Introduction
The offered research is created with the pivotal aim to investigate the impact of cross border e-commerce on China’s international trade. The topic for the investigation is chosen because of the growing importance of the online business and, at the same time, the robust economic power of China which now becomes one of the leading states in the world with the significant presence in the international market. The scope of the selected issue is also proven by the fact that such platforms as Amazon, e-Bay, AliExpress, RED, or Taobao generate significant income every year and continue to grow. For this reason, the study offers information acquired from relevant literature and devoted to the selected problem. The given section provides the background of the research, rationale, and the primary objectives of the project.
Background
E-commerce is one of the crucial elements of the modern world. With the evolution of technologies and development of the Internet, companies acquired the chance to sell their products by using available digital channels online platforms such as social media, websites, or specific application. It indicated the rise of the era of e-commerce with its unique peculiarities and a significant impact on global trade (Laudon and Traver, 2014). Today, the given mode of business relations is considered one of the most beneficial and promising approaches to distributing goods and cooperating with partners in distant locations.
Nowadays, China can be viewed as one of the flagships of e-commerce. Today, the state devotes significant attention to the development of this sphere and considers it one of the strategically important areas that can help to generate stable and high revenue. The market size of e-commerce reached about 2,7 trillion yuan ($302 billion) in 2018 and continued its annual growth by 63,2% (Feifei, 2019). Moreover, sales revenue from e-commerce accounts for 20% of the whole online market of the state, which proves the importance of the sphere for China (2017 China cross-border e-commerce (export B2B) report, no date). This number can grow up to 30%, which demonstrates the fundamental role of e-commerce in the economy of the state (Fan and Backaler, 2019). There is also an idea that e-commerce has a positive impact on the promotion of international trade of China every year because of the emergence of multiple opportunities for the cooperation, business, and increased revenue. Under these conditions, the purpose of this project is to analyse how e-commerce impacts Chinese global trade.
In such a way, it is possible to admit that the modern business world is characterised by the dominance of different forms of e-commerce that evolve due to the evolution of technologies and their integration in various spheres of human activity. For this reason, it is critical to analyse the selected issue as its improved understanding is vital for the better vision of the international discourse.
Justification
The choice of the problem for the investigation is preconditioned by several factors. First of all, the success of companies such as Amazon, e-Bay, and Alibaba demonstrates the increased importance of e-commerce and benefits that might be acquired from using the Internet for trade and business aspects. That is why, there is a tendency for the emergence of new companies that focus on working with clients on the Internet and providing opportunities for other trends to use their platforms for this sort of cooperation (Laudon and Traver, 2014). Second, China can be considered as one of the leaders in this sector as it manages to combine the powerful national economy and developed industries with the use of technologies to create unique offerings for customers and meet their requirements to comfort, convenience and diversity (Distribution of cross-border import e-commerce, no date). Finally, for China, e-commerce became a force facilitating the evolution of international trade and the increase in national income (Eckart, 2013). For this reason, there is a critical need for the investigation of the phenomenon to acquire its improved understanding.
Objectives and Research Question
The pivotal aim of the study is to determine the relationship between cross-border e-commerce and Chinese international trade. That is why the following research questions are formulated:
What is the correlation between cross-border e-commerce and Chinese international trade?
How does cross-border e-commerce impact Chinese international trade?
The goal formulated above will be achieved by following the objectives:
- To define cross-border e-commerce and its peculiarities
- To analyse the unique features of e-commerce in China
- To identify the correlation between e-commerce and the Chinese international trade
- To define the current state of international trade in China
- To determine if there are positive or negative effects caused by e-commerce on the international trade of China
In such a way, the given research framework impacts the whole project, preconditions the choice of research methods, and conclusions formulated at the end of the study.
Literature Review
The critical importance of cross border e-commerce and its links with international trade are evidenced by the relevant literature. Thus, researchers state that business transformation due to the popularisation of online interactions can be viewed as one of the unique features of modern international trade (Yousefi, 2015). Accepting the benefits of this mode, multiple corporations improve its online presence as it helps to avoid excessive complexity linked to managing numerous departments, renting trade spaces, and other challenges traditionally associated with physical firms (CIW Team, 2019). Companies acquired an opportunity to cooperate with clients directly and minimise the response time, which resulted in increased income (Yuan, Wang and Zhang, 2011). The importance of e-commerce and its critical role in the modern world is evidenced by the fact that in 2019 it managed to generate about $3.5 trillion in sales and it is forecasted that by 2021, the number will reach $4.9 trillion (Retail e-commerce sales worldwide from 2014 to 2023, no date). That is why online trade becomes a powerful tool that should be considered by national economies as one of the ways to facilitate their international trade and ensure the improved position at the global market.
