Abstract
Business enterprises operate in competitive environments, which compel them to use data mining methodologies to convert unstructured data into information for business intelligence. The data consisting of millions of transactions is used to fragment existing and target markets according to consumer behavior.
Here, the business intelligence information gained from data mining is also used to detect fraud, understand consumer behavior, gain deeper insight into business operations, and to benchmark business operations based on data classification, prediction, and association rules.
Introduction
Many organisations struggling to remain competitive in the market use data mining to gain business intelligence information. Business intelligence is important for forecast demand management, supply chain management, cost management, category management, and to exploit existing business intelligence opportunities to improve the core business processes (Giudici 69).
For instance, Intel uses data mining to strategically access business intelligence information, which yields accurate information for effective decision making to enhance value creation opportunities at different strategic levels of the organization (Giudici 89).
Literature review
Many organizations have established that data mining is a new powerful tool that has been integrated into the business practices of different firms for analyzing large amounts of unstructured data to discover new and emerging trends in the fiercely competitive markets. Here, business organizations use automatic methods to analyze data from large databases to establish previously unknown patterns of data.
The amounts of business data, which is generated from millions of transactions, cannot be processed promptly using traditional mechanisms. However, with the advent of new technologies, which have high processing powers, large amounts of unstructured raw data can be mined and processed in a short time form large data warehouses (Delmater and Hancock 2).
Intel is one of the examples of firms, which mine data from different data warehouses to evaluate the company’s performance by benchmarking her business processes against successful business practices. The tangible benefits that accrue from lintel’s business processes include the elimination of unnecessary costs using analytical reports to determine the performance and trend of the business.
Data mining process
The data mining process consists of data classification, prediction, and association rules.
To ensure that the data, which is mined for business intelligence is used appropriately to meet Intel’s business goals and objectives, Intel first classifies unknown data according to established classification rules. The process includes identifying 90% of the portions of data of the organisation, which has not been classified for current and future use by ensuring that the classification process factors the goals or the purpose for, which the data to be used.
The classification process captures data from different sources in different unstructured forms, which when processes into information is used to determine the economies of scale, switching costs, business capital requirements, the degree of fragmentation and concentration of the business, the potential for globalisation, bargaining power of suppliers and buyers, threats of substitutes, business growth rates, the cost advantages of the business, and the degree of intensity of competition (Kudyba and Hoptroff 34).
The data is derived from the millions of transactions involving the suppliers, information about the customers, and the day to day transactions and operations.
Data mining for business intelligence
A case in point is Intel. Intel uses data mining to shift through large amounts of data to establish the relationship between data sets, anomalies in business activities, significant business facts and patterns, existing and emerging trends, and to make decisions on the approach to use to make sales.
In addition, it is used to determine product ranges, establish and develop better marketing strategies, and determine the strategic approaches for creating customer royalties (Sofaer 23).
Market segmentation is used by companies to determine and classify customers with the same buying behavior.
In addition, the data provides accurate predictions of trends of loyal customers for competitors to predict and avoid customer churn, determine fraudulent transactions, identify the most appropriate interactive marketing strategies, establish the purchasing trends of customers, and establish the purchasing trends and behavior of the customers (Larson 39).
Sources of data
Organisations look for different sources of data, which is mined to address different business needs in different environments and the typical sources of data include website data mining, journals, and e-commerce stores. Such data can be precious when launching new products into the market.
Problem statement
Many business organisations make inaccurate decisions because they have not integrated data mining tools to make real time and accurate information to establish, predict, and determine accurately the market segments, detect fraud, and determine the marketing strategies for effective decision making.
To address the problem, this study will analyse the data mining processes, and its benefits, which organisations use as a source of business intelligence reports for accurate and effective decision making.
Objectives
- Determine how organisations use data mining as a tool to generate business intelligence information
- Identify the data mining process that is used by organisations to organise unstructured data for decision making
- To determine areas where organizations can use data mining for effective decision making
Scope
The scope of the study is to cover study data mining as a process, the areas where data mining can be applied in business organizations, its use in business organizations such as Intel, and the sources of data that is used in data mining.
