Introduction
An event that serves as the basis for the following case study, analysis of strategic management and factors impacting decision-making revolves around International Business Machines Corporation (IBM) and its desire to meet the new requirements of society and its members by buying Red Hat company.
IBM is an American multinational corporation that operates in 170 countries globally and significantly impacts the market of technologies (IBM, 2018). Its central office is located in Armonk, New York; however, there are many departments in other strategically important regions. The corporation manufactures, designs, and sells hardware, middleware, software and provides diverse consulting services in the area of innovation and nanotechnologies (IBM, 2018).
At the moment, it is one of the leaders in this market segment with annual revenue of about $79,591 billion (IBM, 2018). The company is managed by the Board of Directors who accept all critical strategic decisions and are responsible for substantial growth. At the moment, Virginia Marie Rometty is the chair and president of IBM who correctly realizes the peculiarities of the company and contributes to its further evolution.
Decision
IBM’s strategic acquisition of Red Hat company with a total value of about $34 billion is taken as the background for the given case. In accordance with the majority of experts in the field of technologies, this purchase signalizes a new era of open cloud services as Red Hat is known as a leading designer and provider of open-source software products that can be used by the enterprise community (Bloomberg, 2018; Carey, 2018).
The given act became one of the potent approaches to support the gradual improvement of IBM Corporation and its focus on dominance in the sphere of nanotechnologies and innovative solutions that can be used by wide populations globally. The scope of this agreement is also evidenced by the fact that it has already been called the biggest open-source transaction of all time, which will reconsider the balance of power in the market and precondition the emergence of new opportunities for IBM (Carey, 2018). That is why the given settlement between IBM and Red Hat becomes the central event discussed within the provided case study.
The choice of this deal offers multiple opportunities for strategic analysis and an improved understanding of factors impacting the decision-making process and planning. Being the leading company in the sphere of innovations, IBM experienced both internal and external impacts that stipulated the appearance of this idea and its realization. For this reason, it is critical to delve into the peculiarities of the purchase to outline the central aspects that should be mentioned to understand how CEOs came to this conclusion.
Structure
The document has some important sections that are arranged logically to ensure that a clear understanding of the discussed events. In the introductory part, the main actors of the panned strategic decision and its details are provided. The next section is devoted to the detailed analysis of all elements of decision-making that affected IBM and preconditioned its choice.
The paper also utilizes the Institutional theory to create the theoretical framework for the investigation and guarantee that all meaningful factors are considered. Finally, there is a concluding paragraph that summarises all provided information and sets the basis for the future discussion of this strategic incentive.
Analysis
Date
On October 28, 2018, IBM made an announcement stating that it was going to buy Red Hat with all rights for products and services created and distributed by the company. Regarding the scope of the deal, the established price was the acquisition was $34 billion, which contributed to the purchase becoming one of the most significant events in the market (Carey, 2018).
The given strategic decision became revolutionary to the field of technologies as it meant that IBM acquired the opportunity to launch a new line of products and support services that gradually become more and more popular in large population groups (Hammond, Porter, & Barinka, 2018). The preliminary work for making this agreement apparently presupposed the in-depth investigation of the existing market trends and the way companies evolve. At the same time, many of Red Hat’s solutions are utilized by various business organizations, which also guarantees stable income and the popularity of future products.
Involved People
Ginni Rometty, IBM’s Chairman, was one of the key actors promoting this deal as it was considered a part of the company’s course aimed at the continuous improvement and focus on higher-value, more profitable markets. She called this transaction a game-changing event in the world of technologies as it had the potential for reconsideration of the cloud market and transformation of IBM into the world’s leading hybrid cloud provider offering corporations solutions satisfying their current diversified demands (Rometty, 2018).
Correctly realizing a competitive advantage generated due to the given agreement, Rometty was one of the main promoters and supporters of these strategic incentives because of the necessity to create the basis for the further evolution and overcome rivals by offering new and unique products to clients with the high level of expectations. The positive impact of this step can be evidenced by the fact that the company’s shares increased in value and specialists predict further growth (Leprince-Ringuet, 2018). It means that there are multiple opportunities for IBM’s evolution and it is becoming a central actor impacting the rise of the market.
Preparations
Considering the long-term perspectives arising because of the discussed deal and its scope, the given decision can be taken as a well-thought-out step that resulted from the combination of factors impacting IBM at the moment. Moreover, there is a 20-years history of IBM’s attempts to conquer the web segment and provide customers with services related to it (Moody, 2019).
In 1998, it created the first Apache Web server as a central component of the WebSphere product family, which signalized the first movements towards the creation and utilization of cloud services (Moody, 2019). In such a way, the given deal can be taken as a result of complex and hard work performed by the corporation to evaluate all potential advantages and disadvantages of developing this segment. Additionally, the necessity to move forward was also one of the central factors preconditioning the agreement and making it real.
