Abstract
Tiffany is a popular company that deals with the manufacture and sale of jewelry products across the world. The company has established its market in the United States and other parts of the world, such as Japan. However, the rising costs associated with externalities in the marketing environment are affecting the growth of the company. Since an internal and external analysis of the company explains the need to engage in marketing, diversification, and rebranding of its products so that it can counter competition and technological advancements.
Introduction
Tiffany is a jewelry company founded by John Yong and Tiffany Charles, and it commenced its business in 1837 as an organization that dealt with the sale of fancy items and stationeries. In 1853, the company shortened its name to Tiffany & Co. under the control of Tiffany Charles, who emphasized on the manufacture and sale of jewelry. The company produces and sells jewelry by marking the items using price tags, a factor that reduces the exploitation of consumers by retailers, who change prices irregularly.
Moreover, the company enjoys a wide market share and recognition from potential consumers of jewelry and has several distribution points globally. The ability to achieve customer perceived quality makes the company successful since it leads to increased sales and revenues. Hence, it is within this context that the paper analyzes external opportunities and threats, internal strengths and weaknesses, strategic options, and recommends the strategies that Tiffany & Co. can adopt to achieve its objectives.
External Analysis
Opportunities
Technology and Demography
Some of the opportunities that the company enjoys in the external marketing environment include factors such as changes in technology, demography, political structures, and economic environment. As opposed to internal factors in the marketing environment, external factors are beyond the control and influence of the organizations (Pan 115). Currently, company management facilitates the structural manipulation of products to match the prevailing externalities in the marketing environment.
The company has recently witnessed pronounced technological advancements that do not only shift the cost of production, but also influence consumer demand. Therefore, the company has to adjust to the provisions of technology so that it can be in line with the advancements.
The fact that the majority of individuals in the target market are young or middle-aged and are lovers of technology presents a very good opportunity for the jewelry industry. As a result, the opportunity arises because most of the individuals in this age bracket are lovers of jewelry and purchase the products frequently. The company has an easy task of understanding their preferences and tailoring their products to match the expectations of clients.
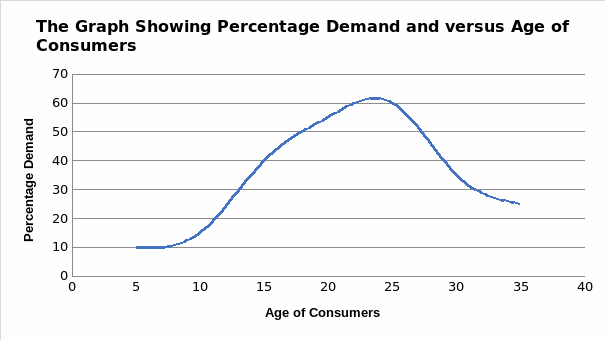
Political Structures and Economy
Another opportunity that the company enjoys in the market is the stable political structures in various countries that it supplies its products. Notably, peace and tranquility are key ingredients in successful manufacture and sale of products in an organization. Since several countries have effective political institutions that facilitate peace, production, and sale of jewelry thrives.
The increased income level of individuals has turned into an opportunity for the company as it amplifies the amount of income that potential clients can use in purchasing jewelry. The enhanced income level of people in society materializes due to the stable economies among various countries in the world.
According to Faarup (92), changes in social and cultural perceptions of individuals in modern societies are opportunities that help change consumer behavior. In the contemporary environment, several consumers are increasingly purchasing jewelry under pressure from peers and friends in the society.
Threats
Competition, Inflation, and Recession
Increasing competition, inflation, recession, terrorism, and technological advancements are some of the threats associated with the external marketing environment. These threats affect the company since they are beyond its control and influence. Competition from major jewelry industries like Pandora, Sisma, Blue Nile, and Shenzhen Chow Tai Seng Diamond and Jewelry poses a threat that the company faces when selling its products and retaining its market share.
Since competitors produce complementary and substitute products at low prices, clients often opt to purchase these products as opposed to original products from the company (Pan 107). Also, competitors deliver similar products to customers at fair prices.
Due to increased competition, the company faces a threat of reduced sales since it has to compete with its competitors for time, attention, and market share. Another threat associated with the external environment is the recent inflation and recession that saw a significant number of individuals dismissed, and thus, greatly affected their purchasing power.
