Introduction
Countries across the world have built bilateral and multilateral business relationships that have been maintained for decades. These arrangements keep changing depending on the fluctuations of the countries’ needs and perception of each other. As such, the world has been described by The European Business Review (2020) as an unsteady flux of trading arrangements among nations. The United Arab Emirates (UAE) has had a strong relationship with the west, especially the United States.
The UAE-US relationships began in 1971 after the UAE gained its independence from Britain. Diplomatic relationships were established in 1972, after which the UAE became a critical ally of the US in the Middle East. Today, the UAE cooperates with the US on such matters as non-proliferation, defense, law enforcement, trade, cultural exchange, and energy policy. Besides the US, the UAE also has relationships with other western countries, specifically those forming the European Union (EU). However, it can be argued that the UAE has not made as much effort with eastern countries as it has done with the west.
The purpose of this paper is to express the need for UAE to start focusing on eastward expansion, meaning building stronger trade and diplomatic relations with the eastern countries. The term ‘east’ is used in this paper to refer to those major countries in Asia, including China, India, Korea, Japan, and other ASEAN. Countries Some of these countries can be described as emerging economies, a term used to express countries with rapid economic development. Such countries offer the potential for both trade and diplomacy, especially considering that such countries as India and China are increasingly becoming global powers. The argument presented in this paper is that these countries have the potential to offer huge benefits to the UAE.
The structure of the paper includes a brief description of the current state of affairs regarding the UAE’s relationships with the west. The progress and benefits gained from western expansion are also highlighted. Second, the paper explores the current state of the relationship between the UAE and eastern countries, which should serve to express the gaps for further exploration. The most important section addressed the rationale for Easter expansion, taking into consideration the nature of the eastern countries and the potentials that can be exploited. A recommendations section offers a summary of proposed courses of action for both the short and long-term efforts to build stronger relations with the east.
UAE’s Relationship with the West
It can be argued that UAE’s major western partner in the US due to the nature of the relationships between the two countries. The US Department of Justice (2020) states that the UAE is a key strategic partner in the Middle East that cooperates with the US on such matters as energy policy, trade, law enforcement, and cultural exchange. Additionally, the two countries have been working together to promote security and peace in the region and to support economic growth.
Other areas of bilateral cooperation include education, defense, and non-proliferation. Recent government regimes of the US have taken multiple initiatives that serve as evidence on the degree and nature of the relations with the UAE. For example, the Trump government made an effort to normalize the relations between the UAE and Israel to foster peace and security in the region. Such actions show that peace and security of the Middle East are critical for the interests of both countries, and the cooperation allows them to achieve this objective.
Security and defense is a particularly sensitive strategic issue and area in which both the US and UAE cooperate. According to Katzman, the UAE hosts an estimated 3500 US military personnel at the country’s military facilities. Additionally, the UAE is one of the countries in the world that buys military US military equipment, which includes combat aircraft and missile defense. Most importantly, the UAE supports the US’s agenda and policy towards Iran.
This serves as evidence that the US relies heavily on the UAE in its pursuit of the country’s national interests in the region. The UAE is not the only strategic partner to the US in the Middle East. Israel is also heavily dependent on the US in matters of defense and security, which means that it is in the best interests of the US if the two countries have good relations. Israel hardly has any friendly relations in the Middle East as manifested in the constant conflicts with the Arab countries. As mentioned earlier, the US initiated a process to normalize good relations between the UAE and Israel in pursuit of enhanced security in the region.
While security is a key strategic issue, it is important to acknowledge that it is also a controversial one for the UAE because it can potentially undermine the UAE’s relations with the Middle East. The UAE deal with Israel, which was brokered by the US, is one of the top issues threatening strained relations with Iran. A news article in the Arab News (2020) claimed that Iran had threatened to attack UAE due to this Israel deal. However, it should be acknowledged that Iran and the UAE have never had good relations because Iran has always sought to dominate the region. According to Azodi and Cafieiro (2020), the relations between the UAE and Iran have been contentious since the UAE gained independence in 1971.
