Introduction
Environmental analysis is an indispensable aspect of the environmental studies in modern society. Increased pollution of the environment due to human activities necessitates environmental analysis to establish the nature and the extent of pollution in a certain environment. Fundamentally, environmental analysis involves the application of scientific tools and techniques in the analysis of pollutants in various components of the environment such as water, soil, and air (Reeve, 2002). Analysis of the pollutants is imperative because it aids in the determination of environmental risk factors that predispose humans to diverse diseases and disorders. The increased rate of pollution in modern society due to industrial development and increased human population has led to the development of the environmental analysis as an academic discipline.
Since environmental analysis has become an academic discipline, environmentalists apply it in the assessment of the environment for the safety of humanity. Environmentalists perceive pollution as a major environmental issue that threatens the existence of humanity if no one establishes effective interventions. In this view, different governments are formulating legislations and regulations to curb and reverse the increasing trend of pollution. Academic institutions are also producing environmental scientists who have essential knowledge and skills to design mitigation measures of pollution. In this view, this proposal seeks to convince the university to establish a new environmental laboratory to serve masters students, Dubai community, and other important stakeholders.
Problem Statement
The increasing rate of pollution across the world and in the United Arab Emirates requires environmental analysis for environmentalists to ascertain the extent of pollution and the dangers that pollutants pose to humanity. Given that the United Arab Emirates is a developed country, it has numerous industries that generate and empty their effluence into the rivers and seawater. Industries usually release heavy metals into water bodies, and thus contaminate water for domestic and industrial uses. Moreover, the use of pesticides on the farms is a common form of agricultural pollution in the United Arab Emirates that leads to contamination of water bodies.. Willis et al. (2010) state that heavy metals and pesticides are significant forms of water pollutants, which require effective mitigation measures to prevent them from causing chronic diseases.
This shows that the environmental scientists in Dubai require appropriate infrastructure to perform environmental analysis of the pollutants that affect the population. According to Patnaik (2010), for environmentalists to perform environmental analysis, they require a laboratory equipped with modernized equipment. Given that environmentalists obtain theoretical knowledge and skills from various learning institutions, they should receive empirical experience by working in environmental laboratories. A university that offers courses in environmental studies should have a well-equipped laboratory, so that the young scientists can apply their theoretical knowledge and skills in empirical studies. In this view, establishment of environmental laboratory in the university is timely because the laboratory will assist the university in equipping students with empirical knowledge, help the local community in assessment of their environment, and support environmental bodies in research.
Functions of the Proposed Laboratory
Activities
- Collect samples for analysis from solid wastes, sludge, and sediments, which are present in both domestic and industrial wastes in Dubai.
- Analyze solid wastes such as domestic garbage and industrial waste to establish the presence of pollutants that endanger the lives of people in Dubai community.