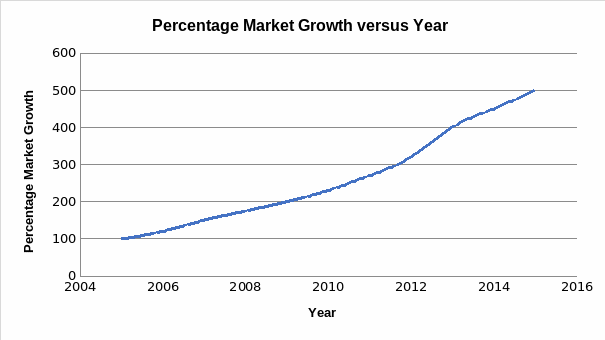
Brand Positioning
To sell its products effectively, the company has to identify its target consumers. Identification of target consumers is crucial as it helps the company design its products in a manner that match client expectations. Remarkably, the majority of the clients targeted by the company comprise of those individuals, who give or receive gifts in the form of jewelry from their friends or colleagues.
These individuals spend hours in jewelry shops trying to get the best necklaces, rings, or earrings for their friends (Faarup 93). Therefore, from the knowledge of the target customers, the company has to position itself strategically in the market so that it appeals to the targeted consumer segment.
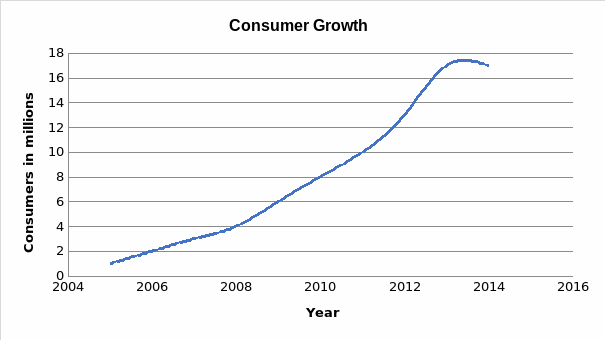
Potters’ Five Forces
The main competitors of Tiffany Company include Pandora, ZLC, Sisma, Blue Nile, and Shenzhen Chow Tai Seng Diamond and Jewelry. The competitors fight for the market share in the jewelry market together with Tiffany. The magnitude of competition between the company and its competitors is high and intense.
The intense competition is due to the increasing cost of production and the prices of products offered by competitors like the Blue Nile and ZLC. It is imperative to understand that competitors of the company provide complements and substitutes for the potential consumers of Tiffany.
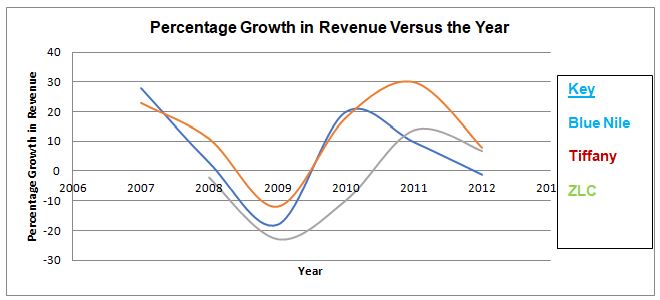
From the illustration, it is evident that the level of competition experienced by Tiffany from its competitors is intense and pronounced. The revenue growth demonstrated by the company fluctuates and follows a trend similar to that of its competitors, such as ZLC and Blue Nile. The illustration is instrumental as it illustrates the revenue growth of Tiffany alongside its competitors, which is evident from 2009. The growth in revenue implies that the company is enjoying a large market share as opposed to its competitors.
Internal Analysis
Strengths
Good Brand Name and Strong Selling Strategy
A good brand name, strong selling strategy, a wide spectrum of offerings, and a good financial sheet are among the major strengths of the company. The fact that the company is one of the jewelry industries recognized globally and in the United States is very instrumental in the sale of its products and a wide market share. Also, the fact that the company is established and has existed for a long period implies that a considerable number of consumers love associating themselves with its products.