This is because Iran sought to assert its control over the region’s strategic areas, including three Persian Gulf islands located near Lesser Tunb, Greater Tunb, and the Strait of Hormuz-Abu Musa. To the UAE, Iran has been a hostile, predatory state perceived with distrust by the UAE. Therefore, the UAE’s decision to seek assistance from the US is only plausible since the country has to protect itself from Iran’s advances.
In addition to the defense and security matter, the west, especially the US and the EU, are also trade partners with the UAE. Therefore, it can be argued that the expansion towards the east has allowed the UAE to gain massive markets for its natural resources, including natural gas and oil. The UAE believes that brokering a deal that involves equitable terms with the EU offers the country a market estimated at 512 million people and a gross domestic product (GDP) of approximately €15.3 trillion (The European Review, 2020). Additionally, the EU will be allowed to trade with such places as Dubai, which had a GDP of $102 billion as of 2018, and Qatar, whose GDP was $192 for the same year (The European Review, 2020). Such trading activities offers a near-world record of $69,688 per capita, which means that the EU is a critical region for the EU to expand (The European Review, 2020). These figures are evidence that western expansion has been the right decision for the UAE.
In terms of trade relations with the US, mutual benefits have also been realized by the two countries. To the US, the UAE provides a market whose 2019 GDP was estimated at $405.8 billion and a population of 11 million people. Additionally, the UAE was the US’s 30th largest goods trading partner with exports values at $20.0 billion and imports totaling $4.3 billion. This means that the US had a goods trade surplus of $15.6 billion in 2019 (United States Trade Representative, n.d.). Even though the US seems to be the bigger beneficiary, it is important to acknowledge that the US is a leading producer of some of the goods highly demanded by the UAE, including agricultural products. Therefore, a stable relationship with the US allows the UAE to have a stable inflow of goods. The size of the US market is also significant from the perspective of the UAE, which means that regardless of the trade deficit, the UAE has a strong market for its products.
Lastly, it is also important to acknowledge that the western expansion also supports eastern expansion in certain ways. In predicting the US-UAE relations under President Biden, Pollock (2020) argues that the UAE can address the Iranian threats and mend the rifts with Qatar and Turkey because the bilateral relations with the US are expected to thrive. However, the issue of Iran remains the most pressing one because of the threat Iran holds to the interests of both countries. Therefore, it can be argued that the western expansion has allowed the UAE t thrive, but that has been at the expense of good relations with other Arab countries.
Additionally, the over-reliance n the west has meant that the UAE has not fully exploited the potential of the emerging markets in the east, as will be highlighted in the following section. Even though rere is currently nothing wrong with the current status of western relations, it would be more beneficial for the UAE to find additional partners and allies in the region to strengthen its position in the Near and Middle East.
UAE’s Affairs in the East
UAE’s relationships with the east are arguably not as profound as with the west. The situation with Iran and Qatar, as explained in the above section, serves as evidence for this argument. However, the UAE has been taking several measures and steps towards fostering new relationships with various Middle East countries, including Iraq. According to Arab News (2021), the UAE has planned to invest $3billion in Iraq to explore a new partnership and to help Iraq accelerate its growth. Iraq remains a strategic concern for the UAE because the UAE needs the support of Iraq in fending off the influence of Iran in the region (Aldroubi, 2021).
Additionally, the UAE is considering exploring new opportunities in the region, especially at a time when Iraq is reaching out to the UAE and other gulf countries in its attempt to gain alternative lifelines and investments. However, these efforts are only being considered, which means the UAE’s commitment to the Middle East in terms of investments has not been a top priority.
