- Introduction
- Reasons behind the success of Ryanair
- Sustainability of Ryanair’s Strategy
- The Threat of Substitutes
- PESTEL Analysis of Ryanair
- Recommendation to change environmental situation and justification
- Whether Ryanair should introduce long haul flights
- Strategic sense about bid and future decision
- The leadership of Michael O’Leary and future step
- Reference List
Introduction
The purpose of this report is to analyze the case of the low-fares airline “Ryanair” and find out the answer to six specific questions from the case. Therefore, this report focuses on the key success factors, the prospect of Ryanair in the long haul routes, the strategic leadership of Michael O’Leary, the environmental situation over recent years, sustainability of Ryanair’s strategy and so on. However, the Tony Ryan family has established Ryanair in 1985 with only 25 employees to offer scheduled passenger service between the United Kingdom and Ireland, but now this company has about seven thousands employees with operation in 33 bases and more than 950 routes in 26 countries and 66 million passengers (O’Higgins, 2010).
Reasons behind the success of Ryanair
Johnson and others (2008) pointed out the financial condition of Ryanair before 2004 by arguing that the company was in bankruptcy situation as its share price plunged from €6.75 to €4.86, and its sales revenue decreased dramatically despite low fare and its yield reduced more than 25%. However, this situation has changed within a very short time and O’Higgins stated that this company achieved numerous awards such as Best Managed Airline and 2009 FT-ArcelorMittal Boldness in business due to service quality in European market though it has faced some controversies like conflicts with European Commission. However, there are many reasons behind the success of the company but the main influencing factors are –
Pricing strategy or Low Fares offerings
According to the annual report 2009, Ryanair’s pricing strategy is the main factor of success and it truly asks low fare to the customer. At the same time, this strategy reflects on the target group such as this company is targeting fare-conscious leisure and business travellers and using the secondary airports for the convenience of the operational system (Mintel, 2009);
Leadership
On the other hand, the success of Ryanair also depends on the efforts and capabilities of its top management team, including the CEO of Ryanair Michael O’Leary as they take the major decision to be the global market leader. For instance, CEO fixed the price range from €0.99 to €199.99, introduce offers one-way pricing policy, manage the operating costs, and take many initiatives to recover from recessionary impact;
Customer Service
Annual report 2010 stated that its strategy is to compete with the rivals to serve the best client service performance in terms of better punctuality, less lost bags, and fewer amount cancellations as the competition is very high in this industry;
Regular Point-to-Point Flights on Short-Haul Routes
At present, Ryanair is the leader of the low-cost airlines in Europe in point-to-point short-haul routes though this company concentrates more on the UK to Ireland routes;
Low Operating Costs
O’Higgins and the annual report stated that the main competitive advantage of Ryanair is low operating costs and its operating costs is lowest among the European scheduled passenger airlines or other budget airlines.
Sustainability of Ryanair’s Strategy
The first part of this report concentrates on the key success factors and major strategies and this part analyze the sustainability of these strategies by PESTEL and Porter five forces.
Porter’s Five Forces Analysis

Bargaining Power of Suppliers
The bargaining power of supplier is low to medium for the company as the major providers of aircraft in the industry are Boeing (Ryanair’s potential supplier) and Airbus, and the switching costs of one provider to another is too high as the technicians, experts, crew, pilots and other employees will require additional training, which increases operating costs. On the other hand, the power of other suppliers like airport services suppliers, and fuel suppliers varies time-to-time, such as the main factor includes minor secondary airports would like to carry business from budget airlines, removal of intra-European duty-free, oil prices increased in 2004 due to uncertainty about supplies from Nigeria, Russia and Iraq.
Bargaining Power of buyers
The bargaining power of the buyers is strong because the switching cost of the customers is very nominal due to presence of available service providers, and customer loyalty is absent in the industry and most of the customers focus on the price than the quality.
