Abstract
The increasing innovation in the field of tourism has had a significant impact on the industry. The world is increasingly becoming globalized, and stakeholders in the tour and travel sector are forced to embrace emerging technologies to achieve sustainability in their operations. In this paper, the researcher wanted to determine the impact of increasing innovations on the tour and travel industry.
Data were collected from both primary and secondary sources: primary data was collected from participants who were sampled to take part in the study; secondary data was collected from books, journal articles, and other relevant data sources. The primary data were analyzed using both descriptive and mathematical methods. The findings of the study concluded that although some stakeholders still fear change, innovation has had a positive impact overall on the tour and travel industry.
Introduction
The United Arab Emirates’ economy is increasingly becoming diversified as the government tries to reduce overreliance on oil and gas. According to Weeden (2016), one of the specific areas of the economy that has achieved massive growth over the recent past is tourism. The government has made significant investments to improve infrastructure and to create amenities to attract tourists from all over the world. Currently, the city of Dubai is one of the top global tourists’ destinations because of these developments. Dubai is home to the tallest building on earth, Burj Kkalifa, as well as the largest man-made island, Palm Island. Both these creations have contributed to making Dubai one of the preferred cities for tourists in the modern era. The trend that has been witnessed in this city, and various parts of the UAE, is driven by creativity and innovation.
The government has invested heavily in emerging technologies to transform tourism in the country. It is through this creativity and innovation that both Palm Island and Burj Khalifa was created. According to Morpeth and Hongliang (2015), other innovative structures also make Dubai a desirable city for tourists. Its roads and rail systems were designed and developed in very innovative ways, moving within the city reliable, time-efficient, and cheap. Tourism is currently one of the biggest pillars of the economy of the United Arab Emirates. Increasing innovation is redefining the tour and travel industry and stakeholders in this industry are constantly coming up with new products that they can offer to both local and international visitors. In this paper, the researcher seeks to determine the impact of these innovations on tourism.
Research Questions
According to Knight (2013), when conducting research, it is important to focus on clear research questions that will aid in the data collection. These research questions help identify the data that should be collected from the respondents. The following questions will be used in this study to guide the process of data collection from this industry:
- How relevant is technology in the field of tour and travel in the United Arab Emirates?
- How receptive are the stakeholders in the tour and travel industry towards emerging technologies?
- Is the investment made in innovative technologies proportionate to the returns?
- What is the impact of increasing innovation on the tour and travel industry in the United Arab Emirates?
- What is the future of the tour and travel industry in the United Arab Emirates in an increasingly globalized and highly innovative world?
Importance of the Study
This research project is very important to a variety of stakeholders. To the government of the United Arab Emirates, this document will help inform the process of policymaking in the country. Specifically, it explains why it is important for the government to formulate policies that will promote the use of emerging technologies in the tour and travel sector. For the stakeholders in this industry, this research paper highlights the importance of emerging technologies and why they cannot be ignored. It explains why the private sector should embrace innovation as a way of achieving a competitive edge over rivals in the market. The paper also offers information that can be used when it comes to embracing change in their operations. Future researchers will also find this document useful. It will provide them with information about this industry and how innovation affects it in various ways.
Theory and Hypotheses
Background
Innovation in the field of tourism has been taking shape over recent years as competition in this industry has become increasingly stiff. According to Szutowski (2016), in the past, tourism relied heavily on nature and wildlife as the main attractions for people to come and visit. Countries that had unique natural landscapes and a variety of wild animals would attract tourists from all over the world. However, as competition tightened, the industry started experiencing significant changes in several aspects. The stakeholders came to realize that not all tourists want to see the wild animals or are interested in the natural scenery; many just simply want to have a good time relaxing in the resorts and beaches at their destination. As such, technology was introduced to help promote the security, comfort, and happiness of these tourists. Tourism now goes far beyond just having a highly diversified wildlife and a unique natural environment and landscape. Competition is increasing and cities, and individual tour companies, are forced to be innovative. They have to understand what all customers want and be able to present it to them in the most unique way possible. It is also important for these companies and government entities to anticipate future trends and be capable of adjusting their operations to meet the expectations of future clients.
