Executive Summary
Background
Computers have become as integrated into our work environments as the telephone. All departments use computers for their core activities and when computers or networks fail, the impact on business is perhaps greater than when telephone service is unavailable. Additionally, to ensure business continuity in the event of a disaster, a strong disaster recovery and business continuance program need to be placed. Typically, only those departments that have technical resources and a sizable technology budget can absorb the costs associated with hardware, software, and information technology (IT) staff necessary to support an internal IT organization and infrastructure.
Establishment of ITS
To meet the challenge of IT business continuity and rising IT costs for County departments, we have formed a new service offering called Information Technology Shared Services (ITSS), described in this Products and Services Guide. ITSS has been designed to provide centralized information technology (IT) services that will provide departments with cost-effective access to our IT infrastructure, technologies, and expertise thereby leveraging the redundant tasks and costs associated with Desktop support, File/Print Services, and Messaging Services.
ITSS Mission
The mission of ITSS is to provide reliable, available, and secure centralized IT services to customer departments in a responsive and cost-effective manner for the following IT Services:
- Implementation Support.
- Centralized Messaging and File/Print Services.
- Centralized Desktop Services.
- Business Systems Support.
Benefits
By participating in ITSS, departments benefit by:
Focusing their resources on their main mission tasks rather than on the IT back-office and desktop services.
Freedom from having to recruit, hire and retain technical resources required to care for these types of services.
Reducing costs and improving services through consolidation of hardware, software, and staffing.
Receiving 24/7 support from our Customer Assistance Center.
Being better positioned to take advantage of emerging Countywide IT services such as Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP), Internet content filtering, managed instant messaging, wireless access, Secured Socket Layer (SSL) and Virtual Private Network (VPN) remote access and mobile device access.
Pricing Structure
One Time Costs
Funding to upgrade and/or replace hardware and software, licenses and telecommunications, to meet the Standard, as required, will be provided by the client department. However, at no cost, we will conduct an assessment of the client department’s IT infrastructure, determine hardware/software, license, and telecommunication upgrades required to join ITSS, and provide assistance to the client in completing the upgrade. When the upgrades are completed and the data and files are ready for migration to ITSS, all transfer activities are performed by ISD at no cost.
Ongoing Costs
The rate for ITSS service is $1,325 per client computing device for the fiscal year 2008/09.
This rate provides all the IT Shared Services described in this Guide, including, but not limited to patch management, backup/recovery, security, network connectivity, 24/7 help desk, and support. At periodic intervals, the client department will need to upgrade its hardware to meet changing ITSS standards or to keep pace as new technology emerges.
Additional Cost
There will be additional costs for supplemental services, such as additional mailboxes and data storage. Charges will be determined during the client assessment and added to the monthly ITSS rate. Additional costs will also apply to discretionary software other than the Windows operating system and the Microsoft Office Suite.
Business Description
ITSS Overview
Information Technology Shared Services (ITSS) will provide County departments, agencies and commissions cost-effective access to our infrastructure, technologies, and expertise for the following centralized Information Technology (IT) Services:
- Implementation Support
- Messaging and file/print services using ISD servers
- Network and server support
- Business Support
Client Department Prerequisites
Engage us to Conduct an Information Technology Assessment
The objective of this activity is to review the client department’s information technology infrastructure to: –
- Identify all desktop computers targeted for ITSS enrollment,
- Document those computers requiring a license and/or software-only upgrades,
- Document those computers requiring replacement to meet minimum ITSS requirements,
- Identify required telecommunication upgrades.
- Identify a cost allocation method that fits the customer’s requirement.
Provide Minimum client Hardware, Software, License and Telecommunication Configurations.
To ensure that clients can join and take advantage of all ITSS services offerings, all client personal computer equipment must be at the level defined by the Standards, Standard PC Hardware, and Software
ITSS will advertise well in advance any changes to the Standards. Additionally, ITSS will Synchronize any changes to the Standards in alignment with the County’s budget cycle to allow client departments ample time to incorporate computing upgrades as part of their budgeting cycle.
Pricing Structure
One Time Costs
After Assessment and Gap Analysis, a department shall provide funding to upgrade and/or replace PC equipment, software, software licenses to meet our Standards and any telecommunications upgrade required. However, ITSS will assist the client in this activity.
