Introduction
For decades, all the banks across the globe have focused on earning big money from corporate clients. However, things have radically changed. Banks are awash with excess liquidity; interest rates are decreasing. Corporate do not borrow from banks in a big way due to a variety of reasons like economic slowdown, infrastructural constraints etc. Under this scenario, banks are forced to look into the retail segment for lending, and, therefore, the spotlight has now shifted to the retail sector. Banks across the globe are tripping over themselves to enter new segments – car loans, consumer loans, housing finance, educational loans, credit cards etc. The big bonus for banks came in the form of the Securitization Bill, which gave banks and institutions opportunity to recover from bad debts. Retail Banking is a new mantra for all the banks (Gorton and Metrick 20).
Banks hold a significant share in the U.S economy. The greater portion of money is held in form of credit in banks, mortgage firms and other financial institutions. If the liquidity position of banks is compromised, an instant shortage hits the economy immediately, that is why the results of such a situation are felt in all the parts of the country.
In 2008, the U.S Federal Reserve provided favourable conditions for banks as it reduced the lending interest rates. This replicated in the entire banking sector, which reduced their lending interest rates. People started taking out loans in large amounts. Prices of goods, therefore, increased as a result of greater liquidity in the economy as more money were injected in the economy.
A major problem arose when loans were finally adjusted upwards. Most lenders who had borrowed mortgages from banks firms and those who had taken loans from banks for housing purposes without a sound financial base found themselves incapable of paying such some of money. Majority of the mortgage firms lent assuming that if borrowers failed to repay, their houses would be sold to cover the cash. Most borrowers were unable to repay their debts after adjustable mortgages adjusted upwards, leading to the losses for mortgage firms and other loaning institutions as well as banks (Bookstaber 23).
The United States’ economy is also influenced to some extent by the shadow banking industry. It comprises of non-depository banks and financial institutions to which the investors lend for a short period and after which they receive their funds back. However, the institutions gained very little investments during the 2007 period, which contributed to their eventual collapse. Collapse of the shadow banking industry was a blow to the economy as it reflected a missing financial component/contributor in the US economy (Morris and Shin 15).
The U.S government was compelled to bail out some leading banks that found themselves entangled in the lending crisis. Many banks began running on losses. In order to remain on the safe side, they tried to tighten their lending rules, but the situation had been already out of hand. Borrowing reduced further aggravating of the already horrible situation in the U.S economy which still meant that no profits could be made by banks in the near future.
The Current Retail Banking Scenario
Retail banking includes a comprehensive range of financial and deposit products, residential mortgage, personal and consumer durable loans, loans from subscribing to Initial Public Offers and against equity shares, debit and credit cards, auto finance, bill payment and investment advisory services, mutual funds. These products provide an opportunity for banks to diversify the asset portfolio with high profitability and relatively low NPAs. Today, the most proactive banks have entered the retail banking segment and identified it as a principal growth driver. They are slowly gaining market share in the retail space. For several years now, banks viewed consumer loans with skepticism. Commercial loans dominated the banks portfolio as they generated high net yields with low credit risk. Consumer loans in contrast involved smaller amounts, large staff to handle accounts and high default rates. They were considered substandard by the banks. Even the regulators across the globe have not encouraged consumer finance till very recently. However, over the recent past, fierce competition among the banks lowered the spreads and profitability on commercial loans. With deregulation and increase in consumer loan rates, the risk-adjusted returns in retail sector have exceeded the returns on commercial loans (Bookstaber 42).
Competition, securitization, automation and regulation are the major forces that drive and shape consumer lending. Net banking, phone banking, mobile banking, ATMs and bill payments are the new facilities that banks use not only to lure customers, but also to help them to reduce their total operating costs. For example, if we look at the Indian Retail Banking market, it is dominated by the consumer credit. Even nationalized banks, which control more than two thirds of the banking business in the country, tap the retail lending with great vigour. The enormous competition has led to innovative retail banking products that are extremely customer – friendly.
The growth in retail banking has been facilitated by the growth in banking technology and automation of banking processes that enable extension of reach and rationalization of costs. ATMs have emerged as an alternative banking channel, which facilitate low – cost transactions vis-à-vis traditional branches. It also has the advantage of reducing the branch traffic and enabling banks with small networks to offset the traditional disadvantages by increasing their reach and spread (Bookstaber 36).