According to a study by Zolait (2013), the government of the United Arab Emirates has invested heavily in the field of tourism to help diversify the country’s economy. For a long time, the country has been relying mainly on the oil and gas industries to sustain it. However, the time has come when the country has to look for alternative sources of income, and tourism has been designated as one of the best options available. To promote tourism in a country with a limited range of attractions, such as wildlife, was a big challenge, but the government and stakeholders were able to harness creativity and create something that international tourists had not seen before. The use of emerging technologies made it possible for the government to come up with structures and systems capable of attracting international tourists. Currently, Dubai City is home to the tallest building on earth (Katsoni & Stratigea 2016). The largest man-made island, Palm Island, is also found here. The innovation that has been witnessed in the field of tourism in Dubai has made it one of the top global tourism destinations. However, to keep pace with the global competition, it will be necessary for stakeholders to ensure that they remain innovative.
Literature Review
According to Szutowski (2016), Diffusion Innovation Theory is one of the most common theories that has been used to explain how and why people embrace innovative ideas differently. It is a fact that innovation makes work easier, lowers costs, and improves efficiency in product or service delivery. However, not everyone is open to embracing new and untested ideas. Some people reject the idea of embracing change because of their fear of using new systems that may require training. Others are cautious of the speed at which to adopt innovation because of the uncertainties about the value that such new inventions can deliver. Others just resent their skills being challenged when they are called upon to use new systems and structures.
Diffusion Innovation Theory identifies five categories of adopters of innovative ideas. Figure 1 below shows these stages.
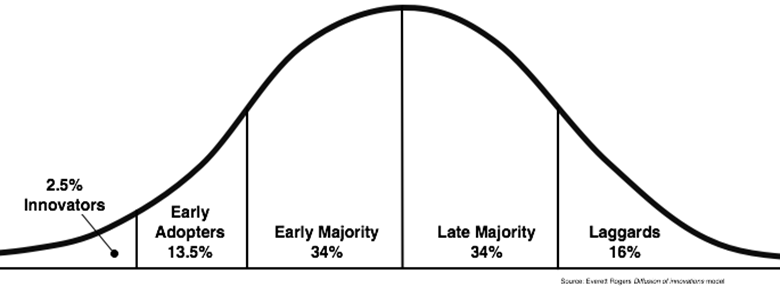
As shown below, the first category is the early adopters who are the minority, often estimated to be about 2.5% of the population. They are very creative individuals who believe in always coming up with new ideas of addressing current or future problems. They use a lot of their time thinking of better ways of handling their tasks and do not shy away from investing their resources in these new methods. They remain very ambitious in their pursuit of innovative ideas. For Katsoni and Stratigea (2016), they do not necessarily register success with every idea; failures are as common as a success.
However, this does not stop them from thinking of better ways of achieving their goals through new ways of thinking. The second category is the early adopters. They form about 13.5% of the population. These are people who understand and appreciate the need for change but lack the know-how to lead the process. However, they are often willing to embrace new systems and structures as soon as they are introduced. They are keen on identifying innovations and investing resources to implement them. Just like the innovators, they get to benefit from the superior value that the new systems and structures have to offer. However, they also face the risk of the new idea of failing to deliver what it has promised.
The early majority, forming about 34% of the population, are those who understand and appreciate the need for change but are keen to ensure that they only adopt systems and structures that have been tested and proven to work. Matias, Nijkamp, and Romão (2016) refer to them as average people who need to be convinced that they stand to benefit from the innovative ideas before embracing them. They take their time to see how the innovators and early adopters are affected by the new systems before making any decisions. If they see that the innovators and early adopters are reaping the benefits of the invention, then they will not waste time in embracing the new system.