The efforts of the UAE to make Iraq a regional partner go being the need for trade and investments. As mentioned earlier, the threat from Iran is serious, and the UAE has been reaching out to Iraq to help in this regard (Aldroubi, 2018). Iraq has long been under the influence of Iran, a situation that both the US and the UAE need to change. The escalating situation in Iran means that Iraq will need new partners, for which the UAE is willing. Ties with Iraq and other countries in the Gulf region will be key to the stability of the region. Unfortunately, the country has not managed to develop many strong and strategic ties with the Arab, which means peace and security remain unguaranteed.
The focus of this paper is to explore eastward expansion, which goes beyond the Arab world. Therefore, it is also critical to explore the current state of affairs with the larger continent of Asia, especially such leading regional powers as China, India, Korea, and Japan. The Republic of Korea (ROK) has had good diplomatic relations with the UAE since June 1980 (Jeong, 2019). The cooperation initially revolved around the issues of construction and energy in the1970s and 1980s.
In the mid-2000s, more issues were added in the cooperation, including food security, defense and security, cultural exchanges, and innovation. Therefore, it can be argued that the ROK has offered the UAE almost similar benefits to those in the US-UAE relationship. The emergence of ROK as a middle power in the Middle East means that the UAE can have a strategic partner in ROK for regional stability, which over-reliance on the US can be reduced.
From the security perspective, it can be argued that all countries are jointly responsible for the security of the entire region. Cooperation with the east should be a top priority because only good relations with neighbors can ensure a lasting peace. Therefore, the UAE has had cordial relations with such regional powers like India. According to Upadhyaya (2019), India has fostered good relations with all the six Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) in the Persian Gulf: Kuwait, Qatar, UAE, Saudi Arabia, Oman, and Bahrain. There exist historic cultural ties between India and the GCC region that has persisted for centuries.
India is keen to retain these ties for two reasons. The first reason is that India has growing energy requirements, and the GCC is India’s main source of energy. Second, the region houses more than 6.5 million Indians contributing to an estimated $35 million in annual remittances (Upadhyaya, 2019). India has successful bilateral trade agreements with the GCC, which exceeds $103 billion, which makes the GCC India’s largest trading block. From the perspective of the UAE, it can be argued that such countries as India have huge potential both economically and diplomatically. India has a critical role to play in the maritime security of the region and has the capacity to help the region maintain peace. Unfortunately, the UAE has not considered this potential and has not prioritized UAE-India economic ties.
However, it can be argued that a strategic partnership between the UAE and India is emerging. Some sources indicate that UAE has been trading with India since the UAE’s independence in 1971 (Anjum, 2017). However, the relationship has been based almost solely on trade. As India has become an emerging economy and pursues international power in West Asia, such countries as the UAE, Saudi Arabia, Palestine, and Israel have initiated the process of striking strategic partnerships with India. In other words, India becomes an enticing partner due to the country’s power and influence in the region.
China is another country in the east that has recorded tremendous growth both in terms of economic and military strength. If the emergence of India has made several countries in the east foster new strategic relations, then the rapid developments taking place in China should b expected to have the same outcomes. China has, over the past two decades, emerged as one of the largest investment and trade partners in the eight countries bordering the Persian Gulf. Such scholars as Habibi (2020).
Explain that this emergence has occurred despite the conflicts and diplomatic tensions among those states. Examples of tensions in the region include Saudi Arabia and Iran and the current disputes between Qatar and both the UAE and Saudi Arabia. The most notable development is that China has rapidly developed ties with those countries heavily dependent on the United States for their external security. Just like India, China’s growing geopolitical power in the east, coupled with the growing military strength, means that the security in the east will cease to be dependent on the US.
Lastly, Japan is a country that has had mutually beneficial ties with the GCC states since World War II. The gulf-Japan ties have majorly been founded on energy, meaning that the region provided Japan with the energy resources. It is also important to acknowledge that the economic development of Japan is vital for the GCC. Japan’s ties with the region have evolved as Japan moved away from oil as its primary energy to include nuclear power and natural gas. In this evolution, the GCC has remained vital for Japan, which has diversified its interests in the region to include education, tourism, science and technology, investments, and security. Therefore, Japan is another key player in the region, but the UAE has retained its traditional relations with the country. The emphasis on the GCC in this regard shows that the UAE cooperates with Japan the same way all other members do without further efforts to build more strategic relations.
