Abstract
This research paper seeks to investigate the relationship between customers’ perception of public relation and customers’ loyalty. The research will also investigate the role played by the brand image in shaping customer perception towards the organization.
Research Design/methodology- The research will use both primary and secondary sources of data. The primary data will be collected from a sample of customers of City Bank with the help of a questionnaire. The research will use two hypotheses.
Findings- The results of the study evidently demonstrate that the sensitivity of clients towards organization’s public relation practice is an indication of their devotion. From the research, it is clear that when there is a favorable brand image among customers, public relation perception will always have a heavy impact on customer loyalty.
Research limitations/implication- This research seeks to expound on the existing research as regards to customer loyalty. The researcher faced the problem of unwillingness since some respondents were unwilling to answer questions.
Originality- The researcher was concerned with coming up with an original piece of research that could be applied in a real life scenario.
Keywords- Brand image, Public relation, Customer loyalty, Customer relations, Finance industry, financial services, the United States
Introduction
According to Hsieh and Li (2008), there is a direct relationship between customer perception of public relation and customer loyalty. These scholars hold that when a customer has a positive perception of public relations of a firm, he or she will tend to be loyal to that firm. This loyalty will further enhance a positive perception of the public relation of the firm.
Brand image plays a moderating role in this relationship. When a firm has a strong brand image in the market, the perception of the public would always be influenced positively towards the firm, and this will increase loyalty of the customers towards the firm (Hsieh & Li, 2008).
The role of marketing in creating and maintaining a pool of loyal customers is becoming more prominent in the twenty fist century. Marketers are under pressure to ensure that loyalty among customers is established. Customer loyalty is always considered a central pillar in marketing activities of the organization. This is because without customer loyalty, it may not be easy to maintain a positive image of a firm in the market.
When a company is able to develop, maintain, and enhance customer loyalty, it gains a competitive edge in the market hence acquiring the opportunity to increase its market share in the market. Customer loyalty can also enhance the image of the organization through positive word of mouth, which in turn leads to increased profit margins for the company.
Scholars define public relations as the management function, which aims at identifying, establishing, and enhancing mutual benefits between the firm and its public. This would determine the failure or the success of the company. Loyal customers are said to enjoy the public relations practices of the company as compared to those customers who buy and go without staying for long in their in the company.
It is essential for the customers to be aware of the organization-public relation since this will promote customer loyalty in the organization, which would lead to increased number of sales (Aaker, 1997).
A recent study shows that there is intense competition in the finance industry. Numerous financial institutions are in existence meaning that competition is stiff (Chaudhuri, and Holbrook, 2001). The management of Citibank should come up with strategies that would enable it manage this competition.
Developing a public relations system would help in increasing the company’s customer loyalty. This essay aims at explaining the relationship between the brand image, public relations practices, and customer loyalty with focus on offering a professional advice to Citibank on how to enhance customer loyalty.
Literature Review and Hypothesis
The finance industry is increasingly becoming competitive. Financial firms are under pressure to deliver more quality services to their customer in order to increase satisfaction (Belk, 2008). This quality is always formed in the minds of consumers.
Public relation is important in influencing customer perception as regards to a given brand (Anderson, & Gerbing, 2002). The figure below shows the relationship between public relations perception of customers, customer loyalty, and brand image, which is the basis of this research.
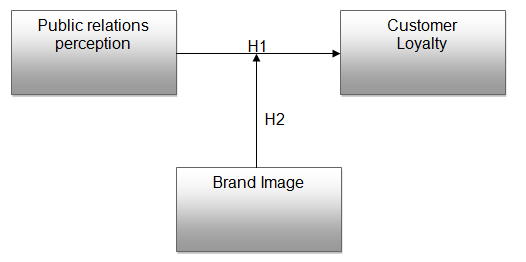
From the diagram above, public relations perception is shown to have a direct impact on customer loyalty. The brand image plays a role of moderating the operations of the public relations opinion and customer constancy. This can be illustrated with the help of the literature review below.
Clark (2000) stipulated that self-congruence theory rest on the idea that consumers evaluate the products of a company in relation to their self-image. When the congruence between the two is perceived to be high, it has been revealed that it influences the attitude of customers towards the brand. It also influences the decision made by customers in purchasing the product, as well as determining the satisfaction of customers.
On the other hand, when there is incongruence, consumers are likely to withdraw from purchasing the products and services of the organization simply because they will fear to be associated with the negative image of the organization (Chaudhuri, & Holbrook, 2001).
