The rapid expansion of technologies in the twenty-first century has increased the production of new gadgets, and smartphones came at the forefront of the range. The modern market is highly competitive in regards to winning the attention of customers to become interested in their products. The most notable players in the smartphone market include Samsung, Apple, Huawei, Xiaomi, Oppo, Vivo, and Motorola, with the first two companies being the most significant competitors for customers’ attention.
Thus, the purpose of the current exploration is associated with the analysis of the smartphone market, with the emphasis placed on Samsung and Apple, which are considered significant rivals in the industry. The popularity of one or the other brands has been attributed to the release of the latest gadgets to the market. However, it is also essential to account for the significant contribution of Huawei to the market as the high affordability of the products as well as the continuous innovation represent a challenge to both Samsung and Apple.
Background: Literature Review
A smartphone is seen as an essential component of global society’s daily life as it represents a tool for business communication, keeping in touch with friends and families, as well as sharing information, and even making money through producing content. At the early stages of smartphone development, the products were innovative yet bulky and unattractive in design (Reid, 2018). Since the conception of the iPhone by Apple in 2007, the industry has changed significantly, with the brand becoming at the forefront of dictating global trends within the smartphone market.
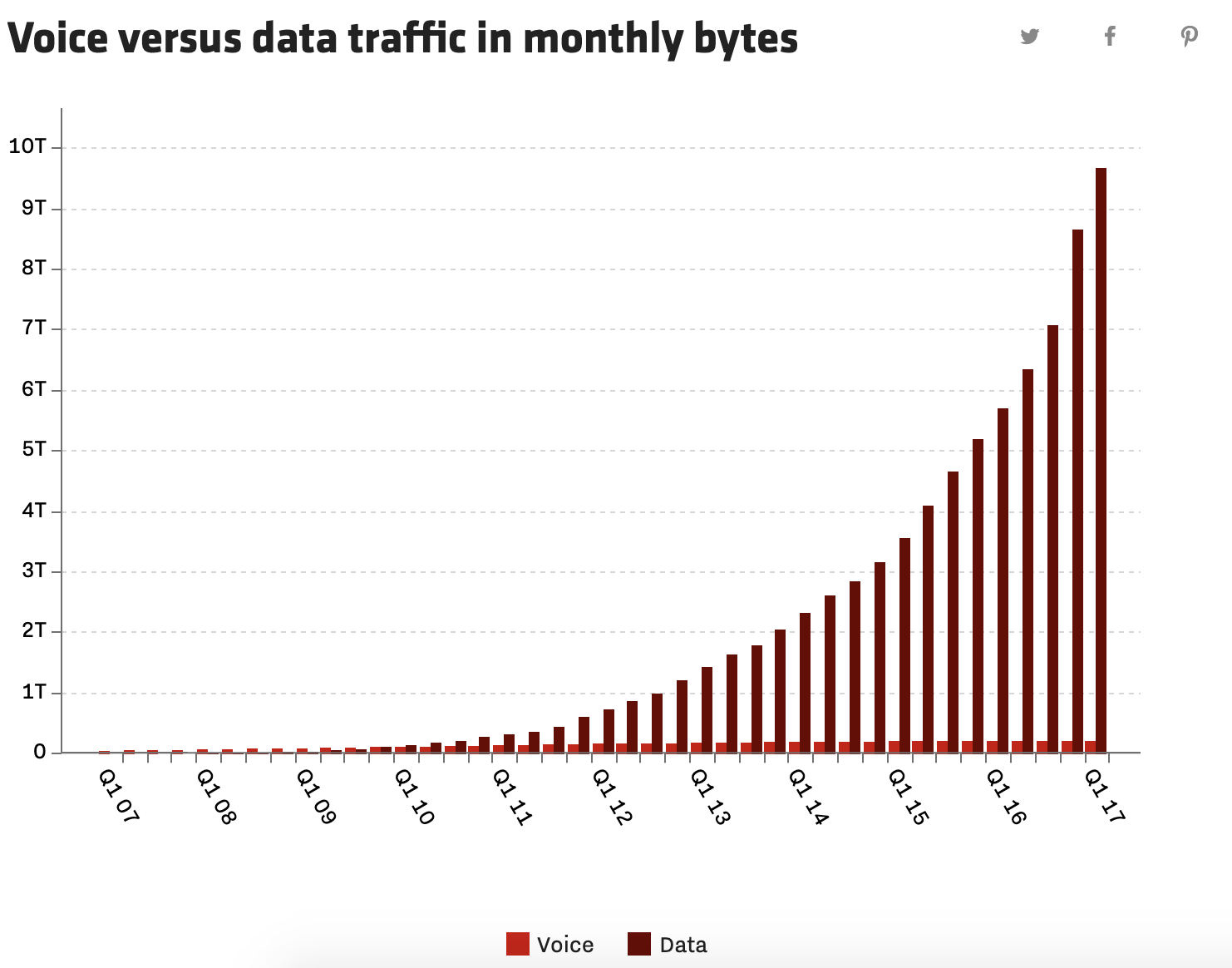
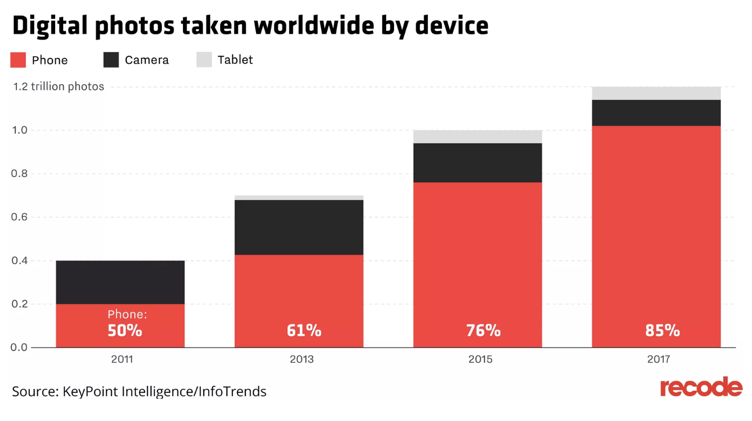
The iPhone changed the industry in several important ways. First, the Internet became an essential part of everyday interactions, with voice communication declining over the years (see Figure 1). Second, photography became a part of everyday life while before the gadget’s invention, it was a hippy. In 2017, the total number of digital photographs taken amounted to 1.2 trillion as compared to 400 billion in 2011 (Molla, 2017) (see Figure 2). Third, the creation of the Apple App Store associated with the integration of games and applications into the smartphone changed how software was developed and distributed (Molla, 2017).
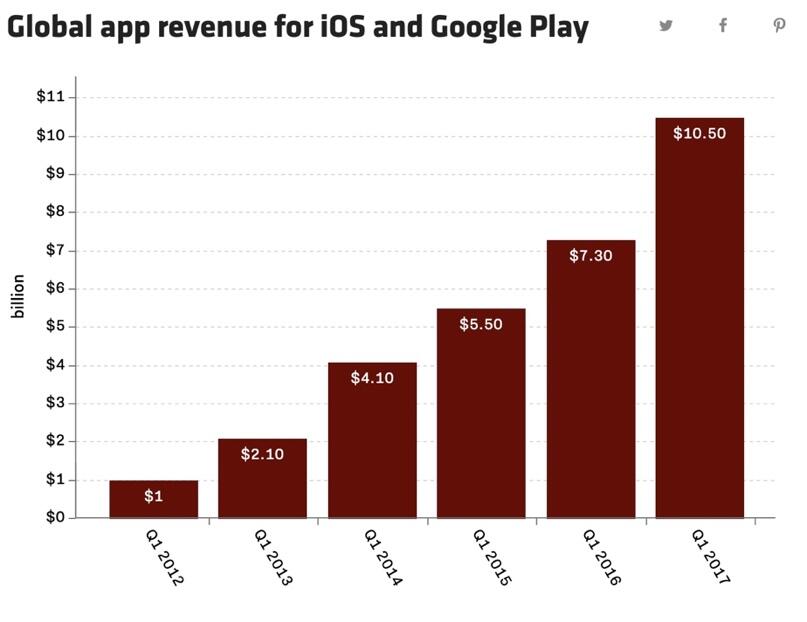
From motion-sensitive video games to maps or accounting applications, smartphones provide a broad range of programs that make life easier while also providing revenue to their developers (see Figure 3). Finally, the iPhone led to the subsequent creation of the Android ecosystem, which boosted the revenue of Apple’s key competitor – Samsung. Also, the new operating system meant that BlackBerry and Nokia would not survive for much longer if they fail to design a similar product.
