Introduction to the Study
The company was established in the middle of 2003. It finally started to operate in November of the same year. The most interesting fact about Etihad Airways is that this company managed to showcase one of the fastest evolutions in the history of airlines. Weekly, the company, manages to send out more than 1000 flights (O’Connell & Bueno, 2016). The company’s destination array includes more than 100 locations, and their fleet contains more than 100 airplanes. Their destinations include all continents, so it allows Etihad Airways to carry 15 million passengers annually. Moreover, the number of passengers also increases yearly and so do the company’s revenues (approximately $10 billion in addition to $100 million net incomes) (O’Connell & Bueno, 2016). Originally, Etihad Airways is located at Abu Dhabi International Airport. The company’s attitudes towards their services and clients reflect the best qualities inherent in Arabian residents – warmth, education, generosity, and friendliness. Another objective of the airlines is to represent Abu Dhabi as an international center of hospitality that connects different parts of the world. The company strives to the greatness by challenging themselves and trying to innovate constantly. It is no surprise that Etihad Airways receive numerous awards and prove that they are a worldwide-caliber commercial aircraft company (O’Connell & Bueno, 2016). Five years in a row, these airlines received the award for being the leaders of aircraft business. Their premium services are highly anticipated and praised by the customers. Currently, the company is still doing its best to improve their services and internal processes. Their key advantage is thoroughly described and supported by factual data in the next chapter of the paper.
Strategy of the Company
The mission of the company is to provide high-quality services that are essentially based on Arabian values. Etihad Airways is committed to embracing the strategy that is based on collaborative growth (Hazarika & Boukareva, 2016). This is done in order to preserve the company’s competitive position in the market and adjust the business in line with the advancements of the global airline business. Moreover, Etihad Airways make the best use of their partnership strategy by means of collaborating with smaller airlines and investing in the airlines that offer captivating destinations and prices (that are not originally available to Etihad) (Hazarika & Boukareva, 2016). By doing this, the company unlocks access to more than a hundred of destinations worldwide. Etihad Airways do not waste their time and improve their business strategy annually. They invest in franchising, connecting with new partners, and building alliances with other enterprises that are interested in the company’s services. Ultimately, Etihad Airways were able to gain shares in numerous companies (Virgin Australia, Jet Airways, Airberlin, and many others) (Hazarika & Boukareva, 2016). Overall, it is safe to say that the company employed a flexible differentiation strategy. On a bigger scale, the company does not measure its productivity, but there are two important indicators that can be used to define the company’s relative success. These two indicators are novel acquisitions and an increasing number of employees. There is a direct dependency between the income levels and the number of workers that were employed by Etihad. In the aircraft industry, productivity is not hard to measure due to the transparency of annual reports and a rather visible impact of the core variables on the success of the company.
Forecasting
There are two conventional methods of forecasting – qualitative and quantitative. The former is usually used when there is not enough information. This method is commonly applied to forecast the success of new products or technologies. Overall, it is based on the experience of those who apply this method and their intuition. Quantitative method is based on historical data and is applied when the market situation is stable. It is aimed at the existing products and technologies and involves a lot of mathematical calculations and approximations. The three categories of forecasting include time series, regression-based, and machine-learning-based forecasting. The first category is used to analyze the data concerning consistent market sales patterns. The second category is mostly useful when it comes to the process of modeling the outcomes of the company’s decisions. By applying this forecasting category, the company will be able to model the influence of their marketing campaigns, assess the decisions regarding the price changes, and plan the promotion of alternative services. The third category is the best when the company has to model the impact of other companies on the market. It is widely used to monitor the competition and forecast the majority of key market moves and their outcomes. If one has to provide examples of time horizons, it is reasonable to mention that medium-term future and long-term future objectives are the focus of Etihad Airways. The company is interested in gaining a loyal customer base and selling as many tickets as possible (Dresner, Eroglu, Hofer, Mendez, & Tan, 2015). Therefore, the booking process is one of the examples of time horizons. Etihad uses specific tools to forecast their financial capabilities that can be perceived as adaptive insights.