- Analyze industrial and domestic sludge to establish the presence of dangerous pollutants such as heavy metals, pesticides, and other chemicals.
- Assess the safety of domestic and irrigation water that the Dubai community uses.
- Analyze industrial and domestic sediments to ascertain if they contain any form of pollutant that is dangerous to human health and the environment.
- Develop protocols that are effective in environmental analysis.
- Teach students on how to conduct various tests of environmental analysis.
- Conduct diverse research activities in conjunction with other environmental bodies.
- Seek funds for research activities and the expansion of the laboratory to develop capacity for environmental analysis in Dubai.
Scope
- The laboratory will specifically deal with environmental analysis of pollutants such as solid waste, sludge, and sediments from domestic and industrial sources.
- The laboratory will only allow students who are doing their masters programs to perform experiments.
- The laboratory will allow other environmental bodies to perform their research activities because they are stakeholders.
- Since the Dubai community is the surrounding community, the laboratory will give it the first priority by analyzing its environment.
- The university will use the laboratory for learning and research purposes.
- The university will permit environmentalists to use the laboratory in performing research activities for the benefit of the community and the university.
- The laboratory will not allow individuals to perform projects, which are unrelated to the environmental science.
- The laboratory will report and publish the findings through the university.
Objectives
- Since the university has no environmental laboratory, establishment of one will improve and enhance the capacity of the university to equip students with empirical knowledge and skills.
- Given that the local community lives in an environment that is prone to pollution, the laboratory will serve the local community by ensuring that the people are in the environment that is free from any dangerous pollutant.
- Students who are undergoing their masters programs need to perform their research, and thus the laboratory enables them to use modern equipment when they are performing their research activities.
- Create a research hub where environmentalists from the university and various environmental bodies can interact and generate novel ideas.
Organizational Structure
The organizational structure comprises of the laboratory manager, quality assurance coordinator, research coordinator, environmental analyst, and learning coordinator. Laboratory manager is the head of the laboratory and has the responsibilities and duties of directing all activities that take place in the laboratory. Quality assurance coordinator, research coordinator, environmental analysts, and learning coordinator are answerable to the laboratory manager with regard to all activities that they perform in their respective departments.
Quality assurance coordinator ensures that the nature of activities and practices that research coordinator, environmental analyst, and learning coordinator perform adhere to standard operating procedures. According to Ratliff (2005), quality assurance coordinator sets standards, monitors the quality procedures and activities, and develops new protocols. Hence, quality assurance coordinator is an indispensable position in the environmental laboratory. Research coordinator operates the laboratory by liaising with other researchers and environmentalists on matters of research.