The retail banking industry is diverse and competitive. In addition to checking and savings account service, banks offer brokerage and insurance capabilities to manage all the aspects of a customer’s financial portfolio. Attracting profitable customers from competitors is essential for long-term success. Retail banking has both pros and cons. In the present situation, the bankers have very little option to promote their business unless they chant the ‘retail mantra’. Today, banks face complex challenges on multiple fronts. Customer expectations are higher than ever, with growing demand for more rapid service delivery and more flexible personalized interaction.
Historical analysis of the bank using the data of the last three years
Deutsch bank has been one of the most influenced financial entities in the midst of the financial duress at different times. It was expected to reap more than 100 billion dollars of assets, which were credit based. The survival of this bank was only made possible through tax bailouts. The financial duress has left a heavy impact on the US economy leaving a considerably great number of the Americans homeless. This was only because the management at Deutsch bank was unaware of the market collapse that was to take place in the future. Deutsch bank was undoubtedly running a very effectual management of risk in the past years before the crisis.
According to the overall economic policy, Deutsch bank made certain changes to its labour team in order to create equilibrium in the US economy at the time of financial duress. This is what we can term as crisis management which is the foremost thing we plan in order to meet the challenges faced by the economy, and it must be organized according to the available resources in order for the entity to determine ways in which organizations can deal with hazardous risk environments.
There is always a chance for the company to place itself in a risky situation because of what it does in order to mitigate a certain risk. Deutsch bank had faced this situation, and this led to a transformation of the organizational capacity. In the years that followed, the company faced problems in creating a balance between its growth and corporate governance principles. Now, it is focused more towards principle-centred approach in its corporate culture. Enterprise learning plays and will continue playing an important role in this transformation.
In the recent years, acquisition has led Deutsch bank to grow aggressively, with more heed towards the harsh transformations. With the passage of time, this particular transformation had been very costly raising some questions both in the US and the UK. This has led Deutsch bank to go across the government regulations and legal environment. Their financial performance was declining. Although there are many factors which are combined to provide such results, productively leveraging knowledge, thus infrastructure impels cultural modification, which should be given most of the credit. Deutsch bank with its focus on extensive growth is aligned now to save time on legal issues and personnel problems concerning divestiture or development. This has led to Deutsch bank utilizing all the time for the company to mitigate its risk in the light of the financial crunch.
This case evidences the change that can be brought in a diverse part of the organization in order to focus its resources and available time to counter the risk aversions due to financial crisis.
Financial statements form the backbone of any manager’s decisions. Without them and their proper understanding, a business manager would be just aiming at his or her company’s objectives in complete darkness. Particularly, the balance sheet assumes additional importance in that regard. First, a balance sheet provides the business manager with the amount of assets that are in use by the company. These include both the current and the fixed assets. This information along with the relevant coverage ratios allows the business manager to judge whether the company is operating with the ideal level of fixed and current assets. An ideal example would be of a situation where the funds lying in the company’s bank account could be used to purchase marketable securities to earn higher return (Weetman 126).
Financial Analysis
Balance sheet
The balance sheet tells the business manager about another side of the accounting equation as well, i.e. the liabilities and equity. This allows the business manager to come to conclusion regarding the ideal level of financing that the company should keep in view the costs and the long term goal of the organization. In the same way, the balance sheet also presents a current view of the business’s assets, liabilities and equity (Bragg 92). This can be applied to the current position by making decisions regarding keeping the working capital at the manageable levels. This is done primarily to have enough liquidity for the company to function, i.e., to meet its everyday expenses in a timely and acceptable manner. The Equity and Liabilities sides are the same. This fact can be used in view of the future position to ascertain whether it would be beneficial for the company to have a Debt to Equity ratio in favour for one or the other. This can be dependent on a number of factors, among which chief would be more beneficial to the company in the long-run. The bank’s balance sheet shows an increase in cash and equivalent being held by the bank together with other assets. The increase in cash was higher during the 2009-2010 periods as compared to 2008-2009. For other assets, it shows that the growth is higher in 2010-2011 as compared to other periods although the current assets are higher in 2009-2009. Comparing the assets to other items of the same year, one will note that the current assets consist of 8.87% of the total assets in 2008, 25.71% in 2009 and 28.21% in 2010. This means that percentages of the current assets to the total ones are increasing at faster rate than other assets. Looking at the percentage of liabilities to the total assets, one will note that percentage of liabilities going up and down mean unclear policy on debt ceiling. The financing of assets was not stable, that is why there is a need to maintain certain level of debt.