Threats of New Entrants
There are mainly three reasons those consider the treatment of new entry is low, these are a huge amount of investment is essential to enter the market, new service providers will need to face high competition in this market, and the space in the airport is difficult to get. However, large market player of long haul could enter the short-haul market by using competitive advantage and financial capabilities while EU deregulation has removed obstacles to entry for airlines based in Europe, though the scarcity of landing slots is also created new hindrance to entry.
The Threat of Substitutes
The threat of substitute products is low for the Ryanair though trains and buses can serve alternative services in the global economic crisis.
Competitive Rivalry
The competitive rivalry in the European airline industry is Intense and increasing because of the deregulation, presence of too many competitors in these routes, increasing power of customers, lack of loyal customers, strategic change, consolidation and rationalisation, Potential trend of competitors, and so on.
PESTEL Analysis of Ryanair
Political factors
Political factors have a significant influence on the business operation of Ryanair and these factors include government policy of foreign countries, EU deregulation to open market by removing barriers, the possibilities of War, the prospect of Euro to gain strength against the Dollar, EU regulations on pollution, controlling advertisement, taxation policy, and some other rules to protect the airlines from terrorist attacks.
Economical factors
The economic position of Ryanair was not in stable condition in 2004, and it also faced the challenge of the global financial downturn in the fiscal year 2008 and 2009, but all time this company recovers its leading position by adopting the decision of top management successfully. However, many economic factors are interrelated those affected the company negatively or positively, particularly, the volatility of fuel price, high-interest rate, investment, debt condition, share price, operating costs, annual revenues and so on. However, the following chart demonstrates that the in 2007 the share price of the company was the highest position, in 2008 this price fallen, and it is now in stable position considering the market environment and position of the competitors.
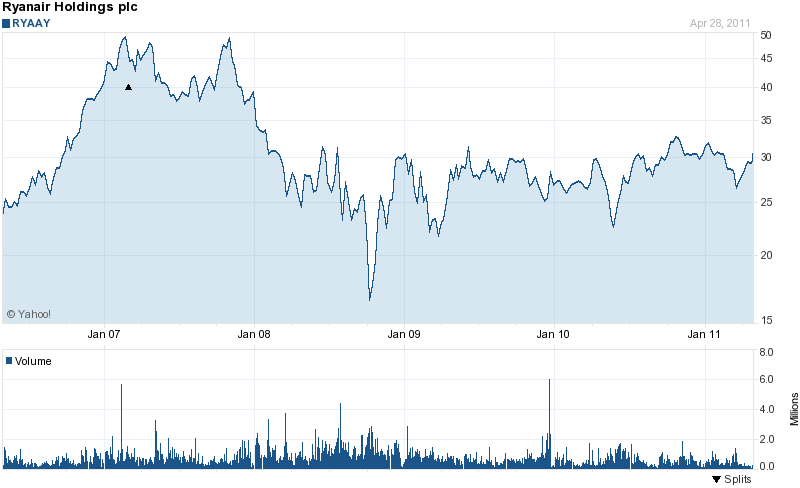
Socio-cultural factors
Ryanair earns significant profits (20.3% of total operating revenues) by providing ancillary services like sales food and distributes accommodation considering the socio-cultural factors of the customers. On the other hand, Ryanair ensures equal opportunities for all employees and it gives the facilities by the requirement of the EU regulation; therefore, it recruits talent people and it never considers social background, ethnic groups, race, and religion. Ryanair spends huge fund to maintain corporate social responsibility and ethical codes, for example, in 2008 and 2009, it invested €18,062,000 and €18,081,000 respectively on Social welfare.
Technological factors
Proper adoption of the technology can bring the extreme success of the company; therefore, Ryanair introduced new Boeing 737-800 aircraft to reduce fuel costs, wireless internet service to developing communication system, and online ticket reservation system to save time and improve the quality of service.
