Project Selection
Emirates NBD
This company is a banking group and the result of the merger between two banks – Emirates Bank International and National Bank of Dubai. It is a regional bank, serving the United Arab Emirates and the Middle East, but it also aims for an international clientele. The merger has been described as a valuation perspective, with both organizations providing powerful legacies form the leading financial institutions in this part of the globe, but with an international presence.
Emirates NBD is a functional organization, in which there are several superiors or supervisors, and the employees are grouped in teams that practice their own specialization or expertise. The traditional approach distinguishes an organization through clear lines of authority depending on the type of work that is at hand. There is the unity of command in that the employees are under one “boss”.
The importance of the merger of the two banks is immense: it has created a powerful and effective financial institution in the region. It is now UAE’s pride, the number one in the region, and the largest in the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) in terms of assets and market capitalization. Information Technology (IT) applications have initially been applied, but this is lacking. The bank has applied for e-banking for its thousands of customers. Its treasury apparatus should also be IT-enabled to provide integrated processing in different aspects. A unique consumer finance system has already been installed to enable a systematic cycle of loans to clients who might be individuals or organizations. E-banking will speed up responses to customer needs and will enhance organizational performance.
The Organizational Structure
With more than 220 branches across the Middle East, Emirates NBD spreads its services across the UAE and internationally. Traditional vertical structure works for Emirates NBD. The Board of Directors is comprised of prominent and successful leaders from different industries. It meets every month to discuss significant banking and business strategies and management, corporate issues, financial reports, internal and external problems, and risks.
The current Chairman is His Highness Sheikh Ahmed Bin Saeed Al Maktoum, the Vice-Chairman is Hesham Abdulla Al Qassim, and directors hail from leading industries in the region, such as H. E. Khalid Juma Al Majid, Ali Humaid Ali Al Owais, Husain Hassan Mirza Al Sayegh, Buti Al Mulla, Khamis Al Shehi, Ahmad Al Hussaini, and Hashem Khoory.
The executive team supervises the Group performance and provides decisions at the Group level, with authority from the Board of Directors. These decisions include the daily operations, the strategic initiatives, and other significant issues that need immediate resolution. The team meets twice a month.
The Group Chief Executive Officer is Shayne Nelson; Subramanian Suryanarayan is the Chief Financial Officer; Manoj Chawla is the Group Chief Risk Officer; Lubna Qassim is the Chief General Counsel and Corporate Secretary; Abdulla Qassem is Group Chief Operating Officer, Suvo Sarkar is the Senior Executive Vice President, and concurrent head of retail banking; Husam Al Sayed is the Group Chief Human Resource Officer; Kevin Flanner is Executive Vice President for International Relations. Saod Obaidalla has been given responsibility in the Private Banking division. He has been with the organization for many years.
Project team members include Abdula Dawood, Assistant Manager for Finance; Amr Shohdy, Cluster Manager; Fatma Kianifar, VIP Relations Manager; Latifa Al Jabri, Assistant Manager Group Risk; Namitha Ashok, Dispute Processor; Pradep Viswambharan, Fraud Monitoring; Ritu Bhatia, Project Manager; Seema Sadanandan, Product Support Assistant; and Hamdan Bin Balmook, Assistant Manager for Finance.
Emirates NBD promotes green credit as a concept of sustainable banking. It is a commonly applied environmentally sensitive financing process among the financial industry worldwide. During its early years of massive infrastructure and economic development, construction industries in the UAE, especially those in Dubai, were heavily criticized for their involvement in several projects that brought damage to the local environment and community interest.
Emirates NBD has evaluated the environmental risk of loans. Other countries have introduced legislation containing both green credit and green insurance policies. Germany and France also issued laws and financial policies to incentivize capital flow to environmentally friendly business, while strengthening environmental law enforcement to increase enterprises’ cost for the violation, which then turned into credit risks. Green financing runs alongside the social responsibility principles and is often fuelled by disastrous events and fierce protests from the public. In the UAE, the green financing movement is a direct result of public outcry and the banking sector initiative.
In western countries, such as the UK, the financial industry is supervised following the Arm’s Length Principle. Environmental risk in these countries largely comes from the market, where environmental law violations are too costly.
