Abstract
This paper is dedicated to Hydroxycitric Acid (HCA), its characteristics, biochemistry, and the role lipogenesis and fatty acid synthesis for the prevention of obesity. The expediency of this work is determined by the significance of the issue of obesity in the present day. The methodology of this research is a critical review of existing scholar literature dedicated to HCA. According to the findings, the impact of HCA on the lipogenesis and fatty acid synthesis may be regarded as examined, however, its contribution to the prevention of obesity is controversial as other factors should be considered.
In the present day, obesity has become a highly disturbing health issue. That is why multiple studies are dedicated to the ways of its prevention, and one of them is the use of Hydroxycitric acid (HCA) as a dietary supplement for weight loss, the suppression of food intake, and the inhibition of lipogenesis and fatty acid synthesis. This paper aims to examine the dietary source of HCA, its biochemistry, and how its role in lipogenesis and fatty acid synthesis was examined through experiments and clinical trials. According to it, while the role of HCA in the animal model may be regarded as established, the impact of this acid in humans is still controversial and requires further research.
Dietary Source of HCA
Hydroxycitric acid (HCA), also known as Garcinia acid, Hydroxycitrate, or 1,2-Dihydroxypropane-1,2,3-tricarboxylic acid, is citric acid’s derivative and herbal dietary supplement known for its benefits for obesity treatment. The molecular formula of HCA is C6H8O8, and its structure may be presented in the way demonstrated in Picture 1.
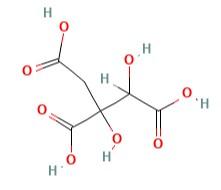
In the present day, HCA has become highly popular worldwide as the ingredient of weight loss supplements. According to Sura and Hiremath (2019), the market value of diet products that contain HCA exceeds $400 million annually. Being an herbal chemical, HCA may be found in several types of plants. In particular, it may be taken from the flowers of Hibiscus rosa-sinensis and Hibiscus subdariffa (Hydroxycitric acid, 2021). However, the main source of HCA is in fruit rinds of Garcinia atroviridis, Garcinia indica, and, especially, Garcinia cambogia.
Biochemistry of HCA
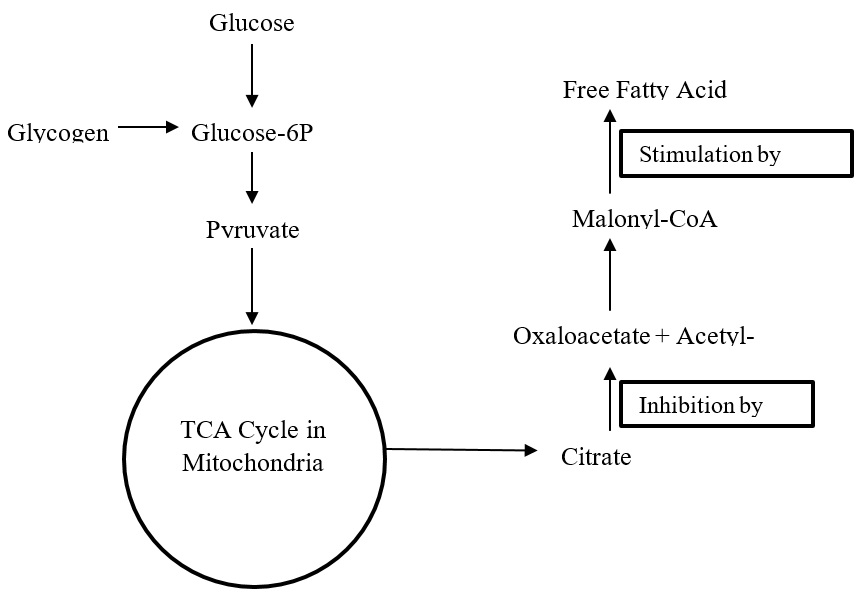
The anti-obesity and weight loss effect of HCA is determined by several biochemical mechanisms. They include the suppression of food intake, serotonin regulation, the increase of fatty acid oxidation, the decrease of de novo lipogenesis, the downregulation of obesity-associated genes, and the reduction in glucose intake rates, leptin levels, and plasma insulin (Tomar et al., 2019). Figure 1 demonstrates the impact of HCA on the process of glucose’s transformation into free fatty acid. According to Tomar et al. (2019, p. 18578), “HCA reduces weight gain by inhibiting ATP citrate lyase (ACLY), an enzyme responsible for catalysing the extra-mitochondrial cleavage of citrate to oxaloacetate and acetyl coenzyme A (acetyl-CoA), a building block of fatty acid synthesis.” Reducing acetyl-CoA and malonyl-CoA, HCA limits the availability of these two carbon groups for the synthesis of cholesterol and fats.
