Executive Summary
The report is prepared for depicting the strategic management of Ryanair, Europe’s largest airline in terms of passengers at low fares. To evaluate the strategic management, Ryanair’s strategic movement has been compared with Emirates, Asia, one of the luxurious airlines with supreme quality of services. The report has been segmented into four parts. The first part is concentrated on the comparison of Ryanair and Emirates. This comparison shows that there’s a huge difference in the strategic management of the two companies. Ryanair’s strategic management is concentrated on low fares in the airline industry. On the other hand, Emirates is considering the quality of services and luxuriousness. Ryanair’s ruthless control over cost makes it gain a higher level of administrative efficiency. Emirates outlandish expenses to provide quality services attract many rich Asians. So, the business model is different. The second part of the report elucidates the main aspirations of key stakeholders and how their aspiration affects the pursued strategy. Stakeholder wants to maximize their profits through dividend payout ratio. When an agency problem arises, the strategy is changed. Ryanair is enlisted in NASDAQ and the Irish stock exchange. From the last couple of weeks, its share price is declining rapidly, means shareholder finds no interest in investing anymore. The third part of the report is illustrated with porter’s value chain analysis. The prime objective for this illustration is to depicting cost leadership and cost management. The process is designated with five steps, including backward and forward operations. The last part of the report is concerned with diversification. This is shown by evaluating several factors, which are indicating the company is firmly attached to the airline industry with associated supportive businesses.
Introduction
To understand the strategic development and to apply it in the real world, it is necessary to understand the key factors of the strategic management process, and it will be best if it can be related to some company. Hence, the report is attached with Ryanair and Emirates to show their strategic movement. Success is built on the strategy. So, to make it effective proper understanding and practical experience is required. The report can fulfil the partial requirement of this objective.
Comparison and contrast between Emirates and Ryanair
Business model
Closely related to the concept of strategy is the concept of a company’s business model, a term now widely applied to management’s plan for making money in a particular business? More formally, a company’s business model deals with the revenue-cost-profit economics of its strategy – the actual and projected revenue streams generated by the company’s product offerings and competitive approaches, the associated cost structure and profit margins, and the resulting earnings stream and return on investment.
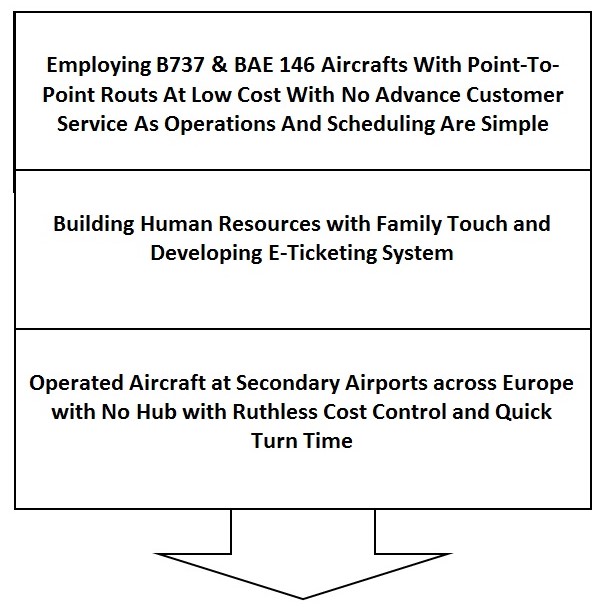
The business model of Ryanair
The business model of Emirates
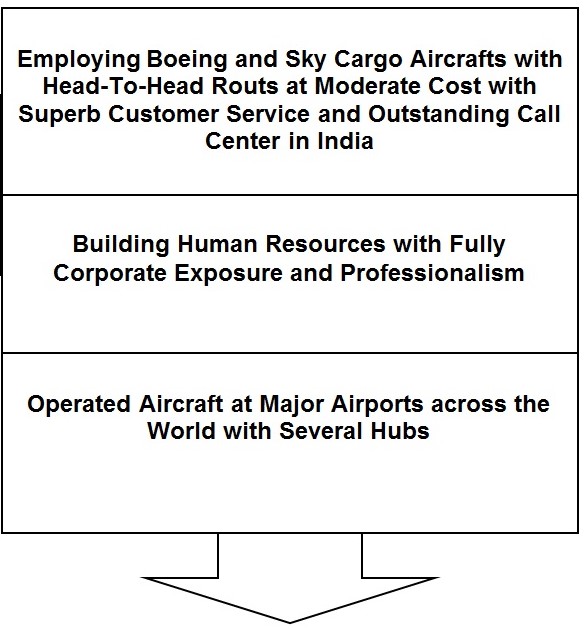
From the above business model, it is seen that there is a converse relationship between Ryanair and Emirates. Ryanair is concerned with cost control. Therefore, it is using secondary airports rather than majors. Therefore, passengers of emirates can avail of extra concession while purchasing goods and services. These are the major sources of revenue that they use.