Initial Assessment activities include, but are not limited to:
- Identifying all desktop computers targeted for enrollment,
- Documenting which computers require license and/or software-only upgrades,
- Documenting which computers require replacement to meet a minimum hardware and
Software configuration,
- Identifying required telecommunication upgrades, and,
- Assisting departments in the acquisition, configuration and installation of hardware,
Software, license and telecommunication upgrades.
We will conduct the assessment at no cost.
IT Shared Services Fee
After a department migrates, ITSS will provide the shared services to each customer department for a flat annual rate of approximately $1,325 per client computing device for the fiscal year 2008/09.
A brief listing of services follows:
Centralized Messaging Services & File/Print Services
- Central Server Management.
- Directory Services.
- Email & Calendaring Services (MS Exchange 2003).
- Data Storage/Data Restoration.
- Disaster Recovery Services.
- Remote access to documents.
- Network printing services.
- Disaster Recovery Services.
- Data Storage/Data Restoration.
- Active Sync Connectivity for MS-enabled mobile devices.
Centralized Desktop Services
- Managed Desktop (MS Office 2003, MS Windows XP).
- Software Distribution.
- Asset and Software Inventories.
- Provisioning and Image Management.
- Roaming User Profiles.
- Remote Monitoring & Troubleshooting.
- Remote and Onsite Support and Repairs.
- Security.
- Contract monitoring & management.
- Providing an ISD Microsoft Enterprise Agreement (optional).
Business Support
- Core liaison services
- Account management
- Service Level Monitoring
The ITSS service fee will vary based on the number of clients being supported. The service fee includes desktops, laptops, and tablets that run the Microsoft Windows operating system and the Microsoft suite of products. The service fee may vary in the future, contingent upon the total number of devices supported. Incorporated in the fee are costs associated with data storage and data restoration costs.
A client computer is defined as any computing device connecting to Shared Services which ITSS is responsible for supporting. Individuals with multiple computers will need to enroll each computer in Shared Services for each computer to be supported by ITSS. ITSS will work with client departments to ensure that any computer connecting to ITSS conforms to the Standard and have the appropriate security software installed.
Additional Pricing
Supplemental Services
Any additional cost, such as charges for additional mailbox storage will be determined during the Assessment and added to the monthly ITSS rate. Costs will be documented in the Pricing Schedule. E-mail limitations and data storage limitations identified in the assessment apply to each account. However, additional charges are only incurred if the aggregate e-mail storage or aggregate data storage for all enrollees in the client’s organization is exceeded.
Service Offering
Implementation Support
Much preparation is required to migrate a County department to full ITSS operation. An ITSS Project Manager will prepare a project plan and manage the migration project throughout the ITSS life cycle. The Project manager will collaborate with the vendor and the client to schedule all tasks.
Customer Initialization
- Define the scope of the project.
- Review client’s mission statement, line of business, Business Automation Plan and other departmental reports providing insight into the client’s IT support needs for messaging, shared file/print and desktop support.
- Review the existing IT infrastructure including software, hardware and daily operations.
- Review IT documentation, procedures and protocols.
- Visit remote sites.
- Document the IT support requirements of the department.
- Ensure the client understands the ITSS migration project and range of services and define client expectations.
- Establish a common understanding of the proposed methods for implementation.
- Agree on the communication plan, client’s responsibilities, and ITSS’ responsibilities.
- Draft a Memorandum of Understanding.
- Define a baseline project schedule.
- Obtain Project Charter signoff from the client to proceed.
Customer Initialization Deliverables
- Project Plan.
- Memorandum of Understanding (MOU).
Assessment Phase
Install ALTIRIS client software on as many workstations and servers as possible to identify and document the following:
- General existing site information
- Network infrastructure
- Server environment
- Desktop environment
- Business software applications
- Procedures/protocols
- Determine risks associated with a migration.
- Determine customer preferences.
Assessment Phase Deliverables
- Software application infrastructure survey.
- IT infrastructure survey, including telecommunications.
- Final Infrastructure Assessment Report.
Gap Analysis Phase
- Identify the client’s strengths and areas that need improvement to meet ITSS standards.
- Provide recommendations to upgrade areas needing improvement in order to meet minimum computing standards to join ITSS.
