Product design specification considerations
The product design specification development for the Water sub-system takes consideration of various factors (Daryll, 2008: 98). The factors are well illustrated in the diagram attached below;
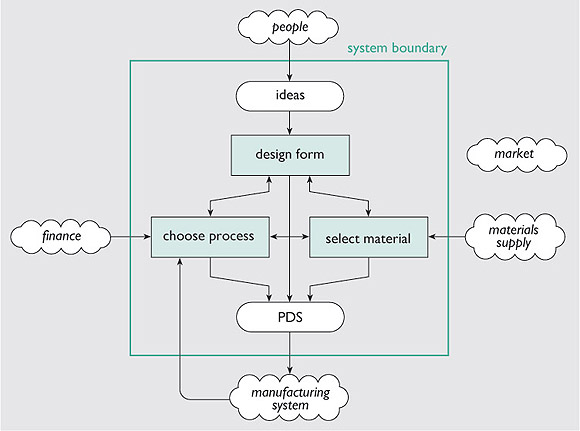
The diagram presumes that there is already a product conceptual design and hence focuses on deciding on of design shape, material selection, and selection of a process to make the design. An output of any design should clearly detail the way in which the product is made and its standard manufacturing/processing procedures (Singh, 2001: 67). The specification takes into account the manufacturer’s capability, materials relative performance, the behavior of the target market and functionality of the overall system (DETR, 2000).
Plumbing system decision matrix
The criteria is described to encompass flexible PDS criteria but were more specific to plumbing systems. The criteria of complexity and implementation are related to the flexible PDS criteria of the system being powering set-up, repeatability of measurement, reduced temperature setup time, and progressive heating/cooling supply temperature (Belfast Engineering Institute, 2009). The criteria of temperature accuracy and thermal capacitance refer to high measurement repeatability and constant heating/cooling supply temperature. The thermal capacitance is a phrase used to describe the amount of energy that will be absorbed into (or from) plumbing parts between the temperature source and the puck.
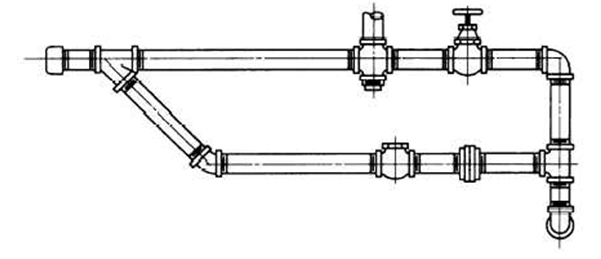
Plumbing systems for a building water system is made up of pipes, fittings, and water tanks as appropriate (Frankel, 2005). The most common pipes used are either metallic or plastic pipes. Fittings are used in coupling of pipe lengths, corner turnings, branching of pipes, pipe size reduction or increment and in connecting the pipes to fixtures like tanks among others. Pipes are often customized to fit the purpose for which they are intended. They differ in diameter, material and make-up depending on the purpose for which they are intended. Indoor pipes are mostly made of copper and galvanized iron with diameters ranging from ½ inch, ¾ inch to 1 inch. Some water supply pipes are made from plastic materials. Ice makers, dispensers for hot water, water filters among others receive their water supply via plastic /flexible copper tubing of reduced diameter (Cummings, 2008). Fittings used are often made of brass or plastic. The double line orthographic drawing below describes the sample piping systems that is to be used in a house building. As seen the piping system is made up of pipes, flanges, connectors and valves.
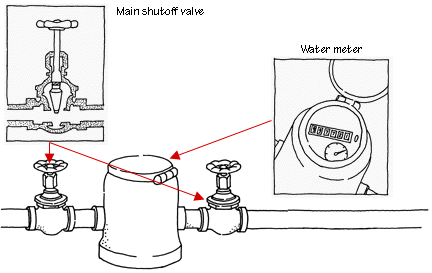
The single-line orthographic drawing below describes the water system for the building. Pipes with large diameters are used in the drain waste vent systems. They are normally 1.5 inches to 4 inches in diameter. Water is delivered into the home via the main pipe which is larger in diameter compared to the rest via a meter from the water-providing company( see figure 2). These pipes deliver the water to the main house tank(s) from where the water will be distributed to the house piping system.
The diagram below describes the water system used for a building.