Capacity Planning
Etihad manages their capacity in a rather efficient manner. Nonetheless, there are several aspects that may impose critical limitations on the company over time. The supply of Etihad Airways is commonly affected by both operational and contractual limitations of the airline industry (Chang, Park, Jeong, & Lee, 2014). Therefore, the company focuses on its tactical scheduling and decision-making processes. Efficient management of capacity at Etihad is represented by adjustments that are made in terms of flight departures (for instance, setting the flights on the dates when demand is low). In other words, the company manages the capacity by means of yield management so as to reduce the impact of limitations inherent in supply management. Despite all the improvements and an increased capacity (80%), Etihad Airways still lose a crucial number of passengers (Chang et al., 2014). There is no excess capacity available and the company has to adjust their sophisticated yield management system to the available solutions. The latter are designed to fix the long-term supply of Etihad Airways even when there is no enough data regarding the demand. If the company needs more capacity, it will explore the existing supply management strategies so as to find flexibilities that may be helpful in eliminating the interruptions in the workflow. It should be noticed that these flexibilities may be utilized to revise the organizational tactic and improve the flight schedule on the basis of the demand. Nonetheless, the company still has to review its strategies constantly. Capacity planning is a relatively novel concept that has a rather inconsequential number of contacts with the commercial airlines market. Etihad has sufficient staff and aircrafts to increase their capacity so the only thing that they have to worry about is optimal flight scheduling.
Process Selection
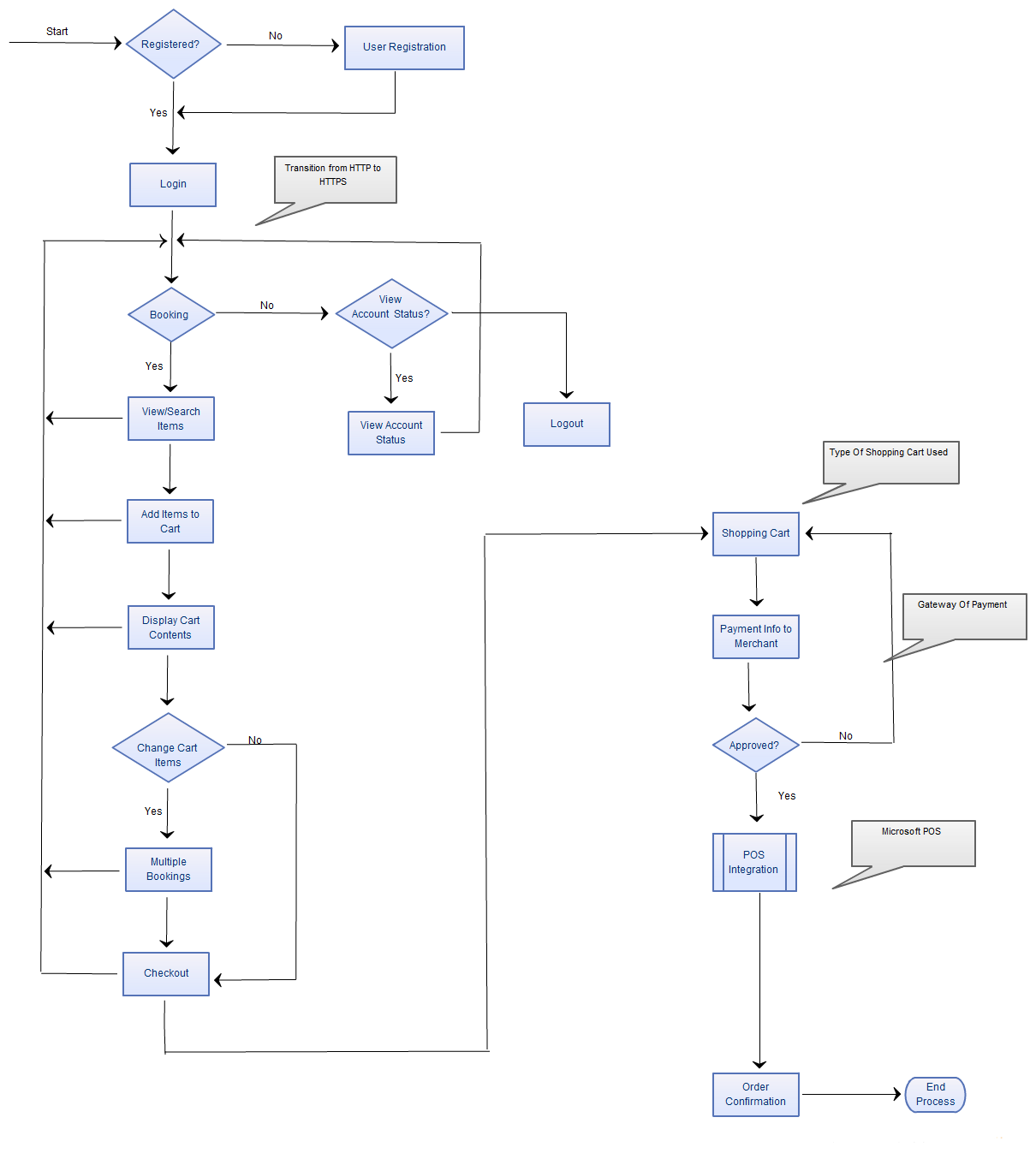
The system of ticket ordering can be found on Figure 1. The core characteristics of ticket ordering at Etihad are cost-effectiveness and uniqueness of the suggestions. The key contributor to this process is the horizontal development of the company’s strategy. Regardless, the process is aimed to provide advantages that will help the customers get the service that they want. Ticket booking process at Etihad is also revolving around advantageous prices and getaway from the undefined market areas (Al-Ali & Ahmad, 2014). The ability of the worldwide-renowned company to showcase its offers in an efficient manner