Introduction
Macroeconomics is the broad study of economics. It pays attention to summative production and expenditure in a financial system. It involves the study of unemployment and inflation. In addition, it also involves the study of interest rates and policies used by governments in their daily running.
As outlined above, unemployment is one element of macroeconomic with microeconomic bases. Unemployment can be defined as the inability of individuals with labor force abilities to find job opportunities. Despite the existence of diverse views concerning unemployment, it is evident that it overheads the economy of many states. Many reasons lead to individuals’ unemployment, and among them include losing jobs, leaving jobs, and completing temporary jobs. There are many types of unemployment but, economists categorize them into four fundamental categories. They include frictional unemployment, structural unemployment, cyclical unemployment, and seasonal unemployment (Filc and Kohler, 1999).
Frictional unemployment
Frictional unemployment is described as the unemployment that takes place because of the movement of people from one occupation to another. The demographic alteration also plays a great role in advancing unemployment. This is evidenced by the high turnover of first-time workers in a given long-term job. Unlike other types of unemployment frictional unemployment allows voluntary movement of workers. Many reasons lead to this type of unemployment, and among them include getting married, quitting unpromising jobs, or having enough savings. Compared to other types of unemployment, frictional unemployment is the least harmful. This is because it involves the movement of people to promising jobs. An excellent example of frictional unemployment is the involvement of college graduates in job seeking.
Structural unemployment
Structural unemployment can be defined as unemployment that arises from variations of customer demands. For instance, a reduction in the need for secretaries leads to the emergence of structurally unemployed employees in the field of the secretariat. Structural unemployment can also be described as a type of unemployment that arises from the variance between available occupations and employees’ skills. It is often caused by variation in the financial status of a given state as a result of a natural tragedy or the emergence of competitors. Unlike frictional unemployment, structural unemployment is long-lasting because many employees undergo difficulties in locating areas to employ their skills. It is the most known type of unemployment.
Cyclical unemployment
Cyclical unemployment is defined as a type of unemployment in which employees lose their jobs as a result of cycle instabilities in production. A good example is the up and down movements in the financial status of a given state. Many states’ economies undergo booms and downturns, and as a result, many businesses avoid spending their wages during a recession period. It is considered as a temporary type of unemployment because it recovers when the economy of a given state unchains from a business cycle (Filc and Kohler, 1999).
Long term unemployment
The term long-term unemployment differs greatly depending on national circumstances. However, the period of unemployment that lays between one year and above plays a crucial role in defining long-term unemployment. Thus, from the description above, long-term unemployment is a type of unemployment that lasts for more than one year. Some people observe it as a pool because it involves the movement of people from short-term unemployment to long-term unemployment (MacDonald, 1999).
Long-term unemployed is measured by observing the duration of time a given population has gone unemployed. This is met by paying into consideration the data provided by the Current Population Survey. The CPS contains statistical information about the official labor force of a given state. For instance, it contains statistical information about the unemployment rate in a given state. To meet its objective, CPS requests the unemployed individuals to provide information concerning the number of years they have spent unemployed. The figure below outlines some information concerning long-term unemployment for individuals who have been unemployed for more than one year in different states (International Labour Office, 2003).
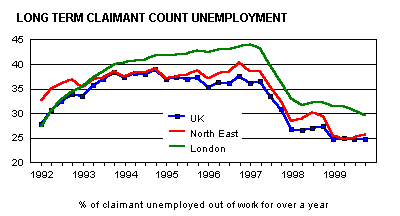
Causes of long-term unemployment
Long-term unemployment is caused by diverse factors, and among them includes sickness, retirement, and discouragement. The economic status of a state also plays a significant role in determining the type of unemployment among its citizens. For instance, an economic downturn has been found to contribute significantly to the emergence of long-term unemployment. This is evidenced by the research carried out in Italy. The majority of the men in Italy were found to move from short-term unemployment to long-term unemployment due to the emergence of the unemployment trap crafted by Italy’s economic downturn.
