Abstract
The purposes of the research are to analyze the service delivery stage of the internal supply chain process typical of the Subway restaurants located in Dubai, the United Arab Emirates; identify drawbacks in these areas for the further improvement; propose the recommendations directed to enhancing the supply chain process.
In spite of the fact that Subway follows the mission and strategy of providing the on-time high-quality services, there are situations when customers are not served appropriately. The mixed methods approach is used for this research. The data is collected with the help of the questionnaire composed depending on the principles of the Supply Chain Operations Reference Model.
The returned questionnaires were analyzed with the focus on the Deliver aspect of the model, and the descriptive statistics approaches were applied in order to determine the average time required for serving customers under different conditions in the Subway restaurants. The flow chart was composed with references to the analysis of the Subway reports and data from questionnaires.
It was found that the reliability, flexibility, and responsiveness in relation to the Deliver stage are significantly influenced by the problem of delays and the lack of resources during the process of fulfilling the customers’ orders. The waiting or lead time are affected by the ineffective organization of steps and the personnel’s work.
After analyzing the averages and the flow chart, the recommendations for improving the supply chain process and the service delivery stage were formulated to be implemented in the Subway restaurants. The recommendations are based on the main principles of developing the responsive supply chain, addressing the Deliver aspect of the Supply Chain Operations Reference Model, decreasing the waiting and lead time, and responding to the customers’ expectations.
Introduction
The effectiveness of the business development depends on the appropriate operations management and efficient supply chain processes. Subway is one of the largest chains of fast food restaurants in the world that was found in 1965. The first fast food facility was opened by Fred DeLuca and Peter Buck in Bridgeport, Connecticut (“Subway: Frequently Asked Questions” par. 3).
Subway leaders state that their mission is to deliver the high-quality, healthy products to their customers in time, and the brand’s slogan is the following one: “Eat fresh” (“Subway: Frequently Asked Questions” par. 2).
The corporate mission is formulated the following way: “To provide the tools and knowledge to allow entrepreneurs to compete successfully in the Fast Food industry worldwide, by consistently offering value to consumers through providing great tasting food that is good for them and made the way they want it” (“Subway: Frequently Asked Questions” par. 4).
In order to address the company’s mission and meet the expectations of the customers worldwide, Subway, as a private company, uses the franchise strategy.
The proposed menus are adapted to the customers’ needs in the concrete region. Today, there are more than 40,000 fast food stores and restaurants all over the world (“Subway: Frequently Asked Questions” par. 1). As a result, the supply chains of the local Subway stores are rather diverse, and the overall control over the supply is provided by Independent Purchasing Cooperative (IPC) regionally.
The goal of IPC is to guarantee that each fast food restaurant receives the enough ingredients at the lowest costs, and their facilities are appropriate to produce high-quality products (IPCA Subway 5). The purpose of this research is to analyze Subway’s supply chain process in terms of its effectiveness and propose the improvements for the concrete stage of the process in order to enhance the quality of operations and the customers’ satisfaction.
Topic Statement
The effective supply chain management is extremely important for fast food restaurants and stores because of the high level of competition in the industry and the necessity of responding to the customers’ needs and expectations. Subway competes in the industry with KFC and McDonald’s fast food chains as the main rivals (“Subway: Frequently Asked Questions” par. 7).
The effectiveness of operations influences the customers’ loyalty, and the key factors in this sphere are the time of delivery, quality of products, freshness, and the inventory control.
From this perspective, Subway continuously works on decreasing the time of delivery, including the external and internal supply chain processes; improving the quality of products and diversifying the menu; guaranteeing the freshness of products while improving the transportation and storage conditions; and advancing the inventory control in the company through the process of applying the ‘green’ supply chains (“Subway: Sustainable Sourcing” par. 5).
Thus, it is possible to distinguish between external and internal supply chain processes that affect the quality of products and customers’ satisfaction. The large external supply chain processes include such steps as the provision of raw materials (meat and vegetables) by suppliers, transportation or logistics, warehousing, production, and the service delivery (“Subway: Sustainable Sourcing”).
The production and service steps of the internal supply chain are rather complex, and they include such steps as the customer’s order and the actual preparation of the product, including cooking and packaging. The purpose of Subway is to make the processes quicker at both external and internal levels, and the inputs, as well as outputs, should be modified accordingly.
