Introduction
Wendy’s restaurant is the third largest fast-food restaurant in the world (Wendy’s, 2013). It only lags behind Burger King and McDonalds in the selling of the hamburger sandwich. Wendy’s is involved in the business of developing, running, and franchising fast-food restaurants, which serve high-quality foods (Wendy’s, 2013). At the end of 2012, the restaurant had 6186 outlets in North America alone (Wendy’s, 2013, p. 3).
Of those, 1427 restaurants were operated directly by Wendy’s, while the other 4759 outlets were operated by 439 franchises (Wendy’s, 2013, p. 3). Outside North America, Wendy’s has 374 restaurants in 26 countries operated under a franchise system (Wendy’s, 2013, p. 3).
Wendy’s generates its revenues by selling the foods cooked at its restaurants and the products at its bakeries, in addition to the loyalities paid by the franchises operating under its brand (Wendy’s, 2013, p. 3). Wendy’s has also partnered with Tim Hortons Incorporated in a real estate joint venture (Wendy’s, 2013, p. 3).
Wendy’s menu includes hamburger sandwiches, chicken nuggets, french fries, chilli, soft drinks, salads, baked potatoes, kids meals, and frosty desserts (Wendy’s, 2013, p. 4). The chain of restaurants also sells promotional merchandise on a limited time basis (Wendy’s, 2013, p. 4).
The company maintains high quality in the preparation of food by training its employees, doing operational audits, and taking its supervisors for instructive visits (Wendy’s, 2013). The only food the company sells to its franchise stores is sandwich buns. New Barkery Company is owned by Wendy’s and is tasked with the responsibility of supplying buns to some of the restaurant’s branches (Wendy’s, 2013).
As of 2012, Wendy’s hamburgers were supplied across the United States by five independent processors (Wendy’s, 2013). On the other hand, Wendy’s chicken were supplied by six other independent processors in the country (Wendy’s, 2013). The suppliers for raw materials have been operating smoothly with Wendy’s (Wendy’s, 2013).
In 2009, Wendy entered into a deal with it franchises, which is known as the Quality Supply Chain Co-op, Inc (QSCC), to help manage its contracts for the purchase and distribution of foods in the United States and Canada (Wendy’s, 2013, p. 5). QSCC ensures a smooth flow of supplies to minimize absolete inventory along the supply chain in Canada and the United States (Wendy’s, 2013, p. 5).
Wendy’s Product Life cycle
Firms normally introduce new products to keep up with the competition and changing consumer demands (Stevenson & Hojati, 2007). A company that does not introduce new products and services will eventually face a decline in its sales and profitability.
This is because the demand for products and services normally declines with time. The product life cycle is divided into 5 stages: product or services planning, introduction, growth, maturity, and decline stages (Reid & Sanders, 2012). The figure 1 below illustrates the product life cycle.
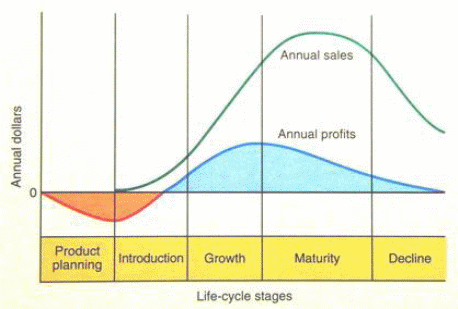
Figure 1: Product Life Cycle
During the product and service planning stage, ideas for the new product are introduced, evaluated, and the final design developed. At this point, no profits are generated, but the costs of development are incurred. The sale of the product begins at the introduction stage where the profits start being generated (Reid &Sanders, 2012). The profit is little because the sales volumes are still low.
At the growth stage, the popularity of the product grows rapidly. The main operation is to keep up with the demand, rather than enhancing efficiency (Stevenson & Hojati, 2007). When the product enters the maturity stage, the sales level off and profits start declining. There is a lot of external pressure from competitors who are copying the product. This makes the company cut its costs and experience lower profit margins.
At this point, efficiency is paramount. The company can put efforts to differentiate its products from those of its rivals (Reid & Sanders, 2012). The last stage is the decline stage where the product becomes obsolete. New and better products replace it or it just disappears due to the lack of sufficient demand.
