Introduction
Published financial statements provide the stakeholders with a narrow insight into the financial strengths and weaknesses of a business. Therefore, it is necessary to carry out a comprehensive financial analysis. The paper seeks to carry out a financial analysis of BMW Group for a period of five years, that is, between 2008 and 2012.
Balances reported
Income statement
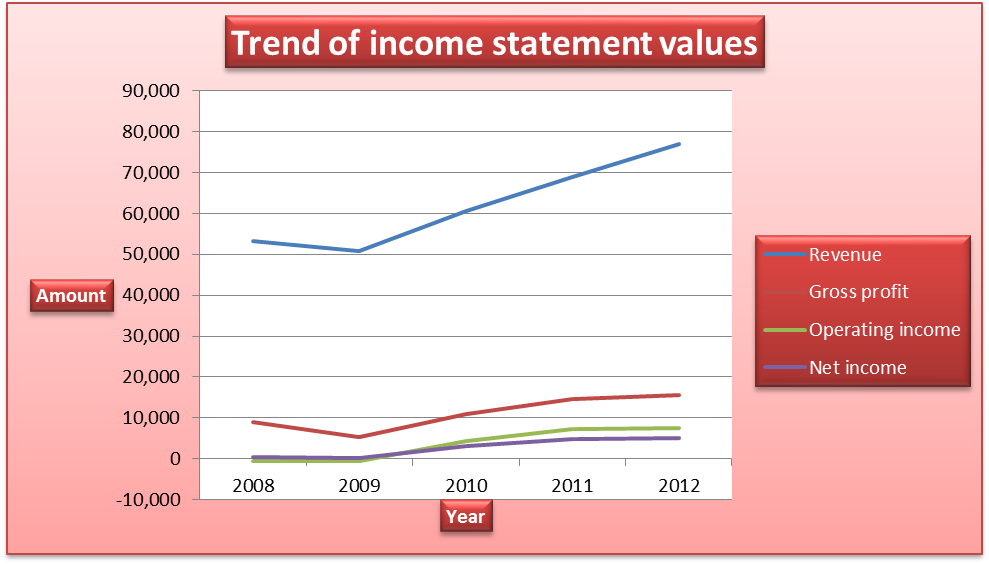
The company reported a decline in the balances reported for revenue, gross profit, total operating expenses, operating income, and net income between 2008 and 2009. The decline was caused by the global economic meltdown and volatile economic conditions. The balances grew significantly between 2010 and 2012. Revenue increased from €60,477 million in 2010 to €76,848 million in 2012. The growth in revenue was caused by the change in the strategies and an increase in the number of sales stores across the world. This strengthened the existing sales network. The operating expenses also increased from €6,587 million in 2010 to €8,023 million in 2012. The increase was caused by a massive investment in technology and an increase in personnel cost. Despite the challenges and the increased competition, the net income increased from €330 million in 2008 to €5,096 million in 2012. Thus, it can be observed that the company reported impressive growth in revenue and profit.
Balance sheet
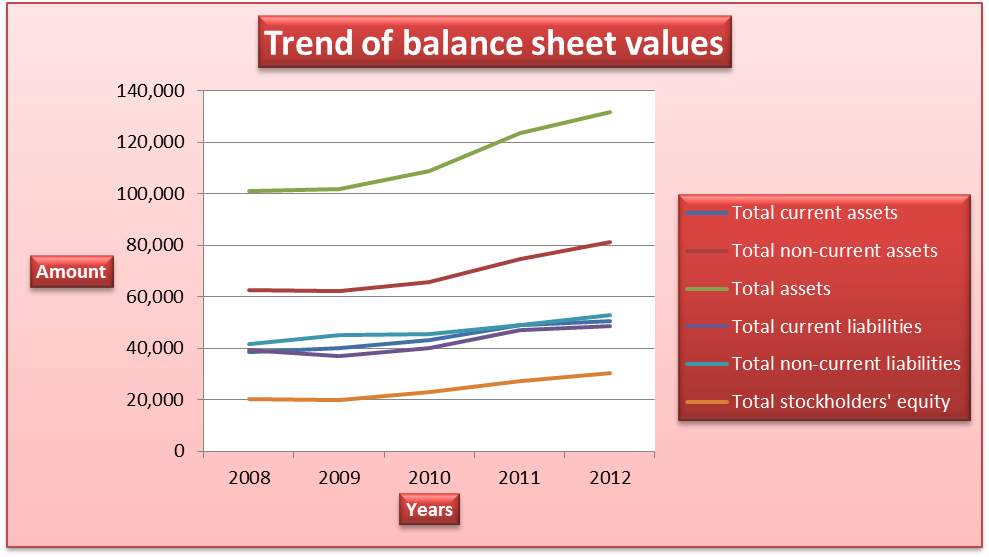
The growth in the income statement values was supported by a corresponding growth in the balance sheet values (Collier 17). The value of total assets increased from €101,086 million in 2008 to €131,850 million in 2012. It can be observed that the value of non-current assets exceeded the value of current assets. This shows that a significant proportion of the total assets of the company are not held in less productive liquid assets. The increase in total assets was caused by the increase in the balances of property, plant and equipment, liquid funds, leased products, and receivables from sales financing.
