Introduction
An electric car is an automobile that uses an electric motor to generate electricity that is used to run its various components. Electric cars originated during the early years of the 19th century (Anderson, & Anderson, 2005). However, lack of certain features that characterized combustion engine cars led to low popularity and the consequent disappearance of electric cars. They were very expensive and could only travel for short distances.
Historical records reveal that the fist electric car was made in 1837 by Robert Davidson, who used galvanic batteries as the power source (Hunter, 2014). Rechargeable batteries were later incorporated into the engine systems of the cars beginning in the year 1859 (Anderson, & Anderson, 2005). Electric cars run on electric energy that is generated by energy storage devices such as batteries. In recent years, high oil prices and technological advancements have resulted in increased demand for electric cars.
How an Electrical Car Works
As mentioned earlier, an electrical car runs using electric energy generated by energy storage devices such as rechargeable batteries. An electric car’s powertrain comprises three major components that include an electric motor, a controller, and rechargeable batteries (Hunter, 2003). The engine includes a battery pack that is made by joining numerous smaller cells.
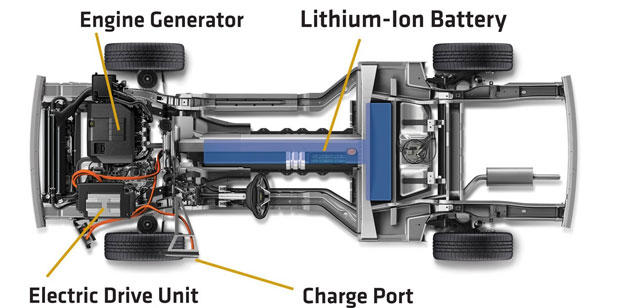
The battery supplies power to an electric motor that runs the differential, which turns the wheels (Hunter, 2003). In addition, the motor recharges the battery as the car moves and brakes. An electric car also possesses electrical devices that convert the electric current from one form to another (Hunter, 2003). An example of these devices is the onboard charger that recharges the battery by converting electric energy from direct current to alternating current and vice versa (Hunter, 2003). The electric motor performs a function similar to that of a gasoline engine.
Types of Electric Cars
There are four major types of electric cars that have different engine composition. They include the hybrid electric vehicle, plug-in hybrid electric vehicle, extended-range electric vehicle, and the battery electric vehicle (Anderson, & Anderson, 2005).
Hybrid Electric Vehicle
Hybrid electric vehicles possess electric batteries and small combustion engines that play different roles. For instance, the electric motor improves the car’s acceleration. The battery is charged by the combustion engine and also during the process of braking (Hunter, 2014). It cannot be charged from an electric outlet. An example of this type of electric car is the Ford Fusion hybrid.
The Plug-In Hybrid Vehicle
A plug-in hybrid vehicle includes a combustion engine as well as an electric motor (Hunter, 2014). However, the vehicle can be charged from an electric outlet to boost the power capacity of the batteries. Many plug-in hybrid vehicles operate up to a certain acceleration speed using the electric beyond which the combustion engine kicks in. Examples of this type include Toyota Prius, Cadilac ELR, and Opel Ampera.

Plug-in hybrid vehicles are the most reliable type of electric vehicles because they can be charged in three main ways that include regenerative braking, plugging to an electric outlet, and from the action of the combustion engine (Anderson, & Anderson, 2005).
Extended-Range Electric Vehicle
An extended-range electric vehicle possesses an electric motor, an engine and a battery. Each of these components plays a different role. In these cars, the wheels are powered using the electric motor only. The only role that the combustion engine plays is to charge the batteries. An example of this type of car is the Chevrolet Volt shown in the image below. An extended-range electric car is less reliable and less efficient that the other types because only one engine component can turn the wheels.

Battery Electric Vehicle
A battery electric vehicle (BEV) possesses batteries that are charged by plugging the vehicle into an electric outlet. Unlike other electric car types, BEVs do not have combustion engines. They have very large batteries that enable them to travel long distances without running out of power (Anderson, & Anderson, 2005). An example of a battery electric vehicle is the Nissan Leaf.

Advantages of Electric Cars
Electric cars have four main advantages that include energy efficiency, high performance, low dependence on oil, and environmental conservation (Boxwell, 2010). Electric vehicles are very efficient because they convert more energy into power compared to combustion engines. Another aspect of their efficiency is the ease of charging. Charging an electric car is very convenient and easy because it involves plugging them into an electric outlet. They have high performance because their motors provide high acceleration and do not produce noise (Boxwell, 2010). In addition, they are very cheap to maintain. Electric cars do not have any tailpipe emissions thus making them environmentally friendly (Hunter, 2014). They play an important role in reducing global warming.
Disadvantages of Electric Cars
The main disadvantages of electric vehicles include limited range, long refueling time, high prices, and limited varieties in the automobile market. Many electric cars have very limited distance ranges of less than 100 miles due to their heavy weights and short-life batteries (Boxwell, 2010). This means that they are inappropriate for long distances. On the other hand, it takes a lot of time to recharge the batteries. This is a challenge especially to drivers who need to recharge their batteries while travelling. For instance, it takes one hour to add electric power that can run the car for 20 to 25 miles. The production costs of electric cars are very high.
Therefore, they are expensive and unaffordable to low and middle income earners (Boxwell, 2010). However, this challenge is compensated for by low maintenance and lease costs. Finally, they limited varieties. Customers have few choices available in the automobile market (Hunter, 2014). Research is underway to develop more efficient and reliable cars that will be affordable to people in different economic classes. In future, the cost and weight of electric cars are projected to decrease significantly. Hybrid cars can be improved by developing cheap and light batteries that can store power for longer periods. These improvements will bring the cost of production and the price of electric vehicles down.
Conclusion
Electric cars run on electric power generated by motors that form part of their powertrain. The cars originated during the early years of the 19th century. However, they did not grow in popularity because of their low distance range, high cost of production, and high purchase prices. Electric cars are divided into four classes depending on whether the car is powered using a motor only or suing a combination of an electric motor and a combustion engine. The battery supplies power to an electric motor that runs the differential. Electric devices convert electric power into various forms needed to run the car in various situations. Advantages of these cars include energy efficiency, high performance, reduction of dependence on oil, and environmental conservation. Disadvantages include limited range, long refueling time, high costs of purchase, and limited varieties in the market.
References
Anderson, C. D., & Anderson, J. (2005). Electric and Hybrid Cars: A History. New York: McFarland.
Boxwell, M. (2010). Owing an Electric Car. New York: Greensteram Publishing.
Chevy Volt: Chevy Volt Review. (2014). Web.
Electric Cars. (2014). Web.
Howard, B. (2012). Will High-Mileage Nissan Leafs Need Costly Battery Replacements Soon? Web.
Hunter, N. (2003). How Electric and Hybrid Cars Work. New York: The Rosen Publishing Group.
Hunter, V. (2014). Electric Vehicles. New York: Barb Gates.