Introduction
The current medical landscape promotes significant advances in pharmacogenomics (PGx) implementation strategies. They support the production of new drugs by facilitating a better understanding of the genetic control of cellular functions (Baskys, 2018). More specifically, pharmacogenetic testing contributes to the personalization of medications to enhance clinical outcomes (Weitzel, Cavallari, & Lesko, 2017, p. 1552). One of its crucial applications implies the treatment of emotional lability, including bipolar disorder. Bipolar disorder is a mental health condition distressing the quality of life of the affected individual through severe emotional instability, including depression, hypomania, or mania. With that said, improved integration of the pharmacogenetics in clinical testing might enhance the overall treatment adherence in bipolar disorder patients.
Overview of Methodology
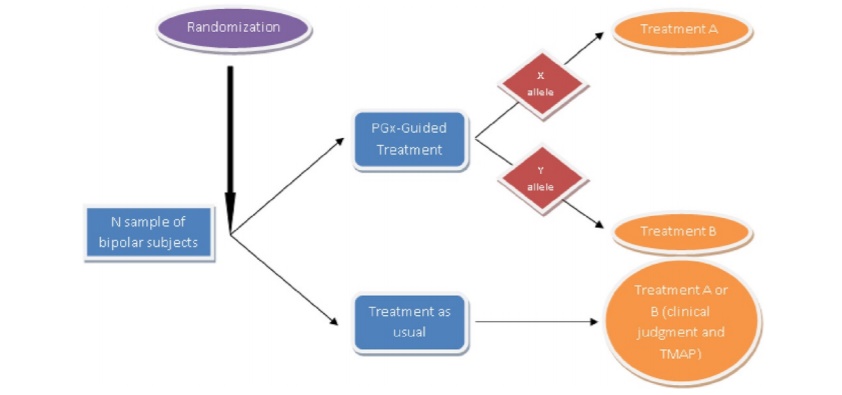
Pharmacogenetics became an increasingly valued method of investigation into the system of drug response for various diseases, including psychiatric disorders. According to Oedegaard et al. (2016), understanding the genes engaged in such a response is crucial to considerably improve the individualized treatment to target-specific genetic alterations characteristic of the particular patient or population (Fig. 1). The proposed method implies that the examined population will be divided into two groups: one is subjected to traditional psychiatric treatment, and the other group is exposed to pharmacogenetic testing. The study will also involve the implementation of clinical and laboratory supervision. Qualified and experienced psychiatric professionals engaged in the study will generally use mood stabilizers or antipsychotic drugs. As such, the healthcare provider will apply the findings of the genetic test to alter the treatment plan.
Hypothesis
The proposed research study will be based on the central hypothesis that pharmacogenetic testing is a beneficial tool providing efficient treatment for patients with bipolar disorder. In addition, pharmacogenetic tests help reduce the aftermath of personal instability in genetics, which needs to be recognized as a fundamental element of the response to medical treatment and drugs. The research study will be guided by the general understanding that PGx is studying genes’ response to certain medicines in the human body. Therefore, such testing is vital to determine the most appropriate treatment interventions for a broad spectrum of mental health conditions.
Study Design
The proposed scientific research will implement an observational study design. According to Bailey et al. (2019), this type of study design is based on observing the effects of a treatment or form of clinical intervention. It is followed by the record of the results or findings, without attempting to change the participants subjected to the examination procedure. The main advantage of using observational research design implies the systematic observation and record of the patients’ behavior. Therefore, it will be possible to learn and clarify the particular characteristics of the group under study or the target setting. Considering that the research involves two different groups, another critical approach will be the case-control observational studies to compare the groups and define the predictors of an outcome (Martínez, Papuzinski, Stojanova & Arancibia, 2019). The key advantage of the case-control studies is based on its simple approach to organizing and generating the hypothesis.
Setting
The proposed research study concerning the use of pharmacogenetics in treating bipolar disorder will be applied in clinical settings, with a particular focus on psychiatry.
Subjects (Population Characteristics, Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria)
The target population for the proposed research study will involve the patients diagnosed with type I or II of bipolar disorder, as defined by the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (2013). However, the final objective is to yield results beyond the target population itself. The study will engage thirty patients with bipolar disorders divided into two groups, with fifteen individuals accordingly. The inclusion criteria start from 18 years and older (50-60 years limit), and the patients selected for the research had to take the baseline medication for at least three months. The test execution and data application for research aims will be recorded in the written form. One group of participants will be treated based on their genetic test results, while the other group of 15 people will be treated with the traditional method.