However, if they determine that the innovators and early adopters are negatively affected, then they will shy away. Ray (2015) says that in most cases these individuals are risk evaders. They are interested in the potential of new systems but they fear investing in something that would not give them a guaranteed outcome. They share the same concerns with the late majority that also forms about 34% of the entire population. These individuals know and understand that change cannot be avoided. However, they are always willing to wait as long as possible to undertake any change. As long as they can use the existing systems and structures to achieve the outcomes they desire, they will avoid any new technology. They only embark on change when it is clear they can no longer avoid it.
The last category, which accounts for around 16% of the population, is the laggards (Pappas & Bregoli 2016). These individuals strongly believe in tradition. They are not easily swayed into embracing any new systems or structures. They are skeptical about change and would do everything possible to ensure that they continue using traditional systems and structures. Druica (2012) says that they fear change because of some factors, including potential increased cost and needing to acquire new skills. They are always the last to employ change, and only when it is mandatory to do so.
Diffusion Innovation Theory also identifies five stages of decision making, as shown in Figure 2 below.
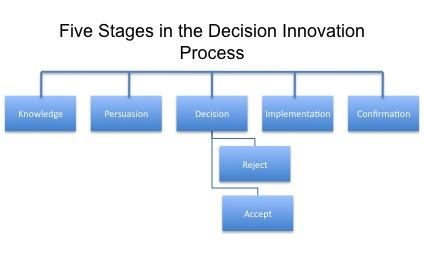
As shown in the above figure, the first stage is the knowledge stage where an individual is exposed to knowledge but lacks proper information. The stage is characterized by a situation where one lacks the inspiration to pursue an innovative process because of limited knowledge. The second stage is persuasion. As more information about the innovation becomes available, one gets increasingly persuaded to take on the innovative idea. An individual will get the drive to search for relevant information. The next stage is the decision-making process, which Carvalho (2015) considers to be the most important stage. One decides whether to accept or reject the innovation based on the gathered information. In case a decision is made to accept the innovation, the next step would be the implementation process. The new idea is put into practice as per the proposed method and strategies. Finally, there is the confirmation stage. At this stage, one evaluates the performance outcome after the implementation. Of interest, at this stage, is to determine if the new system is capable of delivering the value it has promised. If the innovation yields the desired outcome, then more investment may be made, otherwise, it will be terminated to avoid further loss.
Hypotheses
According to Alsos, Eide, and Madsen (2014), the government of the United Arab Emirates, private companies in the field of tour and travel, and other stakeholders have embraced emerging technologies as a way of ensuring that tourism is promoted within the country. Given the massive investments that have been made by these stakeholders into innovation in tourism, it is reasonable to expect to be able to determine the outcome of this investment and its overall impact on tourism. As such, the following hypotheses will be used in the study:
- H1. Increasing innovation is having a positive impact on the tour and travel industry in the United Arab Emirates.
- H2. The stakeholders in the tour and travel industry are receptive to emerging technologies.
- H3. Creativity and innovation will define the future of the tour and travel industry in the United Arab Emirates.
Methods
According to Sheldon and Daniele (2017), a research project should have a clearly defined methodology that identifies individual activities and how they will be undertaken to ensure that the desired goal is achieved. The methodology section is also critical for the users of the document because it outlines how the conclusions and recommendations were arrived at and provide the basis for determining whether these can be taken as reliable and valid. Other scholars who may also be interested in conducting related research may also find the methodology section important because it sets out the steps that can be taken to achieve similar goals in their study.