An individual’s self-concept embraces various self-identities, which range from personal identities to social identities. In the studies that have been conducted before, it has been proved that when public relations practices is strong there is an increased demand for social identity, which in return leads to increased self-congruence (Bruning, 2002).
Public relations practices are therefore entitled to create a profile brand association whereby customers of the organization have to be perceived as generous and kind. They also seek to establish a brand personality where the brand personality is portrayed as being sincere (Brown, & Dacin, 1997).
From the study, it is patent that self-congruence and customer expectations are realized with the help of the top management as expressed through public relations. In this case, if the customer self-concept match with the PR actions, customers are likely to be attached to the company for a long period (Dick, & Basu, 2006).
These scholars observed that public perception towards public relations would always influence customer loyalty. This leads to the first hypothesis below.
Customer perception towards public relations (PRP) will be positively related to customer loyalty
In this hypothesis, psychologists hold the view that the memory of an individual lasts for a very long period meaning that once the information received is stored in it, the information it is likely to stay for a considerable duration.
In the field of marketing, this is referred as the halo effect whereby the influence of a particular attribute is influenced by the general impression of the product as a whole on one hand while on the other hand, the evaluation of an attribute as a whole can create an effect on particular aspects of the object.
This therefore proves that maintaining cognitive consistence helps in deterring cognitive differences (Dutton, Dukerich, & Harquailn, 2004).This indicates that when the brand image of an organization is favorable, the customers, who in return maintain the positive beliefs, and behaviors, will perceive the public relations practices as genuine hence harmonizing the reputation of the company.
However, when consumers perceive brand image in their cognitive processes as unfavorable, it becomes difficult for the PR practices to change this perception.
When there is inconsistency in the memory of customers, they would likely develop a psychological tendency of balanced differences, which creates fear on customers hence a go slow in consuming products and services of that particular company (Ekinci & Riley, 2003). This would lead to the formulation of the second hypothesis, which is stated as below.
The relationship between PRP and customer loyalty is moderated by brand image
Research Methodology
The data of the research were collected from experienced customers of Citibank in the New York branches. This essay looks into the financial firms, as they are the ones, which dictate maximum public relations practices as compared to the manufacturing industry.
The research was conducted in a form of interviews where the sampled customers were asked questions related to insurance companies familiar to them (Chiou and Droge, 2006).
In the research, PRP was considered an independent variable, which was measured in terms of the manner in which customers perceive the commitment of the corporation in terms of time, resources, and efforts towards generating public relations activities.
Brand image on the other hand was used as the moderating variable. In this case, the brand image was measured in terms of experiential benefits, symbolic benefits, and as functional benefits (Ellen, Mohr, & Webb, 2000).
During research, several factors were controlled for the results obtained to be perceived as valid. The controlled factors included sex of respondents, disposable income, altruism, and age.
In the study, altruism was considered the act of utilitarianism, which aims at promoting the welfare of others. In the issue of validity and reliability, the study used various approaches in the analysis of data collected, which includes confirmatory factor analysis, exploratory and reliability analysis (Devellis, 2001).
Analysis of the Results
The results obtained in the research were tested through hierarchical regression. This was aimed at proving the hypotheses that were presented in the study. In relation to the four controlled factors used in the research, it was discovered that altruistic and disposable income variables created an effect on the consumer loyalty.
This indicates that commitment of an organization towards PR activities is likely to increase customer purchases, as well as refer other people to buy company products (Homburg, & Giering, 2001).
In the second hypothesis, PR practices are said to depend on the level of brand image. The brand image is seen as a factor that controls the connection between public relation and consumer allegiance. In the analysis, the results were split into groups of favorable and unfavorable brand image.
It was revealed that a good brand image preserves customer allegiance while inauspicious brand image generates a harmful result to client fidelity (Ellen, Mohr, & Webb, 2000). The management should always ensure that the brand image is improved through such avenues as advertising.
Discussion of the Findings
This study is dedicated to explaining the influence of PRP on customer loyalty since it has investigated how the attitudes towards a brand image affect the relationship. It has been discovered through research that when the brand image of an organization is strong, the PRP is likely to affect the customer loyalty positively.
In the analysis of the results, it was also realized that when the perception of the customers is higher towards the PRP, the customer loyalty would also increase (Garbarino, & Johnson, 1999).
