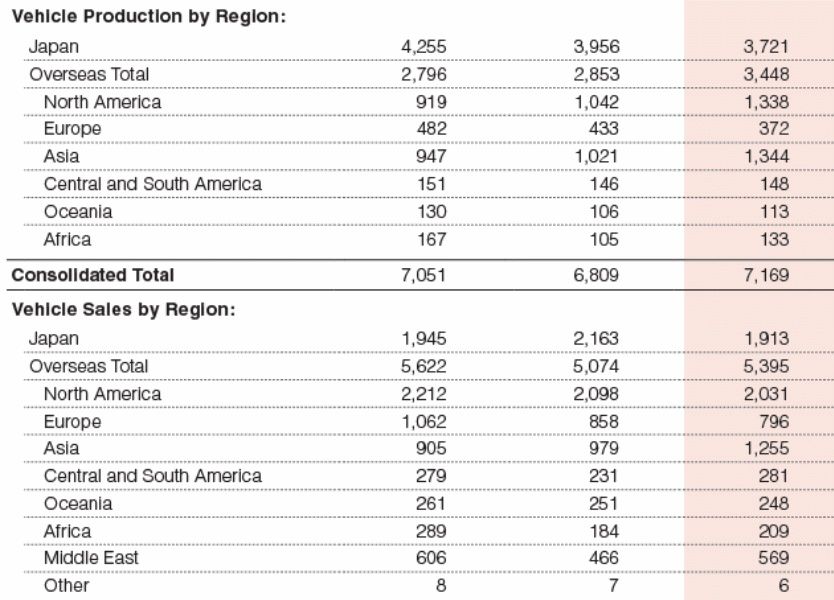
According to this strategy, the marketers divide the markets for smaller groups of buyers considering distinct needs, characteristics, and behaviour; however, Toyota generally follows geographic, demographic, and behavioural segmentation, for instance, Toyota has business operation in Japanese, North American, European, and African; however, next figure shows more details about vehicle production and sales by region –
According to annual report, Toyota has segmented the market considering age limit, family size and life style, income level, profession, nationality and other ways; it also concentrated on the demand of the markets, benefits sought, user status, and loyalty status to segment the market.
Targeting strategy
Different people in different regions like to purchase different models considering demand, choice, and financial position and so on; thus, the product line of Toyota designed considering different people, for example, it produces hybrid car Prius and gas-guzzling SUVs for the conscious people who need environmental friendly car and can afford low fuel cost for safer and best quality cars.
BCG Matrix for Toyota
Hitt, Ireland and Hoskisson (2001) argued that BCG matrix is a portfolio planning process to assess the company considering relative market growth rate along with relative market share; however, Toyota occupied the star position in the matrix and the following figure shows in this regard
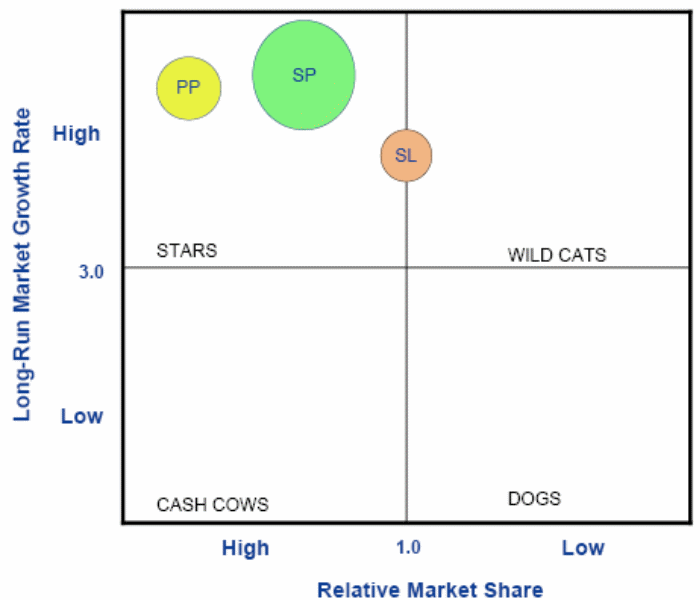
Capon and Berthiaume (2007) stated that important features of the products of Toyota are quality, speed, price, and durability position for which most of brands of Toyota (especially Prius Plus, Sparky and Sparkilicious) experienced huge success in the global market though it is very difficult for any other automobile manufacturer to hold such a strong position.