On the liabilities and equity section, total liabilities increased from €80,813 million in 2008 to €101,448 in 2012 while the total equity increased from €20,265 million in 2008 to €30,402 in 2012. The increase in the total liabilities was caused by an increase in the amount of finance liabilities, customer deposits, and liabilities to banks. The increase in equity was caused by growth in the profit attributed to shareholders. Further, the balances show that the company makes use of debt financing more than equity financing.
Cash flow statements
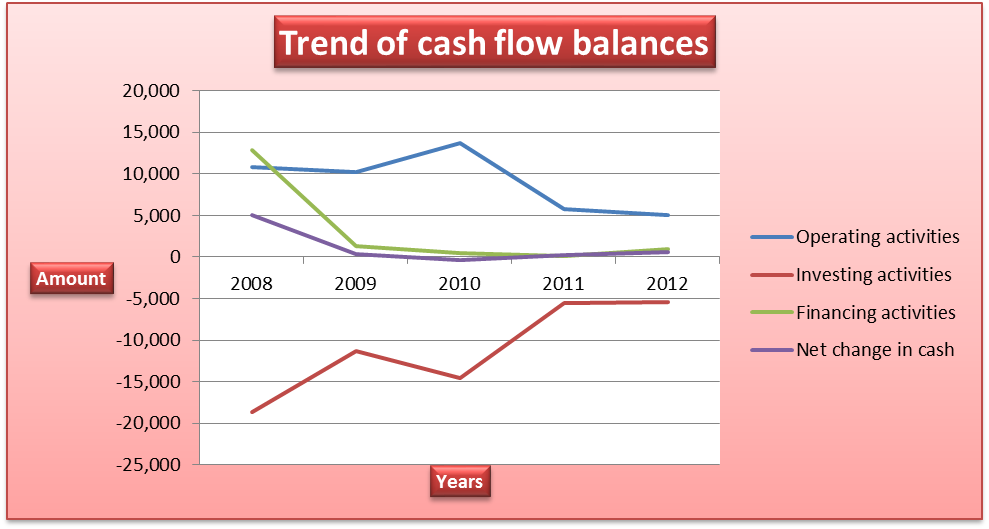
The balances for the cash flow statement declined over the period. The cash flow generated from operating activities declined because of the increase in receivables from sales financing and leased products. Further, the cash flow used in investing activities declined from €18,652 million in 2008 to €5,433 million in 2012. The decline can be attributed to gradual decline in the amount of investment in intangible assets and property, plant and equipment. Finally, the cash flow generated from financing activities increased between 2011 and 2012. This was caused by cash inflow received from the issue of bonds.
Common size financial statements
BMW Group. Common sized income statement
For a period of five years (2008 – 2012)
The values reported in the income statement are expressed as a percentage of revenue (Deegan 83). In the table above, revenues, gross profit, operating income, and net income increased. However, cost of revenues, operating expenses and EBITDA declined over the period. The cost of revenue and operating expenses takes a significant proportion of the revenue earned by the company. The net income attributed to shareholders also increased as a result of an increase in sales and revenue.