According to its structure, HCA is similar to citrate and may be regarded as an allosteric regulator for enzymes involved in fat and carbohydrate metabolism. These enzymes traditionally include acetyl-CoA carboxylase and phosphofructokinase that regulate glycolysis and fatty acid synthesis (Li et al., 2017). According to Li et al. (2017, p. 813), “it had been reported that (-)-HCA has a much greater affinity to the citrate lyase than that to citrate.” In this case the consumption of HCA is expected to change metabolic pathways.
Role of HCA on Fatty Acid Synthesis and Lipogenesis
Prima Facie Evidence
As previously mentioned, Garcinia cambogia may be regarded as a major source of HCA. It is a semi-wild plant that traditionally grows in south India and Indonesia. Having an orange’s size, its fruits resemble small red or yellow pumpkins with deep vertical lobes and a thin skin (Sura and Hiremath, 2019; Jena et al., 2002). Although these fruits are edible, due to a highly acidic taste, their rinds are traditionally used as a flavoring agent and condiment. At the same time, due to HCA in them, the traditional Ayurvedic medicine utilizes Garcinia cambogia for weight loss and control “due to its ability to make one have feelings of “fullness” for longer periods of time once ingested” (Sura and Hiremath, 2019, p. 3163; Gogoi, Gogoi and Neog, 2015). Thus, adding its fruits to a meal helps followers eat less and feel satisfied for a longer period of time after food intake. In this case, it is possible to assume that the evidence
In Vitro Experimental Evidence
According to experimental evidence, HCA plays a highly essential role in the synthesis of fatty aid and lipogenesis. It promotes the cycle of citric acid inhibiting fatty acid synthesis (Peng et al., 2018; Akshay et al., 2018; Lim et al., 2003). After the consumption of HCA, sterol regulatory element that binds protein-1c mRNA level, fatty acid synthase, and ATP-citrate lyase are substantially decreased while peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor α mRNA level increases (Li et al., 2017). In addition, increasing the rates of mitochondrial oxygen and glucose consumption and promoting the activity of pyruvate dehydrogenase, glucokinase, aconitase, pyruvate kinase, succinate dehydrogenase, phosphofructokinase-1, malate dehydrogenase, citrate synthase, ATP synthase, and NADH dehydrogenase, HCA decreases the content of acetyl-CoA in cytosol and ATP-citrate lyase activity (Li et al., 2017). All in all, HCA inhibits and stimulates the chemical mechanisms of fatty acid synthesis and lipogenesis contributing to fat reduction, weight loss, and the prevention of obesity.
In addition, HCA helps suppress the processes of de novo fatty acid synthesis and lipogenesis. Characterized by the synthesis of fatty acids from other sources rather than an exogenous one, de novo lipogenesis is associated with multiple health-related complications, including type 2 diabetes, autoimmune diseases, cancer, cardiovascular disease, viral infections, neurodegeneration, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, and acne vulgaris (Batchuluun, Pinkosky and Steinberg, 2022; Mashima, Seimiya and Tsuruo, 2009). Finally, HCA impact the process of cholesterol synthesis decreasing its rates.