Recruitment and Attrition
Participants’ recruitment is based on the following selection criteria: age range, non-clinical stability, medication adherence, and informed consent. First, bipolar disorder diagnosis has to be recorded at least six months before the beginning of the testing and study participation. The researcher must make sure that the patients involved in the study are 18 years and older, however, under the age of 60. Furthermore, each individual will be provided with the written informed consent before participating in the pharmacogenetic test concerning legislative purposes. The baseline medication consumption for the last three months before the study is also an essential requirement.
Sample Size and Power Calculations for each Outcome Measure
The unique collected sample from 30 participants will be genotyped for GWAS (genome-wide association study). The sample for the proposed research will be assessed longitudinally with the aid of clinical scales, cognitive assessments, and laboratory tests. The STEP-BD sample will include well-documented treatment responses.
Data Collection
The data collection will be conducted with careful monitoring and accompanied by the appropriate scales. Concerning the observational research design, the most effective data collection method implies the observation of the participants. It will be adopted along with examining the non-verbal expression of feelings, identifying fundamental interactions between the patients involved, and defining changes in the selected group. The proposed research study will employ qualitative tools for data collection, such as interviews, observation, and document analysis (Cuéllar-Barboza, McElroy, Veldic, et al., 2020). Data will be gathered on the course of the disease before randomization. It will include the “age of onset for bipolar disorder, amount of prior episodes, past treatment reaction, childhood abuse, health conditions, psychoactive substance use, family history, previous lithium treatment, and prior suicide attempt history (Salloum, McCarthy, Leckband, & Kelsoe, 2015, p. 4). The participants’ history of episodes during the past two years will be used through a life chart method. In general, this information will be used as a covariate to adjust for a natural course in the statistical analysis.
Outcomes of Interest
The current studies demonstrate a relationship between variations in genetics and response to medications or disease predisposition for patients who have bipolar disorder (Espadaler, 2016). Nevertheless, the existing research does not entirely clarify whether pharmacogenetic testing can replace the current (more traditional) methods of clinical treatment. Such an open discussion poses critical challenges that the proposed research study aims to address. The outcomes of interest imply that the study will give sufficient data regarding pharmacogenetics and contribute to medication improvement for patients diagnosed with bipolar disorder. The advanced medications are expected to reduce the side effects and emphasize the pivotal role of personal genetics variability in drug response. Therefore, the main expected results are that the research findings will demonstrate promising data about the benefit of the pharmacogenetic tests measures in developing more effective and tolerated treatment in the alternative and innovative approach of bipolar disorder.
Randomization
The study participants will be randomized to pharmacogenetic test guided treatment or treatment as usual (TAU), meaning the traditional treatment approach. The patients will be divided into groups accordingly.
Measures Applied in the Research Study
The research is based on the implementation of pharmacogenetic testing and its further application to improve the clinical treatment of bipolar disorder diagnosis. As defined by the World Health Organization (WHO, 2020), there are three main prevention levels in public health: primary, secondary, and tertiary prevention. Hence, the PGx testing in the treatment of Bipolar disorder can be referred to as a primary level of public health because its measures aim at improving the overall mental health of a population affected by bipolar disorder. Pharmacogenetic testing in treating bipolar disorder is considered a mental health promotion campaign helping affected individuals access advanced treatment measures that address crucial psychiatric issues, including bipolar disorder. According to WHO (2020), such health promotion and prevention are defined as involving measures carried out to allow society to increase control over the disease and improve the overall public health outcomes.
Data Management
The previously published data regarding cognitive dysfunction in bipolar disorder and the heritability of particular neurocognitive measures will develop the evaluation strategy for the research study and define the key study domains, such as “attention, verbal learning, and executive function” (Cuéllar-Barboza, McElroy, Veldic, et al., 2020, p. 10). The gene expression data will be applied for promoting the gene expression networks that can be compared between the particular conditions. The received data can significantly contribute to the clinician’s assessment of a molecular diagnosis of bipolar spectrum disorder patients.
Data Analysis
The data analysis will be implemented with the help of SPSS, which is a software package for interactive, or batched, statistical analysis. For characterizing the patient population, the research will apply descriptive statistics and Kruskal Wallis test analysis to define the relevance of medical performance disparities of the PGx test group’s scale scores and the reference group (Salloum, McCarthy, Leckband & Kelsoe, 2015). Also, the man-Whitney U test analysis will be adapted to calculate the significance of treatment effectiveness and the aftermath differences between the reference and test samples.