From the examination of the current state of affairs regarding the UAE’s relations with the east, it can be concluded that the ties between the UAE and the east are not as profound. However, it is also clear that the UAE has had good and mutually beneficial relationships with the region, especially the emerging economies of Asia. The key observation is that the growing strength of the regional powers makes it possible to maintain peace and security and to reduce the region’s overdependence on the US. These findings form part of the rationale discussed in the following section on why the UAE should not focus more on the east expansion. By eastern expansion, the emphasis is that better diplomatic ties and greater trade and cooperation with the east to mirror or even surpass the relations with the east should be developed.
The rationale for More Focus on the East
The primary argument that there are massive opportunities in the east that the UAE can exploit to further its economic and geopolitical interests in the region. The UAE-US relationship epitomizes the needs and interests of the UAE. In other words, the UAE is keen to gain external security because of the instability in the region and the strained diplomatic ties with the gulf. However, the country also needs markets for its natural resources, which means that the eastern markets can be developed further to improve revenues from the region. Most importantly, cooperation and improved diplomatic ties will ensure that the region is safe and secure.
As mentioned earlier, good relations with neighboring countries are the best option to build security. Additionally, the growth of such regional powers as India and China means that it is not only the US and UAE who need the region to be secure. China and India, as well as other ASEAN countries, are vested in the region, and they can collaboratively achieve this goal. Therefore, the rationale for the eastern expansion revolves around security and stability, economic benefit, social and cultural exchanges, and political gains.
Economic Benefits
Asia is one of the largest regions in the world and the most populous. In 2020, the population was estimated at 4.64 billion people comprises 60% of the earth’s population. The Southern Asia region accounts for about 40% of this population, with India being second-most populous in the world. East Asia accounts for another 36% and comprises China as the most populous country in the world (Statistics Times, 2020). From an economic perspective, these two Asian regions have two of the world’s largest markets. Their growth means more demand for oil and other energy resources that the UAE can offer. Additionally, their development in terms of science and technology means that god relations can help the UAE benefit from such advancements.
As emerging economies, the east presents economic growth potential that can be exploited by the UAE through trade investments. When taken as a single unit, the ASEAN countries become a powerful resource and the third-largest market. The economic growth in the region is also one of the highest, which has been estimated at 5.1% (Emerhub, 2018). This means that even when focusing on the smaller economies, the UAE can make lucrative investments in Asia. For India and China, the two countries represent the 5th and 2nd largest countries with 2019 GDPs amounting to $2.9 trillion and $14.2 trillion, respectively (Statistics Times, 2019).
The massive growth means that the UAE can be dealing with two of the world’s largest economies, and trade benefits among them can be significant. The most important economic benefit is that both India and China are among the major importers of UAE’s products, which means that further expansion can result in a growth in the trade value. The figure below shows some economic of India and China to illustrate the economic importance of the two countries to the UAE.
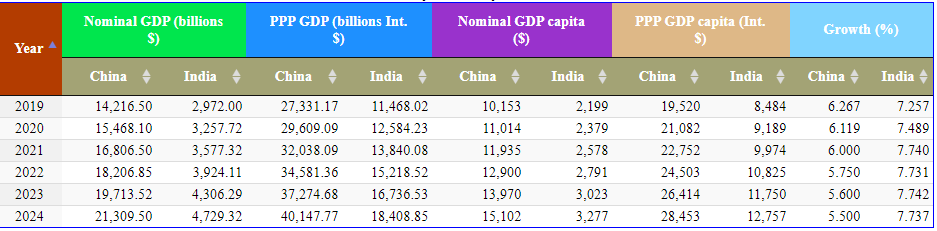
Security and Stability
The security and stability of the east can be achieved through cooperation between countries. The Indian and West Pacific oceans are the critical marine resources shared between the countries and the key concern for the security of the region. The Indo-Pacific Maritime Cooperation among the ASEAN countries means the region is keen to take the initiative to improve security and stability (Damayanti, 2019). Therefore, it can be argued that when the objectives of this cooperation are met, such countries as the UAE will no longer be extremely dependent on external security from the east.
