Introduction
People earn income for use in various activities including expenses, investments and savings. Expenses refer to all activities where money is used to purchase goods or services that do not generate income. Investments are those that involve depositing money in various activities with an aim of making profits in the future. Savings refer to the money deposited in financial institutions like banks for the future.
However, all these terms are connected since an individual must earn before spending, investing or saving. Nations cannot develop if they have many unemployed people or if few people invest or save their money in productive activities and future use respectively. This essay explores various theoretical perspectives regarding savings, investment, income distribution, and growth.
Savings, Growth and Profits
Keynes proposes that a society that has a higher rate of savings will generate a higher growth rate that will promote social and economic development. This argument can be approached from two perspectives to elaborate on the facts about savings and growth. It is important to explain that this theory has been used to explain the link between savings and growth (Hicks 1985, p. 41).
The classical approach uses cartels and competition as main drivers of social and economic development. Cartels ensure that capitalists distribute their profits amongst workers as salaries; therefore, their spending the total profits generated from the production process. The presence and power of a monopoly in a nation determines the shares of profits that national income generates. This is expressed in the following equation.
P = C + A
This means that capitalists’ consumption and gross accumulation determines the levels of investment in a region based on depreciation and appreciation rates. The consumption of capitalists is formed by two components that include the proportional to the level of profits, and an independent of profits explained by the fact that capitalists and cartels have a lot of capital that allows them to get loans from banks.
Therefore, investments determine profits generated by an investor and profits determine production in terms of growth. In addition, the spending of capitalists determines national incomes and rates on salaries earned by individuals (Hicks 1985, p. 46). Therefore; this means that there is a close relationship between monopoly, capitalism and investments.
In addition, credit facilities ensure they charge higher interest rates to traders that are not cautious and are exposed to risks. This means that a secured business will get loans at low rates compared to a risky business. The graph below shows the relationship between risks, interest rates and investments.
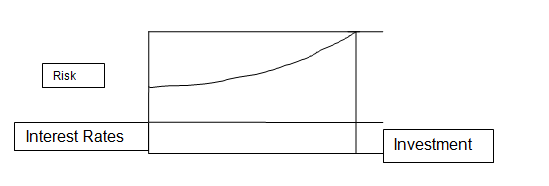
Investment
The Classical approach explains that profits are determined by how people spend money in investments while the popularity of an investment is determined by the risks involved. Those that have many risks attract few people compared with those without risks. The approach uses the perfect and imperfect competitions theories to explain how a decrease in salaries affects investments and profits generated by investors.
A perfect competition is a macroeconomic factor where profits are determined by spending on investments and consumption (Martins 2011, p. 21). This approach explains how capitalists get profits. In addition, even if capitalists borrow money with high interest rates, they will generate profits that will ensure the interests on their loans flow back top them as profits.
On the other hand, people who earn salary cannot repay their loans through profits since they do not have investments that generate profits; therefore, they accumulate debts that make them unable to invest in profitable investments (Paros 2013, p.53).
In this competition prices of commodities will be determined by marginal costs and when wages are reduced there will be low marginal costs and prices will also fall with similar proportions; therefore, there will be no changes in employment. On the other hand, an imperfect competition all prices are fixed beyond marginal costs and can only equal the marginal costs at full capacity.
Therefore, this Classical Smith-Ricardo Marx approach assumes that the profit levels in a capitalist economy is determined by investments in this sector. This means that profits in investments are determined by the profits ploughed back in business. However, investors cannot invest for the sake of production only since this is not their interest in the activity.
On the other hand, wages should not fall or overtake productivity since this will lower profits in the capital and consumption sectors (Paros 2013, p.55). The Keynesian recession explains that the consumption sector should expand its investment capacities while the capital production sector must ensure that wages should not expand or fall less than productivity.
Comparison between the Classical and Kaldor-Pasinetti Approaches to Growth
Marx coined the term ‘Classical Political Economy’ to illustrate the power of the working class in developing their nations. He identified two variables that determine growth in a capitalist society. They include income and savings that play significant roles in determining the growth rate of a society.
However, he failed to highlight how these savings should be used to ensure they generate profits (Luigi 1974, p. 89). It is necessary to explain that a society must be developed before its financial institutions generate enough interest on their savings.
However, this approach fails to explain how people should save to endure their societies grow. Common sense will tell anyone that if money is kept under the bed or in a container it will not make any impact in developing a society.
However, if this money is invested in productive activities like businesses it swill generate income in terms of profits that will help the company to widen its operations and spur growth (Luigi 1974, p. 93). Therefore this theory contradicts itself by assuming that savings alone can make an economy to grow.