Research Design
One of the first steps that a researcher must take is the definition of the research design. As Papathanassis, Breitner, and Groot (2014) note, the research design is determined by the nature of the study. Before a researcher can select a specific design, there should be a clear understanding of the primary goal of the study. In this research, the primary goal is to determine the impact of increasing innovation in tourism in the United Arab Emirates. The design chosen must be capable of meeting this goal in the best way possible. It must aid the collection of relevant data and in its analysis to ensure that the conclusions arrived at are based on evidence. That is why the researcher opted to use a descriptive approach as the appropriate design for this study. The research focuses on something that can be observed and its impact clearly described by the stakeholders who are directly or indirectly affected. The chosen design also allows the researcher to make personal observations in the environment of interest without alerting the subjects.
The researcher can determine how well these stakeholders embrace emerging technologies and innovation in their workplaces and how their performance is affected. Given an appropriate amount of time, the researcher can collect preliminary data about increasing innovation in the field of tourism and its impact on the tour and travel industry through observation. The design also allows the researcher to survey to confirm the information collected through observation. The respondents participating in the study will help shed more light on why some innovations are supported by stakeholders and others are not. They will also explain why other innovations are successful while others are not. When using this design, it is also possible to embrace the use of case studies. Sometimes it becomes necessary to narrow the research focus down to a particular phenomenon and explain how it developed the way it did. Case studies give a clear picture of what happened in a specific organization when an innovative idea was introduced, the approach that was taken by the stakeholders, and the outcome that was realized. It becomes possible to identify areas or weaknesses so that corrective measures can be taken for future projects.
Sample and Data Sources
Data needed for this project can be collected from both government and private-sector employees in the field of tour and travel. It is also possible to collect the data from the experts in this field. Given the constraints on time and resources, sampling was necessary to come up with a manageable size of respondents. Stratified sampling was used because of the need to have respondents from various backgrounds. The first stratum had government employees, the second stratum had private-sector employees, and the third stratum had experts in this industry. In each stratum, simple random sampling was used to identify individual participants for the study.
A sample size of 100 was selected from these three different categories. The participants provided primary data sources for analysis. They are individuals who have been part of the ongoing innovation in the tour and travel industry in the country as policymakers, policy enforcers, advisers, or employees. Some of them have witnessed the transformation in the country’s tour and travel sector and can explain to the researcher how technology and innovation have played a role in that innovation. The primary data sources collected have been used alongside the secondary data gathered from books, journal articles, and other relevant data sources.
Procedure
The procedure used in collecting primary data is in line with the academic guidelines. Before sampling, the researcher sought permission from the relevant authorities. After being granted permission, the researcher then embarked on identifying the respondents through the sampling method discussed above. The researcher contacted the participants to inform them about the study and to request their participation in the project as respondents. A questionnaire was then developed to help in guiding the process of primary data collection. The researcher interviewed the sampled participants who agreed to take part in the research. The primary data were analyzed using a descriptive method.
Measure
In this research project, the independent variable was the increasing innovation witnessed in the tour and travel industry. The dependent variable was the performance of the tour and travel industry. The measure that was to be determined was how the increasing innovation is affecting performance in the tour and travel industry. Using descriptive statistics, it is possible to determine the level of impacting the emerging technologies and innovations have had on the performance of the tour and travel industry within the country. The stakeholders involved will be able to explain this impact by referring to case studies or incidences where they witnessed how innovation affects the industry.
Analysis and Results
The analysis of the results will help in determining the impact of increasing innovation in the field of tour and travel. The primary data will be compared with the findings made during the literature review. In this section, the researcher will analyze the data that was collected from the participants to determine the impact of increasing innovation on the tourism industry.
Descriptive Statistics
The researcher conducted a descriptive statistical analysis to ascertain the views of each individual concerning the impact of emerging technologies on the tour and travel industry. The researcher posed open-ended questions to the respondents. A key question that was posited to the participants was:
What is the impact of increasing innovation on the tour and travel industry in the United Arab Emirates?
