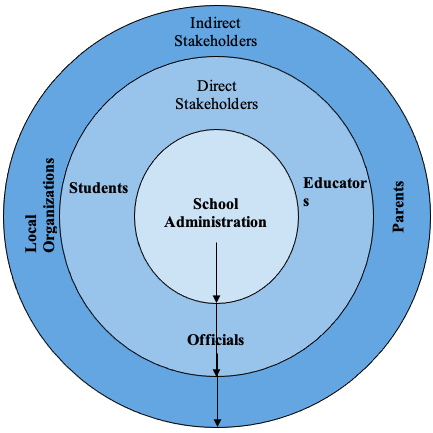
Building an educational establishment that will revolutionize the perception of education as a whole does not require only a clear vision. It involves an understanding of the stakeholders that will participate in the establishment of the program, either directly or indirectly (Beerkens, 2017). Brisbane Southside State Secondary College, The Green School, and Beenleigh State High School want to not only contribute to the future of their students but set the new education standards for other facilities. For this, as seen in the diagram, the schools will require such stakeholders in the community as students, educators, officials, local organizations, and parents.
Within the community, the stakeholders fit either directly or indirectly. For example, in the establishment of the new vision, the direct stakeholders from the community who will reap the effects of the program are students, educators, and officials. On the other hand, indirect stakeholders who play an implicit role are the local organizations and parents (Zurqoni et al., 2018). The leadership then will be distributed according to the roles, going from the school administration, being allocated to the direct stakeholders and then from the direct stakeholders to their indirect counterparts.
As for the roles, the main role is allocated to the school administration that will distribute the tasks and responsibilities, being in charge of the program and its vision. When it comes to the indirect stakeholders, officials will bring the funding for the innovative program (Francisco et al., 2020). In turn, educators will have to incorporate the new vision. Lastly, students will have to absorb the new information and encourage change. Regarding indirect stakeholders, local organizations will provide services for the building or fulfilling the needs of the establishment. In turn, parents will need to ensure the incorporation of the new values and a healthy learning environment. The accountabilities for success involve trust and strong connections and communication between the stakeholders (Singh, 2019). As a result, the success will be measured via random tests that will assess the satisfaction with the new system.
References
Beerkens, M., & Udam, M. (2017). Stakeholders in higher education quality assurance: Richness in diversity? Higher Education Policy, 30(3), 341-359.
Francisco, M. P. B., Hartman, M., & Wang, Y. (2020). Inclusion and special education. Education Sciences, 10(9), 238.
Singh, B. (2019). Character education in the 21st century. Journal of Social Studies (JSS), 15(1), 1-12.
Zurqoni, R., Apino, E., & Anazifa, R. D. (2018). Impact of character education implementation: A goal-free evaluation. Problems of Education in the 21st Century, 76(6), 881.