Methodology
The review of literature is selected for the given study as one of the central methods to collect information and create the theoretical framework for the following discussion of the phenomenon of e-commerce and its positive impact on national economy and trade. At the same time, the literature review is impacted by the paradigm offered for the given project.
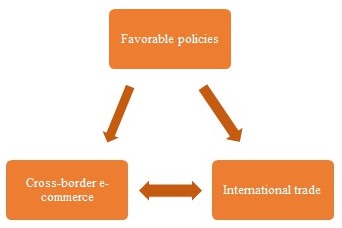
As it can be seen from Figure 1, it is supposed that the cross-border e-commerce is linked to favourable policies promoting the rise of the phenomena and, at the same time, to international trade. For this reason, the selection of sources for the analysis is impacted by the need to find the body of evidence proving the idea that the cross border e-commerce is one of the most important phenomena of the modern business world and it also promotes the empowerment of the national economy via the international trade. As far as the central purpose of the given review is to examine the dominant idea present in the academic field, there is an overview of this subject created by reviewing the relevant articles devoted to the issue of cross-border e-commerce.
At the moment, the literature devoted to cross-border e-commerce has several major themes, such as: the major advantages of e-commerce, the future of this trade option, investigation of current successful firms and brands functioning in the given area, and state regulation related to online trade along with its impact on the local economies and international relations (Terzi, 2011). For this reason, the given literature review is composed in accordance with the central research objectives formulated above and the themes discussed by the majority of authors. The articles selected for the analysis met the following criteria: relevance, e-commerce scope, its impact on the economy and international relations. In such a way, the literature review identifies advantages of e-commerce, its links with the international trade and policies, outlines some successful examples.
Advantages of E-commerce
The basic advantages of e-commerce are central for understanding its value and the critical importance for the modern world. From the perspective of price, transaction cost, and diversity of available products, cross-border e-commerce can be viewed as a factor promoting consumer welfare and improving their buying capacity. In accordance with the statistics, the existence of abundant options, reasonable prices, and extremely low cost of sear, help clients to save about $12 billion annually and increase their satisfaction levels (Feifei, 2019). Additionally, Yuan, Wang and Zhang (2011) assume that the welfare of consumers enhances from the across-the-board reduction in offline trade costs, which means that they acquire free funds that can be spent on other goods and new purchases. For this reason, new opportunities for the rise of international trade emerge. Moreover, e-commerce can help to decrease time costs and information costs, which can also be viewed as a factor improving the welfare of individuals engaged in it and transform them into more active buyers vital for the empowerment of the national economy and cross-border trade.
As for China, the state correctly realises the critical importance of the given feature and multiple opportunities associated with its following evolution and growth. There are several factors that prove this statement. Thus, at the moment, 48.01 million individuals residing in China can be associated with various forms of cross-border e-commerce (Fan and Backaler, 2019). Moreover, Feifei (2019) assumes that the number of people engaged in this model will duplicate in the next year. It means the emergence of a significant stimulus for the evolution of e-commerce and preservation of the high speed of its rise. Li (2016) is also sure that the increase in populations will also precondition the appropriate change in the international trade patterns employed by the Chinese government. Today, such sites as Aliexpress or Alibaba are known in the majority of regions across the world (Eckart, 2013). It can be considered the example of cross-border e-commerce as customers from multiple locations order goods from China and stimulate the evolution of international trade.
Moreover, e-commerce contributes to the effective management of transaction costs, which is considered one of its critical advantages promoting the further development of international trade (Yousefi, 2015). Wang, Wang, and Lee (2017) assume that the positive correlation between the two discussed factors can be explained by the improved ability to overcome obstacles mentioned above (transaction costs) and favourable policies that are established by the Chinese government to cultivate the cross-border e-commerce. In such a way, there is a growing body of evidence stating that recent successes in the sphere of online trade made China also facilitate the rise of its international trade and cooperation with partners from various regions (Yige and Meivitawanli, 2018). For this reason, there are multiple attempts to preserve this tendency and create a positive environment for future growth.