Moyer, McGuigan, and Kretlow explain that in 2006, the earnings of the company demonstrated increased sales as purchases of the most expensive products exceeded that of the relatively less expensive items (69). The strategy that the company adopted, which entailed direct selling and increased distribution channels is another strength that facilitates easy achievement of its objectives. The company has developed various distribution points in the United States, and globally that help it sell its products directly to consumers.
Wide Spectrum of Offerings, and a Good Financial Sheet
The ability of the company to provide and sell diverse products to its consumers facilitates increased sales, purchases, and revenues. Some of the products that the company offers to its consumers alongside jewelry include sterling silverware, diamond offerings, fragrances, and accessories. These products do not only increase the market base for the company, but also amplify the level of purchases.
Fitzen (2) asserts that the increasing competition has led to various strategies such as diversification of products that organizations offer to their customers. Therefore, through the diversification of its products, Tiffany & Co. increased its sales volumes and purchases. The revenues earned by the company because of increased sales volumes lead to a good and stable balance sheet.
The balance sheet enables the company to access loans and expands its supply to other potential consumers. Furthermore, the strong balance sheet is useful for the company can increase its distribution points and market its products in the global markets.
Weaknesses
Sluggish Market Development and Declining Cash Flows
Sluggish development of markets in regions like Asia, declining cash flows, lower returns in profit margins comprise some of the weakness associated with the company. The Asian market was one of the regions in the world that purchased jewelry from companies like Tiffany & Co. However, the rising cost of basic commodities such as food led to a decrease in the level of purchases as consumers reduced their spending and purchases so that they could cater for their basic requirements.
Reduced purchases initiated the slow development of the market in the Asian region. The fact that a considerable number of consumers in the Asian region are priced sensitive implies that increasing food prices greatly affect the purchase of jewelry products.
Furthermore, increased competition led to a rise in the cost of production due to externalities like technology and inflation, which augmented product prices (Faarup 97). The increase in the price of jewelry discouraged a significant number of potential consumers, especially middle- and low-classes, from purchasing the products.
Lower Returns in Profit Margins
The declining cash flows in the company can attribute its emergence to technological advancements that increased production costs and shifted consumer preferences. Competition from other companies that sell jewelry led to a reduction of the purchases in the company as some consumers decided to buy products, mainly substitutes, and complements, from competing organizations. Moreover, competing organizations offered products at prices relatively lower than those of Tiffany & Co.
The decline reduced the number of profits earned by the company since its sales volumes diminished. According to Norton, Diamond, Pagach, the effect of the increased costs of production and competition initiated a reduction in earnings per share diluted by 0.05 in 2004, and 0.01 for the year ended January 2002 (363). The declining sales and diminishing profits are some weaknesses that the company encounter in its attempt to increase sales and achieve its set objectives in the jewelry industry.
Strategic Options and Recommendations
Strengths
Good Brand Name and Strong Selling Strategy
The company should ensure that they develop a good brand name, strong selling strategy as it facilitates increased sales and high-profit margins. Moreover, the company should use its good brand that it has to sell its products and improve its market share in the jewelry industry. Employment of the recognized company brand transpires because it is established and has been in existence for a long time.
The company needs to improve its strategy of direct selling that it adopted since it facilitates easy achievement of its objectives. Also, the company must increase the number of distribution channels on top of the present channels developed in the United States and globally so that it can sell its products directly to consumers.
Wide Spectrum of Offerings, and a Good Financial Sheet
The company has to increase the amount of products its suppliers since diversification facilitates increased sales, higher purchases, and revenues. The need to diversify products is because diversification increases the market base for the company and amplifies its level of purchases. Furthermore, the company must increase its product base to outsmart the increasing number of competitors, who offer substitutes or complementary products to potential customers of jewelry.
It is imperative to understand that through diversification of its products, Tiffany & Co. will increase its sales volumes and purchases. The revenues earned by the company because of increased sales volumes lead to a good and stable balance sheet. The company should use its balance sheet to borrow funds and access loans that it will use to expand its supply to other potential consumers.
Weaknesses
Sluggish Market Development and Declining Cash Flows
It is recommendable that the company focuses on other markets alongside the Asian markets so that it can increase the demand for its products and counter the sluggish development of markets in regions like Asia. The company needs to tailor its products in a customer-friendly manner and maintain its production cost. Customer-friendly priced jewelry increases the willingness to purchase from the majority of Asians and global clients, who are price-oriented.