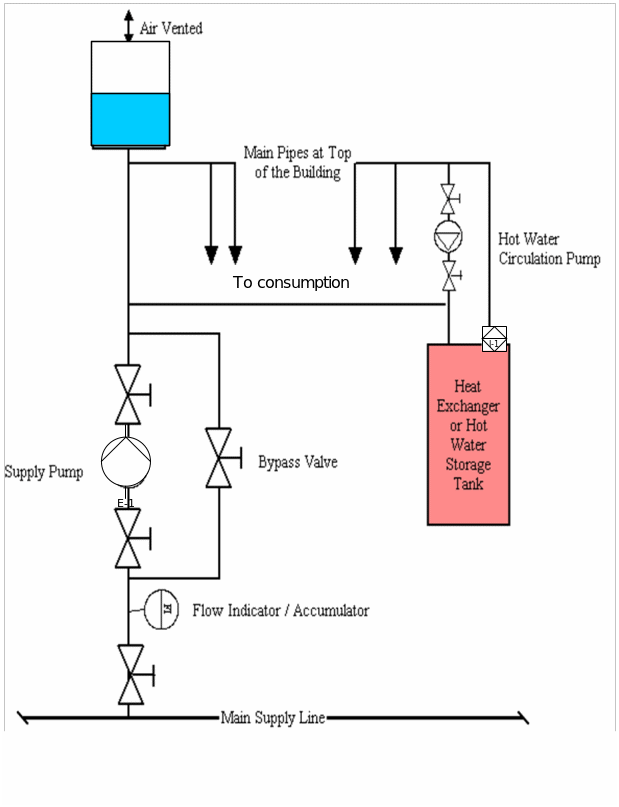
The building water system design
The water tanks are located on top of the building and are placed at approximately 1.2 meters away from the edge of the building. The water pipes in this case are made of copper and are provided with Foam tubing with no sticky-strip type of insulation to reduce the effect of energy losses (Vennix et al., 1990). The thickness determines the level of insulation obtained. For instance, 3/8 inch walled insulation will conserve lesser heat as compared to 5/8 inch wall insulation (see diagram below).

Two kinds of tanks are needed given their different function i.e. one handling hot water and another handling cold water.
Cost estimation
The estimated costs of materials to be used in building the system and the actual construction are summarized in the table below;
Figure 5: Cost Estimation Table
Tanks design
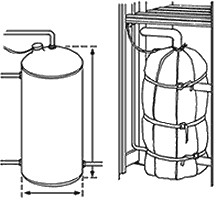
The system is made up of two kinds of tanks. The first tanks carries cold treated water whiles the second one carries hot treated water. Standard insulation jackets are used in reducing the effect of heat losses from the hot water tank (see diagram below).
A range of materials exist for usage in water tanks (Randolph, 2010). These include plastic tanks, fiberglass, concrete tanks, welted/bolted steel tanks, and earthen tanks. In this case a plastic cold water tank is proposed from cold water and a ceramic lined steel tank for hot water. Plastic tank is preferred due its inability to react with any chemicals used in treating water or other present in water. The steel tank for hot water is lined with ceramic internally and covered with external jackets. The ceramic ensures not reactions between chemicals in water and the tank while at the same helping conserve heat alongside the insulation jackets.
Pipe’s selection
Basically two types of pipes are used in construction of the building’s water system. Cooper tubing’s are used in transmission of cold water across the house system. This is due to their inexpensive and durable characteristics.
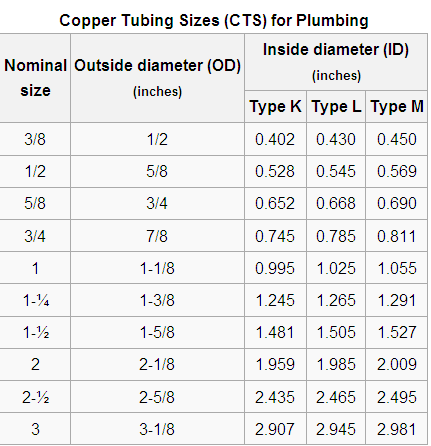
In residential buildings, type bearing medium thickness in comparison to the two is used. The material choice will there fore be type L cooper tubing’s (Sawah et al., 2009). Copper pipes are basically selected due its corrosion resistance activity and its longevity despite costing more than plastic. In supplying, hot water from the hot water tank to consumption, galvanized iron tubes will be used. The galvanized hot water pipes are used due to their ability to their high temperature resistance properties.