Project Charter
Title: Implementation of Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) for Emirates NBD
Scope Overview
Like other complex information systems, Enterprise Resource Planning implementation is a time-consuming and expensive task. Implementations usually take longer than planned, data from old core and legacy systems do not convert smoothly, and the list of difficulties and drawbacks is long. The implementation effort occupies many resources and creates a disturbance in the organization. Changes in business processes to fit the core system create stress and disappointment if not properly managed.
Failure to meet deadlines and target dates creates a tense atmosphere for the project team undertaking the implementation, in addition to the rest of the staff and management. However, this is applicable and is most recommended for this large organization, since Emirates NBD is a banking group comprised of two large banks in the UAE.
Objectives
This paper will focus on general and specific objectives on the subject of IT implementations in organizations.
General Objectives
- To conduct project management on an organization in the United Arab Emirates;
- To determine the impact of the information revolution in organizations;
- To examine the effectiveness of Information Technology in large organizations.
Specific Objectives
- To implement Enterprise Resource Planning on Emirates NBD, a banking group in Dubai;
- To examine the effectiveness of ERP with respect to functionalities of an organization like Emirates NBD;
- To determine project management activities of Emirates NBD;
- To find out how the steps in project management can enhance ERP implementation;
- To inter-connect the bank’s old system with the new system;
- To determine the outcomes of ERP implementation in a large organization.
What needs to be accomplished
In connection with the general and specific objectives, we need to focus on several factors like adequate executive alignment, business processes, end-user adoption, treat organizational flaws and inadequacies, and address information technology configuration issues, infrastructure shortcomings, knowledge transfer challenges, geographic distance, time separation, organizational differences, functional diversity, cultural differences, and language differences.
Computer applications already in place in the bank’s system:
- Core Banking Application (PHOENIX) – consists of General Ledger, Liability Products, Asset Products, Relationship Management, and SWIFT interface
- Treasury Application (QUANTUM) – including ‘Front-end treasury system’, Middle-tier system, Back-office system, SWIFT interface, and PHOENIX interface.
- Branch Application (MOSAIC) – includes functionalities for, among others, Relationship Management, Asset and Liability products, Check processing products, Passbook facilities, Transfers, Checks and drafts, Retail lending, Retail fixed deposits, Product selling vehicle, Greeter functions, Safe deposit box management, and PHOENIX interface.
- ATM Switch-u / SWITCHWARE – This is the ATM switch to automate both ‘Automatic Teller Machine’ (ATM) and ‘Point-of-Sale’ (POS) debit car business.
- Trade Finance Application (IBSNET) – This is the trade finance function that will automate the trade finance functions including among others:
- Letters of Credit,
- Letters of Guarantee,
- Collections.
- Credit Scoring (FAIR ISAAC) – This is the credit scoring application that will be interface at a later stage of this project to MOSAIC. It supports both the credit desk and the credit table that assists the bank in setting weights based on a regression analysis of historical data.
ERP application
IT experts contend that ERP ensures 24/7 accessibility through any type of advanced information system. This connects with and provides functionalities for ATMs, mobile phones, personal computers, emails, etc., and for all types of financial transactions which can be securely conducted online or with the use of the internet.
ERP was first developed by the founders of SAP. There are many vendors offering ERP systems, some of them are SAP and Oracle. ERP combines business management procedures and the common features of technology, with automation for business functions, are introduced. Since Emirates NBD already has automation in some of its business functions, it only needs ERP to integrate all the functions, along with a central database and an ERP server.
However, ERP systems can be very complicated, costly, and needs multiple parameters to implement. It incorporates functionalities, one of which is the Materials Resource Planning (MRP) and Customer Relationship Management (CRM). If implemented successfully, it provides effective innovations and an effective banking system for Emirates NBD. However, users have to get acquainted with this new system and have to adapt to it. The banking group needs to restructure since the unbending features of ERP are complicated for new users. Moreover, the smooth running of a business can be significantly disturbed while implementation is going on. There will be data migrations that may enable confusion on the part of new users, especially employees of the various departments of the bank.
There are risks in ERP implementation but the benefits are multiple. It can increase profitability because the system enhances banking applications and relationships with customers. It might take years to fully have an effective and functional system, but success can be long term. Maintenance and upgrading are quite easy for IT people, as long as the system is already working.
