Disneyland California adventure was opened in 1955. During its first few years, the company had faced many challenges. In its opening day, the company offered 18 attraction sites to the public. The cost of the sites was $17.5 million (Bates & Susan 108). Disneyland was created on five separate lands in the suburbs. As such, the location of the entertainment joint was uncommon in the American entertainment industry, which was majorly concentrated in the city.
During its inception, the company was not as successful as it is today. As such, the company faced many challenges with its limited success. There was the limiting factor of public transport, thus viewers without vehicles could not access the venture. Since its inception, visitors used to access the venture by paying the entrance fee. Later the venture adopted the use of tickets. The other major challenge faced by the company was the illegal entrance by viewers. Most of the first security measures failed allowing a number of the viewers to break through the fences as the others climbed over the walls into the park. In 1968, Disneyland tried to create public relation by establishing a large poster of Souvenir map.
When the venture opened Fantasyland and Pacific Ocean Park (POP) in Santa Monica, it believed that it could increase its returns. Disney invested $16 million into the park with the expectation of improving its success (Sandler 78). However, POP’s low charges of $2.5 were not enough to maintain its facilities. Illegal entrants that sneaked into the park through the ocean worsened the venture’s returns. The adventure was finally closed down in 1968.
Before its failure, Disney attracted more than 60,000 viewers in 1960. Despite the numbers, the company still made huge losses. During the time, the public created a negative opinion about Disney’s cleanliness and entertainment. The majority of the public believed that the best place for Disney‘s entertainment and fan was in Anaheim. The above challenges coupled with higher advertising spending on the attractions led to financial failures. The number of visitors received each year did not meet the anticipated figures. As such, this reduced the company’s profitability. The growth rate of the venture was low and the founder was not satisfied. Actually, the performance of the Disneyland Adventure was average.
A major expenditure spent by California Adventure in recent years includes $ 1.1 billion for the renovation of the theme park, which is located in Anaheim (Warren & Jonathan 1159). The renovations included the introduction of water show and increased 12-acre land for cars. The above renovations were under the plan known as the Real-Life Adaptation for 2006 car films. From the above initiatives, the company realized a total of $ 3.3 billion in terms of sale from both the parks and resorts. These sales represented a 14% increase from the sales in 2012 (Warren & Jonathan 1160). The renovations have made the company popular among its guests. In 2013 during the second quarter, the company earned a net income of $ 1.5 billion, which represented a 32% increase from the previous year. Robert Ige, the CEO, believes that the renovations have increased the number of guests at California Adventure by 25%.
Actually, due to these spending, the company is able to enjoy the future returns since the company has acquired popularity among the guests visiting the resort. It is estimated that the company’s future returns will be improved (Warren & Jonathan 1163). As such, it expects to increase earnings per share by 9% by the end of year 2014. Through this, the company aims at increasing shares to $ 3.78 from $ 3.13 earned in the previous year. Equally, the company will earn up to $46.0 billion as revenue, which represents a 7 % increase from the previous year.
According to the company’s financial records, the recent spending on the California Adventure was utilized appropriately. As a result, the adventure has witnessed improved revenues. The CEO of the company gave this financial report, while expressing happiness due to improved financial position. The company income spend on Cable Networks rose from $340 million to $ 6.0 billion as a result of expansion of ESPN and the Disney Television networks (Warren & Jonathan 1159).
The increased ESPN was due to rise in advertising revenues which were compensated by increased production costs. The studio entertainment revenues rose by 7% translating to $ 1.5 billion, and the operating costs increased from $ 28 million to $ 108 million. The revenues increased by 3% to record $ 6.0 billion (The Walt Disney Company Reports, n.d.).
The increase in costs of operation is due to the improvement in the television and theatrical services. The revenues from Parks and Resorts increased to $3.7 billion, representing an increase of 8% on quarter basis, while the annual revenue was $14.1billion (The Walt Disney Company Reports, n.d.). The management of the company attributes the increased income needed for an operation to spending by the guests and increased attendance. Actually, this means that more night rooms would be occupied. In the long run, the company will be able to maximize its profitability.
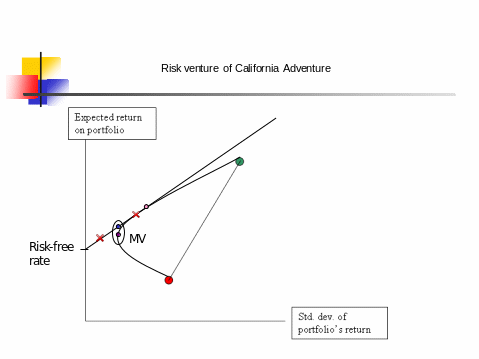
The above diagram illustrates the risk venture of California adventure. From the diagram, it is visible that higher returns are expected when the investment is close to the risk free line. Hence, the California Adventure should try to attain this risk free line. The money spent at the resort was at higher risk since the company dedicated $ 1.1 billion for renovation of the Park in comparison with other spending for the resort (Sandler 80).