Tasks of developing the strategic development
Several interrelated managerial tasks are involved in strategic development. The process is similar for both airlines, but key functions or attributes are different. Below these are described:
Developing a strategic vision and business mission
Ryanair
- Mission: Ryanair’s objective is to firmly establish itself as Europe’s leading low-fares scheduled passenger airline through continued improvements and expanded offerings of its low-fares service.
- Vision: Be the leading airline and best in customer service.
Setting objectives
Ryanair
Ryanair sets the following objectives to implement its strategy:
- Be low-cost leadership
- Cost control
- Build employees to handle multiple jobs at a time
- To save the time of passengers by using point-to-point routs
- Make a quick turnaround
Emirates
Emirate is concentrating on the quality of services. The objectives are presented below:
- To ensure the quality of services with luxuriousness
- To build up outstanding customer services
- State-of-art technology
Crafting a strategy to achieve the objectives
Ryanair
Ryanair pursues a low-cost strategy. It can be viewed at best from the quotation of the CEO of Ryanair, “We want to be the Wal-Mart of the Airline business. No one will beat us on price. Ever”2. While British Airways was receiving fare on an international intra-European route of 180-200, Ryanair was fixed at 50-80. So, it is a huge gap between the two airlines. From the following graph, this can be clarified:
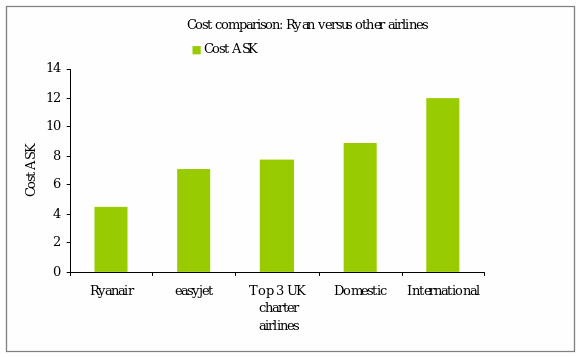
Therefore, to survive in the market with low cost, Ryanair pursues several strategies. These are given below:
- Ryanair uses no hub. Therefore, the takeoff costs, additional customer expenses, and meal costs as reduced.
- As it is using point-to-point the, time to go to destination is reduced. The fuel, administrative and engine maintenance costs are declined.
- Secondary airports are used due to congestion in majors and to save reachable time to airports of customers. This policy is very popular with the customers.
- The airline advertises to convince its customer to believe that its plane is more time-saver than using Buses, Trains and also it is affordable.
Therefore, these are the external strategies used to operate their activities. As the cost control method is implemented effectively, the overall procedures have been conglomerated successfully.
Emirates
Emirates strategies are totally different from pursuing its customers. The main principle of Emirates has to underlie in service and quality. The major undertaking strategies are given below:
- Emirates aimed to expand its service throughout the world and hence increase its seat capacity with large aircraft. So, it was getting the advantages of economies of scale and reduced the cost.
- E-ticket system is a competitive advantage for Emirates. Emirates wants all tickets should be sold online. So, customers can avail themselves of the advantages from anywhere in the world, and administrative costs are reduced.