BMW Group. Common size balance sheet
For a period of five years (2008 – 2012)
The values in the balance sheet are expressed as a percentage of total assets (Haber 41). The non-current assets take a significant proportion of the total assets. Also, it can be observed that the balances of total liabilities exceed the shareholders’ equity. The balance sheet values grew over the period. The balance of property, plant and equipment is made up land, plant and machinery, office equipment, factories, and other operational facilities.
Ratio analysis
The profitability of the company improved over the period. However, the company reported a decline in profitability in 2009 due to the global financial crisis. The liquidity ratios of the company remained stable. The current ratios were slightly above one while the quick ratios were quite low. The ratios show that the company may face difficulties in paying current liabilities using liquid assets (Clarke 380). The solvency position of the company improved over the period. This can be attributed to increase in profitability. The gearing level of the company, as measured by financial leverage and debt to equity ratio, was relatively stable. The company is highly geared as indicated by the high amount of debt in the capital structure. The operating efficiency of the company improved over the period. This can be observed in the increase of efficiency ratios. An increase in the operating efficiency contributed to the increase in profitability. Finally, the investment ratios improved over the period. It implies that the value of the shares and the overall value of the company increased (Arnold 38).
Dividend policy
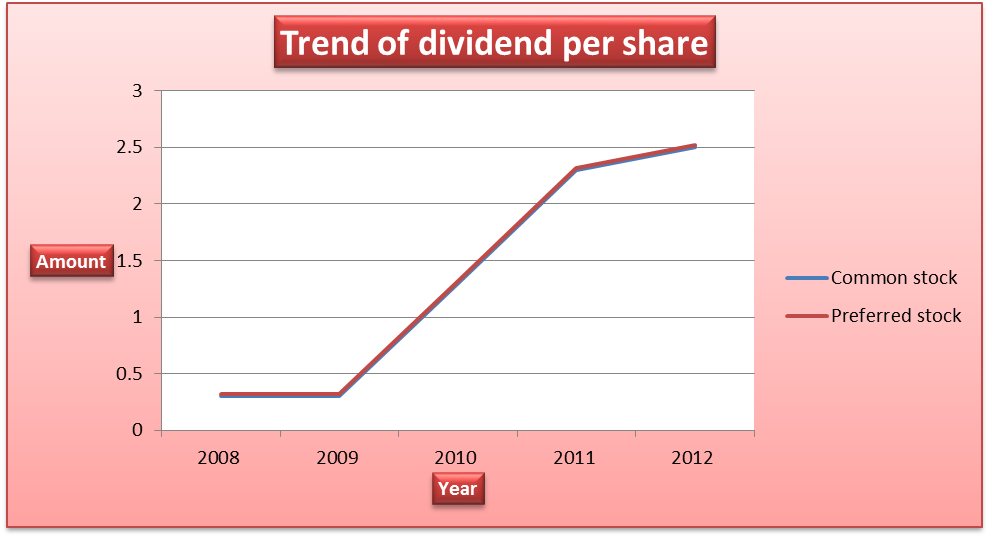
The company uses an open dividend policy. The amount of dividend paid per share depends on the amount of profit earned by the company. Thus, it is expected that as profit increases, the amount of dividend paid also increases. The table presented below shows the amount of dividend paid by the company for the past five years.
Source of data – BMW Group 45
The dividend paid for each common stock and preferred stock increased over the period. This corresponds to the increase in profitability of the company.
Conclusion
In summary, the analysis above shows that the overall financial position of the company improved over the past five years.
Works Cited
Arnold, Glen. Corporate Financial Management, UK: Financial Times/Prentice Hall, 2007. Print.
BMW Group 2012, Annual Report 2012. Web.
Clarke, Edward. Accounting: An Introduction to Principles and Practice, USA: Cengage Learning, 2012. Print.
Collier, Peter. Accounting for Managers, London: John Wiley & Sons Ltd, 2009. Print.
Deegan, Craig. Financial Accounting Theory, London: McGraw-Hill, 2009. Print.
Haber, Jeffrey. Accounting Demystified, New York: American Management Association, 2004. Print.