Given that the main objective of establishing the laboratory is to conduct environmental analysis, environmental analyst plays a pivotal role of ensuring that the process of sample collection and analysis is appropriate to provide accurate results. The learning coordinator deals with the masters students who are learning environmental disciplines and performing their projects in the laboratory. Below the rank of research coordinator, environmental analyst, and learning coordinator are laboratory technicians, who undertake routine procedures and activities of the laboratory.
The chart below indicates the organizational structure of the laboratory and expounds on the relationships of various personnel who work in the laboratory.
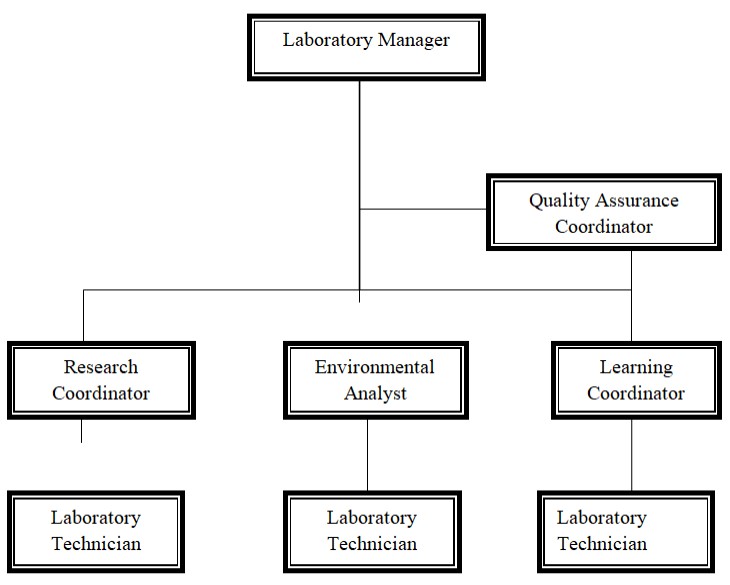
Chart 1: Organizational Structure
General Layout of the Laboratory
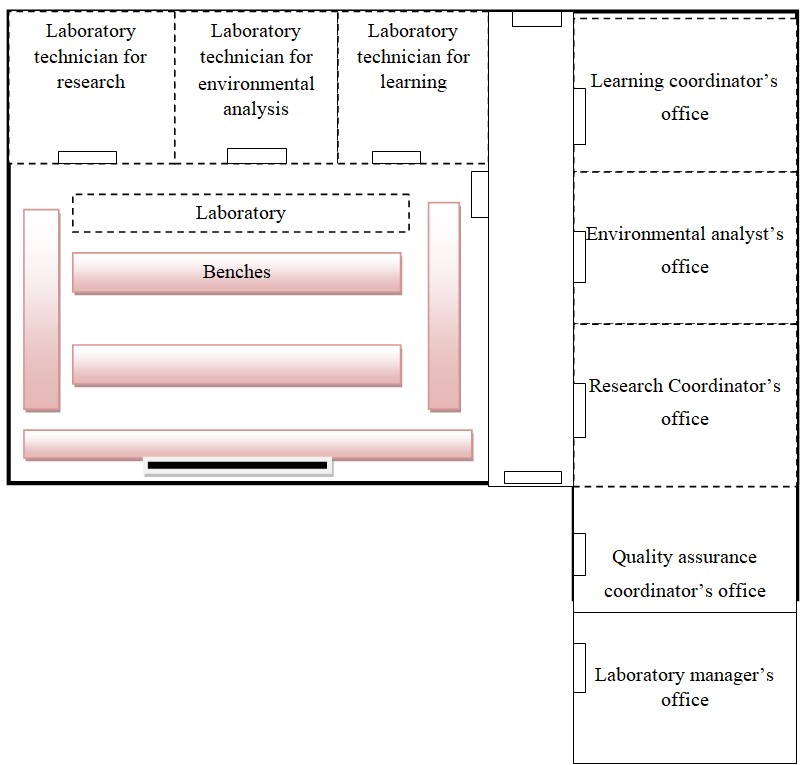
The laboratory layout shows the proposed design of the laboratory. The layout has offices for laboratory manager, quality assurance coordinator, research coordinator, environmental analyst, and learning coordinator. The layout also shows the laboratory environment comprising of benches and teaching board. Beside the laboratory are the preparation rooms for each of the three technicians who represent research coordinator, environmental analyst, and learning coordinator. Therefore, the layout illustrates the design of the laboratory that the university requires to serve the students, the environmentalists, and the Dubai community.
Recommended Location
The recommended location of the proposed environmental laboratory is within the university. The laboratory should be in close proximity to the school or department of the environmental science, so that lecturers and students can easily access it whenever they want to utilize. Accessibility of the laboratory to the lecturers and students will enhance it to achieve its functions and optimize utilization of important resources for the benefit of the university, environmental science, and the Dubai community.
Recommended Experiments
- Mercury analysis in water, reference numbers 245.1, 245.7, and 1631E, in the United States Environmental Protection Agency, Clean Water Act.
- Analysis of sludge for presence of Salmonella typhi, reference number 1682 in the United States Environmental Protection Agency, Clean Water Act.
- Analysis of water for the presence of Escherichia coli, reference number 1603 in the United States Environmental Protection Agency, Clean Water Act.
- Detection of fecal coliforms in sewage sludge, reference numbers 1680 and 1681 in the United States Environmental Protection Agency, Clean Water Act.
- Analysis of pesticides in the municipal and industrial wastes, reference numbers 608, 608.1, 608.2, 614, 614.1, 615, 619, 622, 622.1, and 632 (United States Environmental Protection Agency, 2014).
- Determine the level of organic compounds in drinking water using methods in series 500 of the United States Environmental Protection Agency, Clean Water Act.
- Analyze organic chemicals in industrial and municipal wastewater using methods that are in series 600 of the United States Environmental Protection Agency, Clean Water Act.
- Analyze the presence of microbes and pathogens in drinking water using methods in series 1000 of the United States Environmental Protection Agency, Clean Water Act.
- A method of analyzing sludge and recovering viruses, reference number D4994-89, American Society for Testing and Materials.
- Analysis of sediments, reference number D6145-97, D3974-09, and D7363-13 (American Society for Testing Materials, 2014).
- Determine pesticides in water, sludge, and sediments using method D5175-9 of American Society for Testing and Materials.
Recommended Equipment and Chemicals
The pictures and names of the recommended equipment are attached below.
- Fume hood: a containment device that protects people from hazardous fumes, which volatile chemicals release.