Discouragement is another factor that leads to long-term unemployment. From research carried, it is evident that the percentage of individuals that move into inactivity due to discouragement while searching for jobs in Italy increases with time. For instance, the percentage of unemployed in Italy increased from 35.3% in 2008 to 38.4% in 2009. This is a result of the majority believing that there are no jobs for them in the field.
Retirement is also another factor that leads to long-term unemployment. Individuals who have retired from different organizations end up staying at their respective homes without working. Some of the people do involve themselves in early retirements thus, leading to the occurrence of high rates of unemployment in some states.
The health condition of individuals also contributes to the existence of long-term unemployment. The majority of the disabled people in many states are unemployed. This is a result of physical challenges that bar them from seeking jobs. Additionally, illness plays a significant role in advancing the rate of long-term unemployment in a given state.
Recent and past unemployment durations
Unemployment duration is defined as the period that workers are jobless. From research carried it evident that unemployment duration has been rising rapidly in the recent period. Various factors have been related to the current increase in the duration of unemployment compared to the past. Some of these factors include the change of demographic features of the labor force, that is, individuals below the age of 24 keep shifting from the labor force. Another reason for the current increase in unemployment duration is persistent loss of employment in the current states.
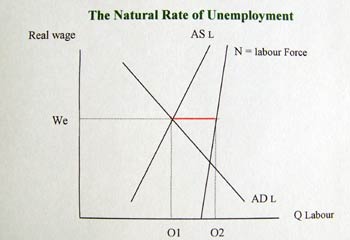
The natural rate of unemployment and past occurrences
The natural rate of unemployment is defined as employment that takes place at equilibrium. It includes frictional unemployment and structural unemployment. The natural rate of unemployment is affected only by supply factors. However, it was broadly identified as structural unemployment (MacDonald, 1999).
Government programs
Unemployment programs are social nets that provide financial assistance to unemployed individuals. Different states observe diverse qualification requirements in the provision of financial assistance. There exist diverse government programs; some of them include unemployment insurance programs, disability programs, Supplemental Nutritional Assistance Program, and Home Affordable Unemployment Program (Scire, 2007).
Unemployment insurance program
Many governments overcome economic downturns via the implementation of unemployment insurance programs. This program plays a crucial role in boosting the living standards of individuals from a given state.
Disability program
Most governments play a crucial role in improving the living standards of the disabled through the implementation of disability programs. Disability programs enable governments to take part in financing individuals with disabilities.
Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program
Diverse governments use SNAP in not only offering nutritional support but also economic support to the poor members of the community. SNAP is one of the largest programs that have succeeded in fighting hunger (Scire, 2007).
Home Affordable Unemployment Program
HAUP is a program crafted by a given government to assist individuals who abruptly lose their jobs in paying their mortgage. It also plays a crucial role in protecting an individual from paying the mortgage for three months after losing a job.
Conclusion
In conclusion, macroeconomics is a broad study of economics. It involves the study of unemployment. Unemployment is the inability of individuals with labor force potentials to find job opportunities. However, many governments employ diverse unemployment programs in solving unemployment challenges. Most governments use the SNAP program in providing nutritional support to their citizens. Job loss is one critical factor that poses a challenge to many governments; many individuals lose jobs while in debt. However, many governments employ HAUP programs in protecting their citizens from money lenders.
References
Filc, W. & Kohler, C. (1999). Macroeconomics Causes of Unemployment: Diagnosis and Policy Recommendations. New York: Duncker & Humblot.
International Labour Office. (2003). Key Indicators of the Labour Market. New York: International Labour Organization.
MacDonald, N. (1999). Macroeconomics and Business; An Interactive Approach. New York: Cengage Learning EMEA.
Scire, M. (2007). Troubled Asset Relief Program (TARP): Treasury Continues to Face Implementation Challenges and Data Weaknesses in Its Making Home Affordable Program. New York: DIANE Publishing.