These facts evidence that the decision to purchase Red Hat was planned in advance and became an integral part of IBM’s strategy aimed at the further diversification of provided services and increased ability to satisfy customers’ needs. Due to the effective analysis and planning department, the companies managed to come to an agreement that signalized a new era in the sphere of digital technologies and cloud services characterized by IBM’s overwhelming impact on the majority of operations and products.
Institutional Theory
The analysis of the given strategic incentive and factors preconditioning its success can be performed regarding the institutional theory that is relevant to modern organizations’ functioning. In accordance with this framework, various components such as rules, norms, strategic decisions and solutions are a result of the organizations’ attempt to conform to easily recognizable and acceptable standards peculiar to the society and popular within a particular field (Crossan, 2015; Puranam, 2016).
The theory also describes that deliberate or accidental choices affect companies, their values, and ideologies, which is critical for outcomes (Kotler & Armstrong, 2015). Functioning and evolving in a particular business environment, a corporation has to mirror its peculiarities and align its development according to the most topical patterns (Bensoussan & Fleisher, 2015). For this reason, IBM’s intention to buy Red Hat can be analyzed through the prism of the institutional theory as it will help to explain the main steps of decision-making and understand the underpinnings of this solution.
Graphically, the company’s decision-making can be represented as a combination of institutional pressures and strategic responses (see Figure 1).
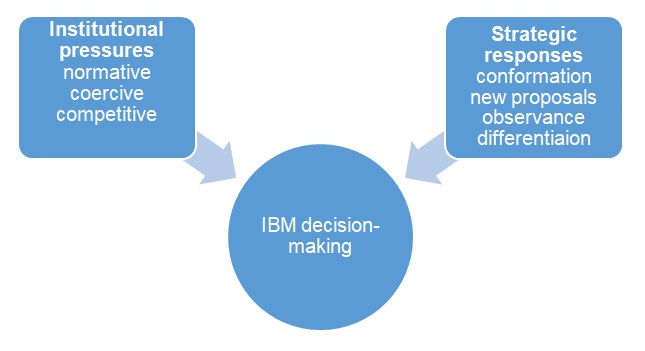
In such a way, analyzing the given step, it is critical to consider the existing institutional pressures that affected IBM while making the decision to by Red Hat and its possible response to these pressures that could have contributed to the improvement of the company’s position at the market and it is becoming one of the leaders with a significant competitive advantage.
The utilization of the given model can also help to understand better what critical factors were taken into account in terms of the necessity to guarantee the emergence of new products that will remain popular with the audience and attract in a prolonged period of time (McPhail, 2014). For this reason, the application of this very framework is critical for the better analysis and formulation of credible outcomes.
Impacting Factors
An outstanding significance of the discussed strategic incentive means that IBM experienced the impact of multiple factors that stipulated a need for an effective solution that would help it to evolved and preserve leading positions. As it comes from the utilization of the above-mentioned model, there were both internal and external pressures and factors presupposing the necessity to alter to conform to the altering environment.
Analyzing all forces that were topical for IBM at that moment of time, one can outline the main causes for the selection of the strategy aimed at the acquisition of Red Hat and focus on new products and cloud services (Vaughan-Nichols, 2018). In such a way, the discussed step will be investigated as a set of impacts and factors that triggered a particular response and shifted the corporation’s priorities.
External Factors and Institutional Pressures
As for the external stressors, it is critical to understand that IBM exists in an extremely competitive environment in which functioning is regulated by multiple normative acts and constantly emerging demands to hardware and software. For this reason, the necessity to generate advantage by acquiring rights for the creation and distribution of one of the most popular products of the modern business world became one of the determining aspects.
IBM has to compete with such giants as Intel, Hewlett Packard, and Xerox, which means that its products should be different to attract customers and increase revenues (Bhasin, 2018). For this reason, the purchase of Red Hat, the leader of open-cloud service provides, can help to make the corporation’s presence in the market stronger.
Furthermore, the growing popularity of open-source systems can be considered another institutional factor impacting the discussed decision. Modern society insists on the increased security of software which can be achieved by using open code (Red Hat, 2018). For this reason, Red Hat becomes a company that can release this pressure because of the existence of outstanding open-source developers who can provide IBM with new products to satisfy customers’ diversified demands (Red Hat, 2018).
This factor became an important aspect impacting the given strategic incentive because of the possibility to create the basis for the future development by devoted attention both to the given sort of software and cloud services which are also become more popular in wide populations. It will also empower IBM’s position in the market because of the ability to capture a wide segment and preserve leading positions.
Finally, society’s demand for change became another sort of institutional pressure that preconditioned the given decision. The fact is that traditional software solutions became less popular because of their inability to meet the diversified requirements and the necessity to provide multiple resources to ensure their stable work. That is why in accordance with the latest investigations, open-source cloud services become the potent business and international cooperation tool that facilitate the further development of various industries and markets (Gall, 2018).