Future of E-commerce and the Impact on the Business World
Today, the whole business society is driven by the idea of e-commerce and multiple opportunities for global trade which are associated with it. The majority of authors of the selected articles accept the idea that the era of the Internet and technologies creates a new virtual space for cooperating between clients and companies, which means that companies can enter a new environment characterised by the absence of such traditionally important difficulties as cooperation between multiple departments peculiar to giant firms, extra fees, and specific client-service issues (Lee, 2001). Today, due to the e-commerce, Web technologies, and availability of mobile devices, companies can reach their target audience in different locations, regardless of some obstacles. This factor became a powerful stimulus for the extremely fast rise of this form of trade, and it is evidenced that at the moment, the total dollar volume of the U.S. e-commerce sphere was estimated about 4,5 trillion in 2005 and continues to grow (Ariguzo, Mallach, & White, 2006). For this reason, the existing body of evidence assumes that today, and in the future, the e-commerce and social commerce, as one of its more developed forms, supported by web 2.0 will become the most powerful forces shaping the international trade and cross-border communication between countries with powerful economies, including China (Li, 2016). Web 2.0 is a term that is used to describe elements, technologies, and factors of an innovative environment impacted by the dominance of a new mode of trade (Diao, He and Yuan, 2016). The decentralisation of relations between clients and companies is one of the distinctive features of this new environment and results in an emergence of giant corporations with extremely effective schemes generating significant income (Gori, 2016).
One of the e-commerce characteristics promoting the better international relations is its ability to consider specific characteristics of every partner, differentiate them in different groups, and structure them in accordance with the current needs (Jain, Jain and Jain, 2016). It helps to work more effectively and avoid delays or mistakes associated with offering incorrect product or item (Wang and Xie, 2014). It also meant that detailed profiles with the in-depth outline of preferences and interests were created and updated constantly, to customise offerings and proposals from multiple brands across the world (Miglani, 2017). From the customer perspective, it became an element that changed the nature of trade and provided them with more convenience and comfort. In accordance with the basic rules of trade, the growing satisfaction of clients means their increased desire to continue their participation with companies and buy new products (Young et al., 2011). Along with the growing well-being of multiple populations, the increased level of convenience means that e-commerce remains and will become the major force facilitating the improved cooperation between nations that produce specific products and consume them (WTO, 2019). From this perspective, Nair (2017) assumes that in the future, the level of services provided by e-commerce will diversify and attract new clients.
Another important feature about e-commerce is the way it promotes international relations and cross-border trade. Analysing the roots of this phenomenon, researchers outline the critical power of individuals to change patters of international trade relations peculiar to states (Gori, 2016). It means that individuals attracted by reasonable prices and convenience drive the evolution of e-commerce and increase the number of items that are sold every day. In its turn, it results in the increased demand for production and contributes to the growth of cross-border trade (Li, 2016). That is why having started as small platforms for individuals all over the world, e-commerce has grown into a force changing global trade relations.
There are also multiple predictions about the future of e-commerce and its effect on states that are known for the increased presence of companies which switched to this mode, such as China. Richards and Li (2018) state that the ability to generate stable revenues and remain informed about the changes in clients’ demands along with the improved customer service, topicality of new offerings, flexibility, and updated content contribute to the dominance of these forms and their becoming the most promising way to evolve (O’Leary, 2019). For this reason, e-commerce will remain a potent driver facilitating the evolution of the business world and improved international trade and cross-border relations. At the same time, Shen (2013) admits the fact that the significance of this option is evidenced by the fact that there are also multiple changes in regulatory measures to ensure that e-commerce will benefit from favourable policies and continue to evolve. For instance, the Chinese government have established multiple laws to protect clients from frauds and unethical actions and ensure a high level of security (Li, 2016). At the same time, there are also changes in the legal field that create the environment favourable for the emergence and evolution of new e-commerce firms (China’s new e-commerce law, 2019). In such a way, there is a specific system characterised by the presence of elements that impact each other. The fast growth of e-commerce promotes the empowerment of the international trade and state economy, and this factor preconditions the appearance of new laws which, in their turn, cultivate the development of e-commerce.