Recommendation to change environmental situation and justification
- Ryanair is in the apex in the success in terms of market share in short-haul flights and profitability, therefore, the company should attempt to enlarge its service range by introducing regular or frequent services in its present airports to boost its profits;
- As it has 272 aircraft and other financial resources, it can easily drive in the long haul flights. In this case, it can sign a merger or joint venture agreement to share their assets and human resources or it can takeover similar service providers to entry in the new routes with competence;
- The research and development team should survey the market, assess the risks, the service quality of the competitors, and recommend a new strategy to compete with rivals;
- At the same time, it should increase the budget for the R&D to increase research to save the company from controversy, as the company creates controversial situation by imposing the charge to travellers to use toilets on its flights, using the picture of the queen of Spain without her permission and implementing unusual conflicts;
- Also, the company should increase the budget for the promotional activities and it should arrange IMC program to develop an awareness of the passenger about the media as the UK television Channel 4 broadcasted in a documentary ‘Ryanair caught napping’ and criticised Ryanair’s training programs, aircraft hygiene and poor personnel morale. The management should concentrate on the internal workplace environment and flight services to avoid any criticism though the management of Ryanair denied these allegations against the company and published its correspondence with Channel 4 on its website;
- As the reduction of operating costs is one of the main factors of its success, it should carry on this strategy and it should control fuel costs more efficiently;
- However, the company should concentrate more on the environmental factors and take more initiatives to reduce CFC and carbon emissions as it has corporate social responsibility;
- Also, it should expand the destination outside Europe like Asia, Africa, and Latin America where trafficking is high, as the company uses low-cost fuel and asks low fares, which will help the company to be the global market leader in short-haul flights;
- Finally, it should always upgrade the IT System to manage the company and it should integrate the latest software to develop customer relationship management (CRM) system and to use financial resources with actual estimation.
Whether Ryanair should introduce long haul flights
The market leader Ryanair should introduce its services in the long haul flights as this company has enough financial capabilities to expand its service and offers low-cost services to the customers. As a result, this report mainly consider the challenges in long haul flights, and the resources and capabilities of the company to decide whether it should drive long haul routes or not –
Physical Resource
Ryanair always follows an expansion strategy and introduce its service in new routes and its physical resources also demonstrate the fact of this statement. However, it always eager to increase the number of aircraft, for instance, it had only 192 aircraft in 2004, but it has now 272 aircraft in operation and is expected this number would be reached 299 within next 2 years (Ryanair, 2010);
Financial Resources
On the other hand, it has strong financial capabilities to face any future challenges and take risks to expand its business in the global market. However, this company faced economic problem due to global financial crisis in 2009 and its profit after taxes was only €169.7 million in this year, but its changes this situation within a year and its profit were € 305.3 million that increased by €286.10 million from the previous year. However, the subsequent two tables show the financial data for Ryanair of the last four fiscal years –
Table 1: Key statistics of Ryanair. Source: Self-generated from annual report 2008 and 2010 of Ryanair.
Human Resources
The top management team and the employees are the main assets of this company and it has more than 2,859 full time and 3,304 part-time flight and cabin crew, and 869 ordinary employees to control all departments; also, it recruits additional 1,200 employees (Ryanair, 2009). At the same time, the top management team has already proved their capabilities to manage these human resources to create a brand image of the company in short-haul routes, which also support the view that it should start operation in long haul flights.
Strategic sense about bid and future decision
In 2007, Ryanair has acquired 25.2% stake in Aer Lingus to capture jointly about 80% of all flights between Ireland and EU countries, to upgrade their dated long haul products and decrease short-haul fares by 2.5% per year, to decrease operating expenses, and to help strategic decision-making process of the company as Aer Lingus have taken some wrong decision. On the other hand, Aer Lingus had rejected the initial bid by claiming it an anticompetitive drive of Ryanair to eradicate competitor at a derisory price, and the CEO of the company added that it is not possible to cork together as direct competitors. Also, Aer Lingus had rejected the second bid with the support of 97% majority vote, and then Ryanair renewed its bid along with some flexible provisions and facilities, like Ryanair proposed to remain Aer Lingus as a separate airline, planned to double its short-haul fleet.