On the other hand, core banking is one of the important applications. This will be integrated into ERP. With regard to its features, the core bank refers to all transactions coming to the back office, where the core data processing system processes the transaction, reports the information and records the transaction for the general ledger system. The core banking system is the heart of the retail bank. In general, core banking systems are comprised of deposit processing, loan processing, and accounting, customer information files, general ledgers, and reporting tools.
Most banks trust a single vendor to provide all these essential elements, but large banks like Emirates NBD need several vendors. In general, a bank will develop a close relationship with its core banking system vendor, often depending on it to drive the bank’s technology investments and strategic implementations. In turn, the vendor, with intimate knowledge of the bank customer’s needs, will work closely with the bank to customize or add functionality to the core banking system to meet the client’s unique needs.
The deposit processing system supports the development of the bank deposit products and the management of all deposit products and the management of all deposit transactions. This includes current accounts, savings accounts, and time deposits, even large deposits made by client organizations. Innovative developments in this area include a library of thousands of bank product components that banks can use, without extensive programming training, to develop customized, unique bank products for customers.
Core banking systems often include consumer loan accounting and servicing systems that are connected to their loan origination systems and channels. The functionality will often include the ability to develop unique loan products, support for a wide variety of loan types (e.g., installment loans, student loans, home equity lines of credit, revolving credit, etc.), collection and recovery management, and statement production.
All these can be incorporated into the ERP application server. The center of the core banking system is the customer information file (CIF). This is the central repository for descriptive information of a bank’s customer base, including account relationships, address information, and household information.
Business case
Information technology has a tremendous influence on the banking sector. This is evident in increasingly more effective and convenient delivery channels of banking products and services, which create new avenues for competition and upgrade banks’ competitive advantage through direct marketing, efficient customer service, and streamlined business processes. Internally, more effective and timely access to critical information has enhanced the decision-making process through consistent management and decision-support systems.
To the customer, IT has enabled banks to develop and implement several products and services whose aim is to satisfy customers’ needs, thus attracting and retaining the most profitable ones. The customer can access the following services at an easy pace:
- Self-inquiry terminals at the bank’s branch which enables the customer to access and view transactions in their accounts;
- Remote banking or e-banking at the customer’s geographic location that connects to the respective bank’s branch through a modem and allows the customer to make inquiries regarding his or her accounts online;
- Anytime/anywhere banking such as ATM (automated teller machines), which offer 24/7 facilities of cash withdrawals and deposits, remittances and inquiry installed on- and offsite, and networking of computerized branches that permits customers in the network to transact from any of these branches;
- Electronic banking, which allows the bank to provide corporate or high-net-worth customers with graphical user interface software on a personal computer, so they can inquire about their financial transactions and accounts, cash transfers, checkbook issuance, and rates without visiting the bank.
On the other hand, a bank can have a wide array of back and front office functions and tasks that include the following:
- Efficient inquiry facilities, enhancing the bank’s business development and related activities;
- Online access to customer data, enabling speedier customer service; and
- Generation of various management information systems reports, periodically, and ad hoc.
Employees’ benefits in IT applications include productivity increase and relief from cumbersome and time-consuming menial jobs; signature retrieval facility, which enables verification of transactions without leaving the terminal; and single-point data entry that eliminates inadvertent duplication of entries.
Milestone schedule
Computerization and the introduction of new technologies have had a multifaceted effect on the customer, the bank, and the employee. Information technology has to be introduced in all functionalities of the bank. This will have a great impact on top management and employees, along with their customers, and expectations are high.
Important milestones of the Emirates NDB merger include: March 2007 – the start of the merger, with Goldman Sachs International given the responsibility as lead financial advisors; 12 July 2007 – terms of the merger were made public; 5 September 2007 – Shareholders approved the terms of the agreement; 18 September 2007 – first offering were closed; 4 November 2007 – announcement of the National Bank of Dubai’s building to be the new main headquarters of the Group (Kumar & Fernandez, 2012).