E-commerce, Chinese Economy, and International Trade
Revolving around the phenomenon of e-commerce and its impact on China, it is also critical to consider the overall state of the economy, the current legislation, and basic directions of the international trade peculiar to the nation. It should be said that the boost of online trade triggered critical changes in the Chinese economy and legal framework (China balance of trade, no date). At the moment, the government recognises the need to support the given trend and offers laws and regulations protecting clients using online purchases, which has a positive impact on e-commerce in general (China’s new e-commerce law, 2019; Wu, 2016). Moreover, viewing AliExpress, Taobao, and RED as platforms vital for the national economy and promotion of the international trade, the state offers wise taxation policy that helps the companies to generate stable income and evolve (Wu, 2016). Researchers state that the combination of the powerful industrial sector characterised by the diversity, fast-growing economy, and the evolving online trade platforms can transform China into one of the leaders of the global trade with the ability to meet diverse demands of clients from different countries (Amadeo, 2019). For this reason, there is a body of evidence proving some positive correlation between cross-border e-commerce and international trade of China.
Analysing the problem, it should also be said that China remains the world’s leading merchandise trader. In 2019, the value of import and export reached $4.51 trillion (31.55 trillion yuan), which evidences the power of the national economy and the focus of the state on playing a significant role at the global level (Chinese foreign trade in figures, no date; Ministry of Commerce People’s Republic of China, no date). To some degree, this significant sum results from the fast rise of e-commerce and income it manages to generate annually (CGTN, 2020). Specialists admit the fact that the current international trade of China is closely linked to online trading and, benefits from the rise of this mode of business as the state boosts its exports by employing the trend and successfully using the relevant changes in the global market (Hollingsworth, 2017).
In general, the success of various forms of e-commerce in China is evidenced by several giant corporations that now dominate the market and attract new clients every day. For instance, Taobao, as a representative of this cohort managed to generate $444 million in 2019, which demonstrates its increasing power and the ability to affect international trade patterns in China (Alibaba Group, 2019; Liu and Jitphrasong, 2019). Another example comes from Xiaohonshu that reached a $1.48 billion revenue in 2019 and continues to grow (Liu, 2018). Finally, AliExpress is one of the most well-known platforms, with 785 million active users who were ready to pay and order goods by using the application (Deyan, 2020). The company enjoys about $10 billion of annual paid GMV and has outstanding opportunities for future development (Annual net income of Alibaba from financial year 2010 to 2020, no date). It operates in more than 200 countries, while the top ten nations by gross merchandise value (GMV) are Russia, Spain, France, Poland, Brazil, the USA, the UK, Netherlands, Israel, and South Korea (Alibaba Group Holding 20-F20192019 FY annual report, 2019). In such a way, the importance of these companies for the promotion of export and import in China cannot be overestimated. They drive cross-border commerce and the evolution of the global market by offering new opportunities both to companies and clients.
Conclusion
Altogether, there is a body of evidence stating that e-commerce is one of the major features shaping the evolution of the modern international trade. Multiple advantages and the ability to cooperate with clients facilitates the rise of this sphere of business and make it critically important for the future. As for China, it experiences a blistering growth of e-commerce which becomes the critical trend of its export and international business relations. Platforms such as Taobao, AliExpress, and RED shape the global online environment and cross-border commerce by offering new opportunities for information and goods exchange. The beneficial character of online trade attracts new companies, increases demand, and revitalises the economy, which, in its turn, results in the corresponding growth of export. Under these conditions, the literature review proves the existence of the link between cross border e-commerce and international trade, which is vital for the research.
Reference List
2017 China cross-border e-commerce (export B2B) report. Web.
Alibaba Group Holding 20-F20192019 FY annual report. Web.
Amadeo, K. (2019) ‘China’s economic growth, its causes, pros, cons, and future’, The Balance. Web.
Annual net income of Alibaba from financial year 2010 to 2020. Web.
CGTN (2020) China’s foreign trade hit $4.6 trillion in 2019. Web.
China’s new e-commerce law (2019) Web.
Chinese foreign trade in figures. 2010. Web.
CIW Team (2019) ‘80% of Chinese consumers’ unplanned shopping comes from social e-commerce’, China Internet Watch, Web.