The current research focuses on the internal supply chain process, and specifically, on the process of the actual delivery of the product to the customer who is waiting in the queue. The importance of focusing on this stage of the supply chain process is in the fact that the customer’s satisfaction is often most affected by the waiting time, the observed flexibility, and the received quality of products.
The research is important to understand what factors can influence the quality of operations and the customer’s satisfaction at the main stage of contacting with the customer when the order is delivered.
Methodology
The mixed methods approach is used for the research in order to conclude about the effectiveness of the final stage of providing the ordered product to the customer. The data on the service staff’s performance, time of delivery, lead time, and the customer’s satisfaction are collected with the help of questionnaire that is composed with references to the aspects of the service delivery (Appendix A). The sample for the research included 50 past and current customers of Subway from Dubai, the United Arab Emirates.
The respondents were contacted and invited to participate in the research with the help of social media, and questionnaires were distributed with the help of e-mail. The respondents were asked to fill in boxes in the questionnaires regarding their experiences in Subway during the past time and past year.
Additionally, the Subway reports and the information from the official websites was studied in order to identify the supply chain strategy followed by Subway in Dubai and globally, with the focus on criteria regarding the quality of the provided services and waiting times.
This research method is appropriate to collect the data that can be effectively analyzed with the traditional descriptive statistics and averages that are actively used for measuring the performance of companies regarding their operations management and supply chain processes in such models as the Supply Chain Operations Reference (SCOR) Model (Georgise, Thoben, and Seifert 15; Irfan et al. 291).
However, for the purpose of this research, the basic level 1 performance metrics are modified to examine the processes of interest. It is important to state that the mixed methods approach allows comparing the quantitative information gathered with the help of the questionnaires to the company’s proclaimed strategies and approaches provided on the websites (“Subway Arabia”; “Subway: Frequently Asked Questions”).
In this research, the focus is on examining the waiting time as the aspect of the cycle time for the final steps of the supply chain process that can potentially affect the level of the customer’s satisfaction.
Results
The services delivery stage of the supply chain process in stores of Subway (Dubai) is organized according to the flow chart presented in Figure 1. While using the returned questionnaires, Subway’s reports, and the official information as guides, it was possible to identify the main steps of the service delivery stage in the supply chain process and focus on the situation that affects the lead time and contributes to decreasing the customer satisfaction level.
The reported situation is observed when the required amount of ingredients that is necessary to compose the options from the menu is not available for the service staff who are preparing ‘subs’ in front of the customer.
The horizontal model of delivering the ordered products allows customers to see how their orders are prepared, and they can control what ingredients are placed in what ‘sub’ (“Subway Arabia”; “Subway: Frequently Asked Questions”). However, the containers with ingredients become empty quickly, and this situation causes customers to change the order or wait for the necessary ingredients in the queue.
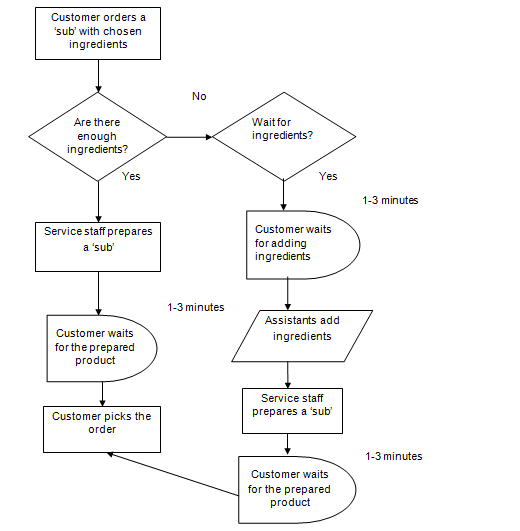
Figure 1. Subway Supply Chain Process: The Services Delivery Stage
According to Figure 1, during the first step of the process, the customer orders a ‘sub’ with the chosen ingredients, and it is expected that the ingredients are available according to the menu options. During the second step, a service person analyzes the amount of ingredients in the containers.