Success criteria
A project’s success formula is governed by a blend of good management and agreement among the project’s stakeholders on the relative significance of each of the terms of the project. Stakeholders external to the project organization use target cost and time for measuring project success, whereas those internal to the project agree that the attainment of the scope of development determines the project’s success. Other success criteria will include:
- Top management support – IS implementation is resource-intensive
- Technical fit – the compatibility of the existing system with the new system
- Organizational fit – congruence between the organizational artifact and its organizational context. A generic solution that applies to a broad market might have an organizational misfit in a specific market.
- Project team competence – the appropriate balance of business and technical skills. This also includes people who have high qualifications and knowledge about the enterprise.
- Interdepartmental cooperation – Implementation of special coordination, communication, and cognitive processes tailored to help teams overcome global barriers. We also have to form a cross-company team to represent each business unit, corporate management, and IT to develop a broad-based but rigorous roadmap with the aim to build consensus around the project.
- True to its mission and objectives – Emirates NBD will provide standards that are achievable and can prove their worth to their clients. Their goals are in line with the public’s welfare and development.
- Project management – IS project performance consists of two different dimensions: process performance product performance. Project planning will refer to the extent to which timetables, milestones, workforce, equipment, and budgets are specified. Project team empowerment refers to the empowerment of the project team members to make decisions and their high position in the enterprise hierarchy.
- We must get to the point of discerning the real consequence of what we do; meaning a project controller has to provide the covered costs of the operations.
- Interdepartmental communication – Communication within the project sections will be implemented by the team members to other enterprise employees.
- Management of expectations – When users are not assigned any formal project development responsibility, user participation and desire to participate still has a significant influence on perceived participation and perceived participation has a significant influence on intention to use and process satisfaction.
- Benefits – Suppliers will be different IT vendors.
- Careful package selection – system reliability, user-friendliness, and fit to the enterprise’s needs are a must. Commercial Off-the-Shelf (COTS) packages embody best practices.
- Data Analysis and Conversion – This may involve different packages such as a database for electronic data, which is a common feature of ERP.
- Whatever the choice of software, ERP will allow us to integrate existing business applications and data libraries to make migration for users easy, avoid downtime due to training, and reduce the costs associated with migrating data.
- Dedicated resources – This will refer to the size of the organization, financial budget, which should be assured during the implementation, and the project manager who is dedicated to implementation duties.
- User training – this is very important in software implementation, and cannot be overlooked or overemphasized. It will contribute to reducing the operational and cultural issues encountered during an implementation project. It is essential for complex systems that entail large-scale changes in jobs’ skills, contents, and computerization.
- Ease of use – This refers to the degree to which the system is perceived to be relatively free from physical and mental effort, and has an impact on the intentions to use ERP.
- Training should involve both the packaged systems features and related work processes.
- Minimal customization – Keeping the IT package ‘as is’ is always recommended by companies implementing computer software and even many researchers for optimal exploitation of the package and for avoiding the technical complexity of customizing the package and the future technical problems in rollouts and updates, especially in phased implementations of these systems.
We have also to consider that, based on the literature, success rates in IS projects are not high, meaning there is a great percentage of failure. This is not to mean that we are losing hope; success will always be in our minds. Success factors for this project will include: on time, on budget, system quality, cost, and effort to meet requirements, user satisfaction, team satisfaction, system use, and net system benefits.
Risks, assumptions, and constraints
How has technology affected the performance of UAE banks, and what is going on in this area? With the merger of the two large banks, this banking group is aiming for effective organizational performance to appease clients and end-users of the system. IT implementation has to gain new opportunities and increase clientele and profitability, rather than lose them. In short, Emirates NBD wanted to make sure ERP implementation was successful. They acquired a number of vendors, provided funds for the project, and appointed responsible IT experts and experienced managers to handle and supervise the project. In their quest to offer superior products and services to all their clientele, the banking group has aimed to be viewed as a technology-driven institution.
Moreover, the ERP system must be operational within the months of December or January. The first phase of this project will focus on the technical side, and surveys will be conducted. A feasibility study will also be conducted to give a chance for top management to decide for a go or no-go scenario, and that will occur at the conclusion of this study. Implementation of the ERP system will commence in July, depending on the recommendations and decisions of top management.
