The retail industry is a very competitive area, which has only become even more intricate and difficult to navigate after the enhancement of the globalization process and the focus on expansion among retail companies. Being the indisputable global retail leader, Walmart has served as the example of implementing the expansion process correctly, both from the organizational and legal aspects of the process.
However, even Walmart’s progress has seen peaks and valleys as the company has been adjusting its operations and standards to state-specific requirements. Observing an organization of the scale as large as Walmart managing cross-cultural tasks and human resource management (HRM)-related objectives in the global market, particularly, in two different cultural settings, will help to define general strategies’ that other companies and follow in order to succeed in their HRM and cross-cultural management (CCM). Therefore, a comparison of Walmart’s stunning success in the U.S. and its recent failure in Germany will serve as the example of how CCM and HRM issues should be managed on a global scale.
Research Question
What were the main CCM- and HRM-related factors that prevented Walmart from successfully entering the German retail market compared to the stellar performance of Walmart in the U.S. retail environment?
Research Objectives
This study seeks to locate and analyze the main cultural and HRM-related factors that have contributed to Walmart’s success in the U.S. retail market and its failure in the German one. Specifically, this study will explore the CCM approach that Walmart has deployed in the U.S. setting and compare it to the CCM framework used in the German context. Similarly, the HRM strategies adopted in the American workplace environment will be paralleled with those that Walmart considered appropriate for the German setting. Thus, the company’s ability to adjust to different locations and its flexibility in managing CCM and HRM will be tested.
Literature Review
Walmart has gained quite an acclaim over the decades of its operations in the American economic context. Having built its reputation around the idea of providing the best price-quality ratio for its products, Walmart has quickly gained substantial support in the U.S. (Nanjundeswaraswamy et al., 2020). However, research states that, up until recently, Walmart’s approach toward HRM, as well as its framework for managing communication within the workplace, has been worthy of serious criticism (Nanjundeswaraswamy et al., 2020). Namely, the refusal to address the needs of staff members due to the prioritization of customers’ requirements has placed Walmart in a rather precarious position recently (Li & Liu, 2018).
Remarkably, a significant shift can be identified in the approach that Walmart has been using in its CCM and HRM frameworks in the U.S. context (Nanjundeswaraswamy et al., 2020). Particularly, unlike several years ago, when Walmart viewed its workforce solely as an expendable resource, the current perception of staff members is based on their needs, and employees’ demands are taken into account for the most part (Nanjundeswaraswamy et al., 2020). Therefore, Walmart has progressed in its management of its HRM issues largely.
United States
The fact that Walmart has not been entirely efficient in its CCM and HRM approaches in the U.S. environment should also be addressed. Specifically, the company had become notorious for its economically predatory behavior in local communities before it gained success in the U.S. setting (Xie et al., 2019). According to Xie et al. (2019), Walmart affected a range of local communities in a most devastating way, making local SMEs going extinct due to its pricing policies (Xie et al., 2019). Moreover., the company’s CCM system has also been causing issues due to a rather flawed approach toward processing feedback and the absence of any tools for customers to contact the staff and file a complaint.
Among more recent issues that Walmart has faced in the U.S. in regard to its CCM approach, one should mention the ineffective communication channel that the company has been using to keep in touch with its buyers. Specifically, Walmart ha ben facing issues with adjusting to the requirements of its millennial demographic, which expects much faster services than its predecessor did. Namely, the absence of the same day delivery option used to be one of the main reasons for Walmart to experience contempt from its American audiences (Kim, 2019). However, despite the specified concerns, the availability of products and the unreasonably low prices have helped Walmart to dominate the U.S. retail market fully (Kim, 2019).
Germany
However, when adapting its approach to the German setting, Walmart appears to have developed an issue in implementing a culture-sensitive approach. Although the two environments under analysis cannot be described as polarizing, there is a significant range of differences between the American and German retail markets. Specifically, when integrating into the German setting, Walmart seems to have dismissed the specified cultural component of the target environment, which has affected the organization’s perception by its German staff members as one of its core stakeholder types (Hamza & Nizam, 2016).
Specifically, studies indicate that, instead of adapting its standards of employee workplace practices to German culture, Walmart transferred its American framework of HRM into the German setting (Hamza & Nizam, 2016). As a result, the environment that was supposed to bolster employees’ initiative and resourcefulness by introducing them to unique scenarios has led to the increase in dissatisfaction in German employees (Kaelberer, 2017).