If the containers were filled in time, the service person prepares the order during the next step, and the typical waiting time or lead time is 1-3 minutes for this step, as it is the Subway’s standard (“Subway: Frequently Asked Questions”). If there is a delay in relation to filling in the containers with ingredients, the service person can notify the customer that his or her order cannot be prepared right now because the available amount of ingredients is not enough.
If the customer agrees to wait for the ingredients (the alternative course of actions and steps are not presented in the flow chart), the service person notifies the assistant about the necessity to add ingredients to the containers.
According to the data provided by the respondents, the waiting time usually doubles as 1-3 minutes are necessary to wait for ingredients, and 1-3 minutes are required for composing the order. As a result, the standard process includes five steps, and the service delivery caused by the lack of ingredients includes eight steps. Moreover, these steps involve the actual participation of assistants in the process.
The results of the quantitative analysis of the service delivery stage in the internal supply chain process in the Subway restaurants are made according to the modified elements and metrics of SCOR Model, and they are presented in Table 1.
Table 1. Supply Chain Process Performance Metrics: The Services Delivery Stage
In their questionnaires, the respondents mentioned buying such types of ‘subs’ as Turkey Breast, Smoked Turkey, Tuna, Meatball Marinara, Roast Beef, Veggie Delite, and Subway Melt proposed in the Subway restaurants in Dubai (“Subway Arabia”). The respondents could mention several products usually bought in the Subway restaurants.
For each product, the respondents identified the time during which they were waiting for the prepared order in seconds, including the cases when the delivery was delayed. The data were referred to the last visit to the Subway restaurant. The respondents also stated how many times the assortment of products, the accuracy of orders, their quality, and the customer services met their expectations or were of the high quality.
The respondents also reported the actual number of cases when the delays were caused by the lack of necessary ingredients in the containers. The results indicate that the average lead time in situations when all ingredients are available is 221 seconds or 3.68 minutes, and this number is slightly higher than the company’s standard. When there is a delay, the average lead time is 411 seconds or 6.84 minutes, and this number is higher than the expected maximum.
The proposed assortment met the customers’ expectations in 77% of cases. The high-level accuracy of orders was observed in 86% of cases, where the highest level of accuracy was observed for Tuna subs. The high quality was observed in 89% of cases. The high-quality customer service was reported in 81% of cases, and the lowest percentages were typical of ‘subs’ for which the highest number of delays was reported: Veggie Delite, Turkey Breast, Tuna, and Meatball Marinara.
Discussion
While referring to the results of the data analysis, it is possible to state that the lead or waiting time, as well as delays in the services delivery can directly affect the level of the customers’ satisfaction and loyalty. The data analysis indicates that the service delivery stage of the supply chain process in the Subway restaurants located in Dubai, the United Arab Emirates, has the potential for the delay that is reported by the customers.
The lead time or waiting time in the queue increases when the containers with ingredients are not filled in time, and the service persons lack products in order to prepare the ordered sub. As a result, the customer should wait longer or modify the order. Such processes lead to increasing the level of dissatisfaction in customers and decreasing the customers’ loyalty levels.
According to the results, the decreased levels of satisfaction with the customer services are typical for those product options for which the delays and long waiting times are often observed. From this point, it is possible to speak about the significant drawback in the service delivery stage of the supply chain process. The problem is also in the fact that such processes are typical of the whole chain of the Subway restaurants in Dubai.
In spite of the fact that the leaders of Subway, as well as the operations managers, state that the supply chain process followed in these fast food restaurants is the ‘pull’ one, and the analysis of the data demonstrates that such process cannot be discussed as completely ‘pull’ one (“Subway: Frequently Asked Questions”). ‘Push’ and ‘pull’ supply chain processes differ in relation to the direction of the order and associated steps.
If the process is started by the customer, it is discussed as the ‘pull’ one, and if the company proposes products in anticipation of the customers’ requirements, the process can be viewed as the ‘push’ one (Smew, Young, and Geraghty 179). The problem is in the fact that in the Subway restaurants, customers initiate the orders, but they receive the products only having the listed number of components previously provided by suppliers and prepared by the cook team.
Moreover, in situations when the necessary ingredients are not available in time or they are of the low quality, the customer cannot rely on his initial choice. Therefore, it is possible to state that the observed problems in the supply chain process can affect the customers’ loyalty and the company’s reputation in terms of the proclaimed strategy.
