Introduction
Banking is one of the prosperous spheres in the modern world. Nowadays, the business environment is unstable, and it involves a plethora of challenges. Thus, the banking segment is under a vehement influence of these matters, and the managers are required to face an extended variety of difficulties. Using the examples and contrasting the products and services of Emirates NBD and Bank of Singapore will assist in understanding the key problems and consequences of the global business environment.
In the context of this paper, utilizing the Iceberg model and EGSOP analysis will have a beneficial influence on acquiring a profound understanding of the situation in the banking sector. Simultaneously, taking advantage of the assessments conducted previously will help design recommendations for the future prosperity of these banks. In the end, the conclusions are drawn to summarize the critical findings of the paper.
Description: Background and History
In the first place, Emirates NBD is one of the most popular banks in the United Arab Emirates with well-develop product lines for corporate and private customers (Emirates NBD: main page 2016). With its main office in Dubai, the bank was developed by the consolidation of Emirates Bank International and the National Bank of Dubai (Emirates NBD: main page 2016).
In this instance, the top of the iceberg is the actual products of the company, which are available for consumers and represented by credit cards, premium accounts, packages, online solutions, and services such as wealth and asset management and insurance (Emirates NBD: main page 2016).
As for its vision, it tends to emphasize its excellence in services and the need to pursue the leading positions in this area, and it is the key concept of this business, which inside and bottom segments of the Iceberg have to cherish as their key priorities. In this case, it has a tendency to reach its aims by focusing on talent recruitment by motivating its employees by financial and other types of rewards (Emirates NBD: how we work 2016). As for the top management of the company, it ensures that the quality of the services meets the perceived expectations, and the managers pay attention to the compliance of employees’ personal growth with the business strategy.
On the contrary, Bank of Singapore is an international bank with its headquarters in Singapore, and its principal offices are located in Dubai, Hong Kong, and the Philippines (Bank of Singapore: main 2016). It started its existence and operations as an independent business entity after being acquired by ING Asia Private Bank (Bank of Singapore: history 2016). This bank also has an extended variety of products and services such as advisory, wealth management, and loans (Bank of Singapore: main 2016).
Simultaneously, it offers typical corporate and consumer banking services while being a subsidiary of OCBC Bank. Its inside of the iceberg is the company’s goal of being transparent in its transactions and operations and ensuring the safety of its clients (Bank of Singapore: corporate governance 2016). It’s bottom up streams control the transparency of all operations and assure that they meet the company’s mission statement. Overall, both banks have similarities in their iceberg structures but having dissimilar strategies is the primary difference.
Key Points
The previous chapter clearly defined the concepts, products, and strategies of Emirates NBD and Bank of Singapore. Nonetheless, applying EGSOP analysis will assist in understanding the challenges that the company has to face. In the first place, it is essential to evaluate the external environment (E), which creates difficulties for both financial institutions. In this case, having an international focus intensifies the competition and decreases the market shares of the companies. Simultaneously, it is predicted that the United Arab Emirates have favorable conditions for the development of the banking sector (Emirates NBD: investor presentation 2016).
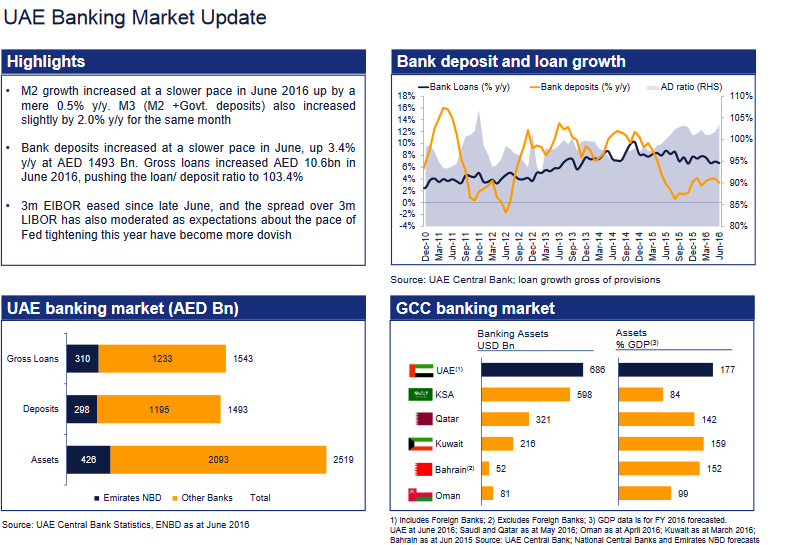
Another aspect to be assessed in accordance with the EGSOP model is the organizational structure (O). Due to the critical focus of the Bank of Singapore on transparency, it has a substantial number of committees to monitor and audit the transactions (Bank of Singapore: corporate governance report 2015). Speaking of Emirates NBD, it has an emphasis on relationships and the presence of the family business concept (Emirates NBD: how we work 2016). It creates a strong bond between the employees and management and has a positive impact on the quality of interactions.