Ansoff Matrix for Toyota
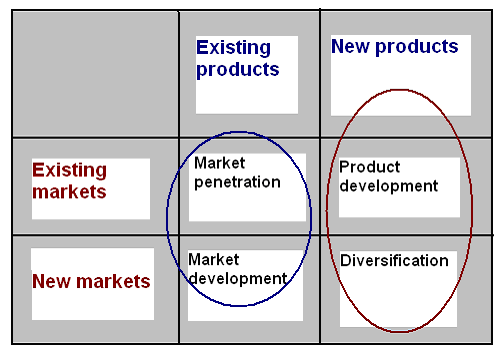
Table 5: – Ansoff’s model for Toyota
Conclusion
This report has analyzed the strategic evaluation of a leading company of the world automotive market – Toyota, which manufactures a wide of differentiated motor vehicles and undertakes various marketing and sustainable strategies to meet market demands and satisfy the target customers by providing safer and quality products at affordable price. From the above discussion, it can be said that business environment is unfavourable for maximizing profit margin because of having many challenges including global economic downturn, earthquake in Japan, volatility of the price of raw materials, and change of exchange rate have forced the company in sacrificing a greater portion of revenues and market share in 2009. However, this paper described that automobile industry is extremely competitive industry due to presence of several strong competitors in the global market, which creates pressure on Toyota to change its strategy over time to hold market share, such as, it introduced a number of eco-friendly hybrid products, and followed different brand expansion strategies including joint venture to enter prospective market.
Reference List:
Berthhiaume, R. Joshi, B. Longdo, E. & Seshadri, V. (2007) Toyota Marketing Strategy for Plug-in Hybrids. Web.
Capon, N. & Berthiaume, R. (2007). Toyota Marketing Strategy for Plug-in Hybrids. Web.
DeCicco, J. & Fung, F. (2006). Global Warming on the Road. Web.
Dobi, S. & Bugár, L. (2008). Japanese Management Strategies. Web.
Fackler, M. (2008). Toyota Expects Its First Loss in 70 Years. Web.
Funaru, M. (2010). Toyota’s Business Strategies in International Markets. Web.
Glukhova, O. (2009). Applied Strategic Management: Toyota Motor Company (Japan). Web.
Hitt, M. A., Ireland, R. D., & Hoskisson, R. E. (2001). Strategic Management. South-Western Thomson Learning.
ILO (2010). The Global Economic Crisis Automotive Industry: Trends and reflections. Web.
Johnson, G., Scholes, K. & Whittington, R. (2008) Exploring Corporate Strategy: Text & Cases. New Delhi, Prentice Hall.
Mikler, J. (2003). The International Car Industry And Environmental Sustainability: Moving Beyond ‘Green-Washing’. Web.
Reuters (2012). Toyota Motor Corp (TM). Web.
Rowley, I. (2007) Toyota set to top 50% market share in Japan. Web.
Scribd (2012). International Entry Strategies. Web.
Stewart, T. A. & Raman, A. P. (2007). Lessons from Toyota’s Long Drive: An Interview with Katsuaki Watanabe. Web.
Sugata (2012). A Seam Is Seen Gaping in Toyota Global Strategy. Web.
TMC (2011). Sustainability Report. Web.
Toyota. (2011). Annual report 2011 of Toyota Motor Corporation. Web.
Ward, D. (2002). Toyota: Core and Diversity Strategy. Web.