- Develop cost/time estimates for license, hardware/software, and telecommunication upgrade requirements.
Gap Analysis Phase Deliverables
Gap Analysis Summary Report documenting the remediation requirements and cost estimates.
Pre-Implementation Review
- Review all specifications new computing devices, software and MS license upgrades and Telecommunication upgrades.
- Map and prepare client data files for transfer to ITSS.
Allocation of Computer Time and Costs
In considering the calculation of overhead absorption rates, the basic aim was to absorb total overhead in products. In practical terms, the cost accountant would have to wait until the end of the accounting period, collect all the cost and production data, and proceed to allot the actual costs to the cost center and cost units. The effect of this practice would be that:
- Product costs cannot be determined until some considerable time after the end of the accounting period.
- The overhead absorption rate will probably vary each period due to top the fluctuations in overhead incurred, the volume of production, and the efficiency of the factory.
In order therefore that management may be provided with reasonably accurate and timely product costs, which are not distorted by seasonal fluctuations, a predetermined absorption rate is calculated. This is a rate calculated in advance of the period in which it is to be used, by dividing the anticipated period overhead by the anticipated period production. Production may be measured on any of the absorption bases already described, e.g. prime cost, labor hours, etc.
The procedure is to record for each job the amount of the absorption base that has been incurred in it. When the job is finished, or at the end of the accounting period, this amount is then multiplied by the predetermined absorption rate, and the total overhead absorbed recorded on the job cost account. If the job is completed, the prime cost plus absorbed overhead will be transferred out of the work-in-progress account to finished goods or cost of sales plus absorbed overhead to the next accounting period. The total overhead absorbed is credited to the next accounting period. The total overhead absorbed is credited to the overhead account.
The use of the predetermined rates can be extended to apportionments from service departments so that each service cost center is credited with the amount of service given multiplied by the predetermined rate. In this way, it is possible to obtain simple measures of the efficiency of operating the service.
The subject of predetermined rates lead to standard costing and budgetary control because we are now in the field of applying planned costs instead of historic costs. Before leaving the subject, it is necessary to consider the problems involved in computing the predetermined rate.
Pre-Implementation Review Deliverables
Pre-Implementation Review Summary Report verifying
a). Specifications for all client software, hardware, licenses and telecommunication hardware and/or software that is being used to meet ITSS Standards, and,
b). Verification that all client, cost associated with IT department usage.
Remediation
- Assist the client to come up with methods of allocation of IT resources.
- Assist the client to Implement infrastructure upgrades such as network devices, connectivity and telecommunications equipment.
- Accomplish the “imaging” of the client accounts department to allocation methods described above to enable easier resource allocation.
Remediation Deliverables
A checklist will be utilized to document successful completion of each task.
Implementation
- Implement resource allocation software in the company as per the number of PC’s or using activity based costing.
- Perform comprehensive testing.
Implementation Deliverables
- A completion report for each task required for ITSS resource allocation.
- Implementation Summary Report indicating that the client’s finance departments operate fully under the new structured software for the purpose of resource allocation.
Post-Implementation Review
- Monitor and evaluate the performance of the finance department and implement a network that connects all the departments.
- Track all the costs
- Monitor resource usage and allocation among the departments
- Evaluate system responsiveness, system functionality and reliability.
Post-Implementation Review Deliverables
Project Closure Report.
Messaging and File/Print Services
Centralized Messaging Service
- Provide a single, scalable Active Directory running on Windows Server 2003 enabling Centralized, secure network management, including user accounts and network distributed resources.
- Each customer user will have a single logon to the central Active Directory environment.
- Active Directory domain characteristics:
- Enforce password history: 6 passwords remembered
- Maximum password age: 90 days
- Minimum password age: 1 day
- Minimum password length: 8 characters
- Password must meet complexity: Enforced
- Allow users to encrypt files: Enabled with use of EFS (Encrypted File System)
- Home directory size: 200 MB
- The Active Directory credential is the key that automatically unlocks all of the MS applications, such as Outlook, that clients have been authorized to use.
Any computer joined to the ITSS domain will allow the user to connect to their mailbox, to their network files, and local printers.
Users gain automatic access to local resources. When users log in to the network from a computer other than their regular computer, Active Directory will utilize group policies to make network resources, including local printers and file servers, available to the user without requiring manual changes to system configuration settings.