It is important to acknowledge that the security and stability of the east are dependent on the relationships between the US and emerging powers, including China and India. This is because such countries as Japan are already allied to the US. Besides the nuclear developments taking place in North Korea, North-East Asia has been a relatively secure and stable region, which is manifested in China’s efforts to take advantage of the stability to build its influence (Menegazzi, 2017).
However, China and the US are not always on good terms, which means that the behavior of these two countries will be a key determinant of the security of the region. The UAE can find itself in a crossfire between the two countries on account that it is a key ally of the US. The growing influence of China through the explosion of diplomatic ties with the region means that the UAE can miss on the opportunity to make the necessary investments. Most importantly, the UAE can play a key role by making sure that the interests of both China and the US can be without jeopardizing regional security.
The basic argument is that all countries in the region have prioritized the peace, security, and stability of the region to allow all countries to grow and develop. Most importantly, such countries as India and China have vital interests in the region and are key players in regional security. Therefore, the alliances with the US and the east should not work against the UAE’s aspirations to join forces with the like-minded nations in the region. Most importantly, the influence of the US will ultimately dwindle due to the rise of China and India, which means that these two countries should be the UAE’s strategic partners on matters of defense and security.
Social/Cultural/Religion
Social and cultural exchanges have taken place between the UAE and the eastern countries since independence. The current status of UAE’s relations with the east examined above has revealed that in almost all countries that have diplomatic ties to the UAE, social and cultural exchanges have been a key item for cooperation. The example of the ROK and UAE by Jeong (2019) illustrates this key point. Additionally, it has been established that other countries in the east have been reaching out to the GCC region, including India and China, to form strategic partners. Therefore, this should be a sign for the UAE that new relations are emerging, and a change or a diversification will only be good for the country.
In terms of culture and religion, the UAE is largely a Muslim state, as is the case with the members of the GCC. However, the ASEAN, Southern Asia, and North-East Asia regions are more diversified in terms of religions, with both Christians, Buddhists, and Hindus forming among the largest religious groups. Exchanges with these countries will foster good relations in the region, which will be the key element needed for regional cooperation and stability. The GCC hosts about 6.5 million Indians, which should serve to illustrate the key argument that the UAE and the east should foster further cultural exchanges (Upadhyaya, 2019). With its resources, the UAE is one of the countries that import labor from Asa and other continents. Cultural and social integration are key to facilitating these relationships and continued cooperation with the east.
Political Gains
From a political standpoint, the UAE stands to gain massively by more focus on the east. Central Asia is a particularly interesting region because the fall of the Soviet Union meant that Russia no longer has control over the resource-rich region. The UAE has been in a leading position in the efforts towards stronger relations with Central Asia. While all the GCC countries are working towards this goal, it is the UAE that has more political influence in the region.
Central Asia is predominantly Muslim, and the rivalries between the Islamic visions in the region can take center stage. Therefore, the UAE has the opportunity to divert Central Asia from the politically aggressive vision held by such countries as Iran. The geopolitical rivalry in the region affects the security and stability, and bringing in more players to these conflicts could only escalate the situation. Therefore, the UAE stands to become a regional political power with adequate influence over the newcomers to the Asian conflicts and rivalries.