Despite the vital role of the iPhone in expanding the profitability of the smartphone market, its influence continues to dwindle. China’s Huawei has been growing its sales over 2018-2019, challenging its global leaders, Samsung and Apple. For a while, the company has been near to reaching the position of the world’s second-largest smartphone seller. Huawei has taken over Apple for the first time in 2017 and continued switching from one place to another throughout 2018.
When it comes to Apple’s performance, its shipments decreased from 52.2 million in the first quarter of 2018 to an estimated 36 to 43 million in the same quarter of 2019 (Savov, 2019). The company’s marginal product (MP) is directly associated with the costs of manufacturing. Apple usually hires workers to the point in which the marginal revenue product is equal to the wage rate. Notably, the company has recently stopped reporting iPhone sales in earnings reports, which complicates the current analysis. The performance of Samsung also decreased in shipments, from 78.2 million to 71.9 million in the same timeframe (Savov, 2019).
In addition, a range of other international brands that used to have leverage in the global phone market is also suffering from the impact of Huawei. The sales of Sony keep declining, with the company intending to decrease its staff working on the mobile business by half. In addition, LG reported to stop manufacturing phones in South Korea and transferring operations to Vietnam to cut costs. HTC, moreover, is only technically in the smartphone business, with its sales dwindling with each quarter.
Market Analysis
Apple’s Performance: SWOT
Apple Inc., which was incorporated in 1977, is a company that markets and manufactures mobile devices, personal computers, and other digital products. In the smartphone market, Apple plays a central role by dictating trends and being at the forefront of innovation. Due to the sales of the high-end iPhone X, Apple managed to garner more than 50% of the global smartphone market during the fourth quarter of 2017. The high sales were linked to the holiday shopping season, which allowed apple to capture 51% of the worldwide revenue for smartphone sales, which was more than the rest of the industry combined (Mawston, 2018). In the fourth quarter of 2016, Apple had a 48.5% market share. Samsung was in second place with 15.7% of the market share in the same period.
Strengths
As mentioned in the Strategy Analytics report on Apple’s performance, the company’s total revenue (TR) reached “US $61 billion in the quarter, helped by solid demand for its premium X model, and Apple now accounts for more revenue than the rest of the entire global smartphone industry combined” (as cited in Reisinger, 2019, para. 3). The average selling price of iPhones has approached around US$800, which is approximately three times higher compared to the average in the smartphone industry. The significant profits for the company have always been attributed to top-level technologies, proficient research, sustainability, and the iconic quality of Apple as a brand.
Weaknesses
However, in 2018, the company’s sales in the smartphone segment declined significantly along with the demand for them, despite the large supply. During the fourth quarter of 2018, Apple earned 15.8% of the market share during the period, which was down from 17.9% in the same period of 2016. This drop is considered the most significant decline of any large smartphone producer during the period (Reisinger, 2019). The dramatic decline in performance can be attributed to the changes in the smartphone market and consumer behaviors. In addition, upgrades in the iPhones brought to the market were not as substantial as expected, which led to customers keeping their old devices for longer (Mishra, 2019). Also, the economic weakness in some countries limited the expected sales of Apple devices, with users taking advantage of affordable batter changes instead of buying the latest gadget.