Wendy’s introduced the Pretzel Bacon Cheeseburger on July 2013 (Breslouer, 2014). The introduction of the product was a successful move. The product planning stage took a year to develop the burger. The only weakness at this stage was the lack of customer participation in relation to the flavors they would prefer for the burgers (Breslouer, 2014).
The process of product introduction was expensive as it involved testing the burger in restaurants in Miami, Sacramento, and Cleveland (Breslouer, 2014). Another challenge of introducing the Pretzel Bacon Cheeseburger was that it cannibalised other burgers at the Wendy’s Restarant (Breslouer, 2014).
There is a need to develop a vegetarian burger made from eggs. The product name should be unique to differentiate it from those of its competitors. It is important to trademark the design to discourage competitors from copying it. This product should be cholesterol free. Most people are avoiding food rich in cholesterol to improve their health status.
During the introduction stage, proper advertising campaigns should be employed to attract new customers. It is important to ensure the product does not cannibalise other products, which are at the maturity stage of the life cycle. Constant improvement in relation to the flavors of the burgers will allow the firm to avoid the decline stage.
Components of Wendy’s Supply Chain Management
The key elements of Wendy’s supply chain is the supply of of raw materials, such as beef, pork, vegetables, and coffee; the storage of the raw materials; and the distribution of finished products, such as coffee, burgers, and salads among others (Wendy’s, 2013; Breslouer, 2014). Before the year 2010, the supply was done by Wendy’s to all its major restaurants (Wendy’s, 2013).
As from 2010, the supply of raw materials is done by a purchasing co-op (Wendy’s, 2013). The most important issue in the supply of raw materials is ensuring uninterrupted delivery. Interruption in the supply of the raw materials at Wendy’s can harm the business greatly.
The incorporation of the purchasing co-op allows Wendy’s to ensure a consistent supply of raw materials. Another important issue is the compliance of the food supplies with the United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the United States Department of Agriculture’s (USDA’s) terms and conditions. Wendy’s ensures this compliance is met by all its suppliers (Wendy’s, 2013).
Inventory control is a major area of concern for Wendy’s. The company prides itself in selling fresh burgers, which are never frozen. To ensure a smooth flow of the burgers, the supply must match the clients’ demand. The Quality Supply Chain Co-op Incorporated (QSCC) is tasked with the responsibility of managing the company’s inventory.
This ensures that there is no obsolete inventory along Wendy’s supply chain in both Canada and the United States (Wendy’s, 2013). QSCC is also responsible for the distribution of food products to various Wendy’s restaurants and franchises across the two countries. The main challenge in distribution is ensuring the timely delivery of the food products.
Another challenge is the rising gasoline prices, which could increase the costs of logistics (Wendy’s, 2013, p. 11). Food related diseases and conditions, such as obesity, have been attributed to fast-foods. This could lead to a decline of Wendy’s sales. The solution is to research on healthier food products and provide them to its clients.
Total Quality Management Tool
It is important for Wendy’s to maintain high standards in its operations. This will enable the company to retain loyal customers and attract new ones. To do this, it is important to adopt a total quality management tool. The basic total quality management tools include: cause-and-effect diagrams, check sheets, pareto charts, scatter diagrams, stratifications, histograms, and control charts (Broday & Andrade, 2013, p. 381).
Wendy’s should adopt the Pareto chart tool of quality management (TQM). The pareto chart TQM divides large problems into smaller manageable ones (Broday & Andrade, 2013). Wendy’s is a multinational company that runs many franchises. To manage the whole business, the management should be sub-divided to tackle specific tasks.
The Pareto chart allows the company to divide problems in the order of importance and then represents them on a bar graph (Broday & Andrade, 2013). The use of the Pareto chart will help the company to improve its working relations with the suppliers, allow a continous improvement of its foods and services, and enhance its communication with the customers.
Communication with customers allows the company to understand their needs better and develop products that fit their preferences best. Wendy’s should also focus on the improvement of its employees through motivation and training.
Training them will help to improve their skills to serve the customers better (Stevenson & Hojati, 2007). The TQM tool will also make the company flexible enough to respond to the changing customers’ demands. This tool will promote team work among its employees and improve coordination through its management’s social structure.