Dissemination
The outcome measures of the sample might serve as a baseline sample for the future research and replication of results. The dissemination of the research findings will be focused on the target audience:
- commissioning organizations,
- community nursing service provider staff,
- patients and the public,
- external statutory organizations (Department of Health, NHS Information Centre, NICE, Quality Observatories),
- academic researchers.
Potential Limitations
The pharmacogenetics studies of psychiatric conditions are exposed to some methodological issues and limitations. First, there can be a lack of reproducibility between the studies conducted so far. This can be explained by the various criteria used by many studies for examining the medications response (Fortinguerra, Sorrenti, Giusti, Zusso & Buriani, 2020). Considering the diverse criteria, the research findings cannot be directly compared between the studies. However, the International Society of Pharmacogenomics designed the recommended criteria to direct researchers in the new studies. Particular limitations derive from the complex nature of bipolar disorder.
Conclusion
Within the rapid development of the healthcare system, pharmacogenetics confronts pivotal difficulties regarding data integration into clinical practice. The existing genomic data has the power to maintain a personalized treatment approach to bipolar disorders by providing the most suitable pharmacological therapy for each individual. Pharmacogenomics can guide the clinicians towards a safer application of drugs, including antidepressant medications, based on the polymorphisms on the HTR2A gene. A pharmacogenomic test should be implemented to verify the efficiency of drugs in a given subject, predicting each medication’s effectiveness profile and safety. Such an approach will considerably improve therapeutic success and reduce the possible adverse effects.
References
American Psychiatric Association (2013). Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (DSM-5 (R)), 5th revised edition. American Psychiatric Association Publishing.
Bailey, R. L., Sahni, S., Chocano-Bedoya, P., Daly, R. M., Welch, A. A., Bischoff-Ferrari, H., & Weaver, C. M. (2019). Best practices for conducting observational research to assess the relation between nutrition and bone: an international working group summary. Advances in nutrition, 10(3), 391–409.
Baskys, A. (2018). Application of pharmacogenetics in clinical practice: problems and solutions. Journal of Neural Transmission, 126(1), 109–113.
Cuéllar-Barboza, A.B., McElroy, S.L., Veldic, M. et al. (2020). Potential pharmacogenomic targets in bipolar disorder: considerations for current testing and the development of decision support tools to individualize treatment selection. International Journal of Bipolar Disorders, 8(23), 1–15.
Espadaler, J., Tuson, M., Lopez-Ibor, J. M., Lopez-Ibor, F., & Lopez-Ibor, M. I. (2017). Pharmacogenetic testing for the guidance of psychiatric treatment: a multicenter retrospective analysis. CNS Spectrums, 22(4), 315–324.
Fortinguerra, S., Sorrenti, V., Giusti, P., Zusso, M., & Buriani, A. (2020). Pharmacogenomic characterization in bipolar spectrum disorders. Pharmaceutics, 12(1), 13.
Martínez, D., Papuzinski, C., Stojanova, J., & Arancibia, M. (2019). General concepts in biostatistics and clinical epidemiology: observational studies with case-control design. Medwave, 19(10).
Oedegaard, K. J., Alda, M., Anand, A., Andreassen, O. A., Balaraman, Y., Berrettini, W. H., Bhattacharjee6, A., Brennand, K. J., Burdick, K. E., Calabrese, J. R., Calkin, C. V., Claasen, A., Coryell, W. H., Craig, D., DeModena, A., Frye, M., Gage, F. H., Gao, Garnham, J., Gershon, E., Jakobsen, P., Leckband, S. G., McCarthy, M. J., McInnis, M. G., Maihofer, A. X., Mertens, J., Morken, G., Nievergelt, C. M., Nurnberger, J., Pham, S., Schoeyen, H., Shekhtman, T., Shilling, P. D., Szelinger, S., Tarwater, B., Yao, J., Zandi, P. P., & Kelsoe, J. R. (2016). The Pharmacogenomics of Bipolar Disorder study (PGBD): identification of genes for lithium response in a prospective sample. BMC Psychiatry, 16(1).
Salloum, N.C., McCarthy, M.J., Leckband, S.G., & Kelsoe, J. R. (2015). Towards the clinical implementation of pharmacogenetics in bipolar disorder. BMC Med, 12(90), 1–15.
Weitzel, K. W., Cavallari, L. H., & Lesko, L. J. (2017). Preemptive panel-based pharmacogenetic testing: The time is now. Pharmaceutical Research, 34(8), 1551–1555.
World Health Organization (2020). EPHO5: Disease prevention, including early detection of illness. World Health Organization, WHO. Web.