- Customer service is a distinctive competence for Emirates. It has been established with 43000 square feet in area with the capability to manage 300 call centres in India, which is best ever known.
- Market segmentation is another strong strategy to pursue. Emirates segmented its market into students, tourists, corporate and business groups with state-of-art technology.
- To expand its brand recognition, Emirates is creating its Brand awareness like in sports.
- Besides transferring passengers, Emirates wants to boost its revenue by extending its business line with sky cargo. In the fiscal year, Emirates has transferred 947000 tonnes of cargo.
Implementing and executing the strategy
The managerial task of implementing and executing the chosen strategy entails assessing what it will take to develop the needed organizational capabilities and to reach the targeted objectives on schedule. Below the implementation and execution strategy of both aeroplanes is presented:
Building an organization capable of carrying out the strategy successfully
Ryanair
Ryanair is operating 74 aircraft in 127 routs and has a confirmed order of B7C7. The major routes include Dublin Airport, London Stansted Airport, Orio al Serio Airport, Rome Ciampino Airport, Shannon Airport, Pisa Galileo Galilei Airport, Brussels South Charleroi, Frankfurt-Hahn Airport, Cork, and Liverpool John Lennon.
Emirates
Emirates has 114 aircrafts 65% are Airbus. Emirates has established a state-of-art call centre in India to meet the queries of Australia and the USA with the collaboration of major telecoms like Airtel, Vodafone and 8000 cabin crews are recruited. The largest civil aviation maintenance named “Emirates Engineering centre” is established to execute the strategies in Dubai with a total area is equal to 17 soccer fields. The total number of pilots is increased to 339 for rapid and Continuous development.
To carry out goods for export and import, Emirates has established an import-export processing zone named with Sky cargo.
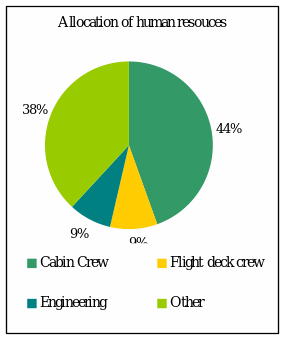
Allocating company resources to operate current activities and for future needs
The allocation of resources to pursue its operation is presented below by using a chart:
Establishing strategy supportive policies and operating procedures
Ryanair
To support its main operation Ryanair uses tourism business affiliated with main concern. Car arrangement, hotel booking, tourism, recreation management are considered most. The customer management has been transferred to a third party to have control over the cost.
Emirates
Emirates is building in line with IATA to simplifying the business activities aimed at a 100% e-ticketing system. Establishing more retail outlets for brand identity with extensive sales and training program. Sponsorship, promotion and events are organizing to expand the brand awareness to support its original strategy.
Evaluating performance, monitoring new developments and initiating corrective adjustments
Ryanair
Ryanair always compares its competitive strengths with other major operations. From the investors’ presentation, the following table has been presented:
The points are representing one is worst, and five is best. Except for values for money, and Ryanair has clearly ahead. Its management efficiencies have surpassed all other major airlines.
Emirates
A team of service audit managers has been formed to audit at least 500 flights, 8 destinations, 180 audits on the call centre. This ensures the quality and standards. This audit team also inspects the other six major competitors to set up the benchmark. A total of 14 stations are audited per year, and close scrutiny is conducted over the passengers’ satisfaction. Corrective steps are always taken if any mistakes are found in opportunities. The gigantic equipment is relocated to other places as opportunities are more.
Competitive strengths and weaknesses
Competitive strengths and weaknesses can be contrasted with different factors. The comparison is given below:
PEST analysis for Ryanair
- Political: Any political condition changes the business environment, increase or decreases the risk. Suppose if Government wants to hike up the oil price for political turmoil, it has an adverse impact on the business. Recently, the UK has signed up in the single European currency. This must have a direct impact on the business. Like Ryanair and other airways will face the changes in the exchange rate.