According to the respondents, technology has had a massive positive impact on the field of tour and travel in the United Arab Emirates. For instance, the emergence of Airbnb has completely changed the approach that stakeholders take in this industry. Tourists from all over the world can now rent apartments or hotel rooms via an online platform even before starting their journey. It makes their work, and the work of the tour and travel companies, much easier. In the case of overbooking, hotels in Dubai have a platform where they can share and find alternative accommodation for their clients to eliminate or reduce cases of dissatisfaction among customers. According to one of the respondents, for the United Arab Emirates to reach its goal of 20 million tourists by 2020, integration of innovation is a fundamental requirement. Emerging technologies also make it easy for the industry to enhance and improve security provision for visitors and to ensure that they can move with ease from one location to another.
The following question was aimed at determining the future of the tour and travel industry in the country, given an increasingly globalizing and innovative world.
What is the future of the tour and travel industry in the United Arab Emirates in an increasingly globalizing and highly innovative world?
The respondents feel that the country’s tourism sector is more likely to grow if the stakeholders continue implementing innovations to improve the quality of their services in the market. One of the respondents noted that within the next 10 years the tour and travel sector will account for about 15 percent of the country’s GDP if the current growth is maintained. The respondents noted that emerging technologies in such a globalized society will play an even greater role than they currently do.
Other Types of Analyses
The researcher conducted a statistical analysis to provide further clarification of the descriptive analysis. The researcher wanted to determine the view of the respondents regarding the relevance of emerging technologies in the country. The following question was posed to the respondents:
How relevant is technology in the field of tour and travel in the United Arab Emirates?
Figure 3 below shows the outcome of the analysis of the response that the participants gave to this question.
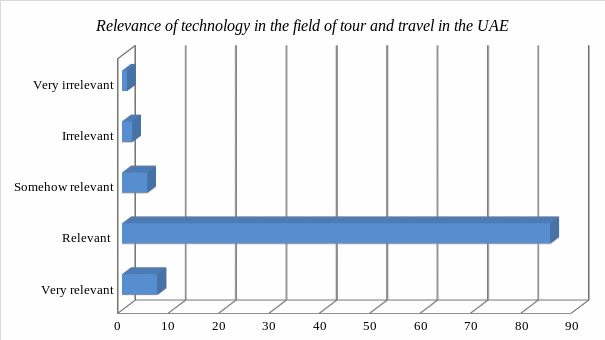
As shown in the above graph, the majority of respondents (over 90%) felt that, indeed, technology is very relevant in the tour and travel industry in the United Arab Emirates. Only a few of the respondents (less than 5%) felt that emerging technologies are not relevant. They cited issues such as cyber threats as factors that have negatively affected tourism. Some also argued that the increasing use of technology is reducing the physical interaction between tourists and the local tour operators.
The researcher also asked the respondents to give their views about how the local stakeholders have received the emerging technologies. The following question was asked:
How receptive are the stakeholders in the tour and travel industry towards emerging technologies?
The response that the participants gave was analyzed using mathematical methods and the graph below shows the outcome.
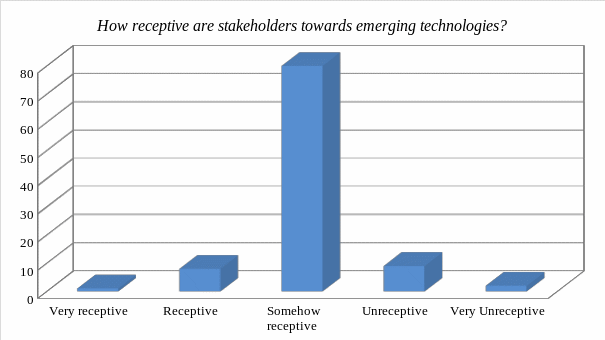
As shown in the graph above, an overwhelming majority of the respondents felt that stakeholders are somewhat receptive to emerging technologies. Many stakeholders appreciate the need for emerging technologies but the fear of the unknown, coupled with the financial consequences of introducing some of the technologies, often slows down the pace of implementation.