Opportunities
For the company, the main opportunities are linked to the expansion of services that are being offered to customers, which increases supply. For instance, Apple applications made phones smarter and more efficient in terms of the services that are being offered to users. Also, the advent of the iPhone transformed the advertising industry transformed significantly. Mobile marketing has become necessary due to the increasing time potential consumers spend on their phones and the need to attract their attention through advertising.
Threats
As China plays a vital role in Apple’s performance, it is also essential to note that the economic condition in the country can either boost or slow down the company’s growth. The trade dispute between the US and China could not be resolved amicably, which meant that consumers were reluctant to purchase expensive phones because of the geopolitical tensions (Ovide, 2019). It is possible that dwindling performance in the last year caught the company by surprise, with executives failing to forecast any potential red flags for the business.
Also, the continuous rise in iPhone prices makes customers think twice about whether they want to get a new gadget, which decreases demand on a long-term basis. In big smartphone markets, phone companies have for years been offering customers iPhones at artificially low prices. Coupled with this factor as well as less drastic changes to each model of the iPhone or other smartphones and the rising costs on new devices, has led users in the US to keep their smartphones for more than three years (on average) (Ovide, 2019). For example, iPhone X’s cost to make is $357 while it was initially sold for $999, making the marginal cost $642, which is a higher-than-average price among other smartphones sold by competitors. Moreover, Apple predominantly sells its phones to people who already have one of their previous iPhones.
Thus, the sales of new iPhones depend on whether some customers will keep their gadgets for longer or decide to upgrade them (Ovide, 2019). Therefore, it is imperative to mention that the smartphone market has always been seen as having inelastic demand, which means that consumers were not sensitive toward price changes. However, with Apple’s strategy of continuous price increases, price elasticity may change in the other direction within a decade.
Samsung’s Performance: SWOT
Strengths
Throughout 2018, Samsung has been showing a boost in performance, beating Apple in the global market of smartphones. In the fourth quarter of 2018, the company’s TR was USD 70.2 billion. Among the 3.6 billion active smartphone users worldwide used in June 2018, Samsung was the most popular brand, reading 893 million active devices during that period and a market share of 27%, which is 3% more compared to Apple (Mourdoukoutas, 2018). Compared to Apple, the marginal cost of Samsung smartphones is lower even though they are also expensive to produce. For example, the Galaxy S8 costs $307 to manufacture while it is currently sold for $499.99 on the company’s website. The steady increase in the company’s profitability has been attributed to the wide selection of budget devices, which is an important criterion for markets such as India.
Weaknesses
Samsung has to work very hard to compete with Huawei as well as such Chinese entry-level brands Xiaomi, Oppo, and Vivo, which are gaining steady popularity in Asian markets, including India. In addition, the new trend of dual-brand strategies among Chinese phone manufacturers allows them to capture new and broad customer audiences, including younger clients who only start investing in the latest gadgets, and Samsung does not have such a strategy.
Opportunities
The reason for Samsung’s growth is rooted in Apple’s failure to attract a broad customer base as it has always been targeting the profitable high end of the smartphone market and introducing more expensive and sophisticated smartphones. For example, even the budget-friendly version of the iPhone XS, the iPhone XR started at $749, which is a price that only a premium market while some of the cheapest Samsung models start at $179 (Samsung, 2019). Therefore, while Apple managed to stay profitable through increasing prices on the latest devices, Samsung and other Chinese smartphone manufacturers increased demand by targeting the low-end of the market, mining the “fortune at the bottom of the pyramid” (Mourdoukoutas, 2018). The disposable income in the hands of customers at the bottom of the global income pyramid is counted in trillions, which represents a significant potential for expansion.