- Economical: The central bank can use monetary and fiscal policy. Changing the interest rate can directly influence the business. Recently the central bank of England cut its interest rate to 5%. This will change the money supply in the UK market. Like Ryanair and other airways will take more loans from financial institutions and can invest in their specific concern. So, changes in the economic situation affect the investment strategy of the firms.
- Social: Society, people, friends, etc., change the economic conditions. Their behaviour, attitude, demand has a direct relationship with the business. In the UK, people are changing their attitudes toward dieting and health. So, this situation can change the business structure in two ways.
- Technological: Changes in the technology sector will impose a direct impact on the organization or the overall business process. The transaction cost or information exchanging cost can be reduced as 24 hours call centre. Internet facilities are establishing more. The technological changes speed up the organization, production process, creates employment. The quality of goods and services is increasing as more corrective steps can be taken through technology. In the UK, the technology sector is reshaping the overall production process.
SWOT analysis of Ryanair
Porter’s 5 Factor model analyses
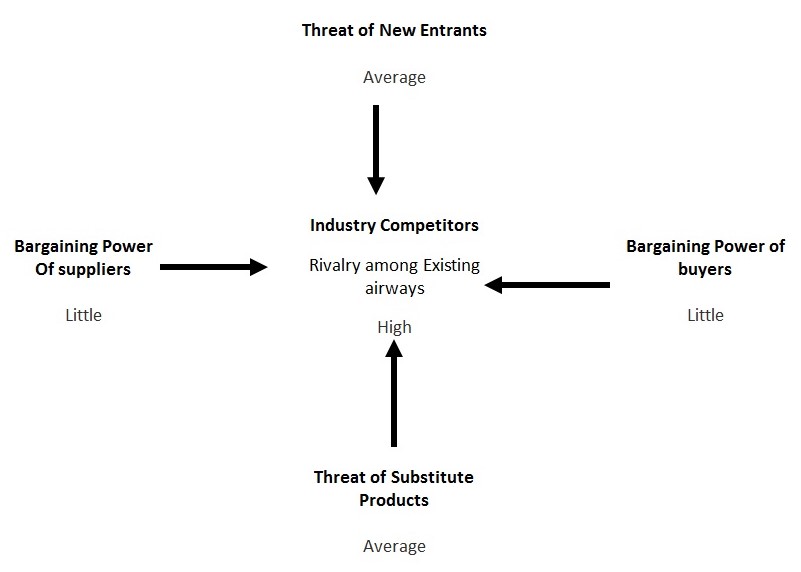
The above figure shows the factors that are affecting industry competitors. As fare is low, buyer bargaining power is poor. Threats of substitutes are low as the market is saturated. Bargaining power with the supplier is poor as they can switch towards another way at any time.
Analysis of competitive strength by using Porter’s value chain analysis
According to Porter, A company’s value chain and the manner in which it performs each actively reflects the evolution of its own particular business and internal operations, its strategy, the approaches it is using to execute the strategy and the underlying economics of the activities themselves. The value chain of Ryanair is analyzed below:
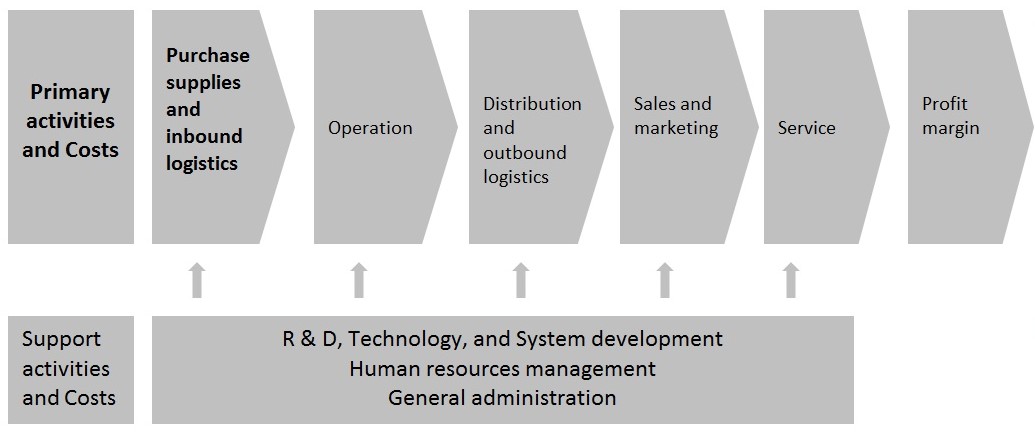
Ryanair is creating a cost advantage by reducing the cost of materials. Once Ryanair establishes the value chain method, the assigned costs can be differentiated through different steps. In which segment cost should be minimized or in which segment cost should be increased can be known. There are ten cost drivers related to Ryanair value chain analysis; these are:
- Economies of scale
- Firm’s policy of cost or differentiation
- Learning
- Timing of market entry
- Linkages among activities
- Institutional factors (regulation, union activity, taxes, etc.)