Income statement
Comparing annual changes of income statement items, one will note that the gross profit of the bank has decreased and is expected to lower the forecasted results as they reduced by 19% in 2008-2009 and by 8% in 2009-2010 and are expected to decrease by 12% in 2010-2011. Thus, the expenses appear to be reducing. It lowered by 23% in 2008-2009 while it is expected to reduce by 43% in 2010-2011. The bank control expenses by looking at the possible sources of cheap suppliers of services and goods. Currently, banks are facing cutting down of costs to wade away financial crisis. Even when it comes to the administration and other expenses, there was not any increase or decrease. The Net income reduced very much by the year 2011, which is mainly due to the recession. If the items are considered horizontally, it will be noted that income is drastically decreasing because the revenue is also reducing. The effects of this are the financial crisis, which was experienced in the year 2008/2009. The expenses increased by 45% in 2008-2009, but decreased by 3% in 2009-2010 later on.
Liquidity Management Analysis
The net working capital of the bank is not adequate for their current operations considering that their total current liabilities are more than the amount of their cash and marketable securities at available and recommended rate 2:1 for a bank. The net working capital ratio of the bank has remained stable which means that the ratio is stable considering that liabilities are increasing. Thus, such case provides many liquid assets to pay for the liabilities in case they are going to be required by suppliers and creditors to pay at a certain time. Ideally, any bank should have more cash at hand than what they actually need to prevent themselves from being cornered by creditors and even employees whose wages need to be paid on a constant basis.
The trend graph below shows what was happening during three years:
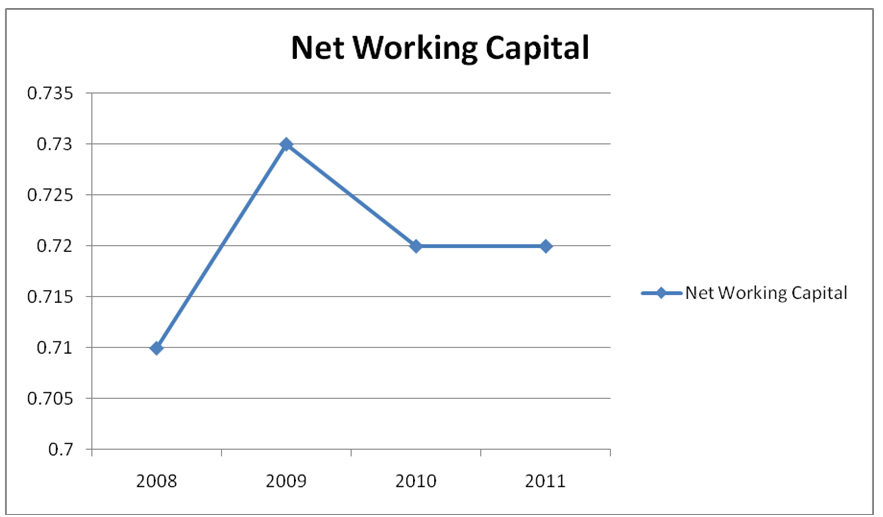
Quick and current ratios show that the bank tries to maintain stable liquidity after the year 2008. Probably, it is because of the bail out which helped the bank to maintain liquidity. This ratio involves measurement of company current assets against current liability. Since it has been determined that working capital for that period was positive, it can be assumed that the current ratio will be greater than that one. The CR for the financial year 2009-2011 was 1.00 while the figure for the period 2008-2009 was 0.3. This indicates that in 2011, 1.0 of current liabilities will be satisfied with current assets as shown in the excel appendix. The trend is shown by the trend graph below.