- Analytical balance: used for weighing samples and chemicals in the laboratory.

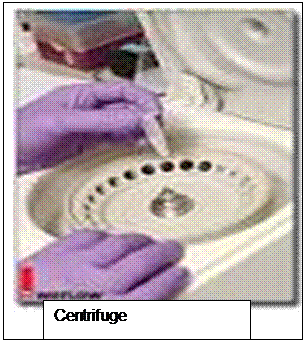
- Centrifuge: it is equipment used in separation aqueous substances according to their sizes in terms of sedimentation rates.
- pH meter: used in measuring the degree of acidity and alkalinity.
- Sediment sampler: it is used in collecting and sampling sediments from wastewater.

- Burette: it used in measuring chemicals and water during the process of titration.

- Ion exchange chromatography: a column chromatography of separating charged molecules.
- Titration analyzer: used in titration analysis of samples and solutions.

- Wastewater controller: separates wastewater into different constituents for analysis.

- Mass spectrometer: it is used in the determination of masses of various compounds, which are present in the analytes.
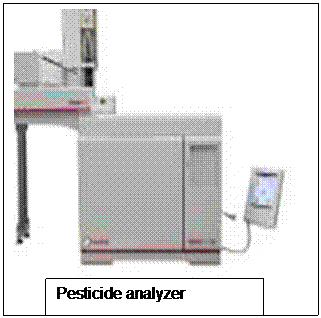
- Pesticide analyzer: used in the analysis of pesticides in wastewater and sludge.
- Microscope: used in the examination of microscopic particles in the laboratory.
- Beakers: for storing and measuring solutions.

- Conical flasks: for storing and measuring solutions.
- Test tubes and racks: used in holding samples and performing various tests in the laboratory.
- Fridge: for storing volatile samples that are not stable are room temperature and pressure, and preserving them.

- Oven: used for drying substances in the laboratory.

- Gas cylinder: provides a source of heating gas.

- Mercury analyzer: used in the analysis of mercury in various samples.
- Micropipettes: measuring micro amounts of solutions.

- Eppendorf tubes: it is used in performing tests.
- Digestion vessels: tubes used in digestion of metals in samples.
- Autoclave: it used in sterilization of substances and vessels.

- Fire extinguisher: it is used in putting off fires in the laboratory.