Roaming user profiles provide the ability to store unique user information such as user favorites, screen saver settings, desktop settings, etc centrally within Active Directory. This allows users to get the same desktop look and program settings when they use any other ITSS configured system on the network.
Offline file folders allow a user to have full access to their network files if they are disconnected from the network. Windows XP and Active Directory policies automatically keep network files synchronized to an offline folder on each user’s local computer. When the computer reconnects to the network, any files modified in the offline folder are automatically synchronized between the user’s computer and the appropriate servers.
Provide a shared, scalable Microsoft Exchange 2003 environment to the client enabling the centralization of departmental e-mail solutions. This environment will provide server-based anti-virus and anti-spam tools and will allow the client to access their e-mail remotely via Outlook Web Access and Outlook Mobile Access.
Exchange mailbox characteristics:
- Maximum sent message size: 10MB
- Maximum received message size: 10MB
- Maximum recipients for a single email: 5000 addresses
- Mailbox size warning issued at: 95MB
- Mailbox send prohibited when mailbox size at: 200MB
Server-based anti-virus and anti-spam protection for email are provided by Symantec’s Brightmail AntiSpam product. This software stops spam attacks in real-time without compromising accuracy and utilizes numerous different filtering technologies for maximum protection against spam, email-borne viruses, and another unwanted email.
Customers will have remote web-based access to e-mail via Outlook Web Access (OWA) and Outlook Mobile Access (OMA).
- OWA allows customers with a non-County Internet connection and web browser to securely access their Exchange mailbox, public folders, rules, and mailbox options.
- Both methods provide remote access to e-mail, calendar, contacts, and tasks. Additionally, access is secured by the use of RSA SecurID tokens. For customers needing remote access to their mailboxes, ITSS will coordinate customer purchase of SecurID tokens with Data Security.
Provide administration for the Countywide LDAP directory. The LDAP directory is a centralized repository of County e-mail addresses which is searchable from computers on the County’s Enterprise Network.
Provide 24/7 monitoring, support, and issue resolution for all Centralized Messaging components.
Centralized File/Print Services
Provide a shared, scalable File and Print services environment centralized at the ITSS data center. This service will allow customers to place their data within a highly secure, fault-tolerant, and redundant solution. Customers connecting remotely will have full access to any data they placed in this environment just as if they were working at their regular office computer.
Provide remote access to documents. Each user has access to a “Public” network drive for sharing documents and a “My Documents” network drive for personal work files.
Provide network printing services enabling more usage of centralized printing within client offices. Users will benefit from simplified common printing tasks, such as sharing, finding, and connecting to network printers. Windows Server 2003 includes intelligent print services: fault-tolerant, discoverable, server-based printing that improves printer reliability, manageability, and security.
Provide seamless access to network data and files. Windows Server 2003 also provides strong security.
Provide backup and restore functionality and support to clients, including backup management and disaster recovery, for data stored in the “My Documents” folder and the end user’s private network-based drives. All of the data is replicated to the County’s local recovery center for disaster recovery purposes.
Help Desk staff will troubleshoot messaging and shared file/print issues through the use of a Problem Priority scale support strategy with Urgent tickets receiving the most rapid response:
Priority Definition
- LOW Component/service is unusable; bypass or work around is possible with no operational impact; non-critical; deferred maintenance acceptable.
- MEDIUM Component is down/degraded; service is unusable or difficult to use; non- critical but restricted function; some operational impact
- HIGH System component is down; service is unavailable; critical impact; alternative or bypass is unavailable
- URGENT Critical system component is down; service is unavailable; critical impact; alternative or bypass is unavailable
Centralized Desktop Services
The client is responsible for equipment inventory control, Internal Certifications Control Program (ICCP), and budgeting as needed for future equipment replacement. All new computing devices must be maintained according to the Standards. ITSS will introduce new ITSS standards in alignment with the County budget cycle to allow departments to plan for the acquisition of new equipment or services.
- Provide 24/7 centralized support for client computers including: operating systems, office applications, telecommunications, anti-virus, patch management, system security and computer provisioning, deployment repair and disposition.
- Help Desk staff will troubleshoot desktop support issues through the use of a Problem.