Namely, the absence of a rigid planning strategy and clear instructions for specific scenarios with delineated steps to be taken has defined the increase in stress levels among staff members, forcing them to resign instead of allowing them to develop new skills gradually (Hamza & Nizam, 2016). Consequently, the situation within the German economic setting could be described as the ultimate failure of HRM, as well as CCM. Specifically, Walmart should have deployed a cross-cultural strategy that would have allowed the company managers to identify the key characteristics and needs of German employees.
The Walmart Germany case represents a unique situation in which the cultural values and needs of the target population were misrepresented so profoundly that the company could not function in the target environment completely. Namely, as the existing reports on the subject matter specify, Walmart’s disregard for the high rates of diversity in Germany became the main stumbling block on the way to building a rapport with the staff. Specifically, German teams turned out to be composed of people from a variety of cultural backgrounds, which created a very diverse setting that was highly prone to conflict (Kaelberer, 2017). However, instead of examining the intricate characteristics of the target environment, Walmart chose to ignore it and reinforce the traditional homogenous framework instead.
From the perspective of Hofstede’s cultural theory, the misalignment between the U.S. and German perception of workplace relationships served as the major cause of the problem. Specifically, Hamza and Nizam (2016, p. 210) explain that “amongst the five dimensions of Hofstede’s three (Power distance, Individualism and Uncertainty avoidance) found to be significantly influential and discussible in the case of the Wal-Mart successive failure story in U.S. and Germany.” In other words, Walmart should have utilized the same approach that it adopted in the U.S. setting once it received strong pushback from its staff members belonging to ethnic and racial minorities in the U.S. setting (Kaelberer, 2017). However, by mistakenly presuming that German culture was close enough to American one, Walmart suffered a rather devastating defeat in its first attempt at integrating into the German market.
Relationships with Stakeholders
Additionally, the failure of Walmart’s CCM in the German setting can also be explained form the perspective of the theory of empathy. The Simulation Theory of Empathy (STE) has been produced only recently, but has already received a massive impetus for development due to the effect that it has had on the improvement in communication between companies and their target audiences (Gallagher, 2020). Offering an opportunity for companies to establish a rapport with their target population, STE postulates that the focus on empathy in building relationships with customers is vital to the further increase in customer loyalty rates (Gallagher, 2020).
Applying the specified theory to the failure that Walmart suffered in Germany, one will realize that zero effect has been put into creating an emotional bond with the target audiences (Neebe, 2020). Specifically, Walmart ignored the idea of showing empathy to its target audiences by offering the product that would address their vulnerabilities. Instead, Walmart applied the same aggressive marketing framework and communication technique that it used in the U.S. (Neebe, 2020). As a result, the German population could not see Walmart as a legitimate partner in their purchase process since Walmart failed to cultivate the same level of trust in the German setting as it did for its American audiences (Neebe, 2020). Arguably, the observed issue could be seen as the extension of the problem identified after the application of Hofstede’s model.
Namely, the absence of cultural awareness has served as the main reason for Walmart to detect the concepts that would have helped it to build an emotional rapport with its target audiences. However, on further assessment, it will become evident that, unlike the cultural awareness principle promoted by Hofstede, the STE framework highlights the role of cultural empathy as the main problem that Walmart encountered in the development of a CCM strategy. In the German market. Although the specified notions are seemingly similar, they represent an important nuance, namely, the presence of an emotional connection in the form of empathy (Neebe, 2020). Therefor, from the standpoint of the STE, Walmart’s main problem in CCM was represented by the lack of empathy.
Main Factors
Thus, when considering the main factors that have prevented Walmart form entering the German retail market, one must list poor CCM and the resulting failure to identify customers’ needs correctly. As a result, Walmart has failed to communicate the importance of its services to the target population and prove that it has a unique value [proposition that the target customers needed. Specifically, with its focus on its established CCM and CRM approaches, Walmart ignored the significance and role that market research and, particularly, the analysis of cultural factors, played in the development of sustainable and effective tool for attracting customers’ attention and gaining their trust.
Applying the Value Proposition Canvas model to the case in point, one will realize that the developed value proposition, while working perfectly for American audiences, did not coincide in any shape or form with the profile of a typical German customer (Krämer, et al. 2018). namely, Walmart failed to recognize the importance of cross-border shopping opportunities for German customers, as well as their willingness to explore new shopping options and trying new products outside of their traditionally selected brand (Krämer, et al. 2018). The specified issue appears to have particularly strong negative implications for the company that has been known for incorporating multiple brands and offering a high variety of brands, showing impressive rates of product diversity (Krämer, et al. 2018).
Namely, the fact that Walmart’s CCM approach mismatched the required one so poorly that even the partial coincidence in the customer profile could not avert it from the inevitable failure indicates thorough lack of research and extremely poor understanding of the needs of the target demographic.