Resource estimates
The human resource will be a combination of IT experts, mostly internal to the project while others came from the donor organization. However, there will be those external who come from IT companies. The overall project manager takes charge of the entire operation. Since this is a vertical set up, the overall project manager report to the Steering Committee. Vendor representatives report to him, including the business units that include operations, retail, accounts, credit corporate, special assets, treasury, and so forth. It is estimated that this will cost approximately $10 million for Emirates NBD, but it might exceed further. The exact cost can be determined during its completion, i.e. after the installation, testing, and actual use by the end-user.
The Stakeholders
The stakeholders in the implementation of the project include:
Steering Committee
This is chaired by the Chairman General Manager, and composed of the head of administration, chief financial officer, chief information officer, and other chiefs of office with significant functions;
- This Committee owns and oversees the whole project – the Donor – and is considered the supreme authority as far as the project is concerned;
- Deals with high-level issues such as handling bottlenecks, resolving conflicts, taking strategic decisions, approving budget deviations, approving project plan modifications, and approving scope changes.
Overall Project Manager
Emirates NBD nominated its CIO to be in charge of the whole project management and coordination. He/she has the following responsibilities:
- Creating the sub-project task forces and coordinating with the various business units of the bank for this purpose;
- Coordinating all project activities among the various vendors, project teams, steering committee, and end-user divisions;
- Calling for, preparing the agenda, and following-up on the meeting of the steering committee;
- Deciding on issues to be reported to the steering committee;
- Setting task priorities among the various jobs and sub-projects;
- Garnering the direct approval of the chairman, general, or the project steering committee for project-related business decisions that may lead to conflicts between business decisions.
Vendors
Vendors are significant players in this project. The companies they represent can be considered suppliers. This time they are dealing with intangible products which are very important to the smooth flow of business and for other organizational matters. In order for the project to run smoothly each vendor must assign a project manager who assumes the following responsibilities:
- Full coordination between the vendor’s company and the overall project manager;
- Bypassing the overall project manager and going directly to the steering committee when the need arises;
- Coordinating with the overall project manager in preparing a detailed project plan for that part of the application that is related to the vendor;
- Coordinating with Emirates NDB project teams which are headed by selected IT project coordinators assisted by business staff/ consultants.
IT Coordinators
Appointed by Emirates NBD, and have the following responsibilities:
- Coordinate with the vendor teams on detailed project tasks;
- Coordinate with end-users, especially on deliverables;
- Report regularly to the overall project manager especially on any unforeseen barriers;
- Take responsibility for the detailed implementation plans and work accordingly;
- Maintain related documentation;
- Perform their duties in full compliance with IT policies and procedures. They should facilitate the job of vendors as long as this does not conflict with policies and procedures, in which case the problem should be escalated to the overall project manager for immediate resolution.
- IT coordinators represent the different departments which are the direct beneficiary of the IT innovation.
End users
These are the ultimate owners of the application in the sense that they will be using it on implementation on a regular basis to increase their efficiency. End users comprised of the employees and staff of Emirates NBD. They have the following responsibilities: Assist in the analysis of the project; seek proper authorizations of business decisions from their superiors; perform system user testing, to include user acceptance testing; attend training courses and be ready to train their colleagues; coordinate fully with the IT project coordinators and abide by the project charter.
Librarian
Is assigned by the overall project manager and assumes the following responsibilities:
- Maintaining all project-related documentation including project initiation documents, licenses, and delivery notes, project implementation plans, minutes of the meetings, analysis sheets, user acceptance tests, technical documentation, system references, user manuals, project-related software, compiling IT documents;
- Compiling IT documents before final publishing
- Coordinating document distribution.
Audit
The audit department is required to be on board from day one of the project, in order to promote a technical solution that is compliant with best practices and regulations. The project team on all compliance and security issues consults the audit department during both the analysis and the user acceptance testing phases of the project. All related documentation shall be routed to the audit department for review. Finally, the audit department is required to comment on issues during any of the project phases.
Team operating principles
Emirates NBD has a strategy of seeking accredited international vendors in order to address its needs as far as software for banking applications is concerned. This large organization does not support the in-house development of its core applications. The bank, however, is well aware of the fact that regardless of how efficient and comprehensive may the application be, it needs to have some “satellite” applications for the automation of non-core but mission-critical applications.