- Interrelationships among business units
- Capacity utilization
- Degree of vertical integration
- Geographic location
Ryanair gets economies of scale as it operates the same kind of fleet. EU regulation has forced Ryanair to change its policy, and hence the cost structure has been changed. Geographical location is limited to UK and EU. Capacity utilization is an excellent factor as it can attract more passengers. The load factor is 84% on average.
Purchase supplies and inbound logistics
This includes activities, costs, and assets associated with purchasing fuel, energy, raw materials, parts components, merchandise, and consumable items from vendors; receiving, storing, and disseminating inputs from suppliers; inspection; and inventory management. The major aircraft supplier is Boeing. It has 74 Boeings, and before shifted to Boeings, it used Embraer Bandeirante (1985-1989), AVRO 748 (1986-1989), BAC One-Eleven (1987-1994), ATR-42(1989-1991).
- Operation: The operations are conducted with several features; goods priced at low cost even at free of cost in different zones, e-ticketing system, no-frills, limited crews, alliances.
- Distribution and outbound logistics: Outsourcing and third party dominate the ticketing and customer care system. Quick turnaround is a major attribute of the distribution of services (around 20 minutes).
- Sales and marketing: This includes low-tech marketing, internet sales, low-cost promotions, free publicity, controversy and internet sales. Marketing and distribution costs were 15563 in 2007.
- Services: This includes fewer customer services as Ryanair uses the simplest method to deliver information to the customers.
- Profit margin: Profit margin is increasing sharply for proper maintaining low cost and achieves administrative efficiency. In 2005 the profit margin was about 198 million in euro.
Main aspirations of key stakeholders of Ryanair’s strategy
The share price and EPS are affected by the aspirations of the shareholder as the agency problem is arisen. Management bodies may want to maximize the profit, and stakeholders may want to maximize the firm’s wealth for a greater degree of valuation. So, the firm may change its current strategy for retaining its profit and may go for expansion. A “Stakeholders-are-king” is the philosophy that links the need for culture change to the need to serve the long-term best interests of all key constituencies. The pursuing strategy of Ryanair may be supported by various supportive policies to keep its culture at an optimum level. The culture means the investment policy, strategy for maintaining and implementing, dividend payout ratio and etc. The shareholders’ aspiration affects these factors. The share prices are decreasing over time. It means the company meets the stakeholder’s aspiration, and shareholders are moving their funds to another as a better opportunity exists. Thus, this is affecting the overall valuation of the firm. As a share price is decreasing, the sources of finance may be unavailable.
Recently the acquisition of BUZZ has had an adverse impact on Ryanair as a stakeholder does not see any prospect, and this is one of the major causes for price decreeing. Though EPS is high and increasing over time and has an adverse relationship with actual share price, shareholder sees as the firm is maximizing its profit rather than wealth maximization. The offering product is varying over time. A stakeholder is opposing to shut down the offer of the free fly as the correlation is negative with promotional activities. So, in these ways, the firm’s strategies are affecting by stakeholders aspirations.
From the above graph, it is seen that the process of shares is decreasing over the week. This may force stakeholders to move their money to another market.