However, apart from targeting the lower spectrum of customers that cannot afford expensive smartphones, Samsung has also been dedicated to presenting premium gadgets to the market to compete with Apple in innovation. For example, the release of the Samsung Galaxy S10 5G markets the release of the first Samsung’s 5G smartphone in the market, which was developed through collaboration with network operators and software developers (Samsung, 2019). The starting price for the new phone was $1,299, which is comparable with the price for the Apple XS Max. The success of Samsung in 2019 has been mainly attributed to the release of the Galaxy S10 flagship line. Both the “Galaxy S10+ and S10e individually captured 6% of the entire smartphone market, selling 2 million units each” (“Samsung’s market share surges,” 2019, para, 3).
Threats
With the release of Apple’s iPhone 11 in September 2019, Samsung may have to give up the leading position in the market of smartphones. However, the current performance of Samsung shows that the global public wants to get not only technologically advanced devices but also those that will be affordable. Therefore, the threat of substitute goods offered by Huawei and other Chinese manufacturers is also potentially challenging for Samsung in the long run.
Huawei’s Performance: SWOT
Strengths
During the first quarter of 2019, Huawei reached the highest level of the global smartphone market share of 17% (Srivastava, 2019). The company’s TR for the fourth quarter of 2018 was $107 billion in 2018. Huawei managed to overtake Apple as the second-biggest smartphone brand in the same quarter as the volumes of sales increased by approximately 50% year-on-year. The MC for products is also lower than Apple’s; for example, its Mate 10 costs $290 to produce while it costs $710. Notably, the company became the second-largest brand in smartphone shipments without having any significant presence in the United States, which is highly important for modern technology manufacturers. By the end of 2019, Huawei is still expected to remain ahead of Apple as the company is keeping pace with the latest innovations without having to increase prices. Huawei was the first to introduce such features to the market as reverse wireless charging, onboard Artificial Intelligence, and advanced camera options.
Weaknesses
Despite the favorable position of Huawei on the market, it has struggled with a large number of controversies that influenced its reputation. The rivalry between the Chinese and American market has increased rumors about an espionage controversy, which weakened the image of Huawei in Western countries, which represent a significant market for sales. The company also has an unfavorable position in the US market despite representing the key competition to Samsung.
Opportunities
The dual-brand strategy, which involves the marketing of both Huawei and HONOR companies to build a closer connection to a profile of young consumers and gain an extra market share in China (Srivastava, 2019). In 2019, the company has reached a high level of innovation and now matches Samsung hardware. Following in both the latter’s and Apple’s footsteps, Huawei is also becoming increasingly vertically integrated. What is essential to note about Huawei’s performance is that despite the overall decline in the smartphone market, the company exhibited an increase from 11% to 17% in the share of smartphone shipments between the first quarters of 2018 and 2019 (see Figure 4).
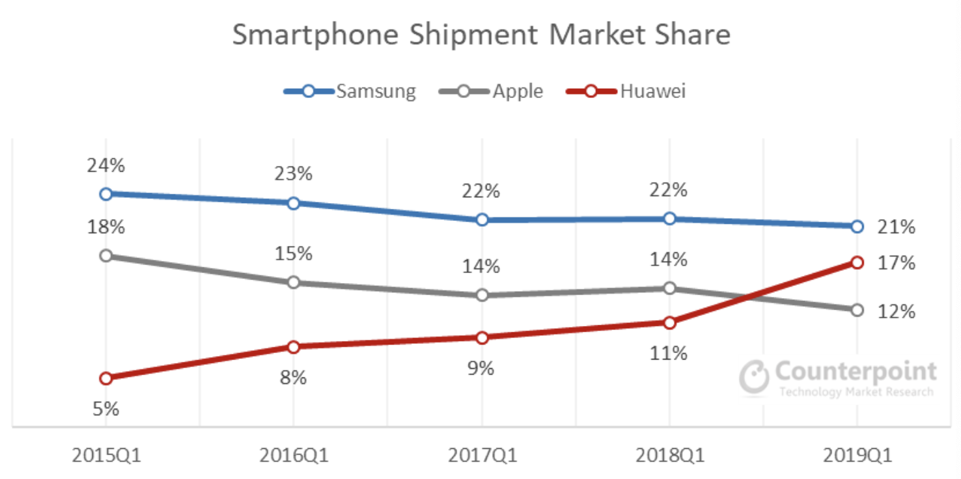
What is essential to understand about Huawei’s growth and the strengthening position in the Chinese market is that the company is coming up with new products regularly. Apple, however, is making updates to an already existing iPhone, which becomes less exciting for customers in the long run. The branding strategy that the company established in China has also been boosted by the trade conflict with the United States. Therefore, a Huawei smartphone is a device that shows direct opposition to the American market.