The reason for tailoring jewelry products in a customer-friendly manner is due to the rising costs of basic commodities such as food. Remarkably, reduced purchases initiate slow market development among the potential clients of jewelry. To counter the challenge introduced by increased technology and competition, the company must supply its products to target consumers at fair prices that are within their purchasing power.
Lower Returns in Profit Margins
Customer awareness and enhanced product quality help the company curb the declining cash flows. Additionally, the company should adopt and use facilities that are in line with modern technology so that the quality of jewelry matches the perceived quality of customers. A combination of jewelry that meets the expected product quality and fair pricing helps the company counter competition, which has reduced purchases in the company.
Through the enhancement of product quality and the use of consumer-friendly prices, the company will experience an improvement in profits because the sales volumes increase. The company can also minimize costs related to marketing and promotion of products so that it increases its profit margins. Effective product marketing improves the willingness to buy jewelry from the company as consumers get increased awareness concerning the products.
Opportunities
Technology
The company should facilitate structural manipulation of products to match the prevailing externalities in the marketing environment. Structural manipulation of the products helps the company cope with technological advancements that increase the cost of production and influence consumer demand. Therefore, the company has to adjust to the provisions of technology so that it can be in line with the advancements.
Coping with technological advancements facilitates easy entry into the market, which comprises young and middle-aged technology-oriented individuals. It is recommendable that the company undertakes market research to ascertain the purchasing powers and buying behaviors of people in their target age bracket.
Good market research leads to the delivery of jewelry that matches buyer expectations in terms of price and quality. As a result, the company has a mandate of understanding customer preferences and tailoring its products to match their expectations.
Political Structures and Economy
Emphasis on countries that have stable political structures is a factor that the company needs to undertake in the supply of its products. It is imperative to understand that peace and tranquility are key ingredients in successful manufacture and sale of products in organizations. The company needs to employ increased income levels of individuals to improve the number of purchases.
Remarkably, enhanced purchase levels of the company materialize because of the stable economies of countries in the world. Pricing, marketing, and product promotion that the company must undertake to elicit changes in social and cultural perceptions among individuals in the present societies. In the contemporary environment, several consumers are increasingly purchasing jewelry under pressure from peers and friends in the society.
Implementation Steps
Some of the policies that the company needs to implement include rebranding, diversification of its products and markets, as well as market research. Since its inception, the company has steadily grown to be a well-known jewelry company in the United States and globally. Therefore, the company can strategically use its brand to sell its products to the target consumers.
Rebranding its products can be one of the major activities that the company must undertake so that consumers can easily recognize its products and associate themselves with them. Also, apart from jewelry and other products that are in its line of production, the company needs to diversify its products and market base to other safer destinations in the world that are unexploited by jewelry industries.
To implement the concept of diversification, good market research is crucial so that the company identifies the diverse consumer preferences in the target regions. Facebook, Twitter, YouTube, and other social sites are very important in identifying the preferences of consumers in the target regions and play an integral role in market research.
Conclusion
Tiffany & Co. deal with the manufacture and sale of jewelry in the United States and globally. Since its introduction to the jewelry industry, the company has risen steadily and gained popularity globally. Over the recent past, external factors in the marketing environment like the competition and technology have affected its growth. Therefore, the company needs to undertake extensive marketing, diversification, and rebranding of its products for it to sustain its market share in the jewelry industry.
Works Cited
Faarup, Poul. The Marketing Framework. New York: Academica, 2010. Print.
Fitzen, Lena. Marketing Environment. London: GRIN Verlag, 2009. Print.
Moyer, Charles, James McGuigan, Ramesh Rao, and William Kretlow. Contemporary Financial Management. New York: Cengage Learning, 2011. Print.
Norton, Curtis, Michael Diamond, and Donald Pagach. Intermediate Accounting: Financial Reporting and Analysis. New York: Cengage Learning, 2006. Print.
Pan, Albert. China Gem and Jewelry Market Overview: Selling Jewelry in China. London: Zeefer Consulting, 2008. Print.