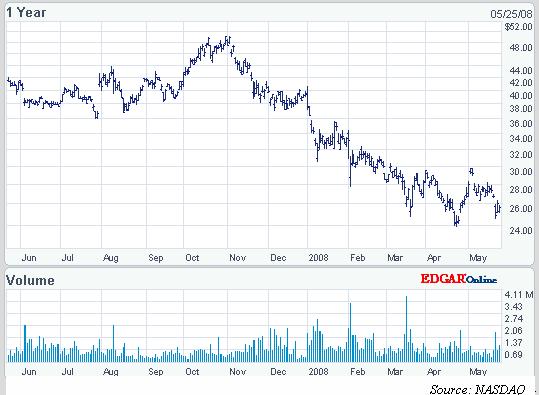
The NASDAQ represents the same structure of share price over the year. It indicates the profitability and financial activities performance is decreasing. Shareholders aspiration includes enhancing the company environment for maximizing profitability and success.
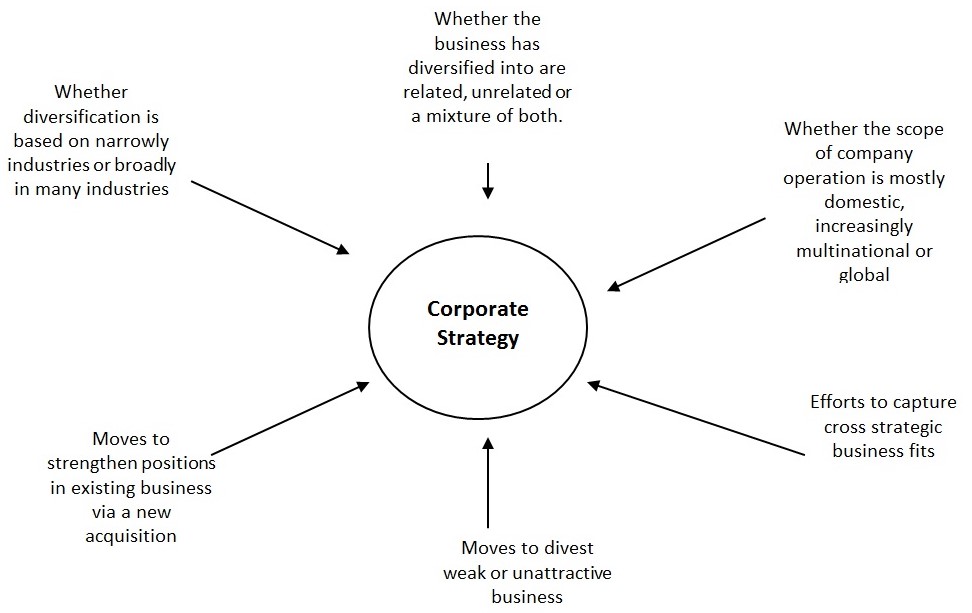
Ryanair’s strategy concerning diversification
The strategy for diversification of Ryanair’s consisting several factors. The significant factors can be illustrated in the figure below:
According to the first option of the graph, whether diversification is based narrowly on industries or broadly industries. Ryan air is based on airline service. Besides firming on airlines, it builds up associated business like food, travelling, tourism. The business is somehow related as associated businesses are interrelated. The scope of the airline is both domestic and internationalized. Major operations are conducted in European base countries. As Ryanair diversifies into business with associated products, similar operating characteristics, common distribution channels or customers, or some other synergetic factors, it gains a competitive advantage. Ryanair acquires the fleet of several other aircraft, not acquires the whole company.