The aspect of the waiting time is as important as the aspects of the order accuracy and product quality. The observed situation in Subway provides the example of how the lead time can be seen by customers as the influential factor. According to the principles of the operations management and supply chain management, the decrease of the waiting time directly depends on the available resources, inventory, and personnel (Kurien and Qureshi 20).
In the case of the Subway restaurants, the problem is in the ineffective work of the personnel and the lack of resources or ingredients, as it is typical of the food industry. The absence of the adequate synchronization of the personnel’s actions can be discussed as one of the causes for the delays (Awad and Nassar 3).
The manager does not control the operations in the restaurant effectively, and it is possible to assume that there are few assistants or too many tasks performed by these employees, and this fact prevents them from filling in the containers in time. The required ingredients are provided to the service persons and cooks too late when the customer needs to wait for the order in the queue. As a result, the whole supply chain process can be disrupted.
The fact that there is the decision block reflected in the flow chart supports the idea that the services staff faces a problem of lacking ingredients often, and there is a plan of actions proposed for such situations. The expected quality of products and the accuracy of orders can be also affected because the personnel spends much time while performing serial actions, and the assistant’s action of filling in the containers can be one of the steps in the supply chain process, but it is more reasonable to discuss it as the parallel process.
Recommendation
Improving the part of the supply chain process typical of the Subway restaurants in Dubai means the prevention of the situation when the customer cannot receive the initial order or has to wait additionally for providing the required services. Therefore, the main recommendation for improving the supply chain process is based on the idea that it is necessary to facilitate the coordination of the personnel’s work and formulate the rules and norms according to which the on-time delivery of required ingredients will be guaranteed.
The actual steps toward the improvement of operations and supply chain management in the fast food restaurants include the implementation of such parallel operations as the services staff’s communication with the customer and the assistants’ regular control over the amount of ingredients in the containers with adding the required components. It is expected that the control is conducted every seven minutes in order to address the flow of customers in the Subway restaurants.
More advanced technologies can be proposed to improve the process in order to prevent the interruption of the services staff or cooks’ work and guarantee that the required amount of fresh ingredients is always available. The Subway managers should complete the following steps to improve the operations and increase the customers’ satisfaction:
- The number of working assistants in a shift should be analyzed to add more workers.
- The amount of ingredients stored in the facility should be efficient.
- The operations manager should propose the technology and the principle of adding or renewing ingredients without interrupting the process of communication with the customer.
- The new technology and inventory should be integrated into the working process to guarantee the parallel operations.
- The manager should improve the control over the work of assistants.
- The schedule for the assistants should be improved with the focus on the necessity to renew the number of ingredients in the containers every seven minutes.
As a result of the implemented improvements, the process diagram will be changed, and the final variant is proposed in Figure 2, where the assistants’ inputs and the communication of the services staff with customers are parallel operations.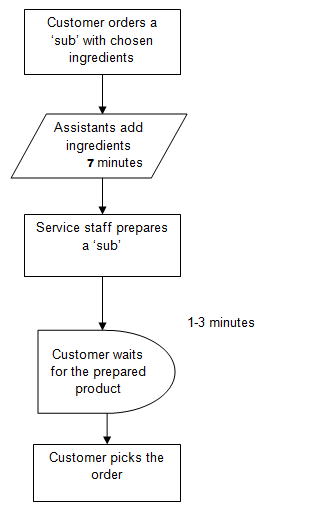
Figure 2. Improved Subway Supply Chain Process: The Services Delivery Stage
The selected recommendation to facilitate the supply chain process is effective because it contributes to reducing the waiting time, coordinating the work of the personnel, increasing productivity, and improving the customer’s experience. The SCOR Model discusses such activities as planning, sourcing, making, delivering, and returning, but for the purpose of this research the principles of the Deliver stage are applied to the project (Erkan and Bac 384).
According to the SCOR Model, the main causes of the decreased customer loyalty are the poor delivery performance, long time for fulfilling the order, the lack of the production flexibility, and the long response time (Georgise, Thoben, and Seifert 15). In this case, the performance measures are effective to be referred to during the analysis stage and while formulating the recommendations. The proposed steps can be viewed as addressing these aspects directly (Irfan et al. 290).