The costs incurred by the resort were distributed among several sectors such as cable network television and the broadcasting services. For instance, the operating income in the broadcasting section was $ 158 million, while the network cable television required $ 343 million. Allocating $1.1 billion as a renovation for the Disney Adventure could be a greater risk in case the project failed to yield the expected results (Keown & John 279).
The main reason for the renovation was to create new attractions, which would eventually increase the number of guests visiting the resort. If after construction of the new features and the introduction of the radiator race the number of guests remained the same, than the company could face huge financial constraints. Actually, spending such huge amount of money on the uncertain project is a greater risk that the company has already engaged in its spending for a year. In addition, this leads to fair distribution of risk and thus the Disney Company incurs less financial failure as compared to the $ 1.1 billion for Disney Adventure.
If the California Adventure is successful in the end, than there will be some synergies and erosions in the resort property. It will open more opportunities for other resorts and parks such as Downtown Disney Spa and Disney Grand hotels. The other resorts include Deluxe villas, Value resort, Deluxe resort hotels and Moderate resort hotels. The success of the Disneyland venture depends on the synergy of all the parks, resorts and hotels the company owns. In addition, the company could venture into other activities outside the Disneyland resorts to increase the returns. The resort property will gain value due to increased demand. In fact, other services such as broadcasting and network cable services will contribute to the Disney Company’s profit maximization.
The introduction of the Radiator Spring racers, which cost the Disney Company about $200 million, was a successful project. Because of this, the company has experienced increased revenues. As such, its sales have increased by 14% to $3.3 billion, which is a significant growth in sales for the Disney Company. Its earnings per Share increased from $3.13 to $3.38 representing 8% from the previous year. This shows that the Radiator race was a successful project for the company and has aided in profit maximization.
By analyzing the opening and the close hours from July 2010 to August 2013, an estimate of the success of the company can be obtained. The average opening and closing hours from July 2010 to June 2012 range from 10 am to 8 pm from Monday to Thursday. For the same period, the average opening and closing hours on Fridays and weekends were between 10 am and 10 pm. From July 2012 to August 2013, the average opening and closing hours were between 8am to 9pm from Monday to Thursday, while Friday and weekends were between 8 am to 10 pm. In most cases, the California Adventure has had an average of long opening hours during both weekdays and weekends. In fact, the company opens for an approximate 12 hours every day.
Based on this, it is apparent that California Adventure is able to attract more customers to increase its revenues. The few changes in the opening and closing hours might have been the adjustments needed to meet the maximum guests while maximizing the company’s profits.
There is a high chance that the Disney Resort will maximize its profits in the future for the company has invested in adding new attraction sites, which aids in increasing the number of guests. For instance, the company has invested $1.1 billion in renovation and introduction of Radiator Spring Racers. The above investment was a high risk venture. Therefore, it might lead to a higher discount rate. In the future, the company’s profits will increase. Therefore, the company will have to come up with appropriate decisions on whether to reinvest or increase the stakeholders’ earnings. During such times, the company should reflect on its discount rates (Ernst and Häcker 89). As such, the company should reinvest before passing the returns to the shareholders. Through this, they will guarantee increased shareholder profits in the future.
Based on the information provided above, Disneyland Park and the California Adventure Park will be able to maximize their profits. This is also the same for its group hotels, which include Downtown Disney, Spa, and Disney Grand California. The Disneyland Resort might engage in other ventures outside the resort, for instance, the sporting activities, which boost the revenues hence maximizing its profits. The company in the future is likely to charge higher park admission fee. For instance, 1-day park admission fee was $10.75 in 1989 and the charges increased to $ 92 in 2013. In addition, the resort might continue to practice the different pricing and discount depending on the number of days the guest spends. Higher discount is given to guests who plan to stay for more days at the Disneyland Resort.
Works Cited
Bates, Colleen and Susan LaTempa. The unofficial guide to California with kids.7 th. ed. Hoboken, N.J.: Wiley, 2010. Print.
Ernst, Dietmar and Joachim Häcker. Applied International Corporate Finance. München: Vahlen, Franz, 2010. Print.
Keown, Arthur and John Martin. Foundations of finance: the logic and practice offinancial management. 6th ed. Upper Saddle River, N.J.: Pearson Prentice Hall,2008. Print.
Sandler, Corey. Econoguide Disneyland Resort, Universal Studios Hollywood: and othermajor Southern California attractions including Disney’s California Adventure. 5 th ed. Guilford, Conn.: Globe Pequot, 2007. Print.
The Walt Disney Company Reports Fourth Quarter and Full Year Earnings for Fiscal. 2013. Web.
Warren, Carl and Jonathan Duchac. Financial & Managerial Accounting, 10th ed. Mason, Ohio: Thomson/South-Western, 2013. Print.