Is the investment made in innovative technologies proportionate to the returns?
When the above question was posited to the participants, their response was mathematically analyzed and Figure 5, below, shows the outcome.
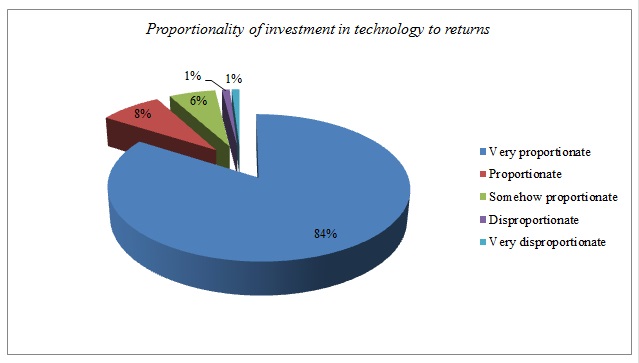
The chart above clearly shows that the vast majority of respondents feel that investment in technology is proportionate to the returns. They noted that when a company invests in innovation, then it is more likely to achieve success in operations than those who shy away from change. The respondents noted that the investment that was made to create Palm Island in Dubai has led to increased revenues in terms of increased numbers of tourists. As the tourists come from all over the world to see the largest manmade island, they end up spending in the local economy. The hospitality industry, tour and travel companies, and even the healthcare sector, all benefit from these additional tourists visiting. Also, the more a company invests in innovation, the more likely it is to come up with products that satisfy the needs of its customers uniquely.
Discussion
The above review of literature and analysis of primary data combines to provide a detailed understanding of how increasing innovation is affecting the tour and travel industry in the United Arab Emirates. As one of the respondents noted, for a long time the United Arab Emirates was known only for its oil and gas. Foreigners who came to the country were primarily interested in the oil trade. However, that changed when the government started making heavy investments in the transport and communication sectors. The movement became easy and security improved.
As the government looked for ways of diversifying the economy, tourism became one of the most viable sectors that could be promoted to help in this strategy. With improved infrastructure and good security in the country, the government and other relevant stakeholders focused on improving the tour and travel industry. However, Peris-Ortiz and Álvarez-García (2015) note that the stakeholders were faced with one major challenge. The country is not blessed with the diversified wildlife that tourists often look for when going on holiday. An alternative had to be found to ensure that the country could compete and be just as appealing to tourists as other countries that do have a wide range of wildlife to offer. The stakeholders turned to technology, creativity, and innovation to help tackle this challenge.
As shown in the analysis of the primary data, technology has had a positive impact on tour and travel in the country. Stakeholders realized that the only way to attract tourists to the country is to create unique amenities not found anywhere else in the world. According to a report by Müller, Lundmark, and Lemelin (2013), Dubai became a focal point of tourism in the country. Through such innovative ideas, Palm Island, as mentioned above, was created. Some of the respondents interviewed noted that the island in particular has been attracting an increasingly diverse set of tourists, from numerous countries around the world. It is uniquely developed and its record-breaking size is a clear demonstration of the level of innovation embraced in this industry.
Tourists come to these manmade islands and can stay for weeks, even months, just to enjoy the beauty that it brings. Through creativity, innovation, and technology, the local stakeholders have found a perfect way to attract tourists despite the country’s limited traditional tourist attractions. The stakeholders have also used innovation and technology to create platforms that encourage expenditure when tourists visit the city of Dubai. Burj Khalifa is currently the tallest building on earth and tourists come from both the developed and developing countries just to see this outstanding manmade structure. However, the stakeholders in the tour and travel industry have come up with ways to encourage these tourists to spend in the local economy as much as possible; Burj Khalifa has numerous shops and stores, selling a wide range of products to its visitors.