Priority scale support strategy with Urgent tickets receiving the most rapid response:
Priority Definition
LOW Component/service is unusable; bypass or work around is possible with no operational impact; non-critical; deferred maintenance acceptable.
MEDIUM Component is down/degraded; service is unusable or difficult to use; non-critical but restricted function; some operational impact
HIGH System component is down; service is unavailable; critical impact; alternative or bypass is unavailable
URGENT Critical system component is down; service is unavailable; critical impact; alternative or bypass is unavailable
- Software supported for ITSS Customers will be as stated in ITSS Standards.
- Provide a central software repository and software version control, central management of client software licensing, and assist procurement and provisioning of client computers.
- Provide Microsoft Enterprise Agreement to cover MS products.
- Provide Asset and Software Inventories using Altiris Software.
- Provide Roaming User Profiles (client profiles, such as favorites, screen savers and desktop setting), are available from any location.
- Provide Image Management.
- System parameters
- Security and anti-virus software
- Patch and system management software such as ALTIRIS to monitor, secure andmanage the desktop environment.
- Provide on-site warranty repair. On site non-warranty repair will be billed on a time andmaterials basis.
- Provide Remote Monitoring & Troubleshooting from Customer Assistance Center.
Shared Messaging, File Print, and Desktop Support
Performance Objectives
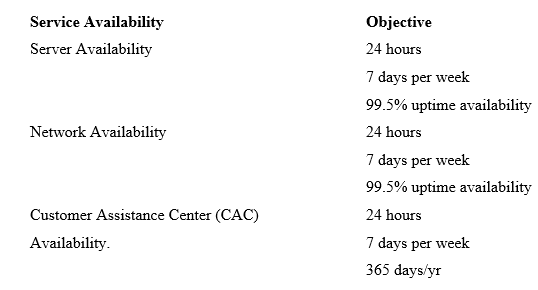
Pricing Schedule

References
Adams, D.R, Powers M.J, Owles, V.H, (1985), Computer Information Systems Development: Design and Implementation, South-Western Publishing Co.
Buchan, J., & Koenigsberg, E., (1963), Scientific Inventory Management, Prentice-Hall.
Copacino, W. C., (1997), Supply Chain Management: The Basics and Beyond, ISBN: 9781574440744, The St. Lucie Press/ /Apics Series on Resource Management, Publisher: CRC.
Donath, B., (2002), The IOMA Handbook of Logistics and Inventory Management, Institute of Management & Administration, John Wiley and Sons.
Intellisoft, (2006), Serial Number Tracking Software Solutions. Web.
Itsuki, R., Shibata, H., Ikkai, Y., and Komoda, N., (2003), The Autonomous Information System Design For Item Management Using, Re-writable RF-ID Tags In Supply Chain, Lisbon.
James C. EMERY, (1987), Management Information Systems: The Critical Strategic Resource, Oxford Univ Pr.
Kendall, K.E, Kendall, J.E, (2002), Systems Analysis and Design, 5th Edition, Prentice Hall.
Khosrowpour M; (2000); Challenges of Information Technology Management in the 21st Century; Idea Group Inc.
Khosrowpour, M. (2001), Pitfalls and Triumphs of Information Technology Management, ISBN 13: 9781878289612, Idea Group Pub.
Kissinger, K and Borchardt S; (1996); Information Technology for Integrated Health Systems, J. Wiley.
Lucas, H. C., (1976), The Analysis, Design, and Implementation of Information Systems, McGraw-Hill.
Michael J. Earl, (1996), Information Management: The Strategic Dimension. ISBN13: 9780198257608, Oxford University Press, USA.
Piasecki, D. J., (2003), Inventory Accuracy: People, Processes and Technology. ISBN 0972763104, Ops Publishing, Kenosha, Wisconsin.
Prichard, J. W. & Eagle, H. R. (1965), Modern Inventory Management, John Wiley and Sons Ltd.
Rosenfeld L, Morville P;(2002); Information Architecture For the World Wide Web; O’ Reilly.
Schwalbe K.,(2004); IT Project Management 3rd edition.
Sherman C. Blumenthal, (1969), Management Information Systems: A Framework for Planning and Development, Prentice-Hall.
Sommerville, I. (2004), Software Engineering, 7th Edition, Pearson Education Limited.