As Britain is saturated, Ryanair is considering moving into Spain, underdeveloped countries, Germany, Italy, Scandinavia, Eastern Europe and Singapore. Ryan was more concerned about the UK to Ireland flights. Later in European Union, it extends its operation. The route is profitable here. From the graph below, it can easily be understood:
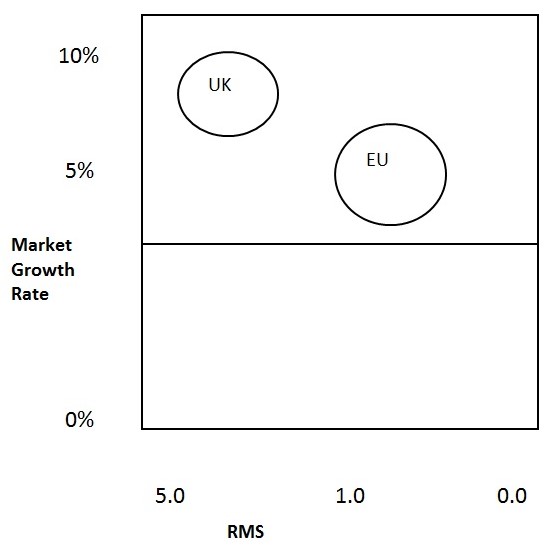
In the EU market growth rate is below the UK, but the percentage in RMS is higher. On the whole, Ryanair feels comfort to conduct its operations in these areas. So the operational diversification is underlying in these areas.
Conclusion
Ryanair is the pioneer of the low-cost provider in Europe in point-to-point routes. It maintains the strategy of administrative efficiency through extensive minimization of costs. It believes in “No frills save money”. It uses the clever and controversial advertisement but results in a huge. For proper maintaining of the customer base, it has become number one customer service in Europe and UK through this division has transferred to the third party. The success of Ryanair has surpassed the major airlines of the UK and in Europe, as it introduces new and unique strategies. Depending on opportunities and market behaviour Ryanair makes its strategic movement dynamic. It is very familiar with taking the chances of opportunities. The relationship with competitors is antagonistic as it is using head to head advertisement and promotional activities. The earning per share indicates the profit margin is increasing over time though the share price is falling over time. The percentage of carrying of the passenger is increasing, and the average growth rate is 21% in comparison with the previous year. Ryanair is not concerned with diversification as it finds more opportunities in UK and Europe. Ruthless cost control is one of the major key success factors of Ryanair. Since the initiation of its operating activities, the pursuing strategy was to follow the cost minimization. As a result, its administrative efficiency is in a peak position. The forward and backward relationship with customers and suppliers is quite good. The chain is maintaining its effectiveness and in a low-cost arena. From the analysis, it can be comprehended that in the recent few years, Ryanair will be the unreachable market leader for its dynamic and aggressive strategy, financial recourses, and strong forward and backward linkage.
Appendices
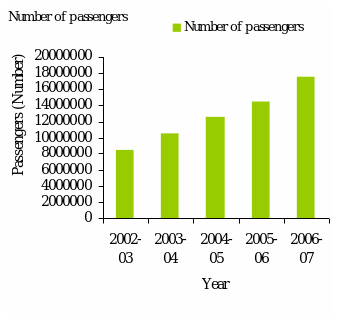
Some statistics of Ryanair
Bibliography
AFP, (2007), Emirates airline boosts Mideast market leader status, CNET Networks, Dubai, Web.
Air fleets (2008), Emirates, Web.
Attitude Travels (2008), Low Cost No Frills Airlines in Europe, Web.
CNET Networks, Inc. (2003), Ryanair completes acquisition of buzz, 2008. Web.
Dibb, S. Simkin, L. Pride, W. M. & Ferrell, O. C. (2001), Marketing Concepts and Strategies, 4th ed., Boston, USA: Houghton Mifflin.
ELFAA (2008), European Low Fares Airline Association Airspace Manifesto, Brussels, Belgium, Web.
Irish Stock Exchange (2008), Ryanair Holdings Plc, Ordinary Shares, Dublin, Web.
Kotler, P., & Armstrong, G., (2008), Principles of Marketing, Prentice Hall of India, 10th ed., New Delhi.
Porter, M. E. (1980), Competitive Strategy, the Free Press, The Free Press, Macilla
Thompson, A. et al (2007), Strategic Management, India: Tata McGraw- Hill Publishing Company limited, 13th edition.
Ryanair Ltd (2008), Cheap Flights – Lowest European Fares, Low Cost Airline, Web.