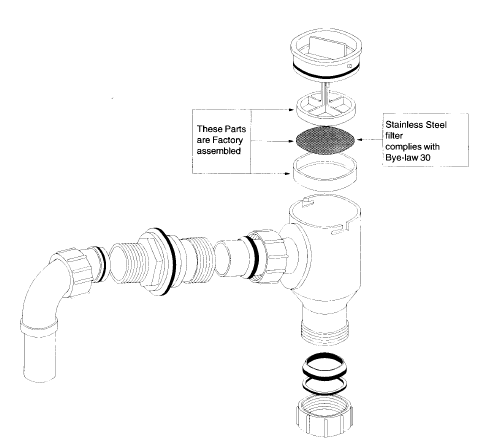
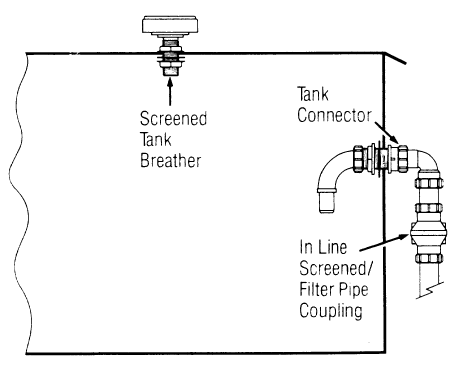
The sample assembly design illustrates the assembly procedures to be employed in setting up of the system.
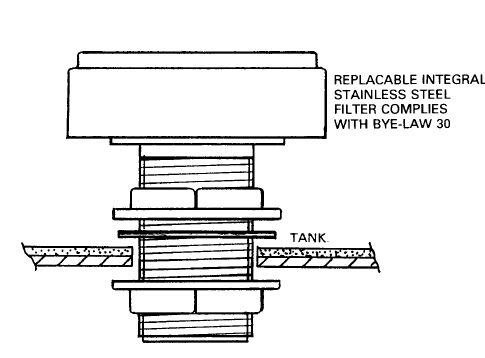
The screened filter is connected to the tank as shown.

Water to be used
The water to be used in the pipes is treated water from supply companies. Such water contains chemicals such as chlorine and is also likely to have corrosive effect on the piping system and the storage tanks. It is on this basis that copper pipes were chosen due to their higher resistance to corrosion, longevity and reduced costs. The effect of water on pipes cannot be ignored as the effect of hot water and cold water may vary slightly. Hot water consumes a lot of energy if exposed to the environment and hence the need for insulation materials. This limits the energy loss.
Conclusion
The choice of design and materials to be used in the piping system is largely dependent on economic considerations, ability of the chosen materials to withstand the conditions of intended operations, and ease of assembly (Brian, 2006). Additionally, durability is taken into consideration. It is noted that corrosion is major cause of piping system failures long before they give back benefits. This is however catered for by choosing in materials selection. The overall design outcome is expected to not only offer an effective piping system but also to be aesthetically appealing to the intended users. Energy conservation is also critical to any manufacture. Noting that the water system will involve a hot system, measures to ensure minimal losses of energy are put in place. Insulation materials are provided to limit heat loss. In general, the earlier described considerations guide the course taken by the design.
References
Belfast Engineering Institute (2009). Resources, Tools and Basic Information for Engineering and Design of Technical Applications.
Brian, P. (2006). Choosing the best approach in assembly and manufacturing. Journal of Manufacturing processes, 45(4), 456-472.
Cummings, S.J. (2008). Australian water closet developments and their role in sustainable sanitation. Department of Industrial Design, University of Canberra, Australia.
Daryll, P. (2008). Product Design Specification: Making the right choices. New York: John Wiley and Sons.
DETR (2000). Building a better quality of life: A Strategy for more Sustainable Construction. Department of Environment, Transport & Regions, UK.
Frankel, M. (2005). Facility Piping Systems Handbook. London: McGraw Hill.
Randolph, J. (2010). Water delivery systems. Web.
Sawah, S. E. et al. (2009). Modeling water resource in the Australian Capital Territory: Knowledge elicitation for system dynamics model building. 18th World IMACS / MODSIM Congress, Cairns, Australia.
Singh, H. (2001). Materials selection processes. India: Prakatch.
Vennix, J. et al. (1990). “A structured approach to knowledge elicitation in conceptual model building.” System Dynamics Review, 6(2), pp.194-208.