At the same time, governance (G) of the companies and their strategies (S) cannot be underestimated. As was mentioned earlier, Bank of Singapore prioritizes transparency as one of its principal goals (Bank of Singapore: corporate governance 2016). All of its financial and administrative reports are available to the public, and it creates an image of safety to its clients while connecting the bank’s mission to the clients (Bank of Singapore: corporate governance 2016).
On the contrary, Emirates NBD has a tendency to pay attention to the exceptional skills of the employees and their talents (Emirates NBD: how we work 2016). The company’s governance is built around this concept and implies that it vehemently involves employees in the decision-making process.
Furthermore, performance (P) of both banks has to be compared to determine the financial orientation and prosperity. In this case, the Bank of Singapore has an annual income of $885 million (OCBC Bank 2016).
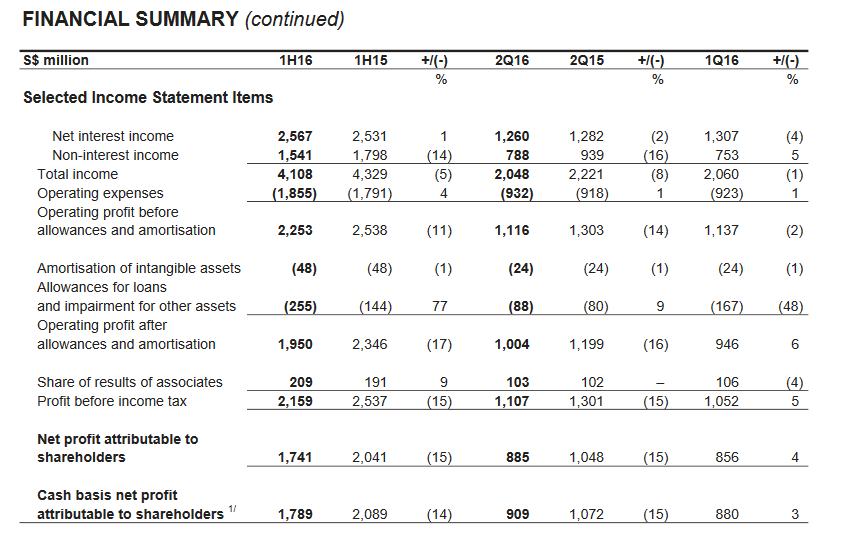
Simultaneously, Emirates NBD experiences growth in sales of its major products due to the positive development of the banking sector (Emirates NBD: investor presentation 2016).
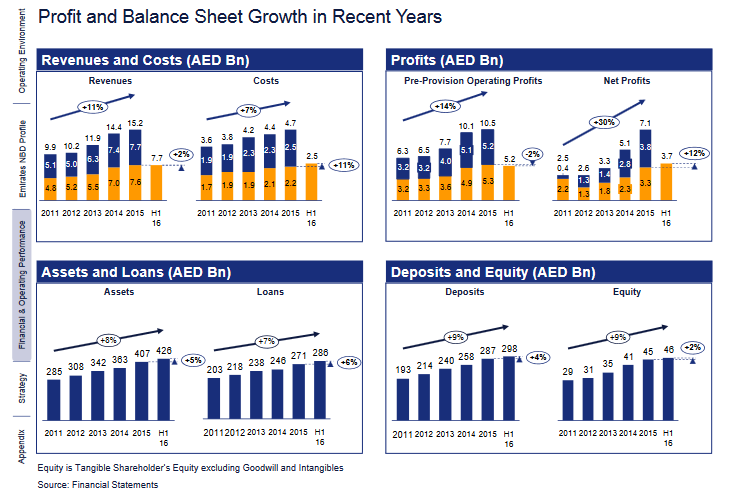
Issues and Problems
Despite the well-defined strategies of both banks, different issues and problems cannot be underrated, as they take place due to the gaps in the current organizational structures, tactics, and governance. It could be said that one of the main issues in the focus of the companies on particular segments. It remains apparent that using these methods creates a distinct competitive advantage among competitors, but the management tends to underestimate other parts of the company (Breznik & Lahovnik 2016). The existence of this gap makes the firms vulnerable to changes in the business environment.