For this reason, IBM’s solution to affect this domain and launch a new product line associated with this technology becomes reasonable regarding the growing need for improved results. Additionally, this cloud software is taken as an innovative approach that can reconsider the further evolution of the sphere by offering a wide range of opportunities.
Internal Factors and Strategic Responses
There is also a set of internal factors that emerged as a strategic response to the above-mentioned pressure and affected the decision-making presupposing the purchase of Red Hat. First of all, IBM has traditionally been associated with a company that utilizes traditional methods while creating its products (Sherman & Kolodny, 2018). Its software did not cover the sphere of top-notch hybrid clouds because of the lack of expertise in this field (Red Hat, 2018).
Now, with the acquisition of Red Hat, the company acquires an opportunity to fill this gap in knowledge and attract new customers by diversifying its products and offering unique solutions to a broad category of clients that were previously unaffected. From this perspective, this very strategic incentive will also help to avoid the institutional pressure due to the consideration of the latest trends and introduction of the ways to conform to the environment.
Finally, the decision to buy Red Hat can be explained by the company’s need to provide appropriate responses to public concerns related to losing their personal data and the low reliability of some traditional services offered by IBM. With the current shift of priority, the corporation will be able to explore the popular and positive image of Red Hat to eliminate the majority of problems related to this sphere (Cortada, 2019).
As far as the purchased firm has significant expertise in this sphere, the knowledge accumulated due to this very deal will contribute to the further successful development of the conglomerate that will be able to use all its assets and power to support new solutions and implement them into the existing environment (Henry-Stocker, 2018). From this point of view, the agreement becomes an effective way to attract new customers and eliminate old fears.
In such a way, the analysis of internal factors and strategic responses proves the idea that the existing environment was beneficial for making the agreement between IBM and Red Hat. This statement can also be evidenced by the fact that in accordance with the majority of forecasts related to this deal, IBM will be able to generate even higher income in the next ten years because of the growing popularity of cloud services and open-source solutions (Agency Staff, 2018).
That is why it can be considered a successful solution that became possible due to the in-depth investigation of all factors impacting the company at the moment and correct realization of all opportunities associated with this transaction. Being one of the most significant events in the sphere of technologies, it reconsiders the further evolution of the sector and its perspectives.
Conclusion
In conclusion, IBM’s decision to buy Red Hat became a successful strategic incentive that created the basis for the company’s further evolution and substantial growth. The central factors that stipulated this agreement were the growing popularity of cloud services and open-source systems, the increased demand for new software, the high level of rivalry, IBM’s lack of expertise in this area, and the existence of an interest in this very problem.
Investigation of the case shows that business planning demands a comprehensive research of the market to determine the existing trends and decide whether the new approach will help to improve the company’s position and its ability to struggle with the closest rivals.
References
Agency Staff. (2018). Why IBM is buying Red Hat.Tech Central. Web.
Bensoussan, B., & Fleisher, C. (2015). Analysis without paralysis: 12 tools to make better strategic decisions. Upper Saddle River, NJ: FT Press.
Bhasin, H. (2018). Top IBM competitors. Web.
Bloomberg, J. (2018). Three things IBM must do to keep the Red Hat acquisition from sinking the company.Forbes. Web.
Carey, S. (2018). Most notable tech acquisitions of 2018. Computer World UK. Web.
Cortada, J. (2019). IBM: The rise and fall and reinvention of a global icon. New York, NY: The MIT Press.
Crossan, M. (2015). Strategic analysis and action. (9th ed.). Vancouver, Canada: Pearson Canada.
Gall, R. (2018).4 reasons IBM bought Red Hat for $34 billion.Packt. Web.
Hammond, E., Porter, K., & Barinka, A. (2018). IBM to acquire Linux distributor Red Hat for $33.4 Billion.Bloomberg. Web.
Henry-Stocker, S. (2018). The future of Red Hat: How will IBM’s acquisition affect the company?Network World. Web.
IBM. (2018). 2018 IBM annual report. Web.
Kotler, P., & Armstrong, G. (2015). Principles of marketing (16th ed.). New York, NY: Pearson.
McPhail, T. (2014). Global communication: theories, stakeholders and trends (4th ed.). New York, NY: Wiley-Blackwell.
Moody, G. (2019). IBM began buying Red Hat 20 years ago. Linux Journal. Web.
Puranam, P. (2016). Corporate strategy: Tools for analysis and decision-making. New York, NY: Cambridge University Press.
Red Hat. (2018).IBM to acquire Red Hat, completely changing the cloud landscape and becoming world’s #1 hybrid cloud provider. Web.
Rometty, V. (2018).Chairman’s letter. Web.
Sherman, A., & Kolodny, L. (2018). IBM to acquire Red Hat in deal valued at $34 billion.CNBC. Web.
Vaughan-Nichols, S. (2018). Why IBM bought Red Hat: It’s all open source cloud, all the time.ZDNet. Web.