Threats
The company is expected to face many threats during its performance. With the brand’s prevalence increasing in the East, it becomes more and more complicated for Apple to maintain its relevance and expand in China, especially due to the pressure from such brands as Xiaomi. However, Huawei has to compete with both American and Chinese brands to stay relevant in the market. Regulatory pressures are also challenging, as the tension between the US and China grows in regards to the economic cooperation of the countries.
Summary and Conclusions
The current economic climate is not ideal for issuing new smartphones to the market, especially those with high price tags. At this time, Apple is experiencing a significant decline in unit sales as more and more people choose to hold on to their phones for longer. Huawei is the only player in the smartphone market that is growing steadily due to the combination of innovation and reasonable prices on their devices. Besides, the trade-related tension between the United States and China creates a favorable environment for Chinese companies to capture larger shares of their domestic markets due to the uncertainty associated with prices set by foreign companies.
Despite the vast opportunities of innovation, research, and development, as well as entertainment as applied to the smartphone industry, the prospects of such giants as Apple remain unclear. With the company updating the already existing flagship product, the attention of the public keeps dwindling while prices get higher. Samsung holds a strong position in the current smartphone market leader due to the company’s dedication to offering a wide range of both high-end and affordable devices so that every customer can make his or her choice.
It is also troubling for both Samsung and Apple is that Huawei is planning to release its operating system to compete with Android and iOS. When the company manages to do so, it will change the entire smartphone market, with Apple having to deal with the most considerable consequences in the sector of Asia. Also, following Samsung’s footsteps, Huawei is working on the release of foldable display phones paired with 5G technology, thus capturing a new segment of customers. Overall, the growth opportunities are vast for Huawei, which is why both Samsung and Apple should work harder to maintain their positions in the global smartphone market.
References
Mawston, N. (2018). Apple iPhone takes huge 51 percent share of global smartphone revenues in Q4 2017. Web.
Mishra, V. (2019). Premium smartphone market collapses 8% in Q1 2019, after Apple shipments drip 20%. Counterpoint. Web.
Molla, R. (2017). How Apple’s iPhone changed the world: 10 years in 10 charts.Vox. Web.
Mourdoukoutas, P. (2018,). Samsung beats Apple in the global smartphone market as Chinese brands close in. Forbes. Web.
Ovide, S. (2019). As stock plummets, Apple can no longer deny the truth about its iPhone business.Time. Web.
Reid, A. (2018). The smartphone paradox: Our ruinous dependency in the device age. Conway, SC: Palgrave Macmillan.
Reisinger, D. (2019). Apple iPhone sales tanked at the end of 2018.Fortune. Web.
Samsung. (2019). Find the perfect phone for you. Web.
Samsung. (2019). The next generation speed and performance starts with Galaxy S10 5G, Samsung’s first 5G smartphone on the market. Web.
Samsung’s market share surges as North American smartphone market reaches five-year low. (2019). Web.
Savov, V. (2019). Huawei’s phone sales are ballooning while Apple and Samsung’s slump. The Verge. Web.
Srivastava, S. (2019). Huawei’s global smartphone market share reaches highest ever level in Q1 2019.Counterpoint. Web.