The period of seven minutes can be discussed as rather short, but it is selected because this period allows making the supply chain most reliable, and it is possible to speak about the responsive services provided by the staff (Wu and Hsu 98). The Subway personnel, including the services staff and assistants, should be informed regarding the impacts of delays in their activities on the overall productivity, responsiveness of the supply chain, and the level of the customers’ satisfaction.
When the lead time improves, this process also affects the overall efficiency of the supply chain. In addition, the increased reliability is possible when the actual number of steps in the supply chain is decreased, but the quality of services is increased (Georgise, Thoben, and Seifert 16).
Finally, the proposed recommendation also addresses the question of flexibility because the proposed scheme allows guaranteeing the on-time provision of all orders to the customers without cases when the order is rejected or cannot be provided because of the delays or lack in the ingredients.
Conclusion
The current research indicates that inefficient procedures associated with the supply chain process can affect the waiting or lead time, as well as overall productivity. In Subway restaurants located in Dubai, it is possible to observe situations when the customers need to wait more for fulfilling their orders because the ingredients necessary for preparing the ‘sub’ are lacking, and the containers are empty.
This situation is an example of a drawback of the supply chain process, and it affects the whole services delivery stage. In spite of the fact that all ingredients can be available in the facility and prepared by cooks, they can be not delivered in time to the services staff to complete the order. This problem can be addressed through preventing the situation of lacking components and coordinating the work of the personnel.
The current research can be discussed as important because it provides actual recommendations in order to improve the concrete stage of the supply chain process and avoid the delays. As a result of implementing the proposed recommendation, it is possible to expect the decreased lead and waiting time, the increased productivity, the highly-coordinated procedure, and the decreased number of cases when orders were not fulfilled because of the lack of required ingredients.
However, it is also important to note that the statistical methods used in this research do not allow concluding regarding the actual correlation between the waiting or lead time, proposed assortment, the accuracy of orders, the quality of products, and the customer’s satisfaction with the services deliver.
As a result, the future research is necessary in order to explore whether there is a correlation between the mentioned measures and the customer’s view of the provided services. Such research can be important to provide the guidelines for increasing the efficiency of the supply chain processes and supply chain management in the Subway restaurants.
Works Cited
Awad, Hussain, and Mohammad Othman Nassar. “Supply Chain Integration: Definition and Challenges.” Management and Technology 1.1 (2010): 1-5. Print.
Erkan, Turan Erman, and Ugur Bac. “Supply Chain Performance Measurement: A Case Study about Applicability of SCOR Model in a Manufacturing Industry Firm.” International Journal of Business and Management Studies 3.1 (2011): 381-390. Print.
Georgise, Fasika Bete, Klaus-Dieter Thoben, and Marcus Seifert. “Implementing the SCOR Model Best Practices for Supply Chain Improvement in Developing Countries.” International Journal of u-and e-Service, Science and Technology 6.4 (2013): 13-25. Print.
IPCA Subway. Introducing IPCA. 2015. PDF file. Web.
Irfan, Danish, Xiaofei Xu, Shengchun Deng, and Zengyou He. “A SCOR Reference Model of the Supply Chain Management System in an Enterprise.” International Arab Journal of Information Technology 5.3 (2008): 288-295. Print.
Kurien, Georgy, and Muhammad Qureshi. “Study of Performance Measurement Practices in Supply Chain Management.” International Journal of Business, Management and Social Sciences 2.4 (2011): 19-34. Print.
Smew, William, Peter Young, and John Geraghty. “Supply Chain Analysis Using Simulation, Gaussian Process Modelling and Optimisation.” International Journal of Simulation Modelling 12.3 (2013): 178-189. Print.
Subway Arabia. 2015. Web.
Subway: Frequently Asked Questions. 2014. Web.
Subway: Sustainable Sourcing. 2015. Web.
Wu, Jei-Zheng, and Chia-Yu Hsu. “Critical Success Factors for Improving Decision Quality on Collaborative Design in the IC Supply Chain.” Journal of Quality 16.2 (2009): 95-108. Print.