It is an extensive area at least cutting into five counties namely Park County in Wyoming, Teton County in Wyoming, and Gallatin County in Montana, Park County in mutant, and Fremont County in Idaho. The area is approximately 2,219,791 acres or simply (898,318 ha) and was established way back in 1872. Its location in the US or coordinates are 44°36′N 110°30′W.
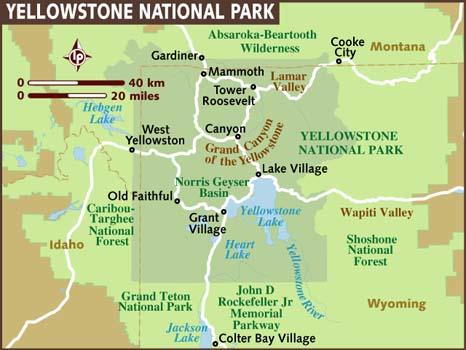
Yellowstone national park is located south of Gallatin national forest. The park is adjacent to Grand Teton National park (Whittlesey and Watry 2-6). It is home to a variety of animals, bacteria, geologic eruptions and other beautiful sceneries. It is ranked as one of the best sites in the entire United States considering the comfort it offers to its visitors. Rooseveltlodge cabins are among the many recreation facilities in existence. Some of the activities one can enjoy include: hiking at the grand canyon of the yellow stone, walking on wooden walk paths to avoid the hot springs valley within the park.
The park has four entrances which give different treatments to the visitors. The northern entrance welcomes one to paradise valley, north east entrance inspiring one tot the red lodge, west entrance and southern entrance. To keep you updated on the best features at the northern entrance (Whittlesey and Watry 4-7). Other than the paradise valley, the yellow stone and Roosevelt arch are all located here. Historians and tourist get a photo session here first because it highlights the respect accorded to the one of its presidents, Franklin Delano Roosevelt. With a rich history spanning 140 years, the park is home to the largest number of geysers in the world. The two million acre park is accessible by road through the grand loop road.
The Roosevelt gate gives the visitors something to smile about. This is where the pronghorn antelopes, which are a rare species, are found. Scientists too get something for their study inside the park as microorganism like bacteria; magafana, elk deer and mouse are found (Kalman 2-8). The bear also comes into the picture toward s the northern entrance which has some cold.
Rocks present in the park
There are a number of rocks open for study to the geologians. Some of these rocks are: Pre-cambian basement, which includes gneisses and schist. Others include, the obsidian, surficial deposits cemented ice, hydrothermal explosion deposits, creek, domesroaring mountain member, Lava creek among others. Scholars have unlimited opportunities to explore and identify the ages of some of the rocks.
How some of these rocks have erupted and changed with time
The palezioic era broke to form the meagher, limestone, Bighorn, Dolomite, Madison, sandstone and even shed-horn (zuckerman 10-12). Analogous to the palezoic, the Mesozoic formed the Ellis and the mowryshale. As such, balsatic lava flows occurred in the northeastern part of the park during the late creataceous continuing into the eastern. Speaking of significance, of all the yellow stones are the laypeople following their visibility.
The Geologic history of Yellowstone Park
The Yellowstone Park is characterized by various land forms and features. Some of these features include different shapes of glaciers and mountainous folds. It must be understood that these features in one way or the other resulted from the processes of weathering. Apart from that, the violent volcanic activity has shaped Yellowstone’s topography (Kalman 2-7). All these activities have all happened due to the rich history of Yellowstone national park. Further, the violent volcanic activity pulled the residents into harvesting the geothermal energy available (Kalman 5-6).
Yellowstone volcanic history
Geologists hold the view that the Yellowstone volcanic activity is the most recent historical event spanning two million years. The Yellowstone ecosystem has a mark coming as a result of the three big caldera eruptions (Whittlesey and Watry 4-12). Calderas are usually large cup-shaped depressions resulting from volcanic activities. With the eruptions, many other stones are formed. Such as: cycle precaldera rhyoliteash-flow-tuff postcaldera contemporaneous plateau among others.
Geologic resources
There are a number of geological resources that visitors to the park can enjoy at will. Fish and fishing, geology wild-land, fire in the Yellowstone, and hydrothermal features are some of the geological features present. None of this features is better that the other as each has its historical character (Kalman 4-6). Visitors to the park cannot leave without a photo shooting moment with some of the geological sites like the hydrothermal and the fire in the yellow stones. These however are not the only resources tourist and guests can enjoy. A resource centre storing guide books to the best scenes are sold as brochures are freely given for marketing purposes (Kalman 15-17). It is worth mentioning that there is something for everybody in the park ranging from activities for kids, photo shooting and multimedia, history to culture for archeologists and others interested in studies as well as place for researchers.
Geological hazards to the ecosystem
Living close to Yellowstone national park can be something to be proud of. But not always as volcanic activity, lava eruption and earthquakes are the realities residents are confronted with. With a competent team that monitors the hazards of the park, earthquakes can be least expected from the park (Piehl 4-7). Records show that the last time the park posed hazards to the community was during the uplift of the park. But ground deformation is the mist recent though it is no risk if scientists are to be believed this does not relinquish Yellowstone from earthquakes as the 3 million Visitor Park experiences 1000-3000 earthquakes yearly (Whittlesey and Watry 5-7). It is yet to be reported that an earthquake that killed animals as far as Nebraska nearly 2 million years ago has not occurred. The normal ones do no last more that 4.8, the latest in a series.
Characteristics making Yellowstone national park hazardous
Grizzlies
From its establishment, grizzlies have killed many people. Grizzlies are not the only killers (Whittlesey and Watry 2-5). Bison too killed a person, geyser basins and geothermal features attract more people than any characteristics in the park. But they not safe either. Documented evidence shows that a six year old boy suffered serious burns after falling on a wet boardwalk in the old faithful area.
Drowning and falling crashes
Visitors to the park should worry about falling, drowning and crashing in the park. The many rivers like Gardner have swallowed lives for years (zuckerman 6-8). The cliff too is as dangerous as a fall over can as well leads to death.Incidents of these deaths have been reported over time geologic problems and solutions a number of geologic problems have been listed but not exhausted. But their solutions not put into consideration (Kalman 2-7). Regular guidelines to the visitors on what to avoid is among the many Resolutions to avoiding geological problems. The government and the park management review team should consider updating their websites on the possible outcomes, when and where. This way they will curb deaths.
Works Cited
Kalman, Bobbie. Yellowstone National Park. New York, NY.: Lancaster, 2009. Print.
Piehl, Janet. Yellowstone National Park. Minneapolis : Mins.: Lerner, 2010. Print.
Whittlesey, Lee and Elizabeth Watry. Yellowstone National Park. Charleston, S.C: Arcadia Pub, 2008. Print.