On the other hand, Kaldor-Pasinetti uses the Cambridge Theorem to approach issues of growth and income distribution. This theory explains that the high profits generated through business activities are a reflection of the abilities of capitalists to save money. This theory assumes that a closed economy that ensures investment opportunities are limited to ensure people can get full employment.
This means that if the capitalists do not control their rates of investments there will never be full time employment and this will destabilise their investments. Therefore, they must keep their investments under control no matter how much profit they generate from their businesses (Luigi 1974, p. 94).
This means that capitalists are deliberately withholding their investment potentials to ensure that workers are kept in full time employment where their salaries are also controlled to limit their abilities to save.
Therefore, these two approaches identify the need to save money as a means to investments. However, the difference is based on the levels and variables that determine developments in a society. The Classical approach assumes that savings alone are adequate to generate growth and this means that there is no need for investments.
Therefore, this approach considers income and savings as key determinants of growth in the society. In addition, it does not specify whether the source of income is from the workers or capitalists (Luigi 1974, p. 89). This makes this approach to lack substantial grounds to prove that high savings can lead to growth.
On the other hand, the Cambridge Theorem approach identifies three variables (income, savings and investments) as being responsible for boosting growth in an economy. It goes ahead to point out that the capitalists are the owners of all means of production including land, capital and labour amongst others.
Therefore, they have all the powers to determine the future of any society in terms of growth. They play a significant role in determining the levels of investments a society can achieve through the salaries they pay their employees. This means that the salary they pay their workers will determine their savings and investments.
For instance, if they pay workers huge salaries they will have enough money for their budgets and also save some for the future. This will give them opportunities to invest their savings in productive activities (Luigi 1974, p. 91).
On the other hand, they can decide to pay them low salaries; therefore, they will not have anything to invest. In both cases, profits, salaries are the main distributive variables that are fixed to ensure that workers have minimal savings and thus they cannot invest. This means that their societies will not grow since there will be no investments to offer new employment opportunities and generate money for people who are jobless.
Interest Rates and Savings
The modern society has been polarised by political economists that have created various avenues to ensure that their interests are safeguarded. It is necessary to state that Kalecki and Keynes identified the need to have a balanced platform in terms of savings and investments to generate growth. However, this is not usually the case in many financial institutions (Keynes 2011, p.6).
Even though, the society has developed and people are adopting modern ways of managing political and economic issues there are some practices that will continue to dominate the political economy in all societies.
There will never be proportional relationships between interest rates and savings since capitalists will ensure they interfere with this balance. When banks start offering high interest rates on savings employers will reduce the salaries of their employees to ensure they have no money to save.
In addition, there will be high interest rates on loans advanced by financial institutions. These loans will be very expensive to pay and this means that the capitalist will afford the loans and invest the money in these banks to enjoy the high interest rates (Harcourt 2006, p. 97).
Kalecki argues that the economic power houses will ensure that prices of commodities continue to rise and this will make life unbearable for low income earners they will use all their earnings to buy food and other basic needs and forget about the high interest rates offered by banks.
On the other hand, when interests rates are low workers will have enough money to save; however, this will not generate meaningful profit that can be used to invest in various activities.
However, when savings increase the interest rates will reduce since there will be a lot of money in the public hands. This means that financial institutions will be directed to offer low interest rates to discourage people from saving their money in banks but instead invest in other productive activities.
Conclusion
Employment opportunities allow people to earn income that is used to buy basic and secondary needs. Excess income is saved in financial institutions to generate interest and for use in the future.
When people have enough savings they will invest in business activities that will give them profits to wide their operations. As a result, societies will develop since there will be many investors involved in various activities. There will be adequate employment opportunities that will reduce the dependency ratio and increase GDP (Gross Domestic Product).
References
Harcourt, G 2006, The Structure of Post-Keynesian Economics: Post-Keynesian Macroeconomic Theories of Distribution, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge.
Hicks, J 1985, Methods of Dynamic Economics. Primitive Growth Models: Adam Smith and Ricardo, Clarendon Press, Oxford.
Keynes, J 2011, The General Theory of Employment, Interest, and Money, CreateSpace, New York.
Luigi P1974, Growth and Income Distribution: Essays in Economic Theory, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge.
Martins, J 2011, Interest Rate Markets: A Practical Approach to Fixed Income, Wiley, New York.
Paros, C 2013, Economics for Investment Decision Makers Workbook: Micro, Macro, and International Economics, Wiley, New York.