In Vivo Animal Model
In order to assess the efficiency of HCA for weight loss, multiple experiments involving animals were organized. According to Tomar et al. (2019, p. 18579), “HCA reduces lipid droplet accumulation via decreasing acetyl-CoA supply and accelerated energy metabolism in cultured primary chicken hepatocytes.” Another research dedicated to the examination of the impact of HCA on broiler chickens’ fat deposition was organized by Han et al. (2016). It was determined by the fact that the accumulation of fat in chickens may not only led to animals’ metabolic diseases but had negative consequences for human health as well. The results of this trial indicated that HCA had a considerable effect on lipid metabolism that related to gene expression. HCA inhibited broiler chickens’ lipogenesis stimulating sterol regulatory element binding protein-1c, ATP citrate lyase, fatty acid synthase (Han et al., 2016). In addition, through the enhancement of the expression of peroxisome proliferators-activated receptor α, HCA reduces fat deposition.
There are multiple studies dedicated to HCA that were conducted on rats and mice as well. Thus, Hayamizu et al. (2003) stated that the consumption of the extract of Garcinia cambogia rind by mice for four weeks led to the decrease in triglycerol, glucose, serum total cholesterol, leptin, and insulin levels. In another studies, the consumption of HCA by rats caused the downregulation of genes that encoded abdominal fat leptin and the increase of lipogenesis in the liver (Chuah et al., 2013; Brandt et al., 2006; Lim et al., 2005). One more study by Leonhardt, Hrupka and Langhans (2001) demonstrated the positive impact of HCA on body weight regain and food intake in male rats after restrictive feeding. Table 1 shows the effect of HCA on cumulative food intake of rats after 10 days (Leonhardt, Hrupka and Langhans, 2001). According to the results, the effect of HCA could depend on the diet’s glucose content and be connected with the inhibition of lipogenesis.
Table 1: Effect of HCA on cumulative food intake (in g) of rats after 10 days. (Leonhardt, Hrupka and Langhans, 2001)
Clinical Trial Findings
Regardless of the fact that the examination of HCA and its impact on animals is excessive, the effect of this acid on humans is controversial and non-conclusive. According to the meta-analysis and systematic review of randomized clinical trials, weight loss is small and insignificant in long term (Onakpoya et al., 2011). At the same time, another randomized controlled clinical trial that investigated the efficiency of HCA consumption in a 12-weeks period showed that HCA could substantially decrease body fat, however, its impact on BMI was insignificant. In turn, other trials demonstrate the failure of HCA to produce fat mass loss and weight loss in both women and men (Opala et al., 2006; Vasques et al., 2014). In this case, it is possible to assume that a person’s health-related characteristics and lifestyle may influence the results of research and contribute to ambiguous results.
Discussion and Future Research
On the basis of a literature review dedicated to HCA and its role in lipogenesis, it is possible to conclude that the sources and biochemistry processes related to this acid are thoroughly examined. In other words, the majority of scientists have a clear understanding of the impact of HCA on fatty acid synthesis and lipogenesis. In addition, the majority of studies imply the organization of randomized controlled trials with the division of participants in groups (placebo and intervention) to compare their results. In general, this experimental design may be regarded as appropriate, especially when a particular aspect of HCA’s effect should be evaluated. Moreover, the interpretation of data was generally reasonable and comprehensive.
At the same time, a considerable number of researchers admitted that the mechanisms of HCA in relation to obesity that has multiple reasons is still unknown. Moreover, the impact of HCA on humans is controversial, and many scientists do not consider the additional factors of weight loss that may lead to biases in the results. Thus, while particular findings are presented, they cannot be regarded as valid. In this case, this topic suggests a wide area for further research as the impact of HCA on human health and its expediency for the prevention of obesity is still unknown.
Reference List
Akshay, K. R. et al. (2018) ‘Back yard malabar tamarind (Garcinia Gummi-gutta): a miracle anti-obesity agent,’ Journal of Pharmacognosy and Phytochemistry, 7(3), pp. 515-517.
Batchuluun, B., Pinkosky, S. L. and Steinberg, G. R. (2022) ‘Lipogenesis inhibitors: therapeutic opportunities and challenges,’ Nature Reviews Drug Discovery, 21(4), pp. 283-305. doi: 10.1038/s41573-021-00367-2
Brandt, K. et al. (2006) ‘Beneficial and deleterious effects of hydroxycitrate in rats fed a high-fructose diet,’ Nutrition, 22(9), pp. 905-912.