The political and economic stability of the UAE and the guaranteed external security from the US make it possible for the UAE to assert its political power in the region. This is a necessity not only because of Central Asia but also because of the growing influence of China and India. Focusing more on the east through diplomatic ties and political assistance to struggling countries is seen as the best strategy to gain political power. The escalating situation between the US and China over different interests in the region means that a stronger political power needs to emerge to play a mediating role. The UAE stands to become this third party, but this can only be achieved when other political powers recognize the UAE as a political player in the region.
Reactions from Western Allies
The reactions from the western allies are hard to judge because the nature of the eastern expansion remains in question. However, it is important to acknowledge that even with the eastern expansion, the UAE will still be invested in the west. The US is a key supplier of military equipment, something that may not be replaced. Trade with the west could also be sustained, with more focus being on the east. Most importantly, the US and China have their own agreements, and other such countries as Japan are already allied to the US. Therefore, there could be little resistance from the west as long as the UAE does not seek to replace the west with the east. The weapons sale to the UAE has been a contentious policy issue of late, as illustrated by the disagreements between President Trump and the US Senate regarding the subject (Aljazeera 2020). While the US remains a key supplier of warfare materials to the UAE, a trade-oriented expansion towards the east should raise major concerns from the west.
Mediating in Asian Conflicts
As part of the eastern expansion, the role of the UAE in Asian conflicts should be examined carefully. Currently, the UAE has been massively involved in the Yemen civil conflict. A direct engagement means that the UAE has had to send its personnel and military equipment to the country. However, it is important to emphasize that the UAE, backed by the US, fought two primary enemies, namely the Houthis and the violent extremist groups, including al-Qaeda and ISIS (Jalal, 2020). The role of the UAE in Yemen cannot be described as mediating the conflict because the country is directly fighting groups perceived to be the UAE’s enemies.
However, the UAE has been one of the greatest proponents of the idea that the conflicts in the region should be mediated by the UN. It means that the UAE is keen to make sure that diplomatic resolutions can be found for the Asian conflicts. The argument is that the UAE has key political interests in such countries as Libya, Syria, Palestine, and Yemen (Gulf News, 2018). The political stability of the UAE means that the country can play a greater role in mediation. Officials in the UAE believe that with an UN-led mediation, the current conflicts can be solved, and future ones can be prevented from emerging. The eastern expansion by the UAE will mean that the country will have become one of the key players in the Asian conflicts. The approach taken in Yemen could only be recommended when the conflicts directly threaten the national security of the country. Otherwise, a mediating role should be expected from the UAE in any conflicts involved its Asian partners.
Conclusion and Recommendation
Conclusion
The UAE has had fruitful strategic relations with the west, especially the US. This cooperation has allowed the UAE to thrive amidst constant conflicts in the region due to the external protection offered by the US. Therefore, it could be prudent to argue that continued relations with the west offer sustained protection ad room for further growth. With the emphasis on the west, the country has had fewer investments in the east.
However, it should be noted that many of the countries in Asia remain key trading ad diplomatic partners to the UAE, including ROK, Japan, China, and India. In most diplomatic relationships with the east, the UAE majorly functions simply as a member of the GCC with little effort to strengthen the ties. The Asian region comprises some of the fastest-growing economies in the world, and all major players in the global economy are already established stronger strategic relations. This trend illustrates the need for the UAE to follow suit and find and exploit opportunities in the east.
The rationale for the eastern expansion has highlighted some of the core issues for consideration. Much of the discussion has revealed that the concerns for security and stability of the region affect the key regional powers, which means that external protection can also come from good relations with such countries as India, China, ROK, and Japan. Therefore, eastern expansion should be halted for fears of security because the major threats, including Iran, can be effectively handled through cooperation with their regional members. Such issues as cultural exchange and political benefits have also been explored, with the emergence of Central Asia being a key consideration. Most importantly, the east provides some of the most enticing economic prospects, which means that more investments and trade ties can massively benefit the UAE.