- Atomic absorption spectrophotometry: it is used in the analysis of trace elements in the samples.
The laboratory requires the following chemicals
- Nitric acid
- Hydrochloric acid
- Phosphoric acid
- Sulfuric acid
- Mercury
- Pesticides
- Sulfates, sulfites, and sulfides
- Chlorides and chlorites
- Alcohols
- Ammonium salts
- Nitrite, nitrates, and nitrites
- Phosphates
- Acetone
- Iodine
General Quality Control and Assurance Procedures
Quality control and assurance procedures are integral in environmental analysis because they enhance the accuracy of the findings obtained. In the environmental analysis, errors usually emanate from the collection of samples in the field. In this view, sample collection is an area in the environmental analysis that should adhere to scientific procedures for the samples to provide valid and reliable results. According to Conklin (2004), sampling is a delicate process in environmental analysis because it has considerable impact on the outcome of any form of analysis. In this view, the laboratory should perform quality control and assurance procedures in sample collection. Sample preparation is also another aspect of quality control and assurance. During the preparation of samples for further analysis, contamination is likely to occur. Therefore, strict adherence to the standard protocols of sample preparation is essential to guarantee the validity and accuracy of the findings.
In this case, more than two people should prepare samples by following standard procedures and the results of the samples compared. Given that analysis is central in determining the degree of various forms of pollutants in the samples, it requires stringent procedure of quality control and quality assurance. The laboratory should utilize replicates and controls in ascertaining the validity and accuracy of various results. Moreover, split sample analysis is the appropriate method of quality control and assurance. The split sample analysis allows independent analysts to perform similar tests for purposes of comparison and enhancing accuracy of results. The split sample analysis is critical in analysis because it helps in detection of systemic errors that are present in the laboratory.
Laboratory Health and Safety Procedures
- Wear all protective clothing (gloves, eye protection, and laboratory coat) at all times when in the laboratory as a safety precaution.
- Label all chemicals in the laboratory to prevent them from causing unnecessary harm.
- All experiments that involve volatile and dangerous chemicals should be performed in the fume hood.
- Separate and isolate laboratory waste properly for disposal.
- Exercise personal hygiene such as washing of hands after removing gloves and when leaving the laboratory to prevent self-poisoning.
- Do not leave equipments running on their own or active experiments unattended as they are dangerous.
- Do not spill water on the floor of the laboratory as it increases the risk of accidents.
- Report any damage of equipment to the supervisor for immediate repair.
- Locate the position and understand the procedure of safety equipments such as safety shower and eyewash (Dunnivant, 2004).
- Know the location of fire extinguisher, fire alarms, and emergency door.
Qualification and Training of Employees
- Laboratory manager: Should have a doctorate level of qualification in environmental science or related field. He/she should have a minimum of ten years experience in environmental analysis.
- Quality assurance coordinator: Should have a doctorate level of qualification in environmental science or related field. He/she should have a minimum experience of 7 years in performing quality control and assurance procedures in environmental laboratories.
- Research coordinator: Should have master’s level of academic and qualification in the field of environmental science. He/she must have an experience of 5 years in environmental research.
- Research analyst: Should have master’s level of academic in the field of chemistry, industrial chemistry, and environmental science as a qualification. He/she must understand numerous tests of environmental analysis with the experience of 5 years.
- Learning coordinator: Must have masters level of academic in environmental science and must be teaching at the university level. He/she must have the experience of 5 years in teaching.
- Laboratory technicians: They must have a degree in environmental science or related degree. In addition, they must be having experience of more than 3 years working in a laboratory environment. Those with a higher diploma level of academic qualification are encouraged to apply if they have an experience of over 5 years.
Conclusion
Environmental analysis is important in modern society because it enables analysis of health risk factors that are present in the environment. Since pollution has increased in Dubai, there is a need to establish an environmental laboratory in the university. The laboratory will benefit the community, university, and other stakeholders. Given the importance of the laboratory, the proposal recommends its functions, organizational structure, layout design, standard experiments, and location of the laboratory. Moreover, the proposal recommends equipment and chemicals necessary, quality control and assurance procedures, health and safety precautions, and qualification of the employees. Therefore, the proposal holds that it is viable and beneficial for the university to establish a new environmental laboratory within its surroundings.
References
American Society for Testing Materials (2014). Water Testing Standards. Web.
Conklin, A. (2004). Field Sampling: Principles and Practices in Environmental Analysis. New York: CRC Press.
Dunnivant, F. (2004). Environmental Laboratory Exercises for Instrumental Analysis and Environmental Chemistry. London: John Wiley & Sons.
Patnaik, P. (2010). Handbook of Environmental Analysis: Chemical Pollutants in Air, Water, Soil, and Solid Wastes (2nd ed.). New York. CRC Press.
Ratliff, T. (2005). The Laboratory Quality Assurance System: A Manual of Quality Procedures and Forms. London: John Wiley & Sons.
Reeve, R. (2002). Introduction to Environmental Analysis. London: John Wiley & Sons.
United States Environmental Protection Agency (2014). Approved general-purpose methods. Web.
Willis, H., Gibson, J., Geschwind, S., Olmstead, S., Hu, J., Curtright, A.,… Moore, M. (2010). Prioritizing Environmental Health Risks in the UAE. Risk Analysis, 30(12), 1842-1856.