We have a good example of a satellite application – the “check-clearing” application. All international applications the bank has so far used do not provide for a proper check clearing mechanism because the said mechanism is so peculiar to the UAE banking environment. Above all, we also must consider user requirements. In an ERP system, all IT products must be streamlined with the bank’s strategic and tactical business direction. It is not acceptable to produce services and systems that do not reflect and match with such direction. Consequently, the IT Business Support Unit ensures that user requirements are clearly understood, fully documented, and properly signed off.
Emirates NBD has a policy to maintain clear technical documentation of each and every in-house developed system so that continuity of services can be maintained. Development should include full accordance with technical documentation, wholly endorsed development environment, and in accordance with the bank’s development standards. End users often concentrate on the business functionality of the application and can ignore their security measures. Therefore, every application developed in-house must observe the security measure even if the end-user has ignored it. IT application should depend on the size of the application and the bank’s operating procedures. It is very important to ensure that changes should take place before the final deployment of the product. Else, ERP might have problems such as reversals or other post-development issues that can delay the full implementation of the product.
After implementation, we may also require some end-user training. This is an important phase in the full development of the IT product, which can be overlooked by developers. The more the end-user is oriented on the new technology, the less work the System and Technical Support Section can encounter.
Therefore, the support group must have proposed training material with the plan that this is going to be used for the end-users. This training material can be introduced with a PowerPoint presentation, or a whole course, wherein the training session logistics must be coordinated with the HR department.
The testing of the software is an important part of the application. Before it can be fully delivered, it has to be tested in a live environment. This can be a short period of time that may involve a few staff members, or it can be complex testing involving an entire organization. The scope and complexity of this activity will depend on the features of the project itself. However, regardless of the project complexity, the support team must include in its activities the proper testing of the product, and with proper documentation.