According to Papathanassis, Lukovic, and Vogel (2012), innovation has made it easier for the local players in the tour and travel industry to offer superior services to visitors. In the past, tour operators would wait for the tourists at the airport. Occasionally, these operates would be scrambling for the visitors, causing concern among the tourists. However, things have completely changed thanks to the technological innovations that have now emerged. Tourists now can contact their preferred tour companies well in advance of leaving their home countries. They describe what they want when visiting the country.
The tour operators then prepare the hotels, travel, and other services that they may need to meet their wishes. In parallel, the hospitality industry, heavily reliant on tourism for its growth, has also been keen to utilize emerging technologies to improve its performance. They work closely with the tour and travel companies via online platforms to ensure that the needs of their customers are met in the best way possible. Morpeth and Hongliang (2015) point to a further innovative idea that is also starting to emerge in the tour and travel industry, that of medical tourism. With modern hospitals equipped with state-of-the-art facilities and highly qualified staff, tourists can choose to visit the country for medical purposes as they visit the beautiful scenery and landscapes that the country has to offer.
Theoretical Implications
The findings of this study will have profound theoretical implications. The city of Dubai has been at the forefront of embracing emerging technologies as a way of improving its tourism sector. It is currently one of the top tourist destinations in the world and unmatched by any other city in the MENA (the Middle East and NortItegion. In fact, it is on par with other top global tourists’ destinations such as Paris (Weeden 2016). It is a clear indication that being an innovator or early adopter can help an entity to achieve great success. It is a reminder that concepts of Diffusion Innovation Theory are indeed important when managing emerging technologies and innovations. It also demonstrates how crucial it is to be an early adaptor or an innovator, especially in an environment that is as competitive as the tour and travel industry.
Managerial Implications
The findings made in this study can be of great help to those in managerial positions when it comes to managing innovation and technology in modern society. One of the most important recommendations resulting from this research project is that top managers should be ready and willing to embrace emerging technologies in their operations. In modern society, managers simply cannot ignore the relevance of emerging technologies. If they do so, they are at risk of putting a company, or even a government entity, into a vulnerable position. Management must not only be flexible enough to embrace change but also be vigilant to know when change is imminent, as well as what can be done to ensure that it is done smoothly.
The study also demonstrates the importance of stakeholders coming together and working as a unit. In Dubai, considerable success has been witnessed in the field of tourism as various stakeholders work as a unit to achieve shared goals using emerging innovations. Managers should learn to be consultative when faced with situations that require change. As shown in this paper, when different stakeholders are involved, then the outcome of a change process will not be significantly biased against any one section. The involvement of all the stakeholders also reduces cases of resistance. Given that the leaders actively involve these stakeholders before implementing change, they are likely to support the new systems and structures introduced.
The study also strongly supports the need to have proper communication channels to pass innovative ideas down to the stakeholders. As such, in the discussion, stakeholders can only be receptive to the emerging technology if they understand how it will affect them. They need to be sufficiently informed about the new technological approaches and how they will individually and collectively be affected. Early communication is also a sign of respect towards stakeholders. In some cases, the stakeholders may need some form of training to help them understand how they can work under the new systems brought about by the emerging innovations.
Limitations and Future Research
It is important to appreciate that this research project had several limitations. The biggest limitation was the time that was available for the study. As with any academic research, the researcher had to complete the project within a specific period, in line with set guidelines. The area covered when collecting the primary data was limited; the researcher mainly focused on Dubai when collecting primary data. As such, it would be beneficial if there could be additional studies that could widen the data collection to include participants from other parts of the county. Future research could also focus on how the local players on the tour and travel can become innovators and early adopters. It has been shown that most of these players are late adopters, always waiting to see how new inventions affect tourism in other parts of the world before embracing it. Rather, they should be encouraged to be creative enough to come up with best practices in the industry that can be emulated by other stakeholders from other parts of the world.