allowed Etihad to make the most out of its ticket ordering process. Nonetheless, the process of booking may seem too complex for some users due to its horizontal directionality. To put it other way, the company’s booking process is aimed at cultivating loyal customers instead of a one-time compliance with the customer’s wishes. It is evident that this process perfectly reflects Etihad’s strategy of collaborative growth as the company wants to build a long-time connection with its customers (Achinto, 2012). The advantage of this process consists in the fact that the majority of Etihad’s competitors exploit vertical development and impose generic offerings on their customers. In perspective, the existing booking process will probably help Etihad to win over the market and monopolize their practice. The company accurately draws attention to user-friendliness of the booking process so it is safe to say that it became of the key contributors to Etihad’s major success. Even though the existing system is not perfect, the company does everything to develop horizontally and improve the overall performance. Gradually, customer satisfaction will increase and Etihad will be able to revise their capacity planning strategy as well.
References
Achinto, R. (2012). Relationship of osmosis: Rise of Emirates, the airline and Dubai, the city. Academy of Taiwan Business Management Review, 8(3), 1-5.
Al-Ali, H. A., & Ahmad, S. (2014). Etihad Airlines: Growth through successful strategic partnerships. Emerald Emerging Markets Case Studies, 4(5), 1-17. doi:10.1108/eemcs-09-2013-0184.
Chang, Y., Park, H., Jeong, J., & Lee, J. (2014). Evaluating economic and environmental efficiency of global airlines: A SBM-DEA approach. Transportation Research and Environment, 27(5), 46-50. doi:10.1016/j.trd.2013.12.013.
Dresner, M., Eroglu, C., Hofer, C., Mendez, F., & Tan, K. (2015). The impact of Gulf carrier competition on U.S. airlines. Transportation Research, 79(2), 31-41. doi:10.1016/j.tra.2015.03.022.
Hazarika, I., & Boukareva, B. (2016). Performance analysis of major airline companies in UAE with reference to profitability, liquidity, efficiency, employee strength and productivity. Eurasian Journal of Business and Management, 4(4), 71-80. doi:10.15604/ejbm.2016.04.04.007.
O’Connell, J. F., & Bueno, O. (2016). A study into the hub performance Emirates, Etihad Airways and Qatar Airways and their competitive position against the major European hubbing airlines. Journal of Air Transport Management, 5(2), 4-12. doi:10.1016/j.jairtraman.2016.11.006.