The installation manual is also a must. The IT application team has to prepare a fully-detailed installation manual, and other information materials to help the Systems and Technical Support System in providing a full installation of the system. This is a significant step so that a full separation between the production environment and the test environment can be ensured.
User manuals should be provided. The team should prepare an end-user manual or all in-house technology applications. Care should be given to ensure the manual is a correct application of what is given in the software. The quality of the user manuals reflects directly on the integrity of the IT department. It is one of the important steps in the application.
Lessons learned
The core system implementation of this merger bank, known as Emirates NBD as described earlier, has had many twists and turns. To conclude, it seems to have made it onto a stable, standard platform but it has been a painful process with plenty of lessons along the way. The route by which Emirates NBD passed through was long and far from smooth. It took several years and one failed attempt. There was a great deal of customization, bringing instabilities. Lately, this has resulted in a major project to upgrade to the latest version of the system and adopt a much more standard version this time around.
Stakeholder Analysis and Communication Planning
Stakeholder analysis
Stakeholder’s interest
Communications matrix
Scope Planning
Resourcing the project
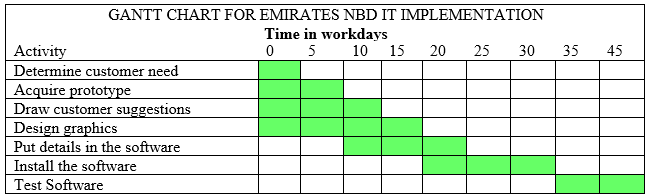
Histogram
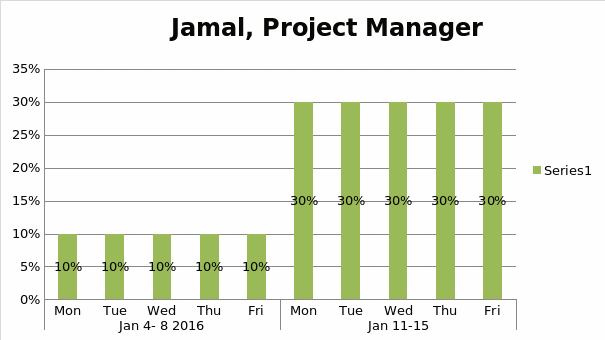
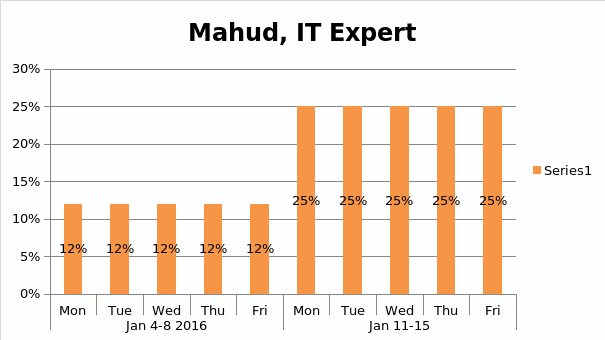
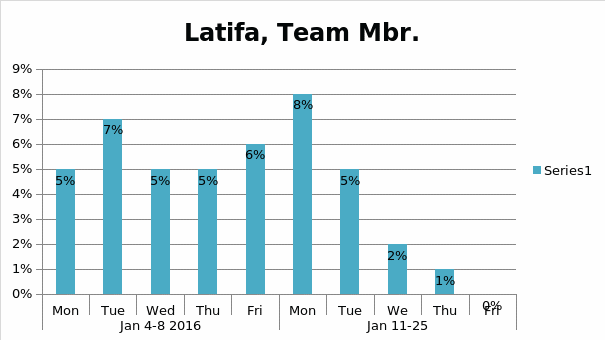
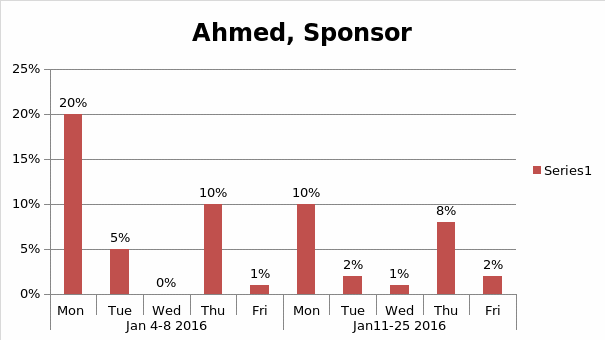
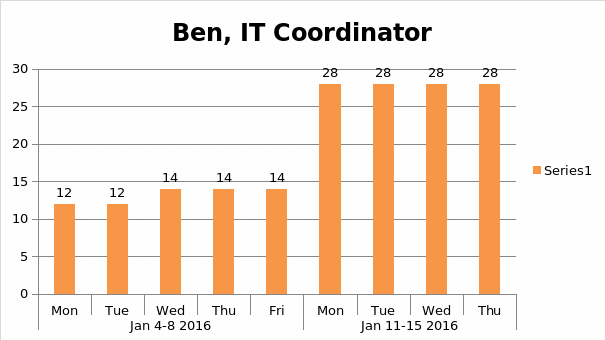
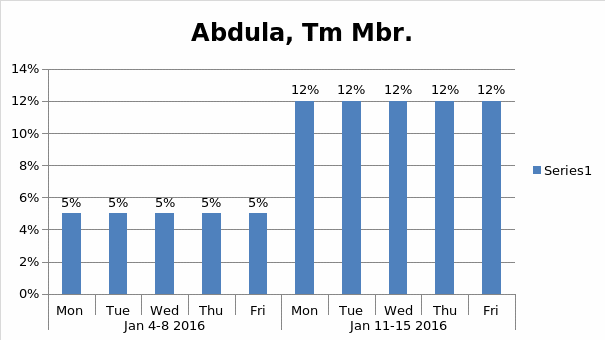
Human Resource Management Plan
The impact technology has had on the banking profession is remarkable. This is evident in increasingly more effective and convenient delivery channels of banking products and services, which create new avenues for competition and upgrade banks’ competitive advantage through direct marketing, efficient customer service, and streamlined business processes. Internally, more effective and timely access to critical information has enhanced the decision-making process through consistent management and decision-support systems. Computerization and the introduction of new technologies have had a multifaceted effect on the customer, the bank, and the employee.
Enterprise resource planning implementations are complicated and risky projects. These involve complicated aspects of reengineering and other complex aspects of ERP technology. All these requirements and more magnify the project management challenges for such undertakings, making them implementation failure-prone. Project planning, which refers to the extent to which timetables, milestones, workforce, equipment, and budgets are specified, becomes crucial in this type of complicated project environment.