In the second hypothesis, the results indicate that brand image acceptance raises the level of customer loyalty towards a corporation. It is therefore suggested that the needs of consumers help in developing products and services of the company. It was concluded that the brand image, as well as the corporate image, could affect the attitudes and beliefs of the company either positively or negatively (Fredericks, Hurd & Salter, 2001).
The management of Citibank should come up with mechanisms that would help in improving its brand image. With an improved brand image, Citibank can increase its customer loyalty by influencing the perception of public relation towards the firm positively.
Implications and Limitations
The study explored the reasons as to why managers should enhance the brand in the improving the image of their organizations, which would help them to gain customer loyalty (Abdullah, Al-Nasser, & Husain, 2000). The study has also expressed numerous details that affect brand image and the performance of the firm.
Moreover, it analyzed the manner in which brand image influences consumer allegiance. Managers should enhance their brand images for the PR practices to achieve their intended goals (Homburg, & Giering, 2001). This will have a positive ripple effect to the firm.
The research had some limitations when. It was limited to customers of Citibank in its branches in New York. This is because of the limited time for conducting research. The research was also limited to the financial industry. Further studies should be carried out based on this in order to prove the hypothesis further (Abdullah, Al-Nasser, & Husain, 2000).
Conclusion
The management of Citibank has a big role to play in ensuring that they develop customer loyalty towards their brand. The management should ensure that it influences public relations perception towards their products.
This would make customers develop a favorable perception towards the company brand. This would also increase customer loyalty towards the brand, a fact that will help the organization increase its market share in this industry.
References
Aaker, J.L. (1997). Dimensions of brand personality. Journal of Marketing Research, 34(3), 347-57.
Abdullah, M., Al-Nasser, A.D., & Husain, N. (2000). Evaluating functional relationship between image, customer satisfaction, and customer loyalty using general maximum. Total Quality Management, 11(4), 826-9.
Anderson, J.C., & Gerbing, D. W. (2002). Structural equation modeling in practice: a review and recommenced two-step approach. Psychological Bulletin, 103(3), 411-23.
Belk, R. (2008). Possessions and the extended self. Journal of Consumer Research, 15(1), 139-68.
Brown, T.J., & Dacin, P.A. (1997). The company and the product: corporate associations and consumer product responses. Journal of Marketing, 61(1), 68-84.
Bruning, S.D., (2002). Relationship building as a retention strategy: linking relationship attitudes and satisfaction evaluations to behavioral outcomes. Public Relations Review, 28(1), 39-48.
Chaudhuri, A., & Holbrook, M.B. (2001). The chain of effects from brand trust and brand affect to brand performance the role of brand loyalty, Journal of Marketing, 65(2), 81-93.
Chiou, J.S., & Droge, C. (2006). Service quality, trust, specific asset investment, and expertise: Direct and indirect effects in a satisfaction-loyalty framework. Journal of the Academy of Marketing science, 34(4), 613-27.
Clark, C.E. (2000). Differences between public relations and corporate social responsibility: an analysis. Public Relations Review, 26(3), 363-80.
Devellis, R.F. (2001). Scale Development: Theories and Application. Newbury Park, CA. Sage.
Dick, A.S., & Basu, K. (2006). Customer loyalty: toward an integrated conceptual framework. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science, 22(2), 99-113.
Dutton, J.E., Dukerich, H.M., & Harquailn, C.V. (2004). Organizational images and member identification. Administrative Science Quarterly, 39(2), 239-63.
Ekinci, Y., & Riley, M. (2003). An investigation of self-concept: actual and ideal self-congruence compared in the contest of service evaluation. Journal of Retailing and Consumer Services, 10(4), 201-14.
Ellen, P.S., Mohr, L.A., & Webb, D.J. (2000). Charitable programs and the retailer: do they mix? Journal of Retailing, 76(3), 393-406.
Fredericks, J.O., Hurd, R.R., & Salter, J.M. (2001). Connecting customer loyalty to financial results. Marketing Management, 10(1), 26-32.
Garbarino, E. & Johnson, M.S. (1999). The difference roles of satisfaction, trust, and commitment in customer relationships. Journal of Marketing, 63(2), 70-87.
Homburg, C., & Giering, A. (2001). Personal characteristics as moderators of the relationship between customer satisfaction and loyalty-an empirical analysis. Psychology & Marketing, 18(1), 43-66.
Hsieh, A. & Li, C. (2008). The moderating effect of brand image on public relations perception and customer loyalty. Marketing Intelligence & Planning, 26(1), 26-42.