Another potential problem is the international presence of the banks. In this case, their profits are dependent on the transactions in the financial markets and the currency exchange rates (Ritzer & Dean 2015). Simultaneously, globalization shifts the number of competitors while making international rivalry more intense (Ritzer & Dean 2015). In this instance, more and more companies with similar products and services are available and, this trend elevates the number of substitutes (Ritzer & Dean 2015). Considering this aspect is vital since it defines the financial benefits of the company and determines the demand for its products and services.
Lastly, tensions with the employees and misunderstandings are present in Singapore Bank, as the management of this organization underestimates its significance. It may decrease the overall quality of products and services. On the contrary, Emirates NBD may have issues with the recognition and brand image, as not focusing on transparency as much as Singapore Bank may damage its social responsibility strategy.
Discussion
To summarize, both banks will have to face a plethora of different issues, which will have an effect on the demand curves of their products. Having an imbalanced strategy, being dependent on the participant of the global trade, conflicts with the workforce, and the lack of social responsibility are the most common problems that the banks face. Despite having a clear connection with the banking segment in the presented text, these issues are rather common in the business world.
They are highly recognized by scholars and business practitioners, as globalization and developing a distinct competitive advantage are the essential attributes of the global business environment (Ritzer & Dean 2015; Breznik & Lahovnik 2016). Nevertheless, the companies should attempt to resolve the issues, as current financial success and growth do not guarantee their financial prosperity in the future.
It remains apparent that the comparison reflected above is vital since it helps see that despite operating in a similar sector, the banks have a tendency to pursue different strategies to differentiate from the competitors. For instance, Bank of Singapore has a tendency to focus on prosperity while Emirates NBD prioritizes its employees as important assets.
Understanding these differences reveals that apart from facing common issues related to globalization and intensified competition, the companies have to overcome difficulties associated with their individual strategies. For example, having analogous products implies that firms have similar value propositions. However, their principles of governance and managerial tactics might make their operations challenging. Overall, this comparison determines that the case of every organization has to be reviewed individually, as they have well-defined strengths and weaknesses.
Way Forward
A combination of analyses conducted above helps understand that the selected organizations have a tendency to face difficulties in different spheres. One of the potential ways to resolve the presented solutions is to copy the best practices of the competitors. In this case, the Bank of Singapore can apply the principles of talent recruitment to enhance the quality of the services and increase customers’ satisfaction. On the contrary, Emirates NBD can take advantage of the concepts of transparency used in the Bank of Singapore.
Alternatively, living in the era of globalization implies that all participants are dependent on each other (Ritzer & Dean 2015). Consequently, focusing on the international strategy will assist both companies in monitoring global trends and taking advantage of the opportunities of modern times.
In this case, reviewing the actions of the rival firms will enhance the product lines and increase the market shares of the banks. Lastly, to avoid the negative consequence and decrease the drawbacks of the current issues and problems, both banks will need to redesign their present strategies. As it was mentioned earlier, adding the concepts of the global strategy, underlining the importance of transparency and talent recruitment, and emphasizing the significance of research and development will assist both banks in enhancing their value propositions while causing an upward shift in the demands for their products and services.
Conclusion
Overall, despite operating in a similar service sector, Emirates NBD and Bank of Singapore have different product propositions and relatively dissimilar values and strategies. The significant difference lays in the company’s tactics since the Bank of Singapore focuses on transparency while Emirates NBD pays vehement attention to the excellence of the banking services. Nonetheless, in spite of having substantial differences in organizational structure and management systems, both banks face intensified rivalry due to globalization. In this case, learning from competitors, redesigning the current strategies, and not underestimating the role of research and development will resolve the difficulties of the modern business environment.
Reference List
Bank of Singapore: corporate governance. 2016. Web.
Bank of Singapore: corporate governance report. 2015. Web.
Bank of Singapore: history. 2016. Web.
Bank of Singapore: main. 2016. Web.
Breznik, L & Lahovnik, M 2016, ‘Dynamic capabilities and competitive advantage: findings from case studies’, Management, vol. 21, no. 1, pp. 167-185.
Emirates NBD: how we work. 2016. Web.
Emirates NBD: investor presentation. 2016. Web.
Emirates NBD: main page. 2016. Web.
OCBC Bank. 2016. Web.
Ritzer, G & Dean, P 2015. Globalization: a basic text, John Wiley & Sons, Hoboken.