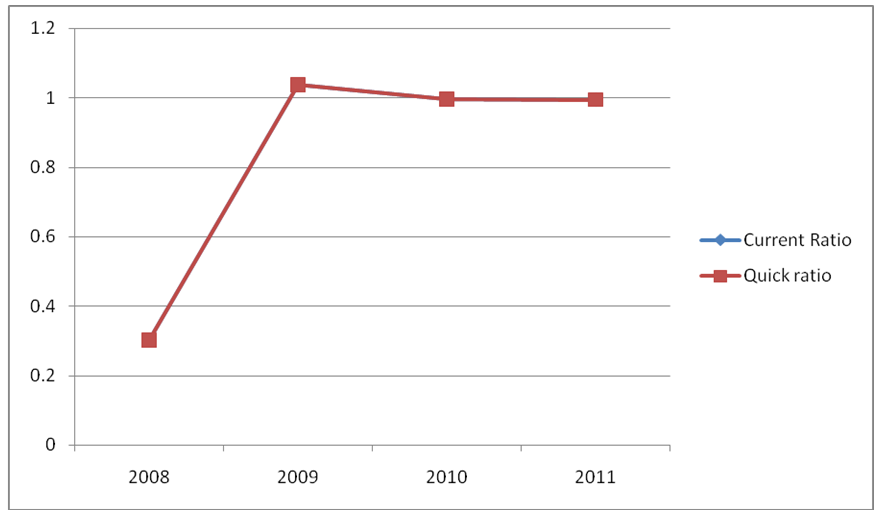
This suggests that in future, the financial health of the bank will continue to improve because the increasing liquidity will allow the management to utilize more funds. Furthermore, strong credit ratings, surplus cash flows, debt repayments and increased levels of payout and retention ratios are few of the benefits which the bank will receive if this trend continues.
Performance Ratio Analysis
Net Interest Margin
Net Interest Margin does not only indicate the profitability of the bank, but also gives a more detailed knowledge about risk management by the bank. The bank wants to keep this ratio high to be able to show that they can lead a good risk management. Whereas Net Interest Margin could be valuable in measuring the success of its risk management in terms of people’s money management, this ratio is for the bank decreasing meaning that the risk of bank decreases annually as shown in the excel appendix. The trend curve below shows how the bank was fairing.
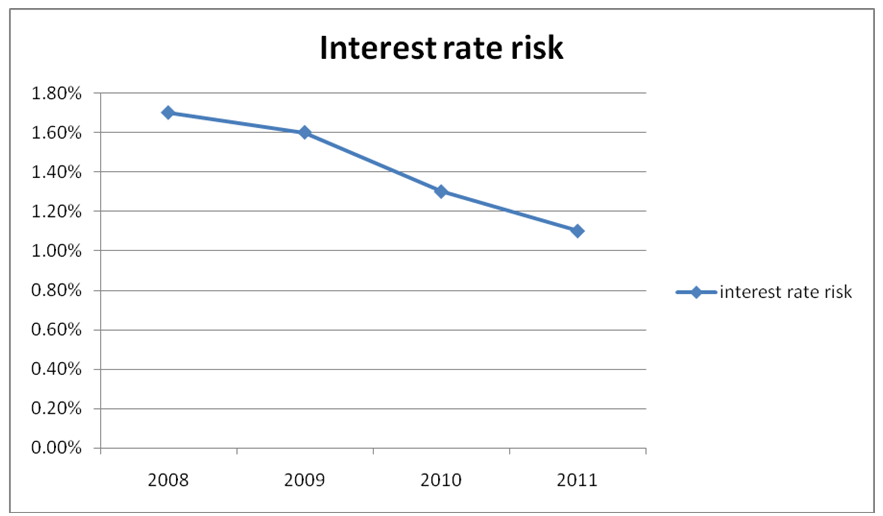
This ratio is important in indicating whether a company has sufficient cash to finance its debt. This ratio is, however, limited in that it does not guarantee that the cash flow from operating activities will increase, that is why this is the main concern for the investor.
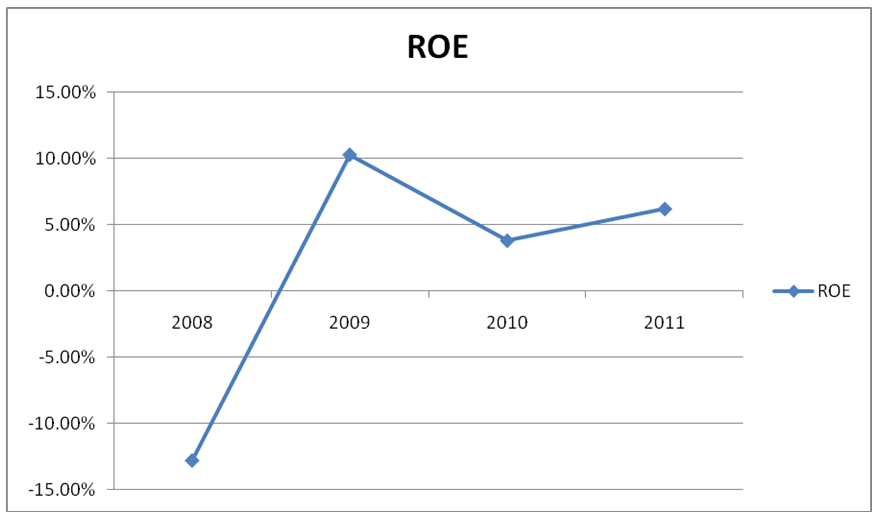
Return on Equity
From the excel appendix, it shows that this ration is on downward trend except the forecasted figure that is wanted up. The 2008 ROE figure was big which is understandable because of the still optimistic economic valuations of investors at that time. A decreasing ROE of the company indicates that they lost the advantages they had already had before the economic crisis. Although the investors stopped seeing things in such a good perspective, they at least started to see companies in a better light, hence the realistic evaluation. The trend below shows how the ratio was fairing during the certain period.