Important individuals, including managers and employees, are instrumental to the full implementation and success of this project. The sponsor company provided for the financing. We have to draw the expertise of the members of the Steering Committee, and this may include the Chief Executive officer, Chief Information Officer, Chief Financial Officer, Chief Operating Officer, the Overall Project Manager, and the various representatives, coordinators, and IT experts, and not to exclude the IT vendors and their coordinators. The stakeholders provided a team of experts and experienced technical and academic experts to provide what Emirates NDB needs.
Employees will have to be trained for end-user training. This is a critical intervention to support the successful implementation of information systems innovations. For this reason, the implementation of IS innovations is typically accompanied by substantial investment in formal training programs. Lack of user training can be a cause for implementation problems or failures. Training is essential for complex systems such as ERP, especially with large-scale changes in jobs’ skills, contents, and computerization. Employees should be aware of how their mistakes may escalate and affect what other users are doing in different areas of the whole system.
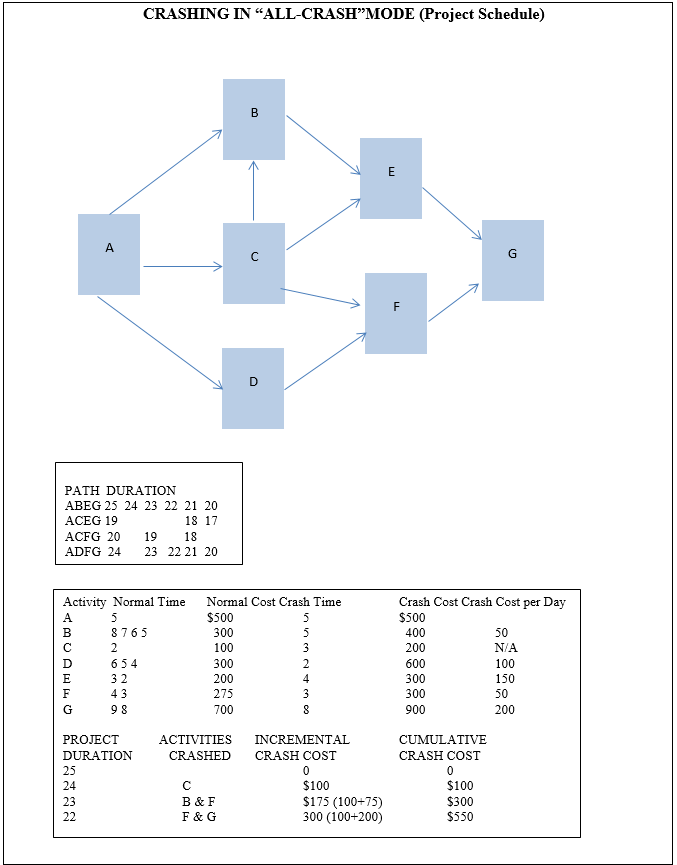
Budgeting for the Project
Implementing ERP will require cost from installation up to maintenance. There will be more staff time and will require an IT team to maintain its effectiveness. A substantial amount of job time will be needed and also cost to pay employees.
First, the cost of acquisition will run depending on the size and scope of IT and the needed software. In the case of Emirates NDB, it will run into millions of dollars since this organization is a banking group with hundreds of client organizations and hundreds of thousands of individual clients. Other costs will pay for human relations and loss of services.
For a typical middle-sized firm, the installation will run from a few hundred thousand dollars to $750,000. We have estimated that the Emirates NDB incurred $10 million, but there could be other costs. IT personnel installing the software are employees of the vendor, and therefore their salaries will be the responsibility of the IT vendor.
The problem lies in the maintenance: Emirates NDB could hire IT professionals to work for the company, and be a part of their regular employees. Their salaries will be higher than ordinary employees, with an additional 20% benefits. The banking group can outsource ERP implementation and incur a lesser cost for IT maintenance. The cost of maintenance will vary since there might be failures along the way and complaints from end-users. The human factor can cause IT failures, therefore, top management has to be aware that this can add cost to maintenance if they outsource IT, people. Hiring the best IT staff and make them permanent employees of the organization is the best option to attain lesser IT costs.