Conclusions
The tourism sector is increasingly becoming one of the most important pillars of the United Arab Emirates’ economy. The sector is currently relying on innovation and technology to ensure that it can deliver quality services to its customers in the global market. As such, in the discussions outlined above, although most of the stakeholders are cautious when it comes to embracing emerging technologies, they appreciate the need to embrace change in their operations. As a country that is not richly endowed with a wide variety of wildlife, the government and other stakeholders rely on innovation and technology to create amenities that can attract international tourists. The city of Dubai is currently home to the tallest building and largest man-made island on earth. It is a clear indication that these stakeholders are increasingly relying on innovation. It is clear that innovation has had a positive impact on the local tour and travel industry and has made Dubai one of the top tourists’ destinations in the world.
Reference List
Alsos, A, Eide, D & Madsen, L2014, Handbook of research on innovation in tourism industries, McGraw Hill, Berlin.
Carvalho, L 2015, Handbook of research on internationalization of entrepreneurial innovation in the global economy, Cengage, New York.
Druica, E 2012, Digital economy innovations and impacts on society, Information Science Reference, Hershey.
Egger, R, Gula, I & Walcher, D 2016, Open tourism: open innovation, crowdsourcing and co-creation challenging the tourism industry, Springer, London.
Katsoni, V & Stratigea, A 2016, Tourism and culture in the age of innovation, Springer, London.
Knight, J 2013, International education hubs: student, talent, knowledge-innovation models, Cengage, New York.
Matias, A, Nijkamp, P & Romão, J 2016, Impact assessment in tourism economics, Wiley, Hoboken.
Morpeth, N & Hongliang, Y 2015, Planning for tourism: towards a sustainable future, Cengage, New York.
Müller, D, Lundmark, L & Lemelin, R 2013, New issues in polar tourism: communities, environments, politics, Springer, Dordrecht.
Papathanassis, A, Breitner, M & Groot, A 2014, Cruise tourism & innovation: improving passengers’ experiences and safety, Logos Berlin, Berlin.
Papathanassis, A, Lukovic, T & Vogel, M 2012, Cruise tourism and society: a socio-economic perspective, Springer, Berlin.
Pappas, N & Bregoli, I 2016, Global dynamics in travel, tourism, and hospitality, Wiley & Sons, Hoboken.
Peris-Ortiz, M & Álvarez-García, J 2015, Health and wellness tourism: emergence of a new market segment, McGraw Hill, New Delhi.
Ray, N 2015, Emerging innovative marketing strategies in the tourism industry, McMillan, London.
Sheldon, J & Daniele, R 2017, Social entrepreneurship and tourism: philosophy and practice, Cengage, New York.
Szutowski, D 2016, Innovation and market value: the case of tourism enterprises, Difin, Warszawa.
Weeden, C 2016, Cruise ship tourism, John Wiley & Sons Publishers, Hoboken.
Xu, J, Yao, L & Lu, Y 2014, Innovative approaches towards low carbon economics: regional development cybernetics, Cengage, New York.
Zolait, A 2013, Technology diffusion and adoption: global complexity, global innovation, Information Science Reference, Hershey.
Appendix
Questionnaire
- How relevant is technology in the field of tour and travel in the United Arab Emirates? (Tick as appropriate)
- Very relevant
- Relevant
- Somewhat relevant
- Irrelevant
- Very irrelevant
- How receptive are the stakeholders in the tour and travel industry towards emerging technologies? (Tick as appropriate)
- Very receptive
- Receptive
- Somewhat receptive
- Unreceptive
- Very unreceptive
- Is the investment made in innovative technologies proportionate to the returns? (Tick as appropriate and explain your choice)
- Very proportionate
- Proportionate
- Somewhat proportionate
- Disproportionate
- Very disproportionate
- What is the impact of increasing innovation on the tour and travel industry in the United Arab Emirates? (Kindly give an explanation)
- What is the future of the tour and travel industry in the United Arab Emirates in an increasingly globalizing and highly innovative world?