HRM Failure
Another factor worth mentioning as the key contributor to the company’s inability to establish a strong presence in the German market is the lack of thought put into its HRM approach. Similarly to the CCM issues, the HRM approach that the organization has adopted in order to integrate into the German market was completely incongruent with the cultural background into which it was planted. The issues similar to those of CCM, namely, the failure to understand the values of German society ad its community members, and the resulting inability to create a strong and immediately noticeable value proposition were the main constituents of Walmart’s failure.
According to the accounts provided by the recent reports, the inconsistencies between the company’s corporate culture and values with those of German people made it virtually impossible for the company to attract any staff members (Xie & Cooke, 2019).
As a result, the approach that Walmart typically adopted toward its talent management led to zero results (Xie & Cooke, 2019). Coupled with the fact that Walmart has only recently started paying closer attention to the needs of its employees, which it had ben refusing to prioritize up until its recent HRM crisis, the reasons for Walmart to fail in the content of the German retail market appear to be quite apparent. Namely, the company’s inability to appeal to its target populations due to the absence of the skills for understanding their aspirations, culture, and values serve as the foundational reason for Walmart to fail tremendously in Germany.
Additionally, applying Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs as one of the main frameworks for evaluating the efficacy of the motivational approach used by companies, one will realize that Walmart’s framework for attracting potential employees also failed due to the inability to meet the needs of the higher tier, namely, cultural ones (see figure below).
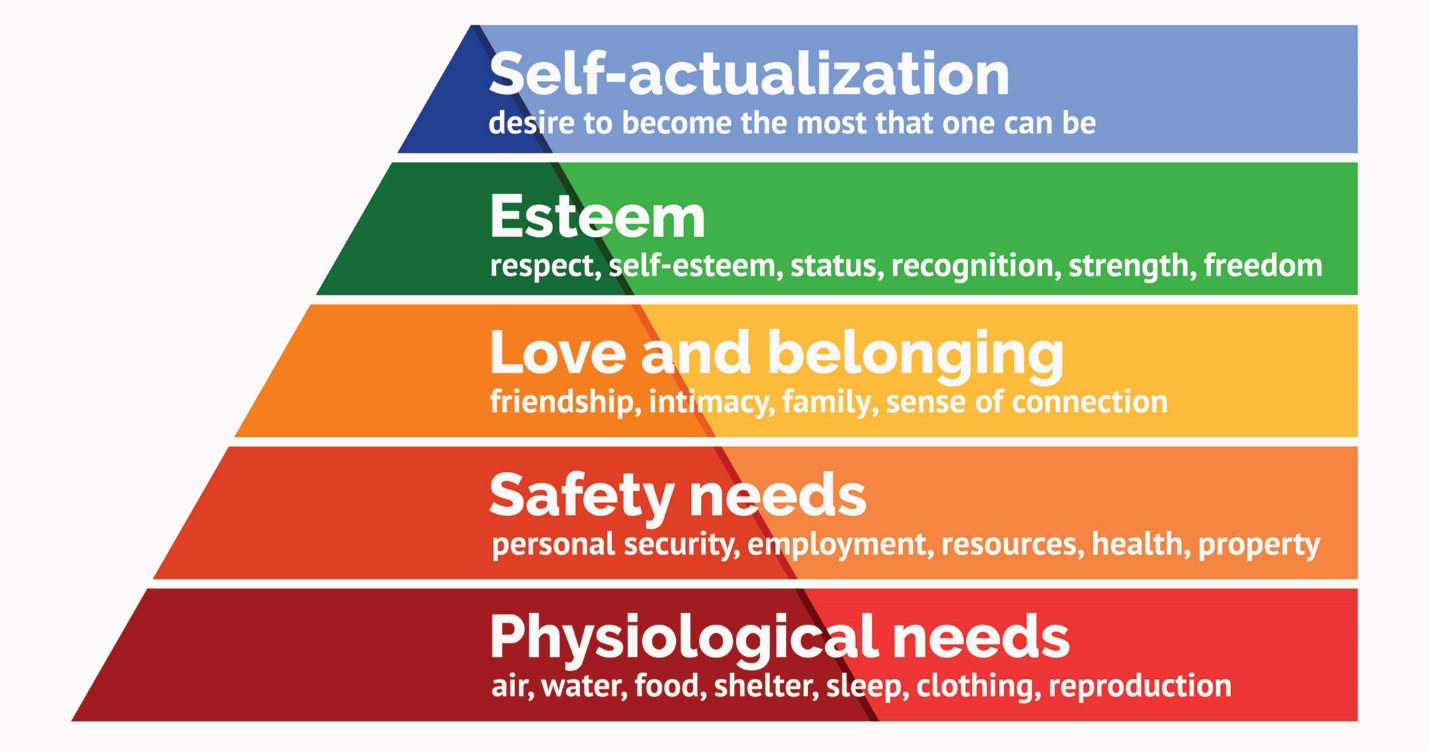
As Figure 1 shows, the need for building esteem constitutes one of the top utmost needs of staff members. Although being less relevant than physiological needs or the needs related to safety, it still constitutes an important part of the motivation level. However, by failing to recognize the values that Germane employees place on their work environment, Walmart made a glaring mistake and created premises for its ultimate failure.