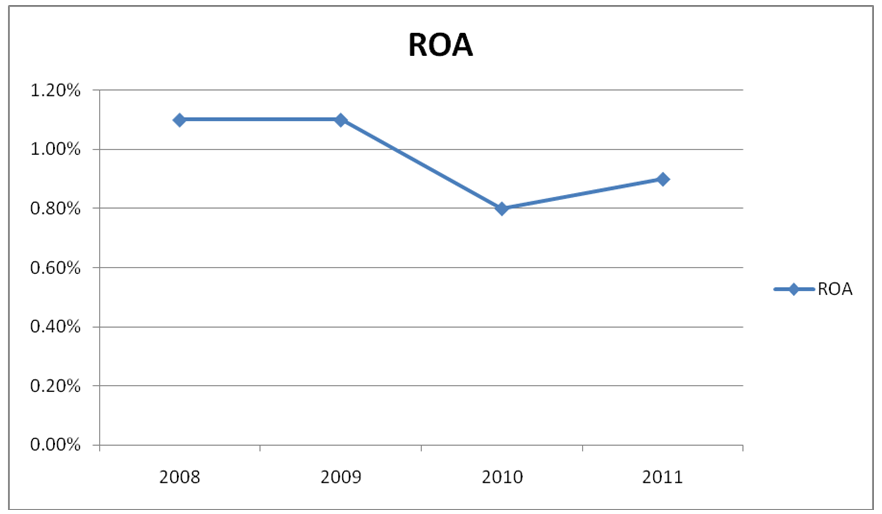
Return on Assets
The excel appendix shows that ROA was poor and nearly remained stable over the period with slight fluctuations. It only reflected the huge impact that the recent economic crisis had on the bank. The good thing about the banks is that they were still able to manage a decent growth in their incomes despite the economic crisis. It shows the resilience of the top management to weather it is able to come up at the top of the situation. The banks can defend their market share as well as reduce any added burdens on their financial statement. The management is very prudent when it comes to their strategies, which account for their continued financial health as well as profitable existence. The graph below is a trend graph depicting the same situation.;
SWOT Analysis
Strength
Deutsch bank has centralized database and provides its major branches to have online access to them. This allows the subsidiary companies to make faster decisions. Internet access helps the bank to increase its efficiency. The bank has a positive working capital that is growing. The bank has a diverse array of revenue sources to earn from. The bank has wealth and asset management programs for the high net worth client as well as foreign exchange services. It is what shielded them primarily from the global slowdown. The bank has a lot of local high net worth individuals as well as substantial sources for asset management fees. The bank is also very innovative as it offers the online banking services that create more value for its clients and serve to attract new clients with the ease and convenience offered by the organization.
Weaknesses
Indeed, Deutsch bank does not differ from other banks in that it has several weaknesses. They were caused by the worldwide recession that started in the USA. The savings rate grew only by 5%, and the loans rate increased by 6%. Nevertheless, such a situation is better than to experience a negative growth rate given by the dire economic situation worldwide. The bank also has some large amounts of revenue based on the foreign exchange market, which is hard to predict in terms of its swings of up and down. The bank is better of placing its investment capital in the securities business.
Opportunities
They are determined to open in Malaysia as in another country that can increase their growth rate and revenues. The bank still has many regions to enter. They can enter the rest of the Asian market and the European banking industry. Although it is unlikely that they will be dominating the European banking scene as it is one of the world’s oldest established economies, they still have a vast field of opportunities in the Asian region where businesses are greatly in need of capital to grow and start on their way to industrialization. The bank also has a certain advantage over other banking institutions in terms of expanding into certain countries.