Chuah, L. O. et al. (2013) ‘Updates on antiobesity effect of Garcinia origin (−)-HCA. Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine, 2013, pp. 1-18.
Gogoi, A. N. K. U. R., Gogoi, N. A. B. A. J. Y. O. T. I. and Neog, B. I. J. O. Y. (2015) ‘Dubious anti-obesity agent hca from Garcinia: a systematic review,’ International Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences, 7(7), pp. 1-8.
Han, J. et al. (2016) ‘(−)-Hydroxycitric acid reduced fat deposition via regulating lipid metabolism-related gene expression in broiler chickens,’ Lipids in Health and Disease, 15(1), pp. 1-13. doi: 10.1186/s12944-016-0208-5
Hayamizu, K. et al. (2003) ‘Effects of Garcinia cambogia (Hydroxycitric Acid) on visceral fat accumulation: a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial,’ Current Therapeutic Research, 64(8), pp. 551-567.
Hydroxycitric acid(2021).
Jena, B. S. et al. (2002) ‘Chemistry and biochemistry of (−)-hydroxycitric acid from Garcinia,’ Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 50(1), pp. 10-22.
Leonhardt, M., Hrupka, B. and Langhans, W. (2001) ‘Effect of hydroxycitrate on food intake and body weight regain after a period of restrictive feeding in male rats,’ Physiology & Behavior, 74(1-2), pp. 191-196.
Li, L. et al. (2017) ‘(-)-Hydroxycitric acid reduced lipid droplets accumulation via decreasing acetyl-coa supply and accelerating energy metabolism in cultured primary chicken hepatocytes,’ Cellular Physiology and Biochemistry, 43(2), pp. 812-831. doi: 10.1159/000481564
Lim, K. et al. (2003) ‘(-)-Hydroxycitric acid ingestion increases fat utilization during exercise in untrained women,’ Journal of Nutritional Science and Vitaminology, 49(3), pp. 163-167.
Lim, K. et al. (2005) ‘(-)-Hydroxycitrate ingestion and endurance exercise performance,’ Journal of Nutritional Science and Vitaminology, 51(1), pp. 1-7.
Mashima, T., Seimiya, H. and Tsuruo, T. (2009) ‘De novo fatty-acid synthesis and related pathways as molecular targets for cancer therapy’, British Journal of Cancer, 100(9), pp. 1369-1372. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6605007
Onakpoya, I. et al. (2011) ‘The use of Garcinia extract (hydroxycitric acid) as a weight loss supplement: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised clinical trials,’ Journal of Obesity, 2011, pp. 1-9. doi: 10.1155/2011/509038
Opala, T. et al. (2006) ‘Efficacy of 12 weeks supplementation of a botanical extract-based weight loss formula on body weight, body composition and blood chemistry in healthy, overweight subjects-a randomised double-blind placebo-controlled clinical trial,’ European Journal of Medical Research, 11, pp. 1-8.
Peng, M. L. et al. (2018) ‘Metabolomics reveals the mechanism of (−)-hydroxycitric acid promotion of protein synthesis and inhibition of fatty acid synthesis in broiler chickens’, Animal, 12(4), pp. 774-783. doi: 10.1017/S175173111700221X
PubChem (no date) Hydroxycitric acid.
Sura, N. K. and Hiremath, L. (2019) ‘Hydroxycitric acid (HCA)-a potent nutraceuticals,’ Research Journal of Pharmacy and Technology, 12(7), pp. 3163-3168.
Tomar, M. et al. (2019) ‘A clinical and computational study on anti-obesity effects of hydroxycitric acid,’ RSC Advances, 9(32), pp. 18578-18588. doi: 10.1039/C9RA01345H
Vasques, C. A. et al. (2014) ‘Hypolipemic effect of Garcinia cambogia in obese women,’ Phytotherapy Research, 28(6), pp. 887-891.