For instance, according to the case report by McDonald (2017), Walmart encouraged its employees to begin their workplace routine by engaging in group chants and exercises, such as stretching. Furthermore, staff members were reportedly made to shout the company’s name during the specified practice (McDonald, 2017). What Walmart managers did not take into account was the fact that most German employees would find the specified practice silly, at best, and obnoxious and demeaning, at worst (McDonald, 2017). As a result, the drastic misunderstanding of the German culture led to the company’s inability to attract local labor force to become a part of the organization (McDonald, 2017).
The observed problem aligns with Hofstede’s theory of Cultural Dimensions, particularly, with it aspects of power versus distance, the juxtaposition of collectivism versus individualism, and, to an extent, with the issue of restraint versus indulgence. Namely, the inability to recognize the independence of German employees and their unwillingness to follow the requirements regarding chanting and shouting corporate slogans, which the German staff saw as ridiculous, led the company to losing its influence in the German labor and retail markets. Specifically, with its inability to develop an approach toward managing human resources that would recognize the agency of staff members and approach the management of the key workplace tasks with due seriousness, Walmart made its further progress in the German market impossible.
Solution
Although the observed failure in Walmart’ attempts at building its presence in the German market setting has been quite notorious, it does not imply that the company will never be able to integrate into the specified environment again. However, to undertake another attempt at its foray into the German economic setting, Walmart will need to develop a new HRM, CCM, and CRM approach based on the principles of cultural empathy and the related concepts that will allow it to build a better rapport with the target population. For this reason, the introduction of the agile CCM and CRM techniques will be required.
The significance of the agile framework in implementing CCM and CRM strategies in the context of the German market for Walmart is vital. With the adoption of the agile framework in its CCM and CRM areas, Walmart will be able to introduce learning algorithms that will help it to understand the specifics of German culture and the key cultural characteristics of its German audiences (A Al-Homery et al., (2019). Namely, the agility principle will help Walmart to align its organizational and production processes with the ones of learning and implementing its research of the specified market.
The ensuing rise in the levels of awareness about the key specifics of customers, their needs, and cultural characteristics will inform the communication strategy and the choice of tools that the organization will deploy in order to attract new audiences (A Al-Homery et al., (2019). As a result, the company will increase the extent and efficacy of its responsiveness, which will lead to a rise in the extent of connection between the customer and the organization.
Specifically, the incorporation of the agile technique as the basis for CCM will suggest that Walmart should help the company in connecting the business strategy that it has been implementing in the U.S. to that one that it plans to integrate into the German market while also linking the selected CCM and CRM tools to the outcomes of the market research conducted in the specified setting. As a result, the organization will be able to choose the framework that will not compromise its current business strategy applied ubiquitously across the global market, while also shaping its approach to meet the specific needs of German customers.
At the same time, it is vital for Walmart to be very careful in its second attempt at promoting itself to the German audiences. When placed in the context of German culture, the second attempt at catering to the target audience’s needs might seem as insincere, pandering, and downright condescending.
Recommendations
Overall, even if Walmart will be unable to enter the German market within the observable future, there are still crucial lessons for the company to learn. Namely, the described experience has indicated that the focus on the cultural aspect of CCM is vital since it leads to a better understanding of customers’ needs and allows forecasting their demands. More importantly, the use of cultural competence in the development of the CCM approach entails an opportunity to create an emotional rapport with the target demographic. Consequently,, the platform for constructing customer loyalty and the resulting long-term relationships with the target population is provided.
Therefore, the development of cultural awareness and the performance of market research with the emphasis on local traditions, perceptions, and philosophy are paramount to the outcomes of the company’s further hypothetical foray into the European market.