Threats
The threats facing Deutsch bank are the fact that they are not experienced as their American counterparts in commercial loans and investment financial services. It has been already proved by multinational financial institutions, such as CitiGroup and HSBC, that they are able to enter any country in the world and create a relatively decent market share for themselves. The bank is also exposed to any possible economic fluctuation whenever the Middle East region is faced with a war with the western nations, like the USA, or a civil war concerning what is happening within the Arab world in the last few months of 2011. The majority of their businesses are also ultimately dependent on the oil industry. Although they have also diversified into other fields, it is still within their own local economy, which is highly dependent on the oil industry. Nowadays, the replacement of oil is considered to be an attractive goal for many countries worldwide because of the constant surge in oil prices.
Performance Forecast for the Next Year
The analysis of Deutsch bank reveals that the company has a sound managerial, strategic and financial health. In other words, the company possesses a clear vision, tested strategic approach and sound financing, which will help the bank to sustain and improve its growth. The forecasted financial position of 2011 is shown in the appendix excel file.
- Interest Rate Forecast. The forecasted interest rate is 8.2% as it is shown in the appendix.
- Six-month action plan. The bank should change its product pricing strategy and enter new markets, such as in Africa.
- Forecasted Income Statement. The forecasted balance sheet shows greater improvement. It is reflected in appendix.
- Forecasted Balance Sheet. The forecasted balance sheet shows greater improvement. It is presented in appendix.
Recommendations
The serious position of liquidity is something that the banks have learnt in the current financial duress, probably a viable industry in certain situations. Though it does not matter what industry we are talking about, the revenues are bound to go down, so the payables can go up. Creditors can lose trust and call for early payments (Ahrens 22). The liquidity plan should be able to pass through the most stressful situations as well. The most viable assurance is to have real cash reserves in a bank which is safe and not prone to economic ups and downs.
Another option to restructure in order to overcome the threats of economic downturns is to change boldly and confidently. Keeping in mind the human resources at act within the organization, the institution must cater to the needs of the consumers accordingly (Taylor 89). This will cause an unbalance of attitudes from employees, but looking at the success factor, this burden will be eased. The financial institution must be more customer centric, and any strategy it implements in order to do so must be in line with the success factor that is available to the employees working for the bank.
Technological advancements also play an important role in the change management across an organization (Prasad and Harker 27). The latest technology, which is capable of producing results and required by the management (financial or non financial), can actually turn out to be not acceptable within the organization if not implemented with their consent. Proper training and development to adapt to the technological innovation must be carried out in order for the change to be implemented successfully.
In their zeal, the core philosophy of change management is the use of organisation-wide change programmes to improve both the structure and the corporate culture simultaneously. A clear implication of the take-up of such initiatives is the rapid improvements in economic value which will improve their viability at the same time (Wignall, Atkinson and Lee 8).
Further reflection, however, suggests that there are three fundamental flaws in the thinking associated with the idea of ‘organisational change initiatives’, especially in banking institutions. First, it has failed to document and clarify the results of change initiative programmes; second, it has been unable to measure their cost effectiveness; and third, it has not managed to acknowledge the difficulty and complexity of risk management in times of crisis.
Works Cited
Ahrens, Raif., 2002. Predicting recessions with interest rate spreads: A multicountry regime‐switching analysis. Journal of International Money and Finance, 21, pp.519-37.
Bookstaber Richard. Demon of Our Own Design, new York: John Wiley, 2010.
Bragg, Steven. Wiley Revenue Recognition: Rules and Scenarios. New York: John Wiley and Sons, 2010. Print
Gorton, Gray & Andrew Metrick. 2009. Securitized Banking and the Run on Repo. NBER Working Paper No. 15223, 2009.
Prasad, Baba. & Patrick Harker. Examining the contribution of information technology toward productivity and profitability in U.S. retail banking. Financial Institutions Center, Working Paper 97-09, 1997.
Stephen Morris and Hyun Song Shin (2008), Financial Regulation in a System Context, Brookings Papers on Economy Activity.
Taylor, John. Getting Off Track. New York: Hoover Institution Press, 2009. Print
Weetman, Pauline. Financial Accounting: an Introduction. New York: Financial Times Prentice Hall, 2006. Print.
Wignall, Adrian , Paul Atkinson and Se Hoon Lee.The Current Financial Crisis: Causes and Policy Issues. Financial Market Trends. 2008. Web.