However, this bid was strategic significance because Ryanair aimed to operate with mutual benefits and increase market share and customer base by ensuring truly low fares though Aer Lingus considered the bid a competing or monopolizing offer of Ryanair. At the same time, Ryanair was committed to providing €180 million to the Irish government but the CEO of Aer Lingus had no proper assessment of the market as the company as well as the CEO had suffered critical time after rejecting the bid, for instance, its share price had plunged noticeably, CEO resigned after controversy, and its loss customers.
As the share price of Aer Lingus has been fallen radically from €1.40 to €0.50 within one year due to the adverse impact of the global financial crisis. Ryanair should not launch another bid for Aer Lingus as it had rejected the bid of Ryanair for two times through the second time it has incorporated several broad options. However, it is highly likely that the new CEO of the Aer Lingus would not reject the new bid considering the present financial position of Aer Lingus, but Ryanair must fall in the Antidumping regulation of European Commission; as a result, Ryanair should not launch another bid for Aer Lingus but Ryanair has the option to bid for another carrier. However, Ryanair should consider several risk factors before launching another bid for any other carrier, such as –
- Adverse economic position due to the global financial downturn increased unemployment rate and restricted credit markets;
- Actual challenge due to continuous price hike of fuel;
- The rule and regulation related to the British Airline Pilot Association (BALPA);
- EU regulation imposed a compensation system to protect the customers from delay, lose of customer’s baggage and other problems;
- At the same time, it should consider the external environment, airport charges, and taxes and so on.
The leadership of Michael O’Leary and future step
From the last quarter of 1990, Ryanair had flown through a great deal of turbulence with losses IR£20 million despite growth in passenger volumes, and then Michael O’Leary had changed some strategic decisions those help the company to recover its situation by 1995 (Done, 2004). The most prominent reason behind the success of Ryanair is the contribution of O’Leary and according to the annual report 2010 of the company, he has employed as a director from 1988 and CEO from 1994. At the same time, Ryanair enjoyed the better financial position and applied expansion strategy such as Ryanair ordered 45 new Boeing 737- 800 aircraft (189-seat capacity) worth $2b in 1998, and the company was joined to the NASDAQ-100 in 2002, and Air Transport World magazine announced it the most profitable airline in the world in 2006.
According to the annual report 2009 of Ryanair, this company is not intended to lose any high-qualified senior executives until getting qualified person for replacement, and this corporate philosophy indicates that he should continue to serve CEO until Ryanair finds out a suitable person for this post. However, the problem arises when he gets involved in criticism due to his rivalry attitude towards the competitors, as a result, the policymakers, regulators, EU commissioner Philippe Busquin, and the competitors like EasyJet, and Aer Lingus have not considered him as a suitable person for this post. On the other hand, present and former employees of Ryanair have praised O’Leary’s leadership style as he can lead people without any kind of leadership training and he has inside power to motivate and encourage the employees as well as the customers.
Reference List
Done. 2004. “Ryanair’s dream comes to an end”. Financial Times 29, No.1: 1-5.
Johnson, Gerry and Others. 2008. Exploring Corporate Strategy: Text & Cases, London: FT Prentice Hall.
Mintel. 2009. Short-haul Airlines – UK – July 2009: Companies and Products. Web.
O’Higgins, Eleanor. 2010. Ryanair: the low fares airline – future destinations? London: FT Prentice Hall.
Ryanair 2009. Annual report 2009 of Ryanair.Web.
Ryanair 2010. Annual report 2010 of Ryanair. Web.
Yahoo Finance. 2011. Basic Chart of Ryanair Holdings (RY4B.IR). Web.