Recommendations
The first recommendation the UAE should increase its efforts and connections with Central Asia. As discussed earlier, the conflicting Islamic visions can be extended to this region, which would be in the best interest of the UAE to make sure these countries are allied with it. The fact that the countries share religion and that Russia no longer has total control means that it is time for UAE to act before such rivals as Iran lures them.
A second recommendation is that the UAE should make an effort to resolve its conflicts with other Arab countries. The peace in the region depends on all the member countries sharing the same vision for security and stability. The UAE’s connection with the US may pose a problem, but there remains a possibility that the shared cultural and religious values can help the countries achieve a neutral position and resolve their conflicts.
Lastly, it is recommended that the eastern expansion should not be a replacement of the western allies. The main argument is that the UAE will need as many allies and markets as possible for its resources and as sources for the critical resources needed by the country. Additionally, that the fact that the US is a world-leading producer of top-notch military equipment means that sustained relations with the US should remain a priority. Therefore, the initial efforts in the eastern expansion should trade-oriented, which would allow the UAE to exploit economic opportunities without upsetting the western allies. Such an approach means that until such a point that regional security and stability are guaranteed, the UAE can be assured of external protection from the US and other western allies.
References
Aldroubi, M. (2018). UAE reaches out to Iraq to counter Iranian influence in the Levant. The National News. Web.
Aldroubi, M. (2021). Iraq’s plan to diversify regional trade relations aims to fend off Iran’s influence. The National News. Web.
Aljazeera. (2020). US Senate backs massive arms sales to UAE after Trump veto threat. Aljazeera. Web.
Anjum, F. (2017). India-UAE: Emerging strategic partnership. European Journal of Social Sciences Studies, 2(5), 179-194. Web.
Arab News. (2020). Iran threatens to attack UAE over Israel deal. Arab News. Web.
Arab News. (2021). UAE to invest $3bn in Iraq. Arab News. Web.
Azodi, S., & Cafieiro, G. (2020). The United Arab Emirates’ flexible approach towards Iran. Iram Center. Web.
Damayanti, A. (2019). Indo-Pacific Maritime Cooperation: ASEAN mechanisms on security towards global maritime governance. Global & Strategis, 13(1), 1-14. Web.
Emerhub. (2018). Southeast Asia economic outlook 2018. Web.
Gulf News. (2018). UAE calls for strengthening conflict mediation efforts. Gulf News. Web.
Habibi, N. (2020). The Persian Gulf and China: The growth and limits of economic ties. The Middle East Brief, 139, 1-9. Web.
Jalal, I. (2020). The UAE may have withdrawn from Yemen, but its influence remains strong. MEI. Web.
Jeong, H. (2019). Beyond resource diplomacy and economic statecraft: UAE-ROK relations in the 21st century. Asian Journal of Middle Eastern and Islamic Studies, 13(2), 226-245. Web.
Katzman, K. (2021). The United Arab Emirates (UAE): Issues for US policy. Congressional Research Service.
Menegazzi, S. (2017). Northeast Asia Security and China’s role. IAI, 1-13. Web.
Pollock, D. (2020). Forecasting U.S.-UAE relations under the new Biden administration. The Washington Institute for Near East Policy. Web.
Statistics Times. (2019). Comparing China and India by economy. Statistics Times. Web.
Statistics Times. (2020). Population of Asia. Statistics Times. Web.
The European Business Review. (2020). Why business relationships between Europe and the UAE Are becoming more important than ever. The European Business Review. Web.
US Department of State. (2020). US relations with United Arab Emirates. State. Web.
US Mission United Arab Emirates. (2020). President Trump announces historic agreement to normalize relations between the UAE and Israel. USEmbasy. Web.
United States Trade Representative. (n.d.). United Arab Emirates: U.S.-United Arab Emirates Trade Facts. Web.
Upadhyaya, S. (2019). India’s maritime security relations with the gulf cooperation council countries – Prospects amid rising Chinese influence. Journal of the National Maritime Foundation of India, 15(1), 1-14. Web.