Deyan, G. 35 remarkable AliExpress market share statistics to know in 2020. Web.
Diao, Y., He, Y. and Yuan, Y. (2016) ‘Framework for understanding the business model of social commerce’, International Journal of Mangement Science, 2(6), pp. 112-118
Distribution of cross-border import e-commerce transaction value in China in 3rd quarter 2019, by platform. Web.
Fan, Z. and Backaler, J. (2019) Five trends shaping the future of e-commerce in China. Web.
Feifei, F. (2019) ‘Social commerce sector on the up’, ChinaDaily, Web.
Eckart, J. (2013) ‘8 things you need to know about China’s economy’, World Economic Forum, Web.
Gori, S. (2016) ‘The growth of e-commerce in international trade and its possible effects on the sustainable development’, International Journal of Development Research, 6(11), pp. 10428-10433
Hollingsworth, J. (2017) ‘China takes first step toward regulating e-commerce’, Sixth Tone, 1 November. Web.
Jain, P., Jain, K. and Jain P. (2016) ‘Electronic commerce and its global impact’, Innovare Journal of Engineering and Technology, 4(3), pp. 1-6.
Laudon, K. and Traver, C. (2014) E-commerce: business, technology, society. 10th edn. New York, NY: Pearson.
Li, Y. (2016) ‘Analysis on e-commerce crisis in China in the international trade environment’, Modern Economy, 7, pp. 71-76. doi:10.4236/me.2016.71008.
Liu, M. (2018). Analysis of the emerging Chinese social media- The Little Red Book. Web.
Liu, Y. and Jitphrasong, N. (2016) ‘The analysis of Taobao c2c e-commerce marketing strategy’, International Journal of Management and Commerce Innovations, 4(2), pp. 172-181.
Miglani, A. (2017) ‘E-commerce and its impact on Indian and global market’, International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology, 4(12), pp. 19-21.
Ministry of Commerce People’s Republic of China (no date) Briefing on China’s import & export in December 2019. Web.
Nair, K. (2017) ‘Impact of e-commerce on global business and opportunities – a conceptual study’, International Journal of Advanced Engineering and Management Research, 2(2), pp. 324-336.
O’Leary, D. E. (2019) ‘Hashtag commerce: “Order by Tweet.”’, Journal of Information Technology Teaching Cases, 9(1), pp. 26–37
Retail e-commerce sales worldwide from 2014 to 2023 (no date). Web.
Richards, J. and Li., M. (2018) ‘The Chinese e-commerce search advertising business: a case study of Taobao’, Contemporary Management Research, 14(4), pp. 121-142.
Shen, K. (2013) ‘An analysis on the influence of e-commerce on China’s international economic trade and relevant strategies’, International Journal of Science and Research, 4(9), pp. 384-386. Web.
Terzi, N. (2011) ‘The impact of e-commerce on international trade and employment’, Procedia Social and Behavioral Sciences, 24, pp. 745-753.
Wang, Z. and Xie, Y. (2014) ‘The influence of e-commerce on international economic trade’, Journal of Chinese & Foreign Entrepreneurs, 35, pp. 1-2.
Wang, Y., Wang, Y. and Lee, S. (2017) ‘The effect of cross-border e-commerce on China’s international trade: an empirical study based on transaction cost analysis’, Sustainability, 9(11), p. 2028.
World Trade Organization (WTO) World trade statistical review 2019. Web.
Wu, C. (2016) ‘Chinese e-commerce legislation current situation, problems and ways to improve’, Asia-Pacific Management and Engineering Conference. Web.
Yige, Q. and Meivitawanli, B. (2018) ‘Effect of cross-border e-commerce on international trade of emerging country in the case of China’, Malaysian E-Commerce Journal (MECJ), 2(1), pp. 9-12.
Young, J. et al. (2011) ‘Impact of e-commerce on international trade — based on a Iceberg Cost Model’, International Journal of Trade, Economics, and Finance, 2(2), pp. 175-178.
Yousefi, A. (2015) ‘The impact of cross-border e-commerce on international trade’, Proceedings of International Academic Conferences. Web.
Yuan, K., Wang, Y. and Zhang, G. (2011) ‘A brief analysis on e-commerce’s influence on international economic trade and strategies’, China Business & Trade, 24, pp. 211-212