Just-In-Time Philosophy at Wendy’s
The just-in-time philosophy allows the company to reduce inventory costs by receiving only the goods required for the manufacturing process (Kootanaee, Babu, & Talari, 2013, p. 8).
This philosophy ensures efficiency and decreases wastage of resources. It demands that the manager should be able to predict the demands and order supplies that match the company’s need. This philosophy allows the company to produce only what it needs at a particular time. The production is based on customer requests and actual orders. The figure 2 below illustrates the just-in-time concept
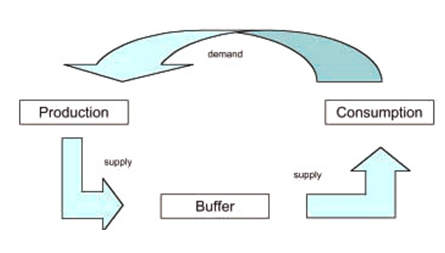
Figure 2: The Just-In-Time Concept, Source: Kootanaee, Babu, & Talari (2013)
Since Wendy’s restaurants only sell fresh burgers, this demands a continous flow of the products from the suppliers to the customers (Wendy’s, 2013). The advantages of the just in time concept for Wendy’s is that it reduces time and costs for setting up warehouses.
This allows the company to lay more emphasis on other processes of production and supply chain management. The just-in-time concept allows employees to process goods faster, as there is no need for a large inventory. Most of the raw materials utilized by Wendy’s are perishable and would require more inventory costs to keep them fresh due to refrigeration costs.
Through the use of the just-in-time philosophy, the inventory costs are reduced. Customers prefer fresh salads, burgers, and other food products. An assurance that the company uses the just-in-time philosphy normlly attracts more sales.
The use of the just-in-time philosophy improves the relationship between Wendy’s and its suppliers. Wendy’s is able to identify reliable suppliers who are able to deliver goods at the time they are needed. The round the clock supplies and deliveries allow the workers to remain focused and productive.
Qualitative and Quantitative Forecasting Methods
Forecasting is the prediction, estimation, or projection of a future occurence, activity, or event in an organization (Reid & Sanders, 2012). There are two types of forecasting: qualitative and quantitative. Qualitative forecasting methods are based on opinions, intuitions, personal experiences, or the decision maker’s opinion. These methods are subjective and do not rely on computations.
On the other hand, quantitative methods use mathematical equations and models to predict future events. They are objective as opposed to the qualitative ones. Qualitative methods are used in short-term forecasting for the company and not long-term prediction, due to the overliance on the opinions of experts, rather than measurable data (Stevenson & Hojati, 2007).
Examples of qualitative models are the market research and Delphi methods (Reid &Sanders, 2012). The market research aproach involves asking the customer’s opinions on a certain product to forecast how people will purchase the product when it is launched. On the other hand, the Delphi method involves asking expert opinions and using them to forecast sales.
Quantitative methods use measurable data to predict sales and prices of particular commodities. Some qualitative models include the indicator approach and the time series method.
The indicator approach uses the relationship between indicators like GDP and unemployment rates to predict other factors (Reid & Sanders, 2012). The time series method uses past data to predict the future. The table below illustrates how the quantitative and qualitative methods can be applied at Wendy’s to improve its operations.
Table 1: Qualitative and Quantitative Forecasting Methods
References
Breslouer, L. (2014). The life cycle of Wendy’s pretzel bacon cheesesburger, from conception to consumption.
Broday, E., & Andrade, P. (2013). Application of a Quality Management tool (8D) for Solving Industrial Problems. Independent Journal of Management & Production, 4(2), 377-390.
Kootanaee, A., Babu, N., & Talari, H. (2013). Just-in-time manufacturing system: From introduction to implement. International Journal of Economics, Business and Finance, 1(2), 7-25.
Reid, D. R. and Sanders, N. R. (2012). Operations management: An integrated. approach. Hoboken, NJ: John Wiley and Sons.
Stevenson, W. J., & Hojati, M. (2007). Operations management (vol. 8). Boston, MA: McGraw-Hill/Irwin.
Wendy’s. (2013). Wendy’s 2012 annual report. Dublin, OH: Wendy’s Restaurant.