Results of Descriptive Statistics and Two-Sample Test
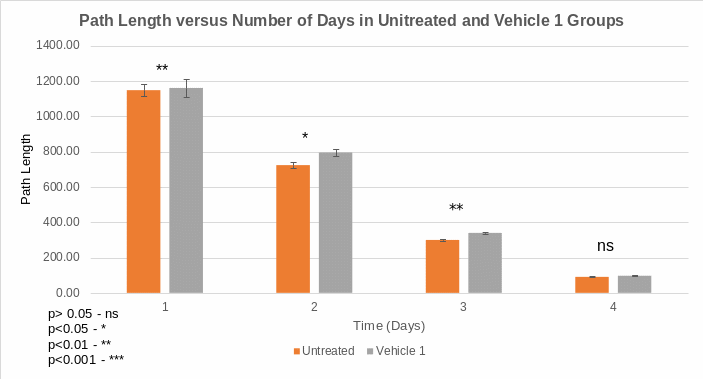
Descriptive statistics (Table 1) show a declining trend of path length swum by rats to reach the rescue platform in all groups in the water maze. Comparatively, the means of path length swum by rats in the untreated group was lower than those in the vehicle 1 group in all days. In essence, vehicle 1 tended to increase the path length that rats navigated before they found the rescue platform. The difference in means of path length implies that vehicle 1 has an effect of decreasing cognitive skills and memory. The two-sample test revealed that there were statistically significant difference in the means of path length during day 2 (p = 0.020) and 3 (p = 0.001) but statistically insignificant difference in day 1 (p = 0.945) and 4 (p = 0.092).
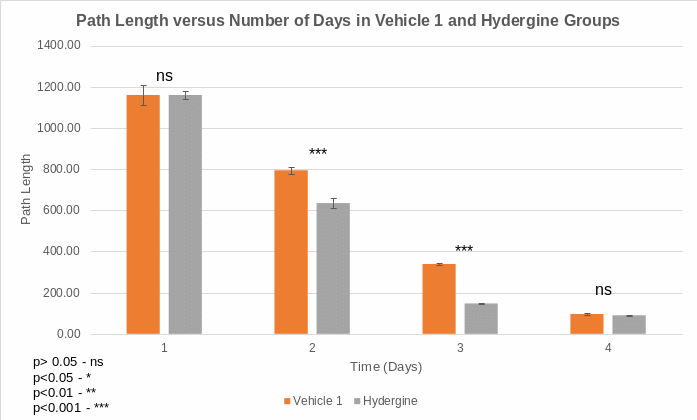
Moreover, descriptive statistics depict that hydergine reduced the path length swum by rats before they found the rescue platform. Table 1 shows that the means of the path length of rats in hydergine groups were lower than those in vehicle 1 groups. The decrease in path length implies that hydergine improved cognitive skills and memory in rats. The two-sample t-test pointed out that the differences in the means of path length between vehicle 1 and hydergine groups were statistically significant in day 2 (p = 0.000) and 3 (0.000).
However, differences in the means of path length between vehicle 1 and hydergine groups were not statistically significant in day 1 (p = 0.844) and 4 (0.070). Overall, descriptive statistics and inferential statistics show that vehicle 1 had a decreasing effect while hydergine had an increasing effect on cognition and memory in rats.
Table 1. Means, Standard Errors of Means (SEMs) and P-values of Untreated, Vehicle 1 and Hydergine Groups.
Graphs Showing Path Length of Treatment and Control Groups
Figures 1 and 2 show the decreasing trend from the first day to the fourth day of the means of path length taken by rats to reach the rescue platform due to learning and memory. Moreover, graphs indicate that treatments account for differences in the means of path length swum by rats to access the platform.
Summary of Findings
Effect of Vehicle 1
A comparison of path length swum by rats in the treatment and control groups shows that vehicle 1 affects cognitive skills and memory. Descriptive statistics indicated that vehicle 1 increased the means of path length that rats took to reach the platform in the water maze. During day 1, 2, 3 and 4, the mean path lengths in the untreated group were 1147.40±34.64, 723.17±18.03, 299.23±5.98 and 90.80±2.70, respectively. In the vehicle group, the means of path length increased to 1160.04±49.10, 794.72±17.45, 339.84± 5.58 and 96.82±3.19 in day 1, 2, 3 and 4, correspondingly. The consecutive increase in the means of path length over time implies that vehicle 1 suppresses cognitive skills and memory in rats.
Hypothesis test using t-test confirms that the means of the path length of rats in the vehicle 1 group were statistically significantly higher than those in the untreated group during day 2 (p<0.05) and day 3 (p< 0.01). However, the means of the path length of rats in the vehicle 1 group were statistically insignificantly higher than those in the untreated group in the first day (p>0.05) and the fourth day (p>0.05).
Effect of Hydergine
Data analysis depict that hydergine decreased path length that rats navigated to arrive on the platform. The examination of the mechanism of action reveals that hydergine improves memory and cognition by imitating the influence of nerve growth factor, which triggers protein synthesis and stimulates the growth of dendrites for the effective functioning of the central nervous system (Sharma et al. 6). Descriptive statistics indicated that the means of path length were 1160.04±49.10, 794.72±17.45, 339.84± 5.58 and
96.82±3.19 in the vehicle group during the first day to the fourth day, in that order. In the hydergine group, the means of path length decreased to 1160.38±19.07, 634.97±23.95, 147.42±4.22 and 90.40±2.50 during day 1, 2, 3 and 4, consecutively.
T-test validates that the means of path length navigated by rats in the hydergine group were statistically significantly lower than those in vehicle 1 group during day 2 (p<0.001) and day 3 (p<0.001). In contrast, the means of path length navigated by rats were statistically insignificantly lower in the hydergine group than in the vehicle 1 group during day 1 (p<0.05) and day 4 (p>0.05). The significant effect implies that hydergine improves memory and cognition on the second day and the third day due to pharmacokinetics.
Work Cited
Sharma, Niti, et al. “Ergot Alkaloids: A Review on Therapeutic Applications.” European Journal of Medicinal Plants, vol. 14, no. 3, 2016, pp. 1-17.