Additionally, the application of the agile framework as the means of establishing a communication channel for the dialogue with customers is critical. Specifically, the agile approach to CCM and CRM leads to the enhancement of information management by breaking down the project into minor tasks that are interconnected and seen as the constituents of a single entity (Harrigan et al., 2020). Therefore, incorporating the agile framework helps to connect different aspects of project management while keeping focus on the project priorities. Specifically, the integration of the agile tool will guide the alignment of changes within every single department, from research and development to marketing to customer communication. As a result, the efficacy of the project implementation process will be amplified.
Furthermore, the improved approach toward CCM and CRM will allow Walmart to deliver the maximum value to its target audiences, which, in the context of a new market, is always vital since it helps to create the first positive impression. While the described opportunity has been wasted in Germany, Walmart may try entering other European markets, such as French and Spanish ones. However, it is also advisable that Walmart should avoid seeking enhanced collaboration and increased presence in the United Kingdom given the recent scandal regarding Brexit and the resulting economic repercussions that the UK has been facing as a consequence (Harrigan et al., 2020). Therefore, it is strongly recommended that Walmart should seek countries with a less strenuous political and economic climate for its further foray into the European market.
Overall, despite the ruined opportunity to establish a presence in the German retail industry, Walmart still has a chance at entering other European markets. However, before integrating into the newly chosen economic setting, Walmart managers will need to examine the target setting by conducting a thorough cultural assessment and the evaluation of key risks associated with the specifics of customers’ buying behaviors.
Thus, Walmart will be able to communicate its values and create a strong and valuable competitive advantage when entering the new retail market. While the company can still retain its main asset , specifically, its inimitable pricing strategy, the company will need to use the language that is commonly understood by the target audience when pitching its products and services to new customers. By incorporating cultural competence and awareness into its approach toward CCM and CRM, Walmart will be able to survive in a newly selected market and appeal to local audiences successfully.
Conclusion
By comparing the strategies that Walmart has deployed in its attempts at establishing itself in the U.S. and Germany, one will be able to recognize the frameworks that can be used to address cross-cultural and HRM-related issues in diverse settings. Moore importantly, the failure that Walmart has sustained in Germany will help other organizations to analyze what decisions are most likely to be unsuccessful. Specifically, the importance of incorporating multiple perspectives into the analysis and selection of key cross-cultural and HRM-related strategies will be acknowledged.
As the case of Walmart has shown, it is instrumental to perform a meticulous assessment of the culture of the target customers even in the settings that seem quite similar to those of the home market. Therefore, analyzing Walmart’s 2016 experience in Germany is critical to understanding how the ability to appeal to the target population’s key cultural values and promoting teamwork affects the overall performance of a firm in a new market.
References
A Al-Homery, H., Asharai, H., & Ahmad, A. (2019). The core components and types of CRM. Pakistan Journal of Humanities and Social Sciences, 7(1), 121-145.
Gallagher, S. (2020). Action and interaction. Oxford University Press.
Hamza, S., & Nizam, I. (2016). Why Walmart failed in Germany? An analysis in the perspective of organizational behaviour. International Journal of Accounting & Business Management, 4(2), 206-215. Web.
Harrigan, P., Miles, M. P., Fang, Y., & Roy, S. K. (2020). The role of social media in the engagement and information processes of social CRM. International Journal of Information Management, 54. Web.
Kaelberer, M. (2017). Wal-mart goes to Germany: Culture, institutions, and the limits of globalization. German Politics and Society, 35(1), 1-18. Web.
Krämer, A., Friesen, M., & Shelton, T. (2018). Are airline passengers ready for personalized dynamic pricing? A study of German consumers. Journal of Revenue and Pricing Management, 17(2), 115-120.
Kim, Y. (2019). Strategic CSR Communication in social media: The effectiveness of stakeholder information, response, and involvement communication strategies factoring corporate reputation. Public Relations Journal, 12(4), 1-24.
Li, C., & Liu, M. (2018). Overcoming collective action problems facing Chinese workers: Lessons from four protests against Walmart. ILR Review, 71(5), 1078-1105. Web.
McDonald, D. (2017). Why Walmart failed in Germany. Medium. Web.
Nanjundeswaraswamy, T. S., Sanjana, C. M., & Kavya, M. A. (2020). Employee retention in manufacturing units. Proceedings on Engineering, 2(1), 3-12. Web.
Neebe, K. (2020). Sustainability at Walmart: Success over the long haul. Journal of Applied Corporate Finance, 32(2), 64-71.
Xie, Y., & Cooke, F. L. (2019). Quality and cost? The evolution of Walmart’s business strategy and human resource policies and practices in China and their impact (1996–2017). Human Resource Management, 58(5), 521-541. Web.