Research Methodology (Qualitative)
The method of inquiry used to achieve the objectives of the study was qualitative research method (Sofaer 45). The method allowed the use of Intel and an example to build the study and the literature on data mining for business intelligence to analyze the findings.
Model
The research model consists of the process for data mining, the use of a typical real-world example, which use data mining to organize unstructured data into information for business intelligence as graphically presented below
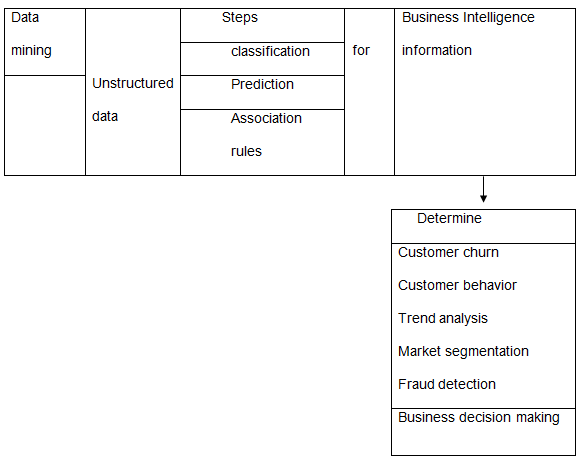
Results and Analysis
The results of the qualitative study, which were based on the objectives and scope of the study, are discussed below.
Objective one
The results of the study showed that business organisations use data mining for business intelligence, which is crucial for determining the current patterns of data consumer behavior.
Intel is one example of the companies, which combine different technologies, architectures and methodologies to mine data for business intelligence, which is used for accurate decision making, which is necessary for conducting cost effective business transactions. In addition, the study shows that Intel uses the data to benchmark its business operations and performance to determine the benefits that accrue from its business operations.
Objective two
The data mining process that companies use to accurately organise unstructured data into business intelligence information includes classifying the data into known and unknown categories. The known category of data exists in established patterns and the unknown category of data has to be organised into specific patterns using the rules that for classifying the data into the known categories.
The prediction process is used to establish the probability of the certain business trends such as the changing buyer behavior according to the dynamic business environment.
Gradually, the association rules are used to determine what and why certain actions have to be performed to achieve business goals and objectives.
Objective three
Data mining provides business intelligence information that can be used to make decisions to determine the right market segments, marketing strategies, to detect instances of fraud, and determine the rate of customer turnover to other business competitors (Howson 75).
Conclusions
The motivation for the study was to determine the rationale for using data mining as a strategic business tool for business intelligence. It was established that data mining is a crucial tool that competing organisations such as Intel use to organise millions of unstructured business transactions into information to influence decision making.
The study showed that data mining can be used to determine market competiveness, consumer behavior, market segmentation, market trends, marketing strategies, and customer movements.
The approach used automated predictions and discovery mechanisms to organise unknown patterns of data into information for decision making. Here, the benefits from the study included Information integration, enhanced presentation capabilities, insight creation, better organisational memory, benchmarking, and effective decision making.
Works Cited
Delmater, Rhonda, and M. Hancock. Data mining explained: a manager’s guide to customer-centric business intelligence. New York, Digital Press, 2001. Print.
Giudici, Paolo. Applied data mining: statistical methods for business and industry. New York: John Wiley & Sons, 2005. Print
Howson, Cindi. Successful business intelligence. New Dell: Tata McGraw-Hill Education, 2007.
Kudyba, Stephan, and R. Hoptroff. Data mining and business intelligence: A guide to productivity. New York: IGI Global, 2001. Print.
Larson, Brian. Delivering Business Intelligence with Microsoft SQL Server 2005. New York, McGraw-Hill, 2006. Print.
Sofaer, Shoshanna. “Qualitative research methods.” International Journal for Quality in Health Care 14.4 (2002): 329-336.Print.